LE3 - Head and Neck 2
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
The right common carotid artery originates from which trunk?
Brachiocephalic Trunk
The left common carotid artery originates from which trunk? (Remember! The Lonely Left CCA)
Aortic Arch (Lonely because it comes directly from the Aortic Arch)
Where do the R and L CCA bifurcate?
Superior border of thyroid cartilage + Angle of Mandible
What can be found inside the Carotid Sheath?
CCA + Internal Jugular Vein + Vagus Nerve
[must know] Arrange the contents of the Carotid Sheath from Medial to the Posterior to the lateral
(most medial) CCA → (posterior) Vagus Nerve → (lateral) IJV
The CCA splits and forms which 2 arteries?
Internal Carotid Artery and External Carotid Artery
[Trick question] Which is found inside the carotid sheath? CCA or ICA
Both are found inside. The only one found outside the sheath is the External Carotid Artery.
Which artery is known to supply most of the structures external to the cranium?
ECA
Knowing that the ECA supplies most of the structures EXTERNAL TO THE CRANIUM, does the ECA supply the Scalp, Orbit and the whole forehead?
NO, those structures are supplied by the Supraorbital Artery from the ICA.
What landmark can you use to spot the ECA?
Superior Border of the Thyroid Cartilage
Is the ECA found inside the Carotid Triangle?
Yes.
Where does the ECA run?
Supero-posteriorly between the Neck of Mandible & Lobule of Auricle
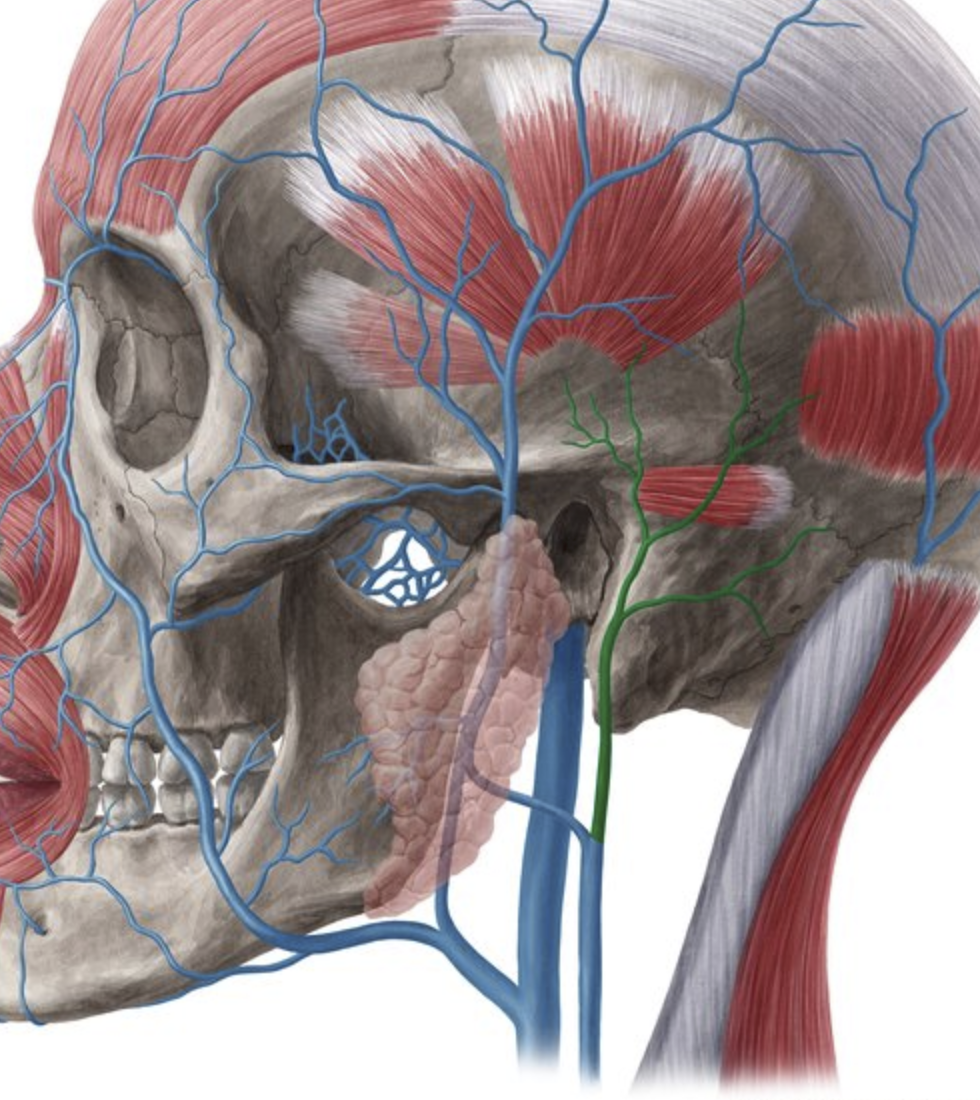
Which Artery is found EMBEDED IN the parotid sinus?
