Mechanisms Guide
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- What can it be made into?, What mechanism, What conditions (environment and substances), How to draw
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Alkanes - What can it be made into?
Halogenoalkanes
Alkanes - What mechanism?
Free Radical substitution
Alkanes - What conditions?
UV light
Draw mechanism for Cl2 and methyl butane under UV light? Name stages
Initiation
Cl2 - 2Cl*
Propagation
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH3 + Cl* → CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2* + HCl
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2* + Cl2 → CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2Cl + Cl*
Termination
Cl* + Cl* → Cl2
CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2* + CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2* - CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH2CH2CH(CH3)CH3
Cl* + CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2* → CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2Cl
Halogenoalkanes - What can it be made into?
Alcohols, Amines, Nitriles, Alkenes
Halogenalkanes - What mechanisms?
Nucleophilic Substitution → Alcohols, Amines, Nitriles
Elimination → Alkenes
Halogenoalkanes - What conditions?
Nucleophilic Substitution Alcohol - heated under reflux, sodium or potassium hydroxide solution, in a (mixture of ethanol) and water
Nucleophilic Substitution Amines - Heated in sealed container, Ammonia solution in ethanol, ammonia in excess
Nuclephilic Substitution Nitriles - heated under reflux, with a solution of sodium or potassium cyanide, in ethanol
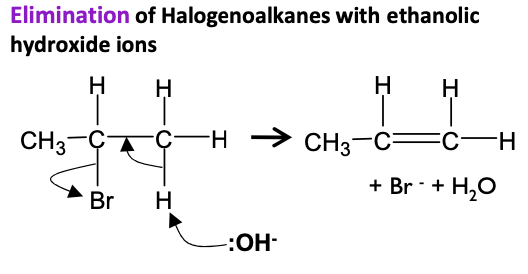
Elimination Alkenes - higher temperatures, concentrated solution of sodium or potassium hydroxide, pure ethanol as the solvent.
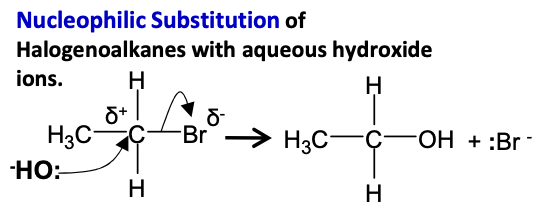
Halogenoalkanes - Draw mechanism for bromomethane in aqueous conditions under gentle reflux with NaOH.
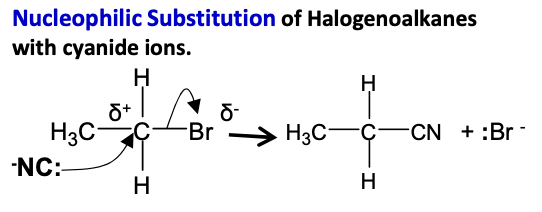
Halogenoalkanes - Draw mechanism for potassium cyanide in ethanol with bromomethane, heated under reflux
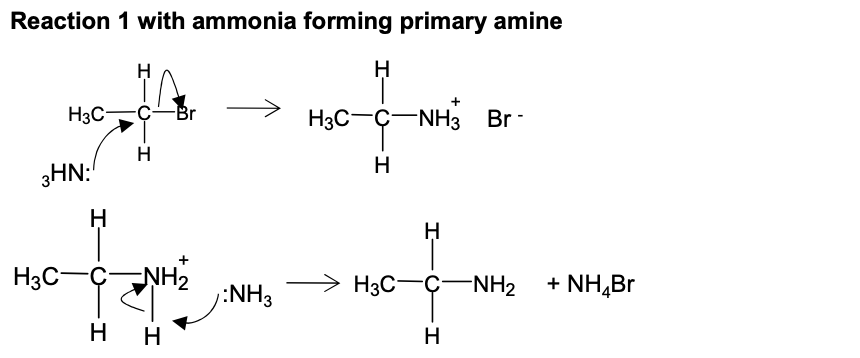
Halogenoalkanes - Draw first mechanism for bromomethane with ammonia in ethanol in sealed container heated with ammonia in excess
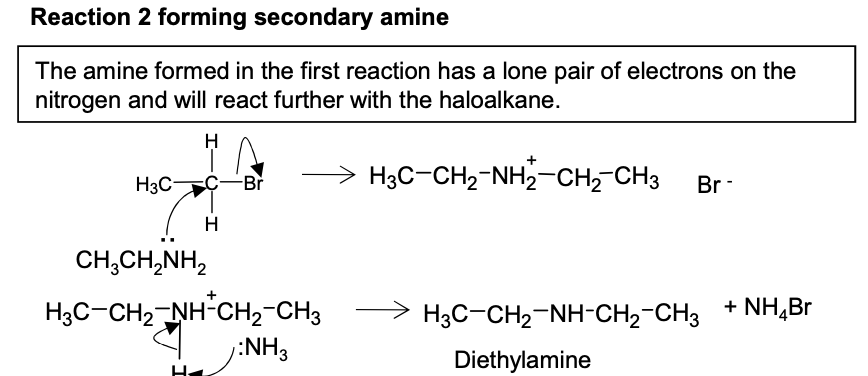
Halogenoalkanes - Draw second mechanism for bromomethane with ammonia in ethanol in sealed container heated with ammonia in excess
Halogenoalkanes - Draw mechanism for bromoethane with ethanolic OH- ions at high temperatures
Alkenes - What can it be made into?
