M2L2: Types of Information Sources
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
NIOS Senior Secondary 12th Library and Information Science (339) module 2 information sources lesson 2 chapter 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
primary sources of information
new raw data, new interpretation of known facts, or new observations / experiment
include periodicals, newspapers, technical reports, dissertations, conference papers, patents, standards, trade and product bulletins
periodicals (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
a publication with definite periodicity under the same title intended to be published indefinitely
each issue is dated and consecutively numbered
all issues in a volume have continuous page numbers
collection of articles by different authors
also called journals
info is timely and more current than books
scientific journals were the first to be published
serial (periodicals)
(periodicals)
any publication issues in successive parts intended to publish indefinitely
common types include research periodicals, trade and business periodicals, newsletters, newspapers, popular magazines, almanacs / yearbooks, annual reviews, indexing / abstracting periodicals
multi volume books and encyclopaedias aren’t serials as they stop publishing after the last volume
scholarly periodicals or peer reviewed journals (primary periodicals)
(primary periodicals)
published by learned societies, R&D organisations, universities, and some reputed commercial publishers
publish research findings and are peer reviewed
basic features of these journals are
its purpose - to report original and significant search in a certain subject, are primary sources and called primary periodicals
the best source for new or current info
written by researchers, professionals, experts - articles are technical and require subject background / knowledge
meant for scholarly audience and called scholarly journals
don’t have ads (usually)
each issue is consecutively numbered and all issues in a volume have continuous page numbers
articles often have abstracts before the main text
abstract → a descriptive summary of the article
each article has the address of the author
articles always cite their sources in bibliographies and / or footnotes
bibliographies contain references to other scholarly writings
trade and business periodicals (primary periodicals)
(primary periodicals)
published by trade organisations and commercial publishers
features include
covering articles, news, trends, and issues for specific businesses / industry
authors being professionals or journalists working for the publisher
covering industry trends, new products, techniques, organisational news
lots of ads → index to the advertisers included
using glossy paper and colourful illustrations when published
might have some jargon but is written for the general educated audience
eg. indian textile journal & chemical week
popular periodicals (primary periodicals)
(primary periodicals)
devoted to particular subject area
written in simple language
features include
meant for general public who don’t have specialised knowledge of the subject
published to inform, educate, and entertain
purpose of science and tech periodicals is to popularise these topics
published by R&D organisations, government departments, and commercial publishers
articles are usually short and sometimes don’t have references
magazines (primary periodicals)
(primary periodicals)
published by newspapers and commercial publishers
entertain, sell products, give practical info, promote a viewpoint
features include
content includes info on celebrities, news, and general interest articles
authors are journalists and freelance writers
glossy covers and lots of colourful illustrations and photographs to distinguish from other magazines
lots of ads
language is simple and designed to meet minimal education level
each issue starts with page one
e-journals (primary periodicals)
(primary periodicals)
any serial produced, published, and distributed via electronic networks
also known as paperless journals and online journals
on CD-ROM is like having printed journal - requires computer and requisite software
many advantages over print journals
CD-ROm has storage capacity of
newspapers (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
publish news of current affairs of political, social, and economic front of a nation or region
different kinds of newspapers → local or regional, national or international
can specialise in economic and financial matters
have in depth analysis of trade, banking, commerce
basic features include
published daily, weekly, or bi-weekly
covers news, current events, advertising, topics of human interest
main purpose → to inform, explain, influence, and entertain
authors are free-lance writers or journalists, can be scholars
articles are usually short
language is simple and designed for a minimal education level
generally has photographs
use of advertising is moderate to heavy
technical reports (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
research reports produced after conducting research in a well defined research area
generally in the field of science and technology
sponsored by government organisations, industries, other agencies, etc
research conducts research for sponsor, writes research results in the form of technical report, and submits it to the sponsor
conference papers (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
meeting organised by learned body by subject experts to exchange and discuss info
every year there are thousands of conferences
experts present their papers
conference proceedings are published after it’s over
contains research papers presented in the conference, discussions, minutes of the meeting, resolutions adopted
eg. proceedings of 8th international convention caliber-2011, goa university, goa, 2-4 mar 2011
dissertations and thesis (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
doc submitted by a researcher for candidature for a degree / personal qualification
in some unis dissertations and theses are seen as the same
in some unis dissertations are submitted at the end of the master’s degree and theses are submitted at the end of the PhD
report original research
eg. digital light photography → a thesis submitted to the department of computer science, university of delhi for award of doctorate degree