External Carotid Artery
What are the Branches of the ECA? (remember! S-A-LFOP-MS)
Superior Thyroid > Ascending Pharyngeal > Lingual > Facial > Optic > Posterior Auricular > MAXillary > Superficial Temporal
Which branch of the ECA is found medially?
Ascending Pharyngeal (Insert Image)
[must know] What are the 2 terminal branches of the ECA?
S-A-LFOP-MS = Maxillary and Superficial Temporal arteries
The Facial Artery, a branch of the __ anastomoses with branches of the – artery?
(1) ECA (2) Ophthalmic artery
What is an alternative route or collateral artery for blood to reach the eye?
Facial Artery
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Ascending palatine artery supplies the?
Throat
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Tonsillar artery supplies the?
Palatine tonsils
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Submental artery supplies the?
Salivary Glands & Area below the chin
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Inferior Labial a. Supplies the ?
Lower Lip
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Superior labial a. Supplies the ?
Upper lip
[must know]Branches of the Facial Artery: What artery supplies the DORSUM and ALA of the nose?
Lateral Nasal Artery (Iba ito sa Posterior Nose)
Branches of the Facial Artery: The Angular a. Supplies the ?
Superior part of the Cheek and the Lower Eyelid
[must know]Branches of the Facial Artery: What is the TERMINAL BRANCH of the Facial Artery?
Angular Artery!
Which artery ascends IN FRONT of the auricle to supply the Scalp?
Superficial Temporal Artery (1 of the 2 Terminal branches of ECA)
Which artery is commonly mistaken for the Parotid Duct?
TRANSVERSE FACIAL artery (a branch of the superficial temporal artery)
Which one of the 2 Terminal branches of the ECA is LARGER?
MAXILLARY artery
T or F? The Facial artery has anastomosis with the Ophthalmic artery and Maxillary artery (Buccal branch of the 2nd part)
TRUEE
What are 2 arteries supplying the Scalp?
Supraorbital and Superficial Temporal artery
What divides the Maxillary Artery into 3 parts?
LATERAL Pterygoid muscle
The 1st part of the Maxillary artery is called the Mandibular Branch. It’s branches mostly supply the Inner Ear, Intracranial Dura and the Mandible, Teeth and Gingiva. Most of the Branches courses UP THE SKULL, except one. Which is it and what does it supply?
Inferior Alveolar (Mandible, teeth and gingiva)
The Deep Auricular and Anterior Tympanic arteries supply the Inner Ear components like the External Acoustic Meatus and Tympanic Membrane. Which part of the Maxillary Artery can it be found?
1st Part!
[must know] The middle meningeal artery can be seen in which Cranial FOSSA?
Foramen SPINOSUM
Does the 2nd part of the Maxillary Artery pass OVER or UNDER the Lateral Pterygoid muscle?
PASSES OVER!
T or F? The 2nd (pterygoid) part of the Maxillary a. is known to supply the muscles found in the cheek?
True! It supplies the masseter, Buccinator, and pterygoid muscle.
Which part of the maxillary a. Has anastomosis with the facial artery?
2nd Buccal Part of the Maxillary a.
In the 3rd (pterygopalatine) part of the maxillary a., the Posterior Superior Alveolar artery is also known as the Dental artery. What does it supply?
Maxillary molars and Pre-Molars
Which branch of the 3rd part of the Maxillary a. Supplies the Inferior Eyelid, Lacrimal Sac, Side of the nose and anastomoses with the Facial and Angular arteries?