halogenoalkanes, alkyl hydrogensulphates, alcohols
Alkenes - What mechanism?
electrophilic addition, direct hydration
Alkenes - What conditions?
Cold - e.g.pure bromine liquid, sulphuric acid
Direct hydration - aqueous conditions, 300 degrees C, phosphoric acid catalyst, high pressure
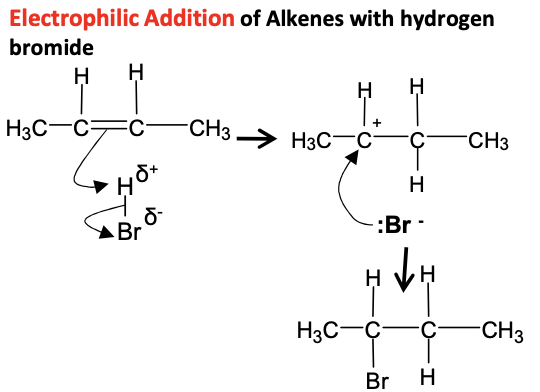
Alkenes - Draw mechanism for but 2 ene with H-Br
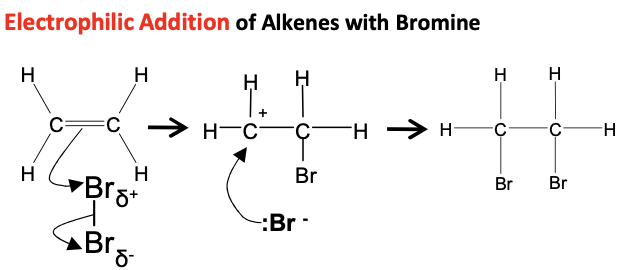
Alkenes -Draw mechanism for ethene with Br2 (l)
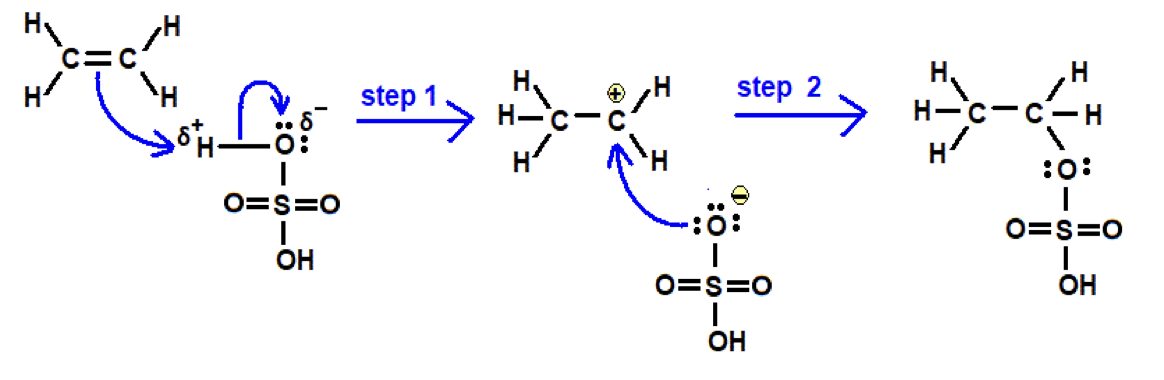
Alkenes -Draw mechanism for ethene with H2SO4 (l)
Alkyl hydrogen sulphates - What can it be made into?