patents (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
granted by government and gives a person or company sole rights to make, use, or sell, a new invention for a certain number of years
can be for a product, process, or design
to protect inventions in R&D activities by patenting with the government
gov grants patent and published the details of granted patents through an official publication
eg. indian patents are published in gazette of india, part 3, and section 2
standards (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
provides requirements, specifications, guidelines, characteristics to consistently quality check materials, products, processes, and services
standard → a set of rules for ensuring quality of a product, process or a service
has two types → fundamental standards & technical standards
ensures that they are safe, reliable, and of good quality
help businesses develop consistent products so it can be used globally
encourages international trade
makes it easier to understand and compare competing products
eg. iso 2709: standard for bibliographic record formats
fundamental standards (standards)
(standards)
based on quantifiable fundamental entities that are basic to all scientific and technical practices
includes measuring length, mass, time, temperature, various forms of energy, force
technical standards (standards)
(standards)
related to product, process, material, or service
ensures that they are safe, reliable, and of good quality
trade and product bulletins (primary sources of information)
(primary sources of information)
information products brought out by publishers, manufacturers and distributors of materials, products, and services
cover every kind of material, product or service
includes books, drugs, chemicals, household goods, complex machinery, research and industry equipment etc
purpose is to describe characteristics of the product to promote its sale to customers
information about the specific commercial product isn’t likely to be published in any other form of lit
secondary sources of information
helps researchers keep track of latest info in their field
includes secondary periodicals, bibliographies, books, reviews, treatises, state-of-the-art reports, reference sources, etc
secondary periodicals (secondary sources)
(secondary sources)
scan the lit in primary sources, select relevant stuff, and arrange them in a helpful sequence
published in weekly, fortnightly, or monthly intervals
contain bibliographical references with or without abstracts
secondary periodical with abstracts is an abstracting periodical
secondary periodical without abstracts is an indexing periodical
bring recently published lit from a specific subject together
indexing and abstracting periodicals are available in every subject field
most national and international secondary periodicals are available in print, CD-ROM, and / or online
indexing periodicals (secondary periodicals)
(secondary periodicals)
relevant items with full bibliographical (bib) details are chosen and arranged under broad subject headings or class numbers
brings all items on the same subject together
bib details help readers and identify and locate the original doc
eg. if the doc is a journal article, bib details will include name of author(s), title of article, title of journal, volume number, issue number, year of publication, page numbers
also provides author and subject indexes of items covered
abstracting periodicals (secondary periodicals)
(secondary periodicals)
contents of the selected items are summarised (called abstracts) and are provided along with bib details
helps reader to decide whether to read the full doc or not
sometimes a well prepared abstract serves as a substitute for the original doc
also provide author and subject indexes
bibliographies (secondary sources)
(secondary sources)
a systematic list of docs that share a common factor - such as subject, language, time period, author, etc
may be comprehensive or selective
enumerative / systematic bibliography - arranged in a certain order, attempts to record / list
each entry provides bib details of a doc
entry for a book contains
name(s) of author(s), title of the book, publisher, date of publication
entry for journal contains
name(s) of author(s), article title, journal title, volume number, issue number, year of publication, page numbers
national bibliography (bibliographies)
(bibliographies)
lists the publications produced in a country
eg. Indian National Bibliography - compiled by Central Reference Library, Kolkata
trade bibliography (bibliographies)
(bibliographies)
list books meant for sale
used by libraries to select books for the library
brought out by publishers, book sellers, distributors, or printers
subject bibliography (bibliographies)
(bibliographies)
lists docs on a certain subject
one important service of the library is to carry out lit search and compile subject bibliography
sometimes they are compiled on regular basis in anticipation of the users’ needs
also compiled on special occasions such as seminars and workshops to provide the latest lit on the topic
university and special libraries offer this service more often than public libraries
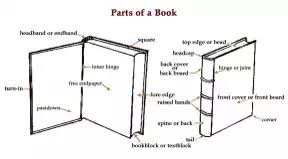
books (secondary sources)
(secondary sources)
a written or published doc of at least 49 pages that communicates thoughts, ideas, or info
pages are glued or sewn together along one side, called the spine - it can be opened at any point
two covers of the book are joined by hinges to the spine
either hardbound or soft bound depending on the covers
hardbound books have covers made of cloth, plastic, or leather over cardboard
a paper cover jacket is often added to protect the cover
soft bound books are also called paperbacks since they have paper covers
parts of a book (books)
(books)
book types (books)
(books)
books are important sources of info and libraries acquire them based on users’ needs
based on contents → can be simple or composite, single or multivolume, fiction or nonfiction, textbook or treatise
based on physical format → can be print or non print medium, pamphlet or manuscript
non print medium includes audio books, video books, multimedia books and ebooks
simple books (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
treatment of subject is continuous and written by one or more authors