INFRAORBITAL artery
Is the Infraorbital artery a branch of the Optic artery?
No!!! It is a branch of the 3rd part of the Maxillary Artery.
The artery of the pterygoid canal is a branch of which part of the maxillary artery? And what does it supply?
(1) 3rd part of the Maxillary Artery (2) Superior Part of Pharynx, Eustachian tube and Tympanic Membrane
[Trick question] What supplies the ROOT of the Pharynx and Inferior Eustachian tube? A. Pharyngeal branch of 3rd part of maxillary artery B. Artery of the pterygoid Canal from the 3rd part of the maxillary artery
Pharyngeal Branch!
[Trick question] What supplies the SUPERIOR PART of the Pharynx and Eustachian tube? A. Pharyngeal branch of 3rd part of maxillary artery B. Artery of the pterygoid Canal from the 3rd part of the maxillary artery
Artery of the pterygoid Canal
[must know] Bleeding from which artery is known to cause Nose Bleeds?
SPHENOPALATINE artery
Nose bleeds is due to damage to a branch of which part of the Maxillary Artery?
3rd part of the maxillary artery.
T or F? The Right Subclavian artery branches directly from the Aortic arch?
False! Remember Lonely Left. the R-subclavian branches from the Brachiocephalic Trunk.
What divides the Subclavian artery into 3 parts?
Scalenus ANTERIOR ms.
Which part of the Subclavian artery does NOT have any branches? :)
The 3rd Part = No branch
Branches of the Subclavian Artery! (Remember VIT- C yehey!)
(1st part) Vertebral, Internal Thoracic and Thyrocervical (2nd part) Costocervical
T or F? The 2nd part of the SUBCLAVIAN artery is found posterior the Scalenus Anterior ms.
TRUE
Tricky! 2nd part subclavian = passes (over or under?) while the 2nd part maxillary = Passes (over or under?)
subclavian = under , maxillary = over (siguro remember SUBclavian = below)
The Vertebral artery is a branch of?
Subclavian artery
The vertebral artery supplies?
Posterior Circulation of Brain
Which cranial fossa can the Vertebral artery be seen exiting?
Foramen magnum
Where does the Basilar artery originate from?
Vertebral artery
What are the branches of the Thyrocervical Trunk of the 1st part of the Subclavian artery?
(1) Suprascapular (2) Cervico-dorsal (3) Ascending Cervical (4) Inferior Thyroid
The Thycrocervical Trunk of the Subclavian artery arises from the _ aspect of the subclavian artery near the - border of the Scalenus muscle?
(1) Antero-inferior aspect of subclavian (2) Medial border of Scalenus anterior ms.
What is the Terminal branch of the Thyrocervical Trunk?
Inferior Thyroid artery
What is the ONLY branch of the Subclavian artery that goes down and passes infero-medially into the thorax?
Internal Thoracic Artery
Does the Internal Thoracic artery have any Cervical branches?
No… pls think
The 2nd part of the Subclavian artery (COSTOCERVICAL trunk) supplies mostly the?
First 2 intercostal spaces and Deep Cervical muscles of the costocervical ms.
Which branch of the Costocervical trunk anastomoses with the OCCIPITAL ARTERY (branch of the ECA)?
DEEP CERVICAL BRANCH OF THE COSTOCERVICAL TRUNK
Which Artery is seen to enter the carotid canal and into the Petrous Temporal Bone into the Cranial cavity?
INTERNAL Carotid artery
T or F? Branches of the INTERNAL CAROTID artery can be seen in the NECK
NO, mostly inside the head na ung ICA.
The Ophthalmic artery ( known to anastomose with the Facial Artery (from the ECA)) is a branch of which artery?
ICA
If the ICA is blocked, it has anastomoses with?
From Ophthalmic → Facial Artery and Branches of the Maxillary artery
[must know]In the case of ICA occlusion, how does the Ophthalmic artery supply the brain?
The Ophthalmic artery allows reverse flow of blood from the ECA via its anastomoses with the Facial artery and branches of the Maxillary artery.
Does the ICA or the ECA supply the most of the superficial facial arteries?
ECA
[must know] Knowing that the ECA supplies mostly the superficial facial arteries, what are the exceptions?