Alcohols

Alcohols - What can it be made into?
Alkenes, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic acids
Alcohols - What mechanisms?
Elimination
Oxidation
Alcohols - what conditions
Elimination - excess hot conc sulphuric acid, aluminium oxide catalyst
Oxidation - potassium dichromate K2Cr2O7 2- ->Cr3+
, H2SO4 heat and distill or heat under reflux.
Alcohols - Draw ethanol with hot con sulphuric acid and aluminium oxide catalyst
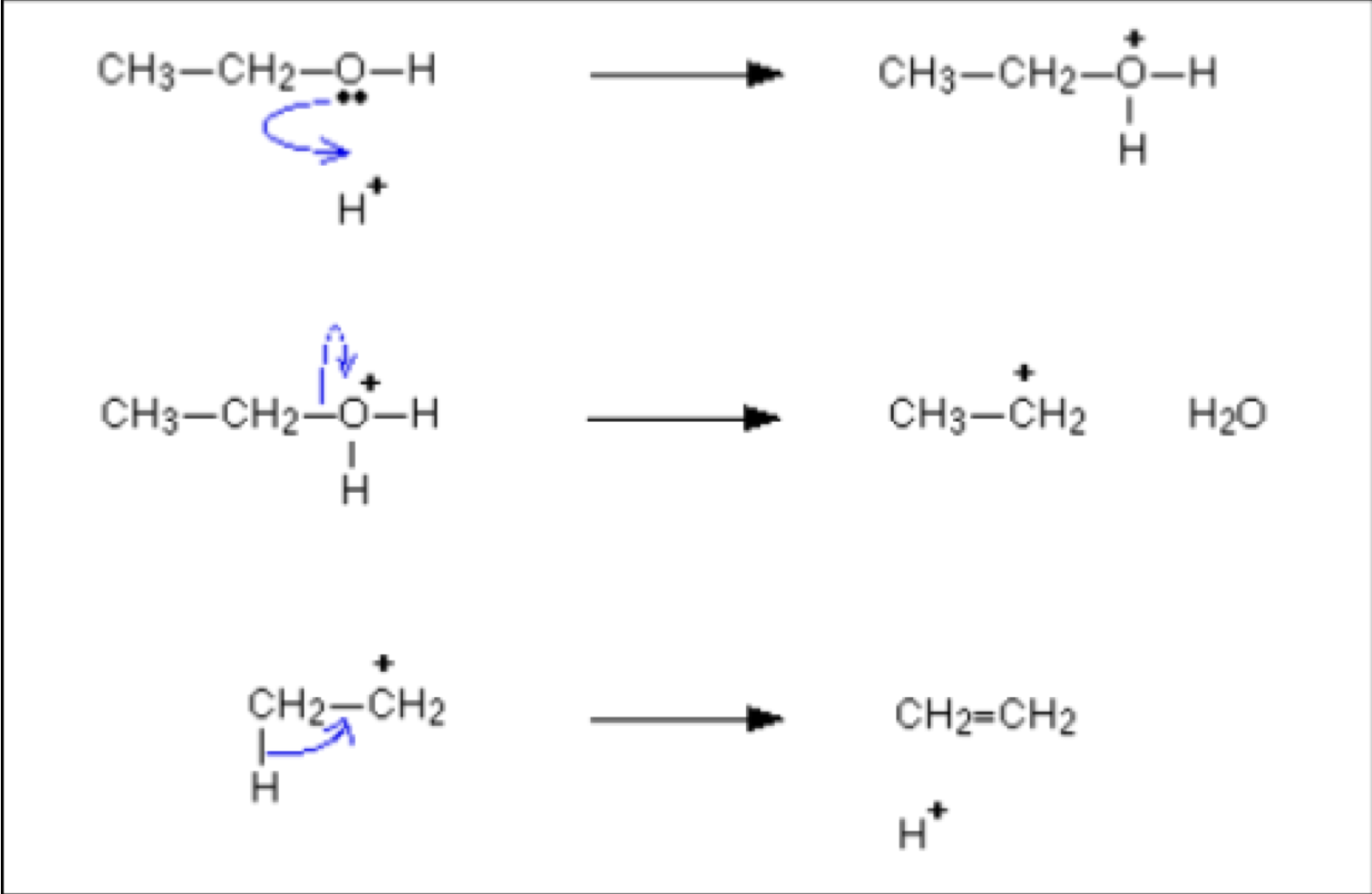
Aldehydes and Ketones - What can they be made into?
