4.2- Particle Model of Matter
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Equation for density

What can the particle model of matter be used for
The particle model can be used to explain
the different states of matter
differences in density.
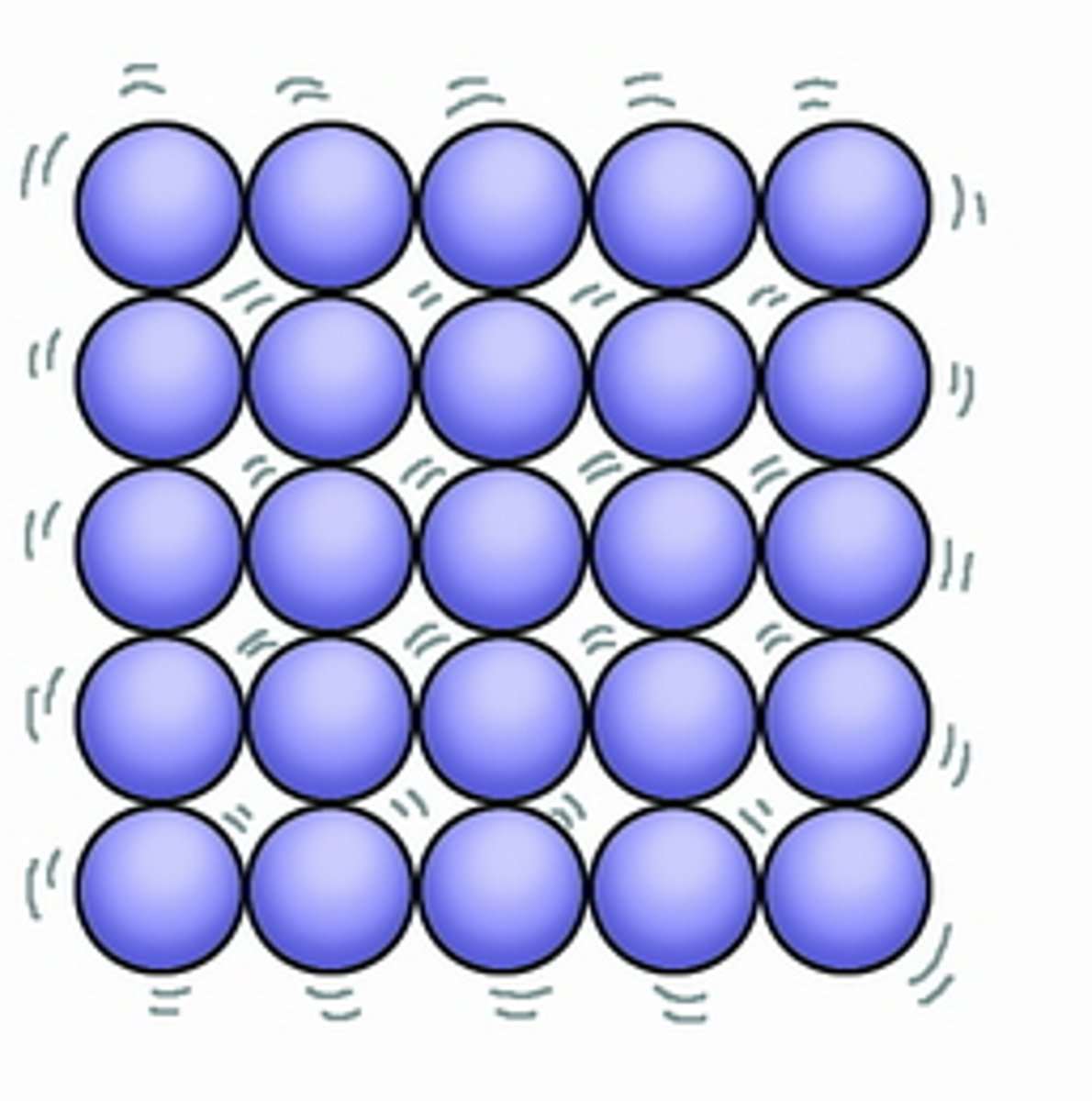
Describe the arrangement and energy of a solid
Regular, fixed position
Strong forces between particles
Small distance between particles
Vibrate on the spot
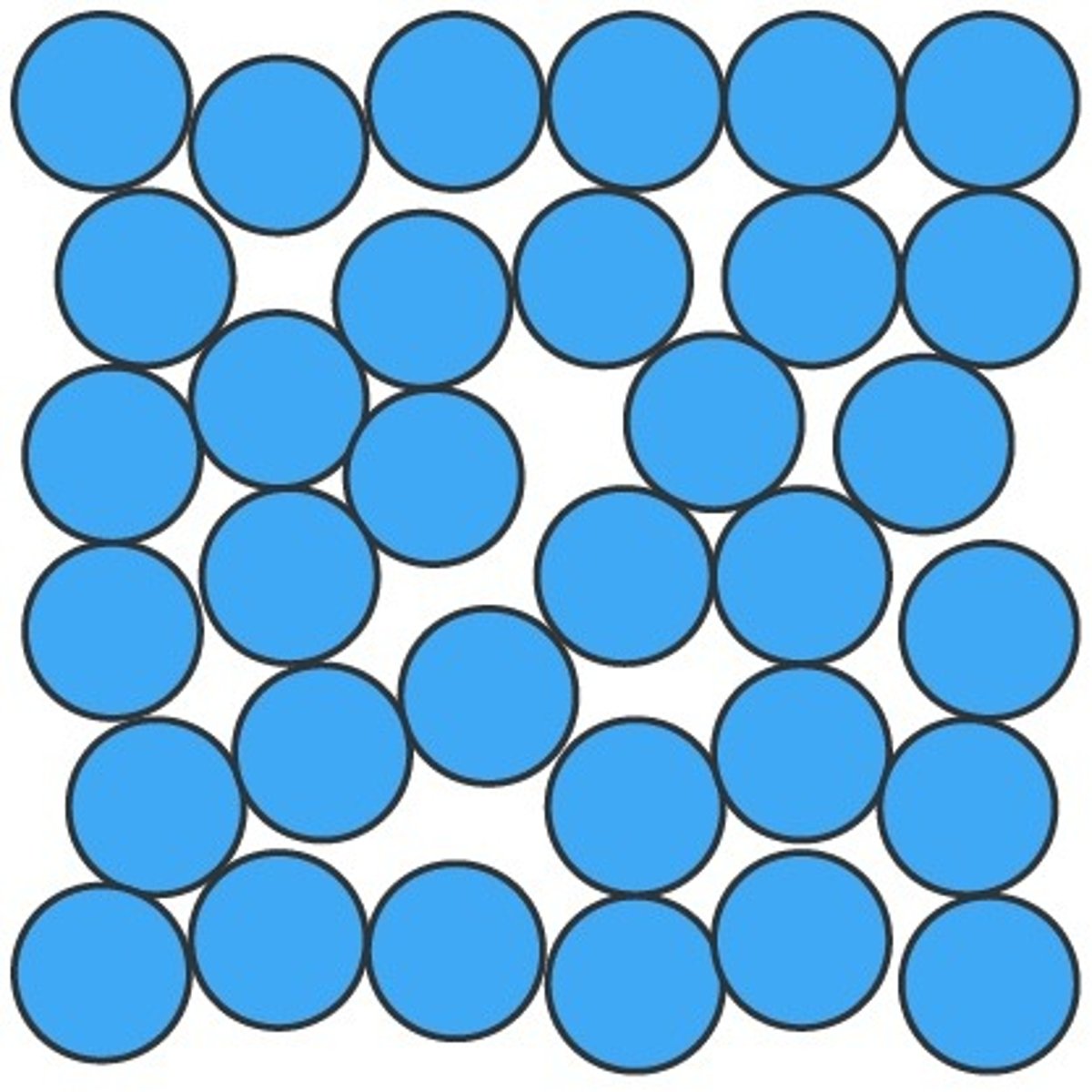
Describe the arrangement and energy of a liquid
Irregular, but still touching
Random Positions
Weak forces between particles
Small distance between particles
Slow particles motion, flow over and around each other randomly
Describe the arrangement and energy of a gas
The molecules of a gas are in constant random motion
Very weak forces between particles
Large distance between particles, not touching, colliding occasionally
Fast motion
Range of speeds, random and different motions
What are the 6 changes of state called
Melting
Freezing
Evaporation
Boiling
Condensation
Sublimation
Why is a change of state a physical change
Changes of state are physical changes which differ from chemical changes because the material recovers its original properties if the change is reversed.
