Anti-Cancer Drugs - Part 1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms

A general term used to denote any of the many different forms of tumors, or an abnormal growth of cells is…
Cancer
In the early 1900s: two main theories on oncogenesis emerged. What were they?
External agents cause cancer
Cancer is a result of inborn errors
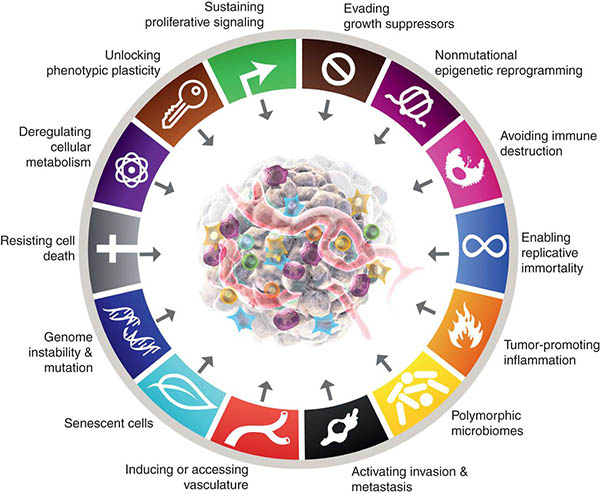
What are some general characteristics of a cancer cell? (stability of genes, life span, contact inhibition, growth factors?)
Genome instability
Infinite life span
Loss of normal growth constraints (decreased growth factor dependence, loss of contact inhibition, anchorage independent growth)