hydroxynitriles, alcohols
Aldehydes and ketones - What mechanism
Nucleophilic addition
Aldehydes and Ketones - What conditions?
NaBH4 aqueous → alcohol
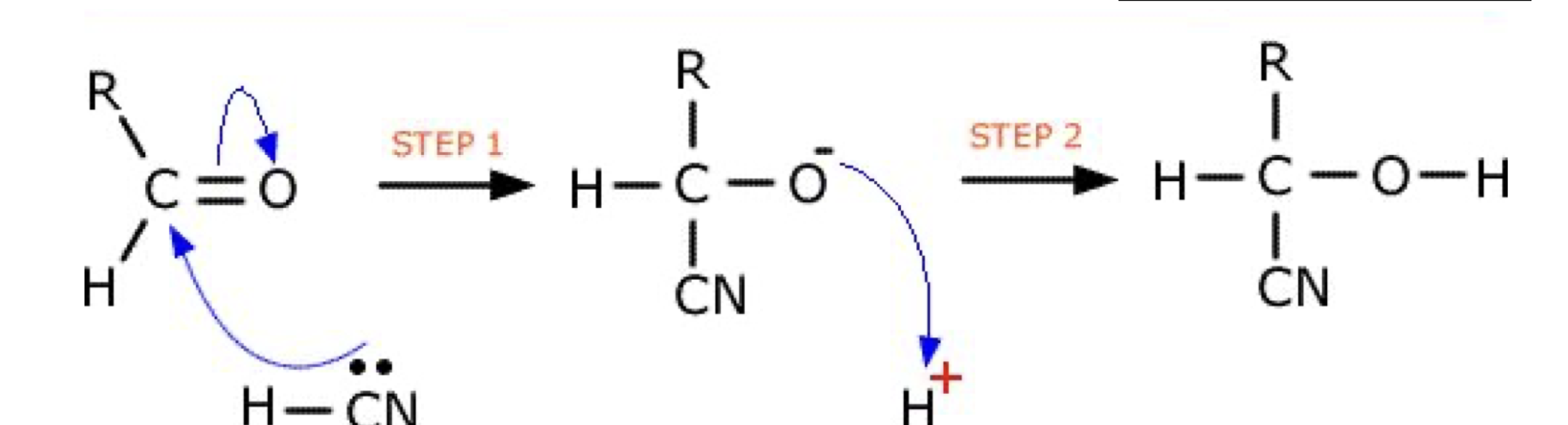
KCN + H2SO4 → hydroxynitrile
Aldehydes and Ketones - Draw mechanism for ethanal with aqueous NaBH4
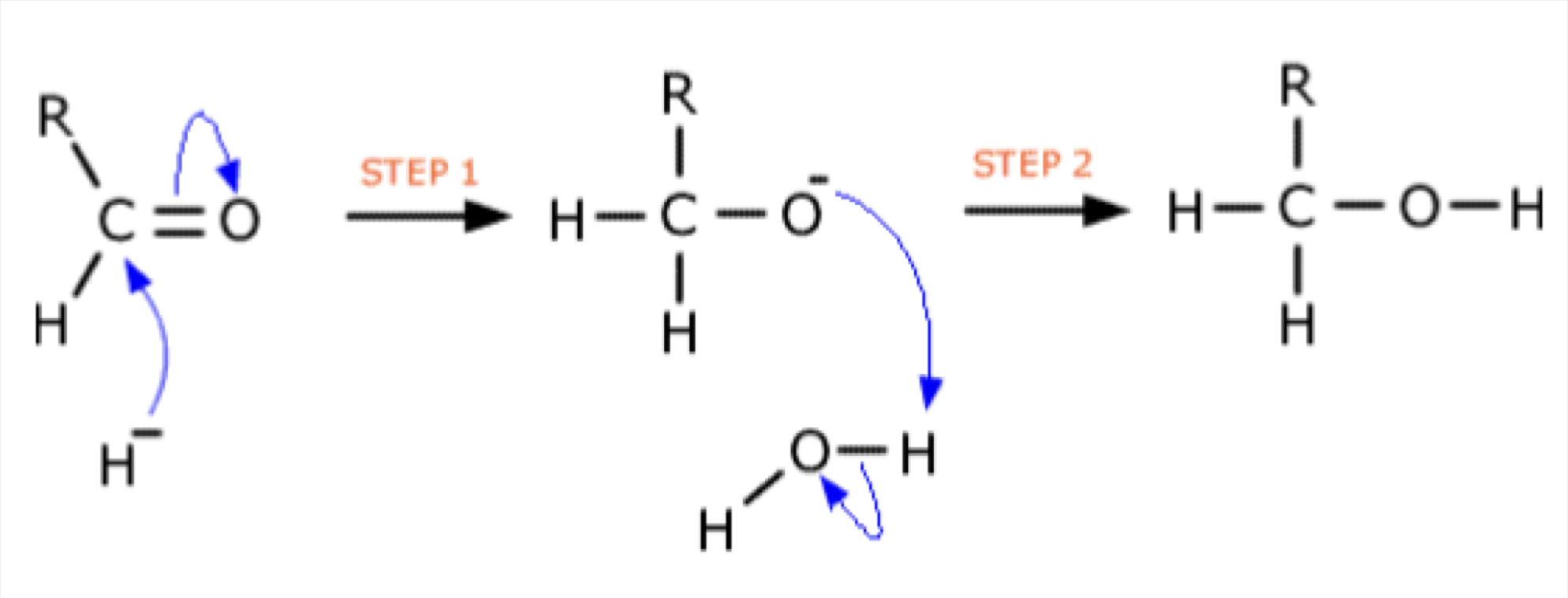
Aldehydes and Ketones - Draw mechanism for propanone with KCN and H2SO4
Name product
2 Hydroxy- methyl propanenitrile
Carboxylic acids - What can it be made into?
esters
carboxylate salts
Carboxylix acids - What type of reactions?
esterification - dehydration
Carboxylic acids - What conditions?
esters —> strong acid catalyst e.g. H2 SO4
carboxylate salts → Na2CO3 (reaction of acid so CO2 and water product)
Esters - What can they be made into?
Carboxylic acid and alcohol
carboxylate salt and alcohol
another ester (transesterification)
Esters - What are the reaction types?