Define internal energy
The sum of all the Ek and Ep in across the particles in a system
Define temperature in relation to the energy of particles
Temperature is the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance
What does increasing temperature do to the particles
Increasing temperature increases the speed of the particles, as well as increasing the speed and force of collisions
Describe a bond between particles
Bonds store energy. If we try to break a bond, we have to do work against it and apply energy. The energy stored between bonds is called potential energy (Ep)
Draw and annotate the graph of a pure substance being heated
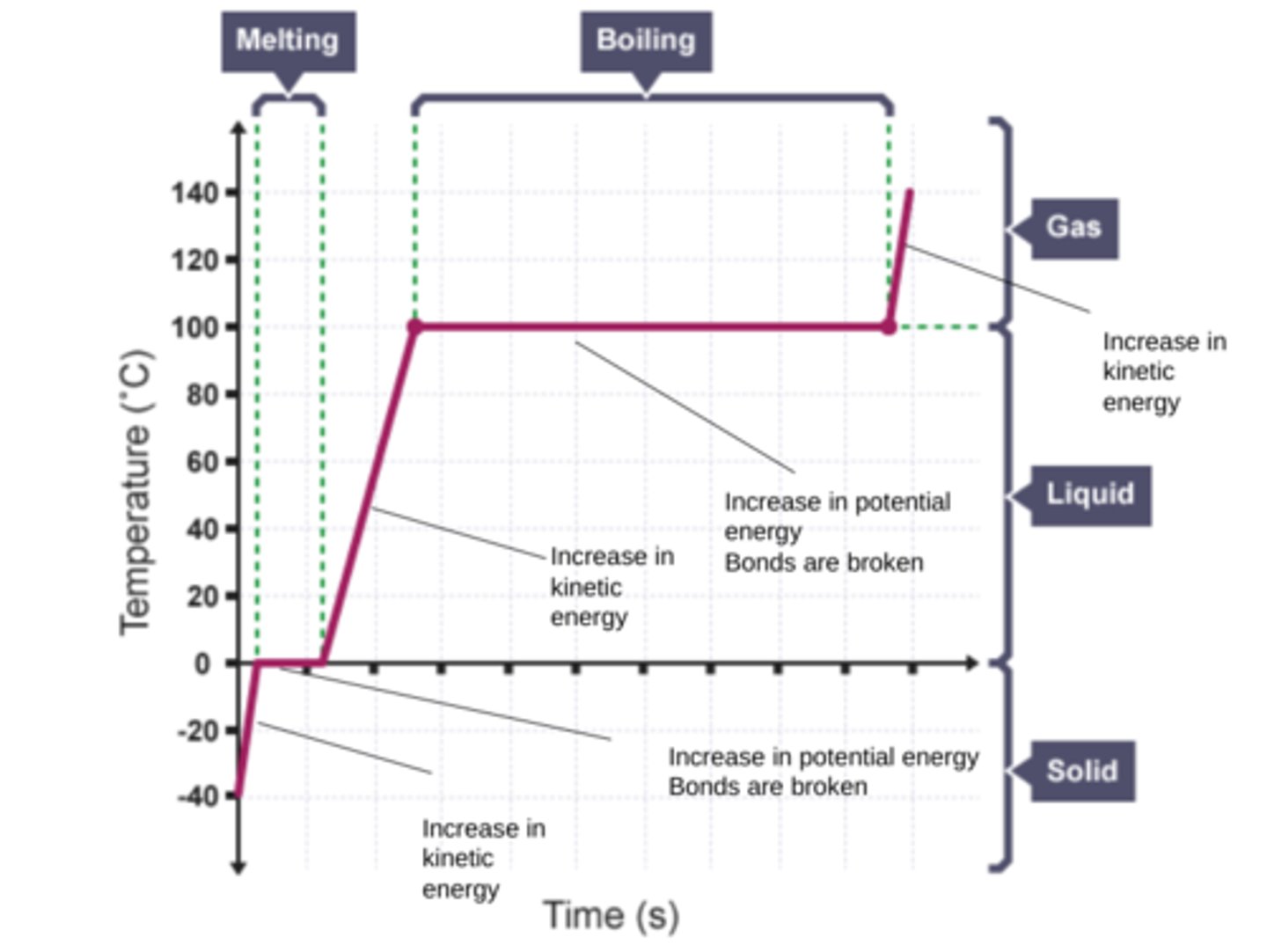
What does heating a system do to the particles
Heating changes the energy stored within the system by increasing the energy of the particles that make up the system.
This either raises the temperature of the system or produces a change of state.
Define Specific Heat Capacity , and give the equation
change in thermal energy =mass ×specific heat capacity ×temperature change
[∆E =m c ∆θ]
change in thermal energy, ∆ E , in joules, J
mass, m , in kilograms, kg