The ICA supplies the glabellar and medial frontal area of the face!
What is the Largest and Main vein of the neck?
Internal Jugular Vein
The IJV is seen exiting through which cranial fossa?
Jugular Foramen
Where are the 2 bulbs of the IJV found?
Superior Bulb - near its origin
Inferior Bulb - near its end, with a bicuspid valve pa!
IJV descends to join which vein?
Subclavian vein
IJV + Subclavian vein = ?
Brachiocephalic Vein
(MUST KNOW) The union of the IJC and Subclavian vein is best observed at?
T1
(must know) Why is IJV catheterization usually done at the RIGHT IJV?
More direct to the (R) atrium
The (L) IJV is longer..***
The EJV drains mostly the?
Face and Scalp
The EJV is formed from the union of which veins?
Posterior auricular
Retromandibular
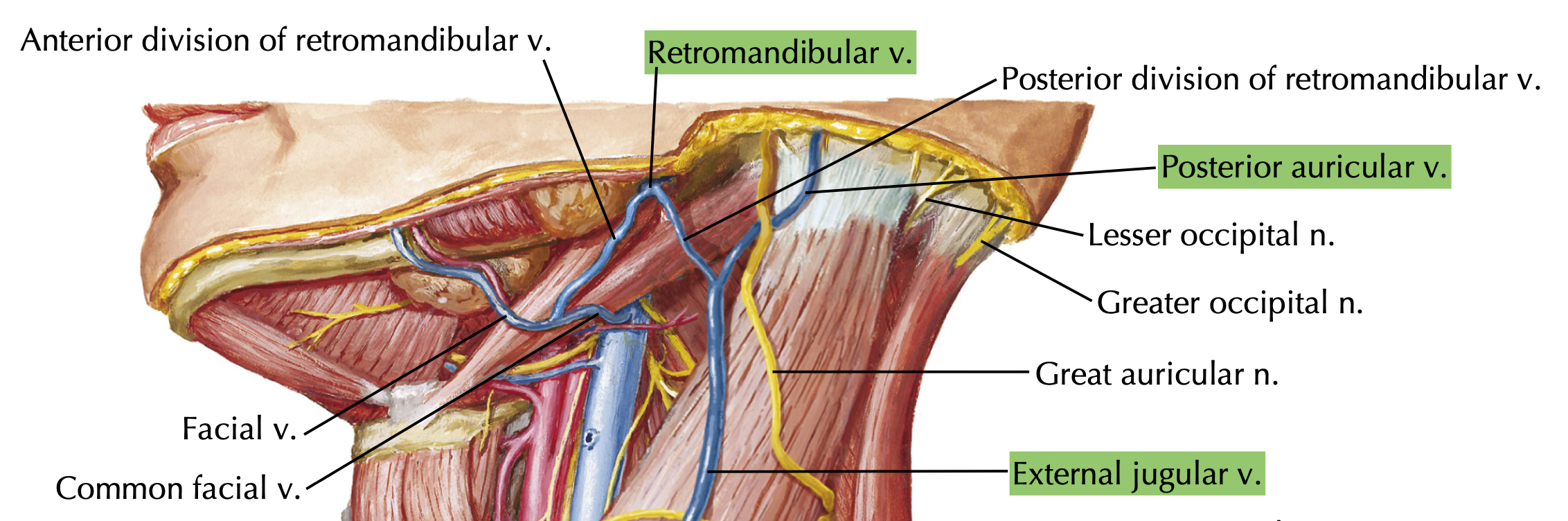
the EJV drains into?
Subclavian veins
The ___ veins are a pair of veins on the paramedian anterior neck, beginning below the chin by the union of small veins.
Anterior Jugular Veins
Where can you find the Jugular Arch, or the transverse trunk uniting the Anterior Jugular Veins?
Above the Suprasternal Notch
T or F? All of the Superficial Veins of the face are valveless.
True!