hydrolysis
transesterification
Esters - What are the reaction conditions and resulting products?
How are these products used?
water + ester + acid→ carboxylic acid + alcohol
(reversible reaction)
aqueous NaOH + ester→ carboxylate salt + ethanol
(not reversible) (saponification)
hydrophobic + hydrophilic properties of sodium or potassium carboxylate used in soap
3 methanol and triglyceride → methyl long chain carboxylate (biodiesel) + glycerol
Acyl chlorides - What can they be made into?
carboxylic acid, ester, amide, N-substituted amide
Acyl chlorides - What mechanisms?
nucleophilic addition -elimination
Acyl chlorides - What conditions?
water—> carboxylic acid
alcohol → ester
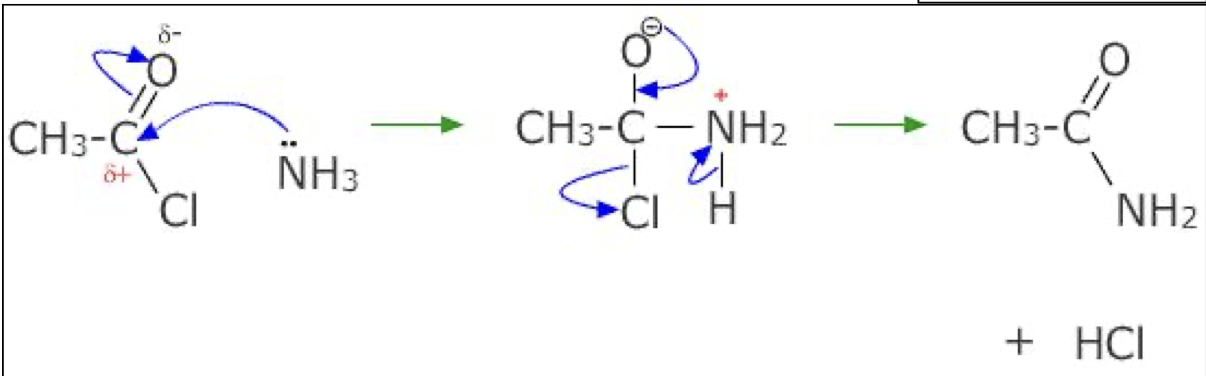
ammonia → amide
primary amine → N - substituted amide
Acyl chloride - Draw mechanism for ammonia with ethanoyl chloride
HCl product
Acid anhydrides - What can they be made into?