Morphological changes

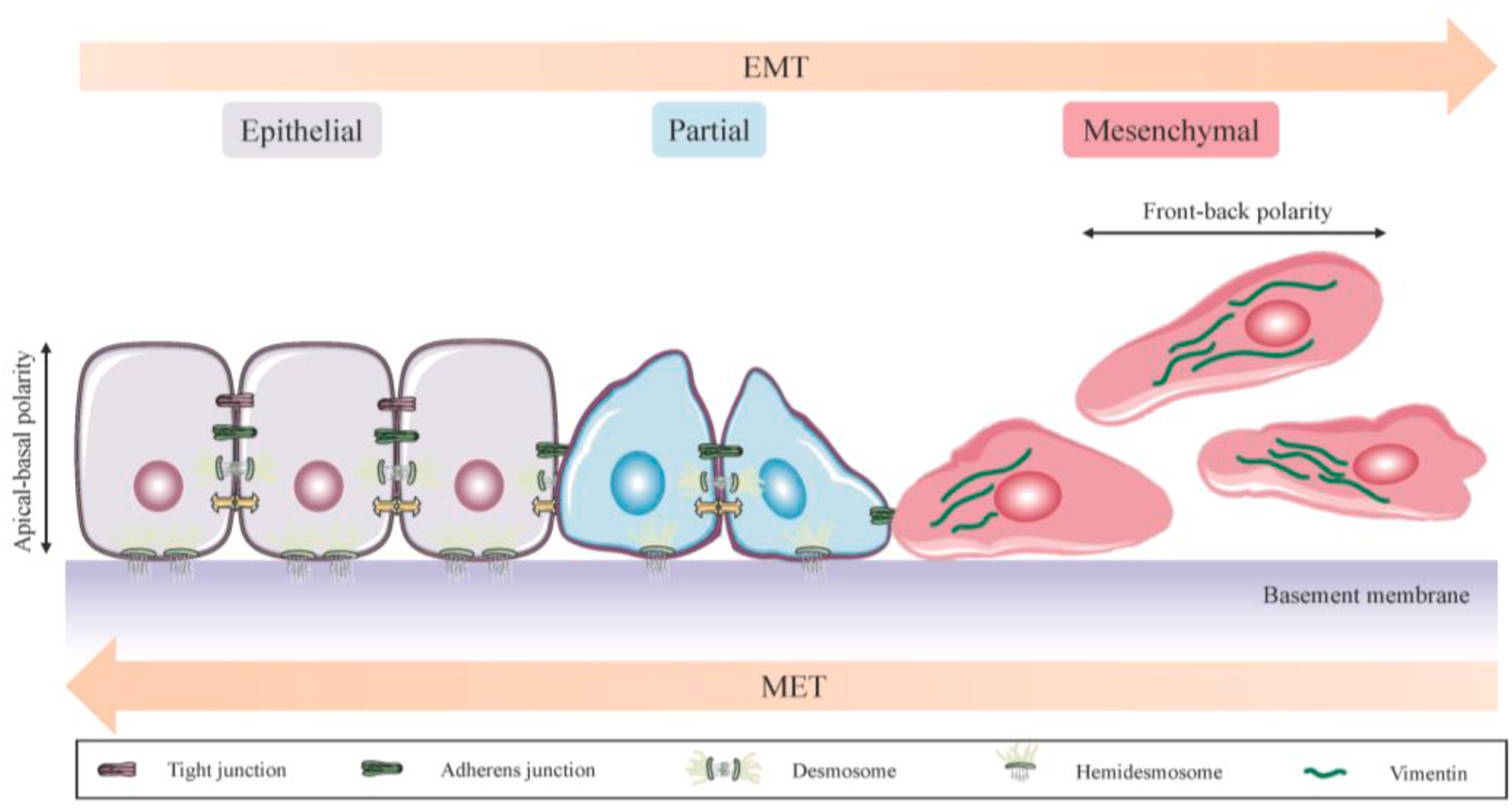
What are the two structures of human organs that cancer can occur in? Which do most cancers grow in?
Epithelium and Mesenchyme
Epithelium - most cancers occur in
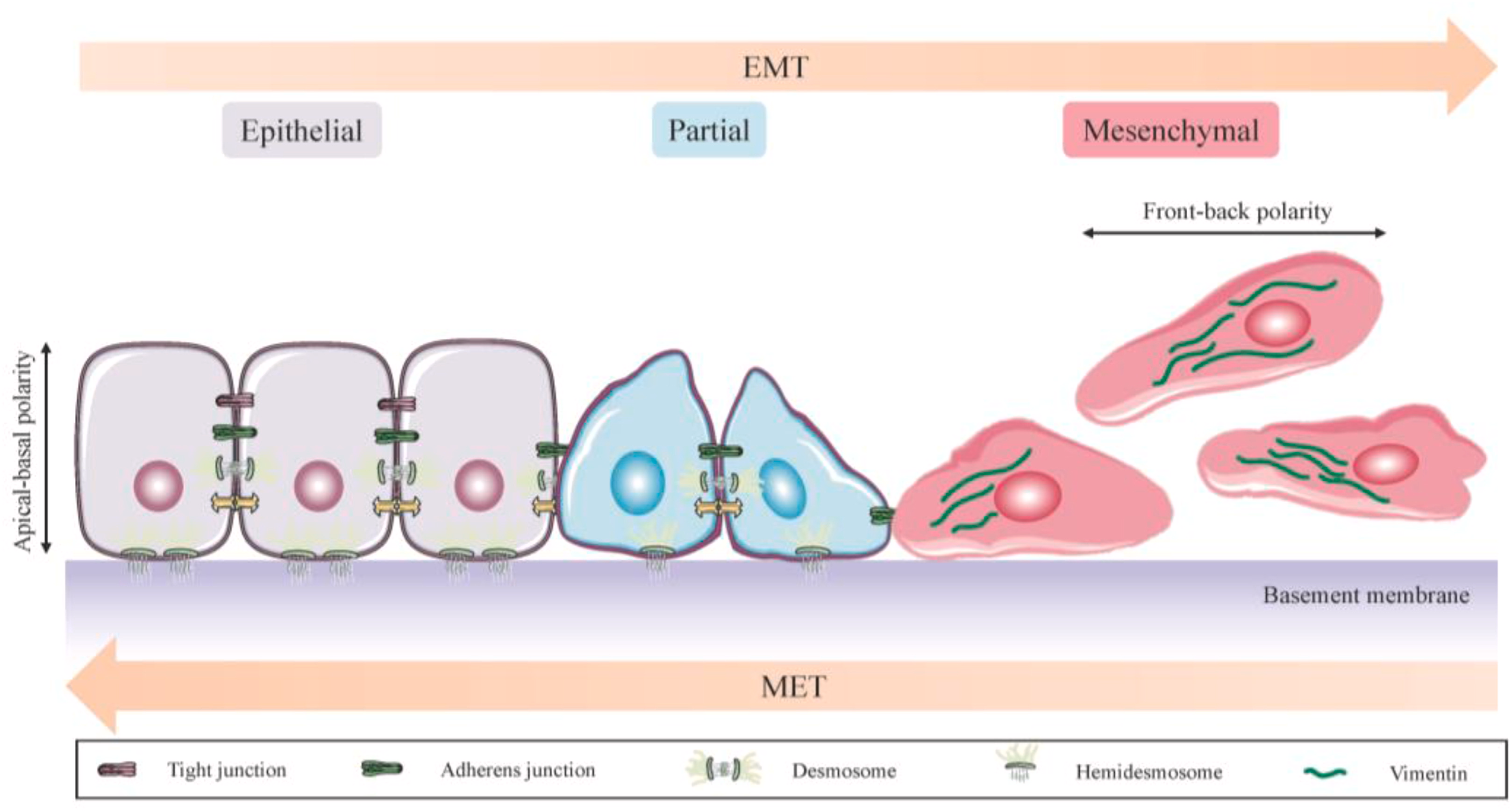
Cancer is primarily a disease state of the ______
Elderly
What is the most common cancer in all ages? What is most popular in children under 15? What is most common for females 15-54?
Lung cancer
Leukemia
Breast cancer
Describe the age-specific incidence of cancer of the colon as people age?
How many deaths of cancer per year?
Incidence rates increase
10,000,000 deaths per year
Cancer by the numbers: describe cure rates over time (1953 to 2015)
30% cure rate = 1953
Cancer mortality declines = 1991
Absolute deaths decline = 1997
60% cure rate = 2002
Cancer death rate declines 26% = 1991 to 2015
The transformation of normal to neoplastic cells is caused by what types of agents (general groups (2) and specific agents)?
Endogenous and exogenous
Chemical/physic agents
Viruses, bacteria, parasites
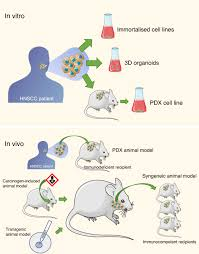
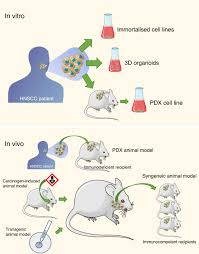
What type of models created in the 1970s were the first reproducible models of carcinogenesis, which identified carcinogens and the metabolic steps/targets to activate them.