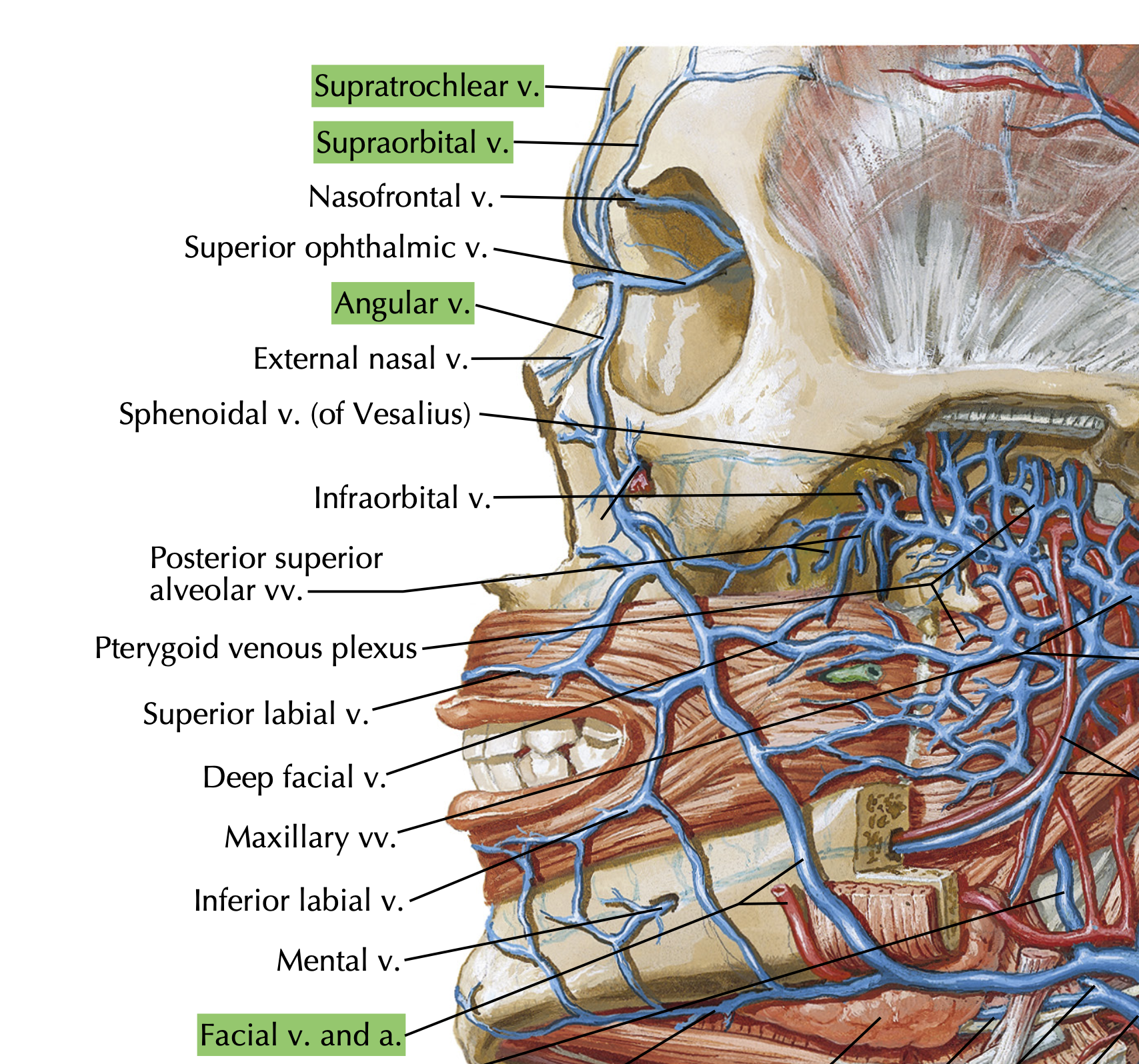
Which 3 veins fuse to form the facial vein at the inferior margin of the Orbit?