specific heat capacity, c , in joules per kilogram per degree Celsius, J/kg °C
temperature change, ∆ θ , in degrees Celsius, °C.
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one kilogram of the substance by one degree Celsius.
Define Specific Latent Heat, and give the equation
The specific latent heat of a substance is the amount of energy required to change the state of one kilogram of the substance with no change in temperature.
energy for a change of state =mass ×specific latent heat
[ E =m L ]
energy, E , in joules, J
mass, m , in kilograms, kg
specific latent heat, L , in joules per kilogram, J/kg
Compare specific latent heat of vaporisation (Lv) and specific latent heat of fusion (Lf)
Lv is the energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance from liquid to gas or gas to liquid, without a state change
Lf is the energy required to change the state of 1kg of a substance from solid to liquid or liquid to solid, without a state change
What is the equation for pressure
Pressure=Force/Area
Pressure= Pascals (N/m2 or Pa)
Force= Newtons (N)
Area= metres2 (m2)
Explain what happens to the pressure of a gas, if the volume remains constant, if the temperature increases
Temperature is average kinetic energy, so an increase in temperature is an increase in the kinetic energy of the particles. More kinetic energy means the particles will move faster, and will therefore collide with the walls of the container more; more kinetic energy also means the particles have more force and will collide with more force (E=Fxd, so E∝F) . Both of these mean more overall force on the walls of the container, and since P=F/A, as force increases, pressure increases
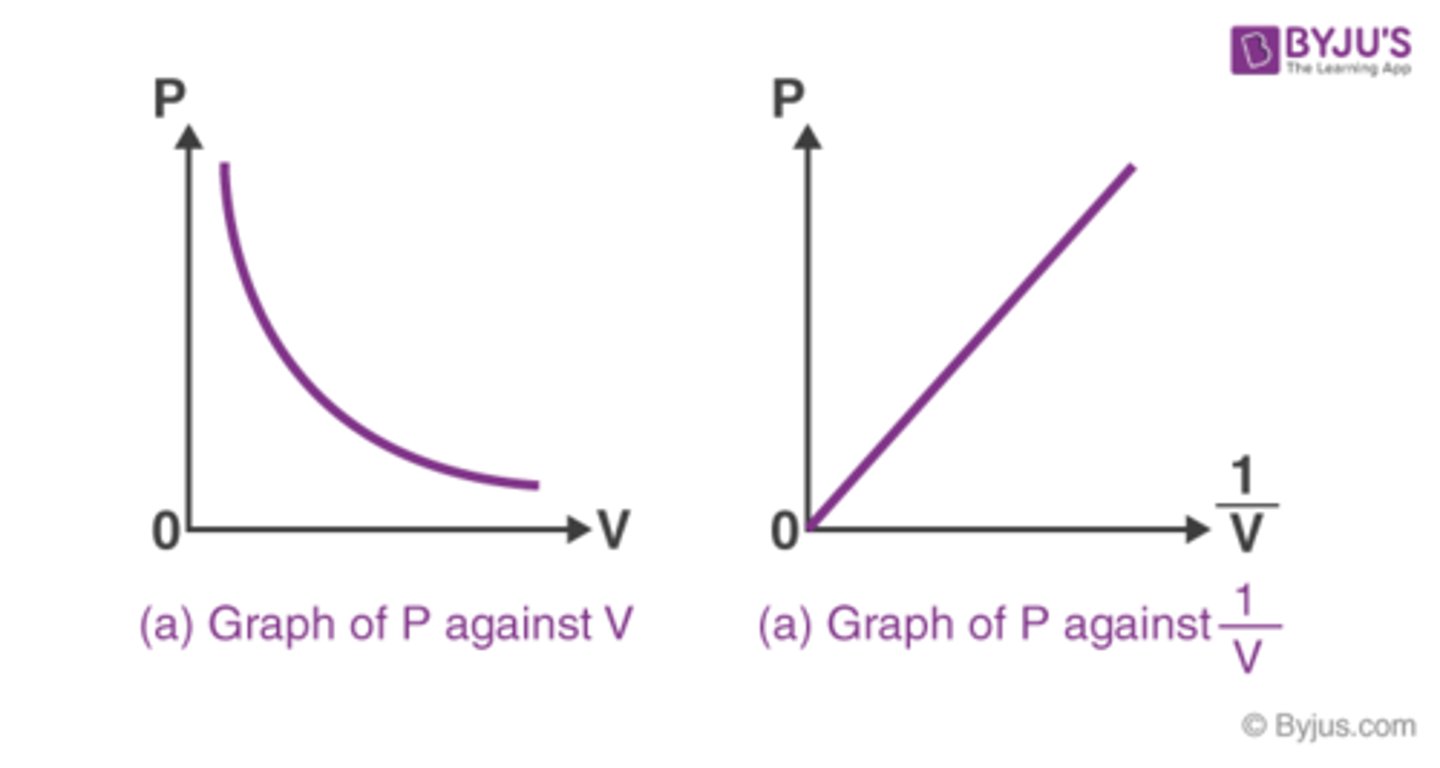
What is Boyle's Law?
PV=k
P∝1/V
P1xV1=P2xV2
What happens if pressure outside > pressure inside
Gas is compressed
This is done to make both the pressures equal
When the gas compresses, the volume decreases so the pressure increases
What happens if pressure outside < pressure inside
Gas expands
This is done to make both pressures equal
When the gas expands, the volume increases, so the pressure decreases
What is the direction of the force applied when a particle collides with a wall
A gas can be compressed or expanded by pressure changes. The pressure produces a net force at right angles to the wall of the gas container (or any surface).
