One Health Quiz 2
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
What are the 4 interactions between living beings and their (x/x)?
mutualism (+/+)
commensalism (+/0)
predation (+/-)
competition (-/-)
Pathogenic microoragnisms
Microorganisms that can cause disease upon colonization of host
Obligate pathogens
microorganism which must infect host to survive and multiply
Facultative pathogens
microorganisms which can infect and multiply in host but also capable of multiplying in the environment
Opportunistic pathogen
microorganism that does not usually cause disease but may become pathogenic under certain conditions
Communicable diseases
diseases that can be spread directly or indirectly from one animal to another
Infectious diseases
diseases caused by pathogens
What are the 5 ways of transmission?
food borne
water borne
air borne
vector borne
fomites
What is a zoonosis?
pathogen that is shared by both humans and non-human animals and can be transmitted from animals to humans
What % of existing human infectious diseases are zoonotic?
60
What % of emerging infectious diseases of humans have animal origin?
75
How does the case of Trichostrongylus tenuis and red grouse demonstrate the role of parasites in the ecosystem?
Trichostrongylus tenuis regulates red grouse so that grasslands have time to recover
When do pathogens become a problem and give an example of case study for each?
When they threaten
our existence (black plague killed almost 50% of europe’s population)
our food production system and economic income (rinderpest in africa caused losses and deaths)
existence of other animal species (christmas island’s rats were first disease-mediated extinction in history)
What was disease thought to be caused by in early times?
imbalance of spirits, bad omens, curse
Now we know that diseases are caused by a wide range of causes, from ______ to _______
genetic/metabolic disorders
tiny bugs
Emerging infectious disease
disease that is newly recognized or newly evolved or has occurred previously but shows an increase in incidence or expansion in geographical, host or vector range
Re-emerging infectious diseases
disease that appears after it has been eradicated or on a significant decline
_____ new human diseases appear every year. ___ are of animal origin
5
3
The WHO’s global surveillance system currently picks up ____ public health threat signals every month
7000
What is the relationship between species richness and hosts?
taxonomic groups with more host species generally hold more potentially zoonotic pathogens
Where in the world is there the largest number of zoonotic pathogens?
tropics
What orders contain the most host species?
rodentia
chiroptera
soricomorpha
primates
carnivora
artiodactyla
What are the 5 reasons for reemergence of diseases and give examples if applicable?
changes in pathogen characteristics (mutation, drifting)
change in environment (lack of biodiversity, climate change, deforestation)
change in population dynamic of host range (population growth, urbanization, hunting/farming practices, trade/travels)
lack in application of control measures
lack of surveillance
Dilution effect
Higher the diversity, lower the risk of being infected because less likely for pathogen to infect correct host
Amplification effect
Higher the diversity, higher the risk of infection because some pathogens can infect different host species
What is an example of a disease impacted by biodiversity loss?
lyme disease
What is an example of a disease impacted by climate change and how?
dengue virus
increased vector abundance and feeding activity
Increased geographical range
Increased human activties during warmer times
What is an example of a disease impacted by land use change, parasites, public health?
adaption of plamodium knowlesi from macaques to humans
How does an abundance of generalist animal species affect risk of infection to humans in agricultural landscapes?
increases risk by increasing abundance of multi-host parasites
What is spillover?
interspecies transmission where pathogen transmitted from reservoir to novel species producing disease
Is spillover always zoonotic?
no
How does canine distemper in Africa demonstrate spillover?
spread from domestic dogs to wild dogs
some local populations of wild dogs went extinct
transmitted to lions
How does bornean felids demonstrate spillover?
test for 4 viruses that usually affect domestic cats
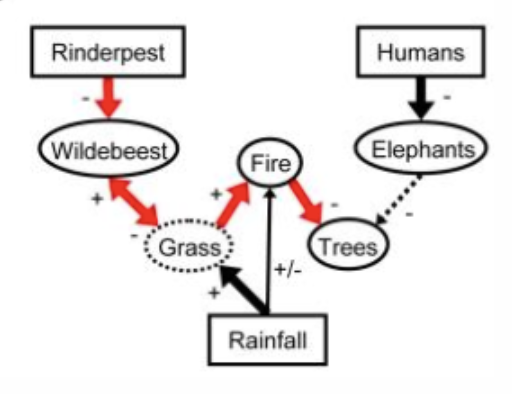
How does rinderpest in serengeti demonstrate impacts on ecosystem? Is it zoonotic?
disease regulated wildebeest population and ecosystem
decrease in wildebeest=grass grows=easier bushfires
not zoonotic but caused death from famine
What was the first pathogen eradicated due to vaccinations?
rinderpest
What happened during the Nipah virus outbreak in Malaysia in 1998?
transmitted by flying foxes
pigs would eat under fruit trees where bats were and become infected
poor biosecurity
pigs transmitted virus to farmers
How do you deal with an african swine fever outbreak?
no vaccine or treatment
eliminate all infected and suspected pigs
What factors does implementation of isolation/culling measure depend on?
characteristics of pathogen
animal species and their value
social and cultural context
economics and politics
Do you have to vaccinate every animal in the herd for effective disease transmission?
no, herd immunity means that you only have to vaccinate enough to reduce transmission
How does conflict and war affect disease management?
deterioration of health systems
pause of vaccination campaigns
migration to safe places and bringing disease along
How does inequity affect disease manegement?
poverty and hunger
unaffordable health care
access to vaccines and treatments
displacement
Why does antimicrobial reisistance occur?
bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites change over time and no longer respond to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing disease risk
What is the name of the main group of pathogens considered of high concern due to their increasing resistance to antibiotics?