Animal models of carcinogenesis
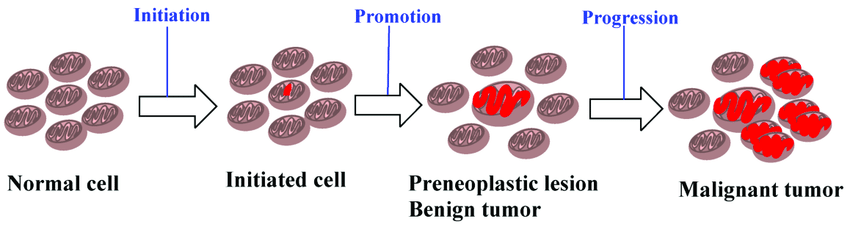
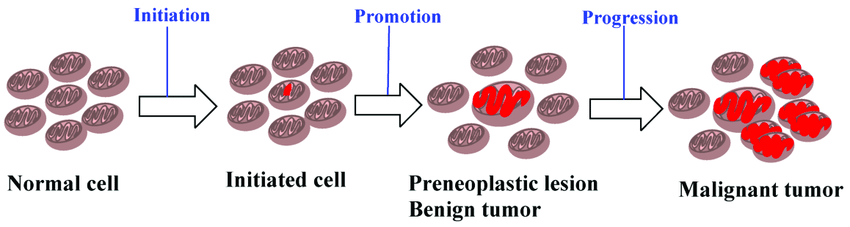
The initial multistage models of carcinogenesis can be divided into what 3 stages?
Initiation
Promotion
Progression
A ______ can be converted into an active oncogene by a ________ mutation, which results in altered or increased gene product activity
Proto-oncogene → oncogene
By a genetic mutation
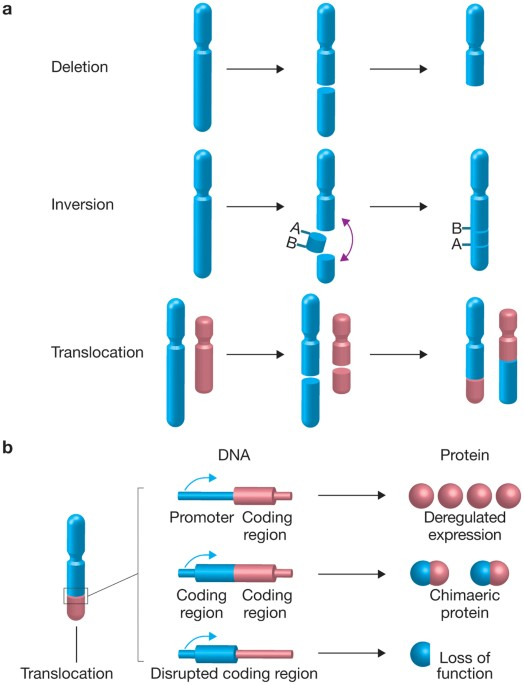
Name 3 examples of genetic mutation that can convert a proto-oncogene into an oncogene?
Gene Amplification
Chromosomal translocation
Gene mutation (base substitution)
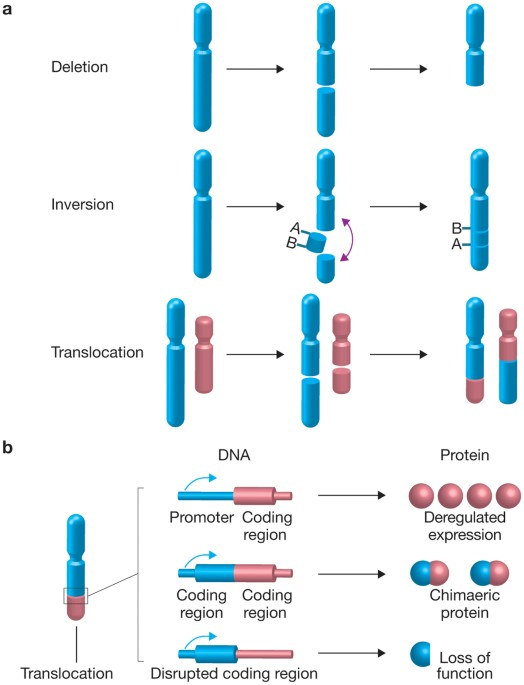
What is a tumor suppressor gene?