Supra trochlear vein
Supra orbital vein
Angular vein
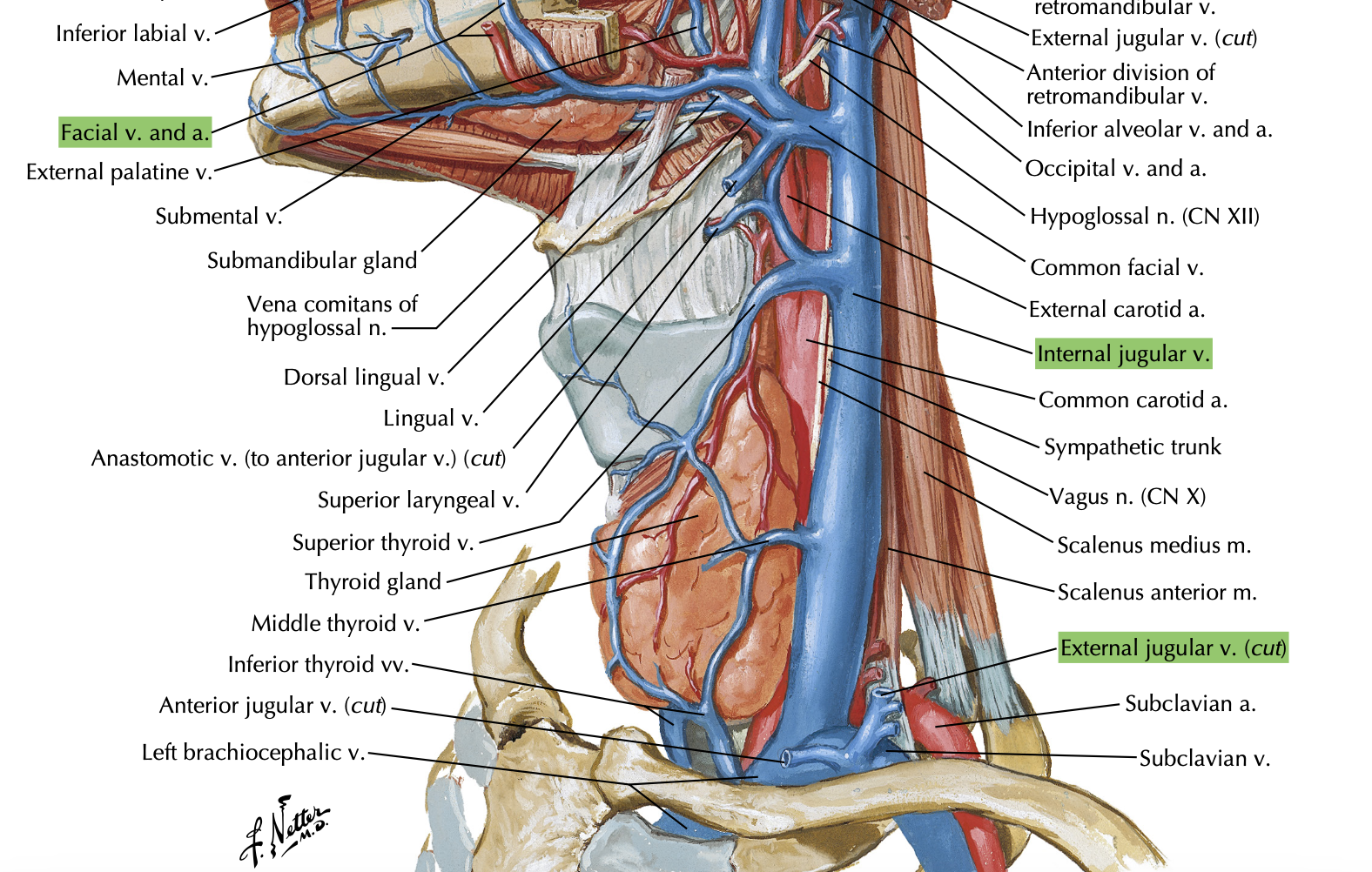
The facial vein drains into the EJV or IJV?
(be careful, although the EJV drains the Face and Scalp, the Facial vein is different? )
IJV
Remember! EJV only drains 2 veins!
Posterior Auricular
Retromandibular
The Transverse facial vein has a zygomaticotemporal branch that anastomoses with?
infraorbital vein
T or F? The Zygomaticotemporal branch of the Transverse Facial Vein pierces the substance of the parotid canal to become the Superficial temporal vein
True?
The Superficial Temporal vein and the maxillary vein join to form which vein?
Retromandibular vein
T or F? The Retromandibular vein has connections to both the EJV and IJV.
True.
Retromandibular vein
Anterior branch → common facial vein → IJV
Posterior branch → posterior auricular → EJV (eto daw main)
Which vein drains the scalp area posterior behind the auricles?