carboxylic acid, ester, amide, N-substituted amide
Acid anhydrides - What mechanism?
nucleophilic addition-elimination
Acid anhydrides - What conditions?
water - carboxylic acid
alcohol - ester
ammonia - amide
primary amine - N-substituted amide
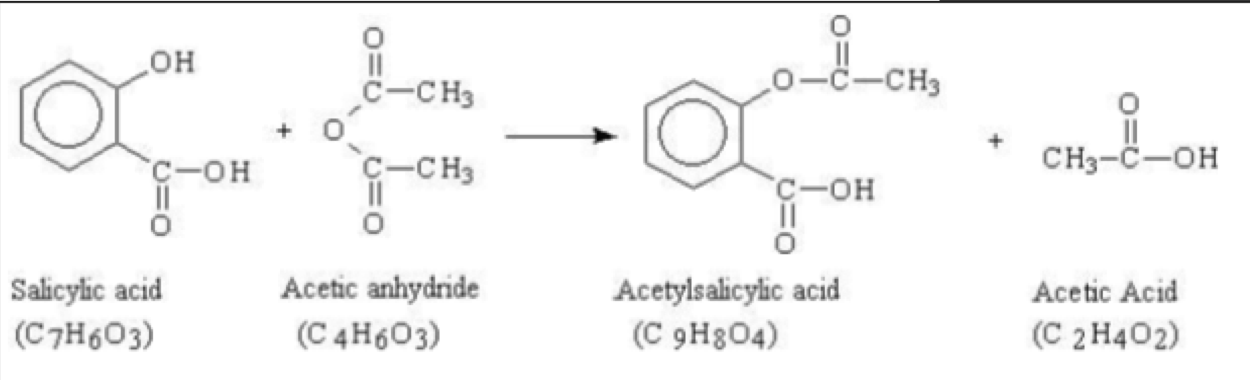
Acid anhydride - Draw mechanism/reaction for ethanoic anhydride with salicylic acid
What can benzene turn into and what are their respective reaction names (not mechanism)
nitrobenzene - nitration, phenylketones - Friedel-Crafts acylation
benzene - What mechanism?
electrophilic substitution
benzene - What reaction conditions?