Gene whose product is NECESSARY for normal cell function
Loss of function causes or contributes to tumor phenotype
Both copies of TSG must be inactivated to reveal tumor properties
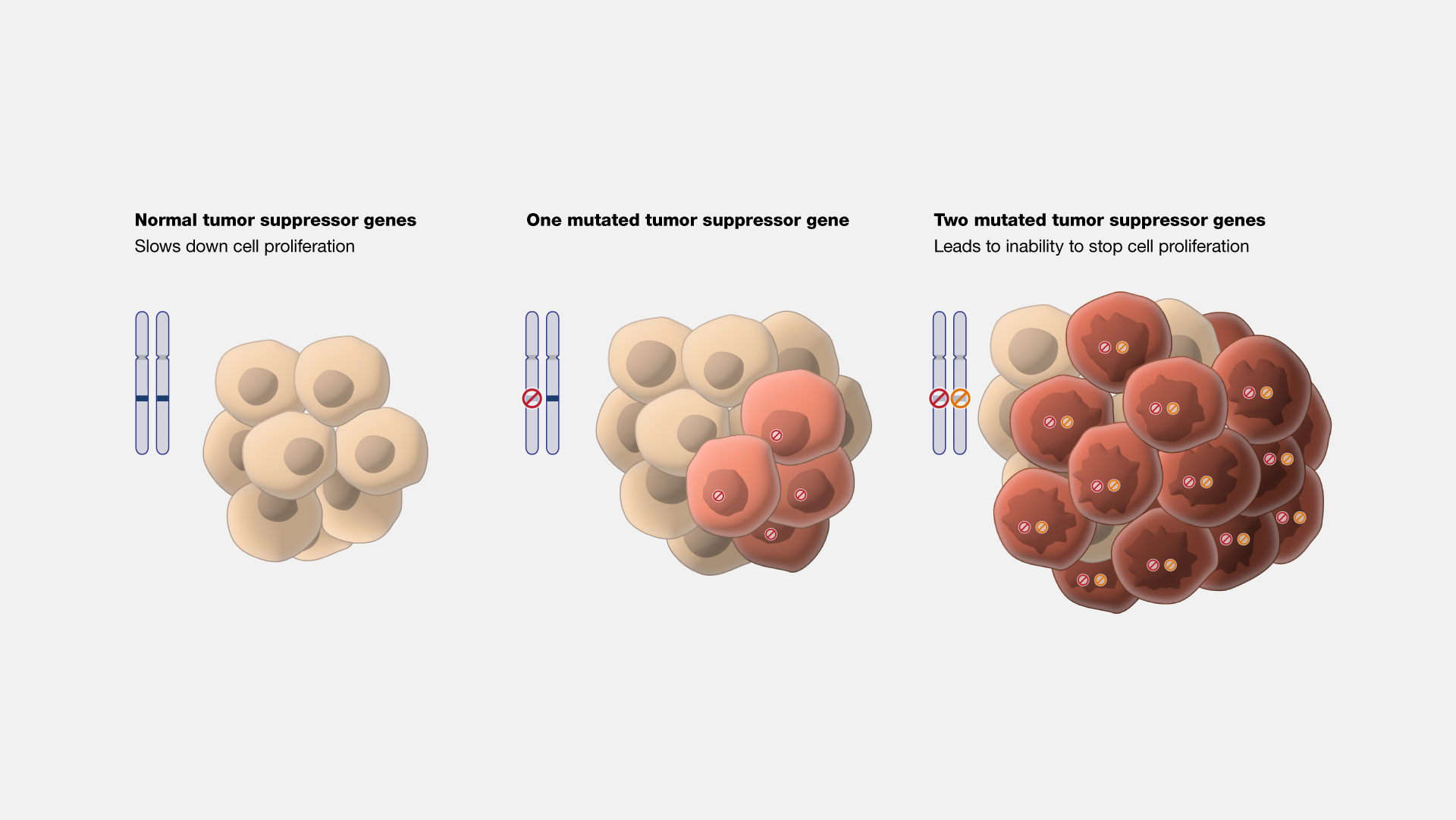
