Resistance Training Adaptations: Neural, Muscular, and Structural Changes in Exercise Science
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What was the perception of resistance training before the 1960s?
It was considered inappropriate except for competitive weightlifters and definitely not for females.
Who was Boyd Epley?
The first strength coach for Nebraska and co-founder of NSCA in 1978.
What are the primary outcomes of resistance training?
To increase skeletal muscle strength and hypertrophy.
What factors contribute to strength increases from resistance training?
Increased protein accumulation and neural activation.
What percentage of their motor unit pool do untrained individuals activate during max effort?
Only 71%.
What are the two main types of neural adaptations from anaerobic training?
Increased neural drive and improved coordination.
What is meant by 'neural drive' in resistance training?
It refers to the voluntary activation of prime movers, enhanced by factors like motor unit firing frequency and synchronization.
What is the time course for neural-induced strength gains?
Neural adaptations occur in the first 8-10 weeks, while hypertrophy occurs after ≥10 weeks.
What is hypertrophy in the context of resistance training?
An increase in the cross-sectional area of muscle fibers.
Which muscle fiber type exhibits more hypertrophy?
Type II fibers (white) exhibit more hypertrophy than Type I fibers (dark).
What are the three primary signals for muscle hypertrophy?
Molecular signaling, hormones, and metabolic stress.
How does resistance training affect protein synthesis?
It activates mTOR, leading to increased muscle protein content.

What role does testosterone play in muscle hypertrophy?
It activates transcription in nuclei, stimulates satellite cell differentiation, and inhibits myostatin.
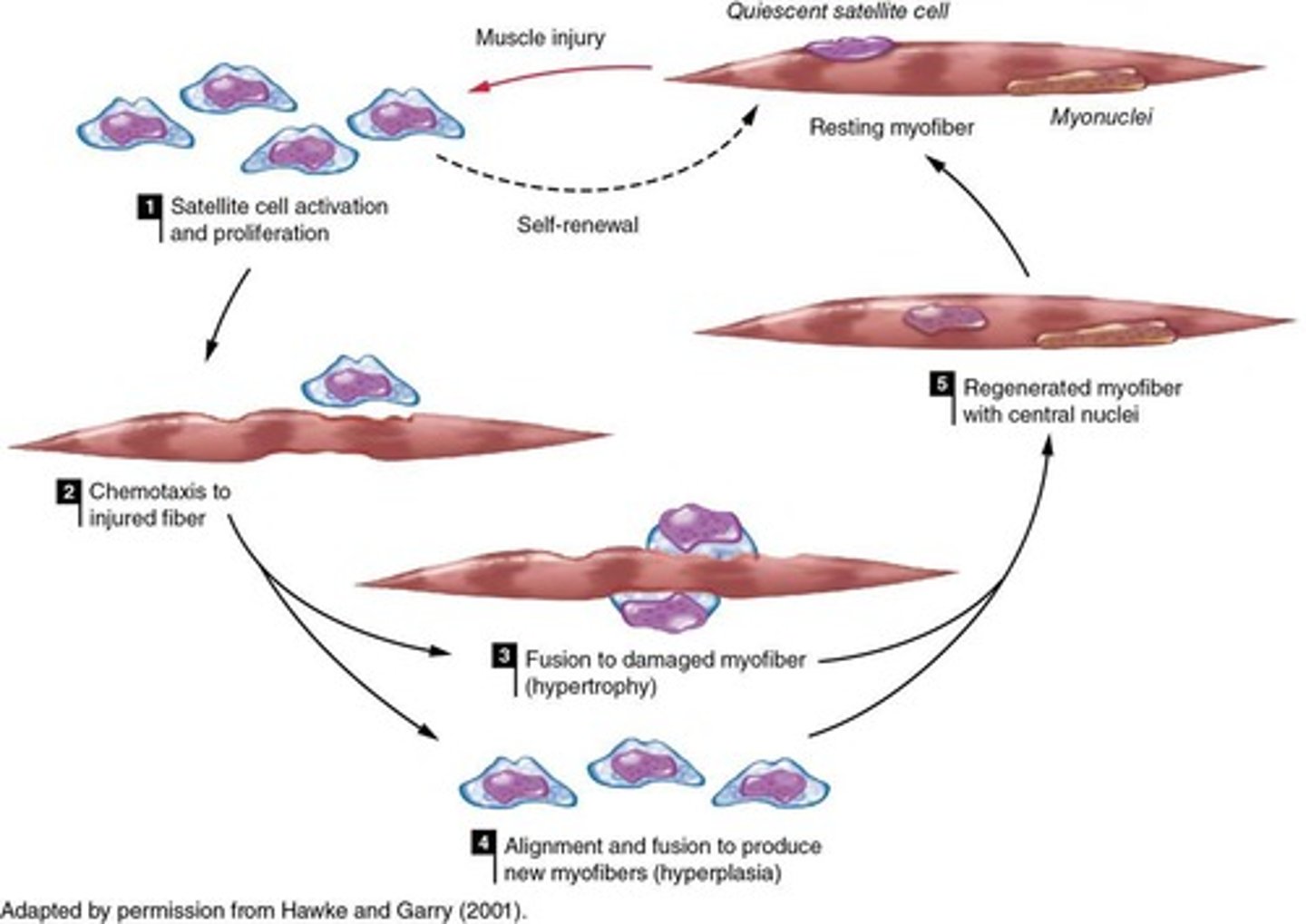
What is the nuclear domain theory?
Hypertrophy requires satellite cell differentiation to generate new myonuclei before increasing cross-sectional area.
What adaptations occur in tendons due to resistance training?
Increased size and stiffness due to larger collagen fibril diameter and increased density of collagen fibrils.
What is the effect of resistance training on bone and connective tissue?
It stimulates adaptations that can aid in the prevention and management of osteopenia and osteoporosis.
What is the impact of resistance training on body composition?
It can increase fat-free mass (FFM) and reduce fat mass (FM), leading to a greater basal metabolic rate (BMR).
How does training status affect strength gains?
Strength gains vary, with untrained individuals seeing up to 40% increases, while elite athletes may see only 2%.
What is the recommended protein intake for muscle mass increase?
1.6 to 1.7 grams of protein per kg of body weight per day.
What happens to muscle when there is a lack of use?
It leads to reduced protein synthesis and strength loss of 3%-4% per day.
What is 'detraining'?
The loss of strength and muscle size due to inactivity, which is reversible due to muscle memory.
What is the effect of resistance training on aerobic capacity?
In some individuals, resistance training can improve aerobic capacity.
What are the benefits of resistance training for motor performance?
It enhances performance in activities like running economy, power, sprint speed, and injury prevention.
What is the significance of 'effective reps' in trained individuals?
Trained individuals require more effective reps to fully recruit their motor unit pool.
What are the adaptations of cartilage to anaerobic training?
Cartilage relies on movement for nutrient diffusion and is positively affected by weight-bearing activities.
What is the recommended protein consumption timing after resistance exercise?
Consume 20 to 25 grams of protein as soon as possible after resistance exercise for optimal muscle growth.
What is the role of metabolic stress in muscle hypertrophy?
It acts as a signal for muscle growth, along with molecular signaling and hormonal influences.
What adaptations occur in muscle fibers during resistance training?
There is a shift from Type IIx to Type IIa fibers, enhancing muscle performance.