for acylation → AlCl3
for nitration → H2SO4
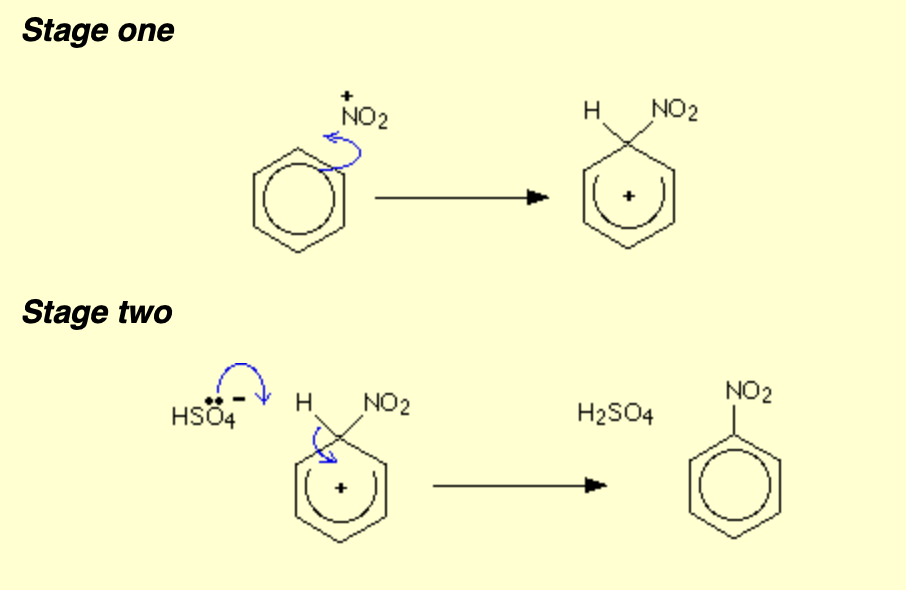
Benzene with sulphuric acid and nitric acid - show the equation to form nitronium ions and mechanism
HNO3 + H2SO4 → (NO2+) +( HSO4- )+ H2O
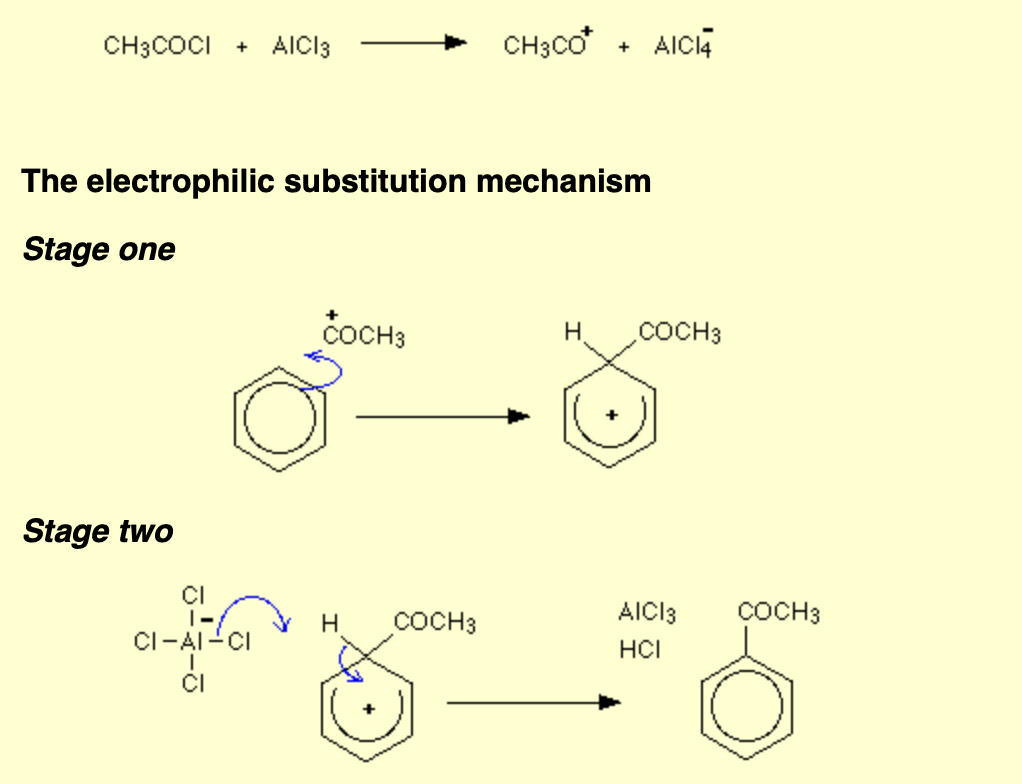
Benzene with ethanoyl chloride and AlCl3
What can nitrobenzene form?
Aromatic amines - phenylamine
What is reaction type?
reduction
What reaction conditions? What is the use of the product?
Sn (tin) and con HCl followed by NaOH (aq)
or
H2 + Ni
used in dye manufacture
What can amines form?
ammonium salts, Amide and N substituted amides
What is the mechanism?
nucleophilic substitution - ammonium salts
nucleophilic addition elimination - amides and N Substituted amide
What are the reaction conditions?
halogenoalkane in excess
( heat under pressure
alcoholic conditions )
room temperature
ethanoyl chloride and ammonia or primary amine or ethanoic anhydride and ammonia or primary amine
What can nitriles form?
amines
What reaction?
Reduction or hydrogenation
What conditions?
H2 and Ni catalyst or LiAlH4