Retromandibular vein
What vein drains the danger triangle of the face?
Angular Vein
Dangerous cuz:
angular v. → superior ophthalmic v. → Cavernous sinus
angular v. → inferior ophthalmic → Pterygoid venous plexus
(Must Know) What are the KEY structures found in the Danger Triangle of the Face?
Remember: 3,4 shut the door, 5,6, pick up sticks. I Can ADD
CN 3
CN 4
CN 5
CN 6
Internal Carotid Artery
The L - jugular trunk of the Inferior Deep Cervical lymph nodes drains into?
Remember Lonely Left
Thoracic duct
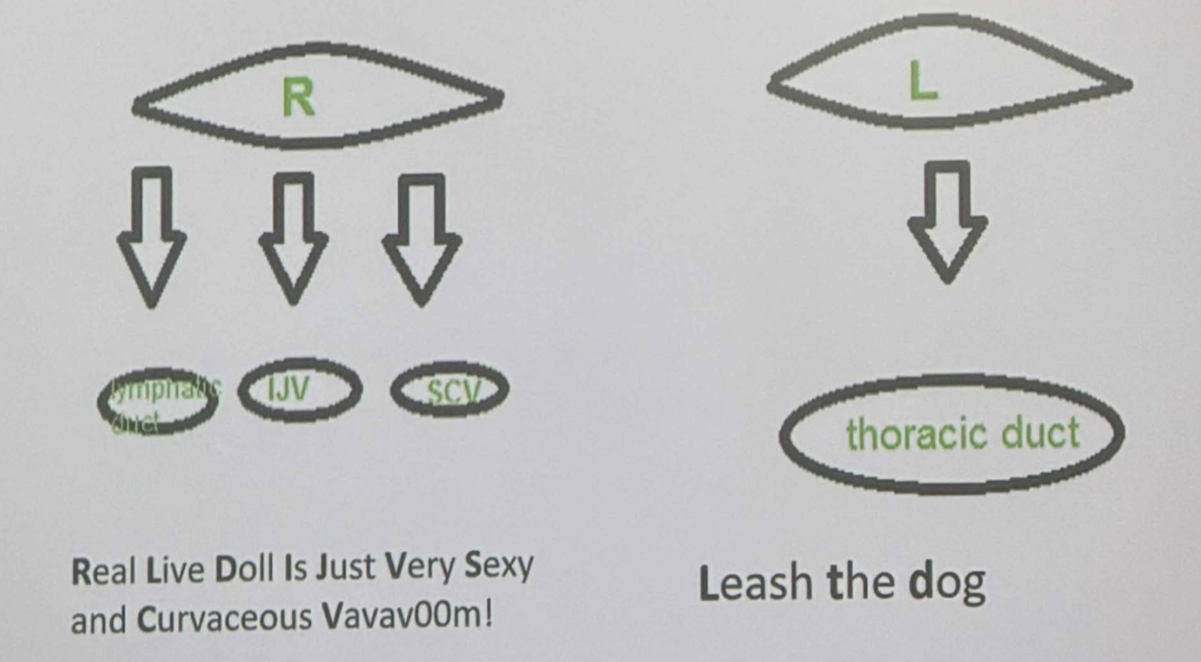
The Right - jugular trunk of the Inferior Deep Cervical lymph nodes drains into?
Right Lymphatic Duct
Internal Jugular Vein
Subclavian vein
What type of nerve is the Trigeminal Nerve?
Mixed Nerve (both motor and sensory)
What is the main sensory nerve of the Head?
Trigeminal Nerve
The Trigeminal nerve has what 3 branches?
Ophthalmic Nerve (CN V1)
Maxillary Nerve (CN V2)
Mandibular Nerve (CN V3)
The Trigeminal nerve provides sensory innervation to which structures?
Face
Teeth
Mouth
Nasal cavity
Dura mater
Paranasal sinuses
skin of the scalp
The Trigeminal nerve provides Motor innervation to which structures?
Muscles of Mastication (DGMS)
Mylohyoid
Tensor Veli Palatini
Tensor Tympani
CN V1 Ophthalmic has 3 branches. What are they?
Frontal
Nasociliary
Lacrimal