ESCAPE
How is AMR a global threat?
threatens progress in healthcare, food production, life expectancy
disrupts balance of microbial community in soil and aquatic systems
How does AMR develop?
whenever there is high number of bacteria, few of them are resistant to antibiotics
antibiotics kill both bad and good bacteria
resistant bacteria can now grow and multiply without competition
some bacteria transfer resistance to other bacteria
What is intrinsic resistance?
innate ability of bacteria to resist antibiotics
What are the two ways of acquired resistance in bacteria?
vertical gene transfer
horizontal gene transfer
What is vertical gene transfer?
genome replication and cell division to produce two new bacteria
What are the three methods of horizontal gene transfer and explain them?
conjugation- AMR bacteria uses pilus to transfer AMR genes to recipient cell
transformation- AMR bacteria dies and transmit genes to other bacteria
transduction- viruses kill AMR bacteria and absorb DNA and infect other bacteria so AMR genes transducted
How is the bacteria changed when they develop AMR?
impermeable cell wall protein to limit uptake of drug
modification of drug target
pumps to increase active efflux of drug
inactivation of drug
What are the 4 drivers of AMR?
inappropriate use of antibiotics in human medicine
inappropriate use of antibiotics in veterinary medicine
lack of hygiene and infection prevent and control strategies
political conflicts, equity, human mobility
_____ of all medically important antibiotics continue to be sold for use in livestock production
two thirds
How can antibiotics in livestock spread to humans?
food borne
manure
environmental
occupational
What are the three systems involved in the One Health approach against AMR?
environmental subsystems
environmental metadata
human subsystems
What are limitations to the one health approach against AMR?
number of sites recruited to compile data limited
sites have access to human data only
AMR data from animal and environment are limited
focus on farm animals
What are the roles of AFCD?
outbreak
trade
inspection
importation/exportation
welfare
diagnostic and surveillance
What are the 6 common species of stray animals in HK and what disease do each of them transmit?
dog- rabies
wild birds- avian influenza
wild pigs- african swine fever
cattle- lumpy skin disease
monkeys- herpes B, monkeypox
bats- coronovirus
Why are stray dogs an issue with disease?
most likely to be unvaccinated
pack behavior- may attack people
rabies
AFCD has statutory responsibility to do what regarding stray dogs?
manage population to prevent rabies outbreaks
reduce nuisance
safeguard public health
What kind of animals does rabies infect?
all mammals
Rabies belong to what
order
family
genus
mononegavirales
rhabdobiridae
lyssavirus
What two continents have the highest risk of human mortality from rabies?
africa
asia
Around 99% of human cases of rabies are due to bites from ___
infected dogs
Is the main animal reservoir for rabies the same worldwide?
no, differ between continents
What are the modes of transmission for rabies?
direct bite
non-bite exposures
rarely, inhalation or transplantation of inflicted organ
What are the two forms of rabies?
furious
paralytic
What must a test include to rule out rabies in an animal?
tissue from at least two locations in brain, preferably brain stem and cerebellum
How did HK achieve rabies eradication?
legislation
enforcement
monitoring, surveillance, research
education & publicity
What are the legislation related to rabies?
duty to report rabies
vaccinations
control of animal imports
prohibits slaughter of dogs and cats
manage stray animals
How was enforcement administered in regard to rabies?
compulsory vaccination and licensing of dogs
control of stray dogs
investigating animal bite incidents
control of animal trading
import control and quarantine
anti-smuggling
When are dogs required to get vaccinated for rabies and how often after that?
5 months
every 3 years
____% of stray dogs have to be vaccinated for group protection against rabies
80
When is world rabies day?
sep 28
What migration route is HK located on?
east asian-australasian flyway
Avian influenza is of what
family
genus
orthomyxoviridae
alphainfluenzavirus
How many influenza genera and how many strains in birds are there?
7
16
What is highly pathogenic avian influenza?
intravenous pathogenicity index greater than 1.2
caused by groups H5 and H7
What are the modes of transmission of avian influenza?
direct contact
indirect contact through fomites and environment
What are methods to test for avian influenza?
PCR
necropsy
immunuoperoxidase test on frozen tissue
virus isolation
What are the three steps of the cephalic index?
dolichocephalic
mesocephalic
brachycephalic
What dermatological problems are seen in brachycephalic dogs?
skin fold dermatitis
otitis externa
primary secretory otitis media
Why are brachycephalic breeds prone to skin fold dermatitis?
hot and humid environment inside folds=ideal place for fungi and bacteria
debris accumulation + commensal overgrowth + toxin production + inflammation
What is otitis externa?
inflammation of ear canal
What are signs of otitis externa?
head shaking
ear scratching
discharge
malador
What breeds are prone to otitis externa?
french bulldogs
pugs
boxers
What are predisposing factors to otitis externa?
pendulous ears
narrow ear canals
hairy ear canals
swimming
manipulation of ears
What are primary factors of otitis externa?
allergy
parasites
foreign body
growth
hormonal
autoimmune
keratinization abnormalities
What are secondary factors in otitis externa?
bacteria
yeast
What are perpetuating factors of otitis externa?
chronic changes going along the otitis
What is the standard treatment for otitis externa?
ear cleaner
ear drops
oral prednisolene
pain killers
What physical changes happen with primary secretory otitis media?
decreased nasopharynx width
increased mucus production
What age dogs does primary secretory otitis media primarily affect?
middle aged
What are signs of primary secretory otitis media?
aural pruritus
neck pain
abnormal vocalization
reduced hearing
secondary otitis externa
neurological signs
lethargy
What breed is chiari-like malformation usually seen in?
king charles cocker spaniel
What are signs of chiari-like malformation?
rubbing face
abnormal pain sensation
abnormal vocalization
body shaking
neurological signs
air guitar pseudo pruritus