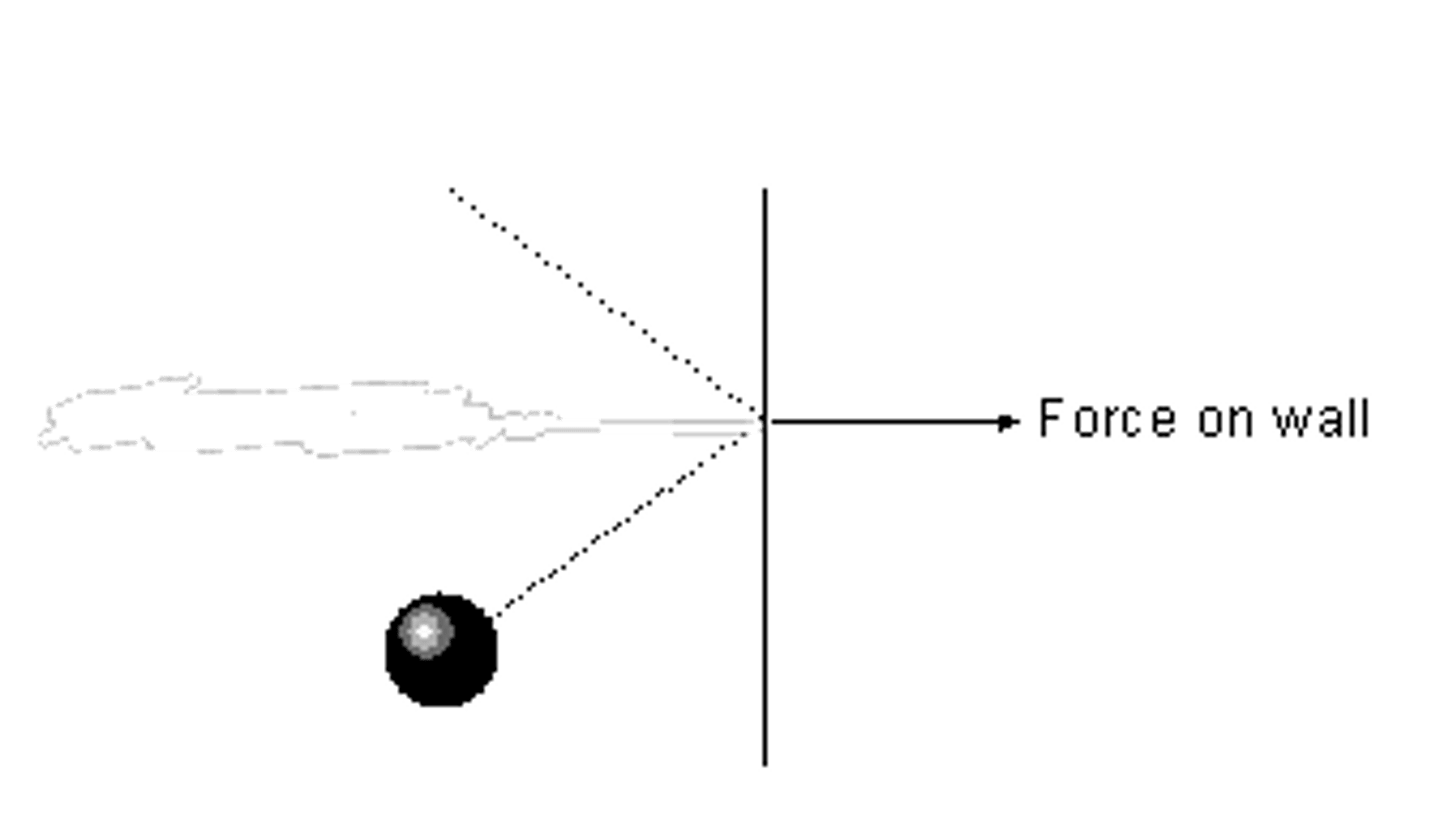
What happens when a gas is moved, such as when a gas is pumped in a bicycle pump
Work is done on the gas
Doing work on the gas increases the internal energy
Temperature of the gas (if enclosed) increases
Why does pressure increase if volume decreases
Less space between particles and the walls of container
More frequent collisions between particles and the walls of the container
Causing a higher overall force on the walls of the container
Pressure is the average force per unit area, so if force increases, so does pressure