eg. the digital scholar by m weller
composite books (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
treatment of subject may not be continuous and each chapter / article is written by a different author
single volume (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
book in one volume
eg. scholarly communication by s l gillenson
multivolume (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
book in more than one volume
continuous page numbers in consecutive volumes
reference books (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
provides answers as brief facts, statistical info, background info, or directs to additional info sources
meant only for consultation or referred for some specific info - not for continuous reading
include dictionaries encyclopaedias, handbooks, yearbooks, almanacs, directories, biographical and geographical sources
fiction books (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
story books, novels, prose writings that focus on imaginary people and happenings
arranged alphabetically by author’s last name
non fiction books (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
about real things, people, events and places
includes subject & reference books
arranged by class number to keep books in the same subject together
textbooks (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
for regular study by a student
designed to inform systematically
start with concepts and then elaborate with more details
most books used in schools are textbooks
graded and instructional in nature
meant for the comprehension level of students
students use textbooks to learn
teachers use them to teach and prepare for class
treatises (book types based on contents)
(book types based on contents)
formal and in depth treatment of a subject
meant for scholars for advanced study
eg. the prince by niccolò machiavelli
pamphlet (book types based on physical format)
(book types based on physical format)
unbound printed publication with no cover or a paper cover
minimum 5 pages
maximum 48 pages
page numbers exclude cover
manuscript (book types based on physical format)
(book types based on physical format)
any document that is written or typed by a typewriter or computer
used to distinguish author’s original version of a work from printed copies
historical manuscripts - handwritten documents from ancient times before the introduction of printing in 1400s
can be traced to certain times or areas by materials used
inside a book (books)
(books)
inside the front cover of a typical book there is a collection of pages called preliminary material
includes title page, copyright page, acknowledgement page, dedication page, preface, table of contents
followed by the body of the book - the text
after the end of the text comes the glossary, bibliography, and index
title page (inside a book)
(inside a book)
first page with title of the book, authors, and publisher
copyright page (inside a book)
(inside a book)
has the name of publisher, date of publication and its details
dedication page (inside a book)
(inside a book)
to whom the author dedicates the book
preface (inside a book)
(inside a book)
also called foreword or introduction
author states aim of writing book and mentions its important features
table of contents (inside a book)
(inside a book)
the list of contents, arranged by chapters with their page numbers
text (inside a book)
(inside a book)
the body of the book divided into units or chapters
glossary (inside a book)
(inside a book)
list of important words use in the book with their meanings
bibliography (inside a book)
(inside a book)
list of books, articles, etc used by author as sources
index (inside a book)
(inside a book)
alphabetical list of names, places, topics, etc discussed in the book with their corresponding page number
tertiary sources of information
based on primary and secondary sources and serve as key to the sources
consistent of info that is a distillation and collection of primary and secondary sources
help locate primary and secondary sources
includes bibliography of bibliographies, guides to literature, directories listing primary and secondary periodicals, etc
electronic sources
publications that need a computer to access the info
can be off-line or online
offline electronic publications are stored on electronic storage media like CD-ROM, DVD, Diskette or magnetic tape
online electronic publications are accessible online on a webpage or an online database
most sources are available in print and electronic mediums
some sources that were in print are now exclusively electronic
even though there are more advantages and limitations to electronic sources, they aren’t likely to replace print sources soon
people still want to read books, newspapers, etc
electronic sources will supplement but not replace print sources
advantages of electronic sources over print sources (electronic sources)
(electronic sources)
more frequently updated than print
more search options
provide access to wider range of info
faster and easier access to info
eg. indexing and abstracting periodicals where back volumes are put into a single searchable database - search is easy and fast
online resources provide links from citations to full text articles
full text data can be delivered instantly
can be delivered in multimedia format and include text, video, and audio
can be accessed by many users at the same time
can be accessed anytime and anywhere as long as there is internet access
back volumes of print materials need to bound and stored which is expensive and space consuming - not a problem with storing back volumes electronically, even on CD-ROM
missing issues, missing pages, and other damages caused by mishandling print doesn’t happen to electronic sources
limitations of electronic sources (electronic sources)
(electronic sources)
use of electronic sources requires expensive equipment which needs to be acquired, maintained, and upgraded
includes computer hardware, software, internet connection, subscription to sources
require computer knowledge despite being user friendly
need to train staff and users - can cost money
most publishers have licence agreements when selling e-publications - they can restrict users in the use of e-resources
reading from the computer screen can cause discomfort to users - some prefer to print out the article or read from the print version