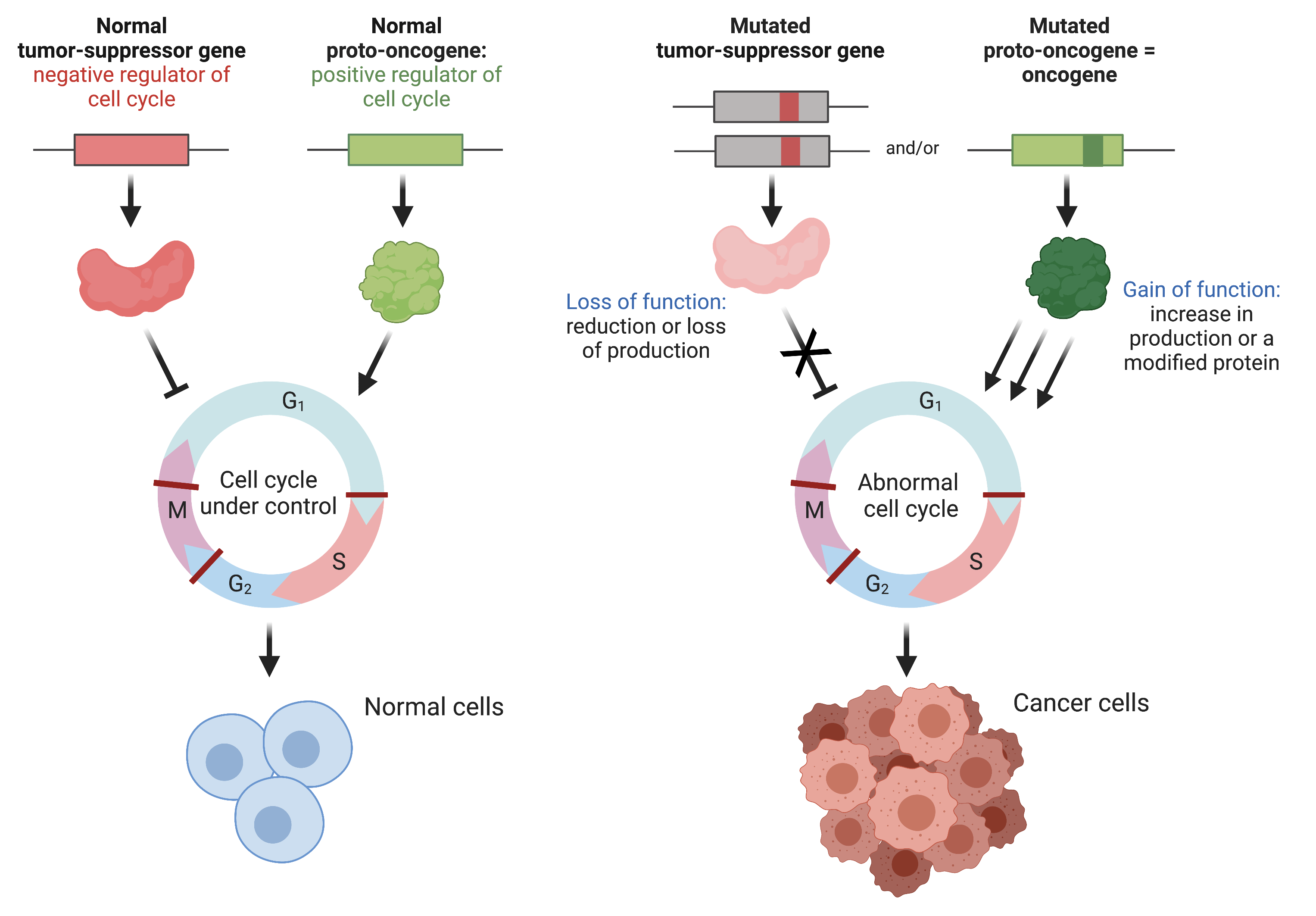
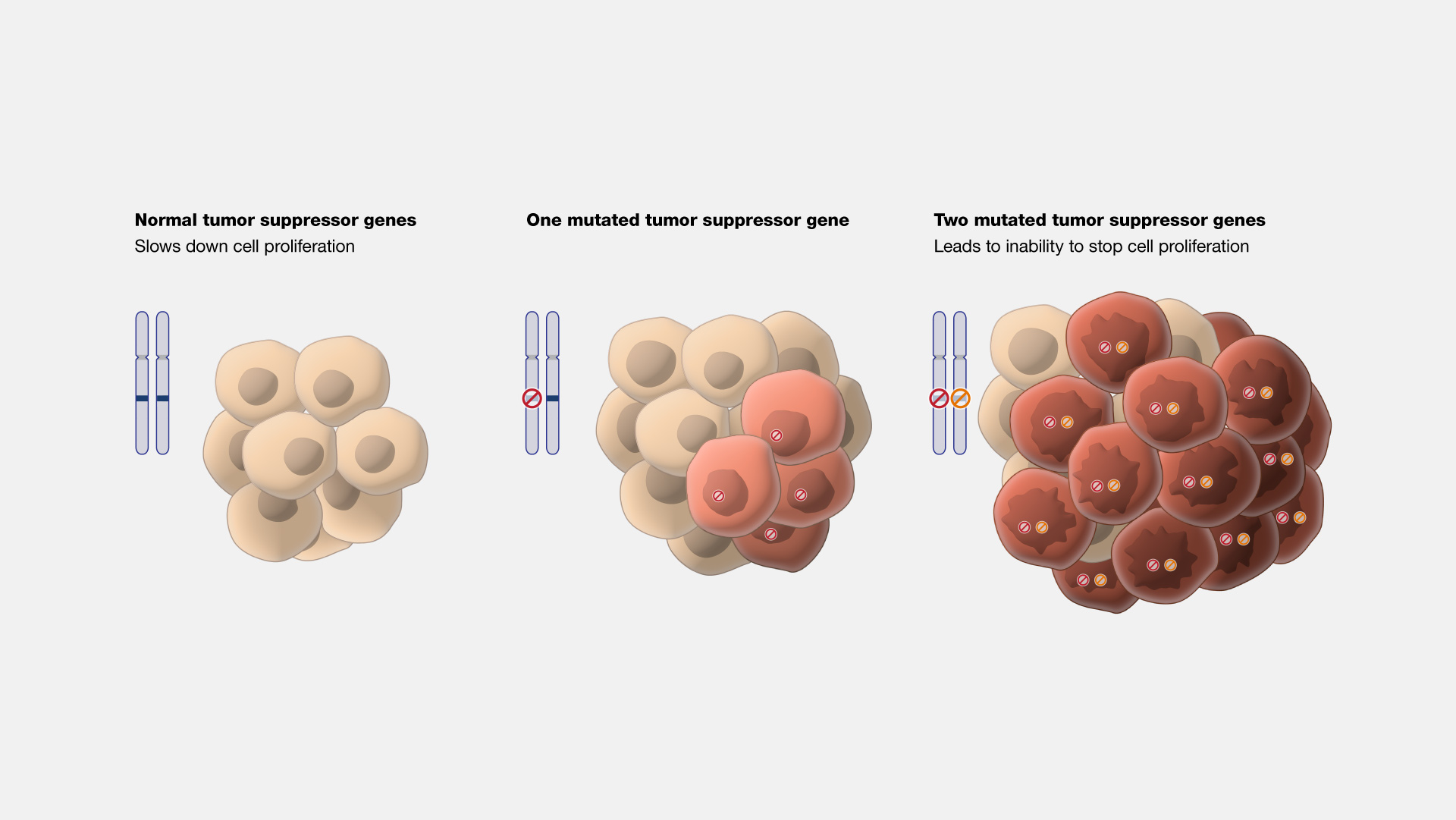
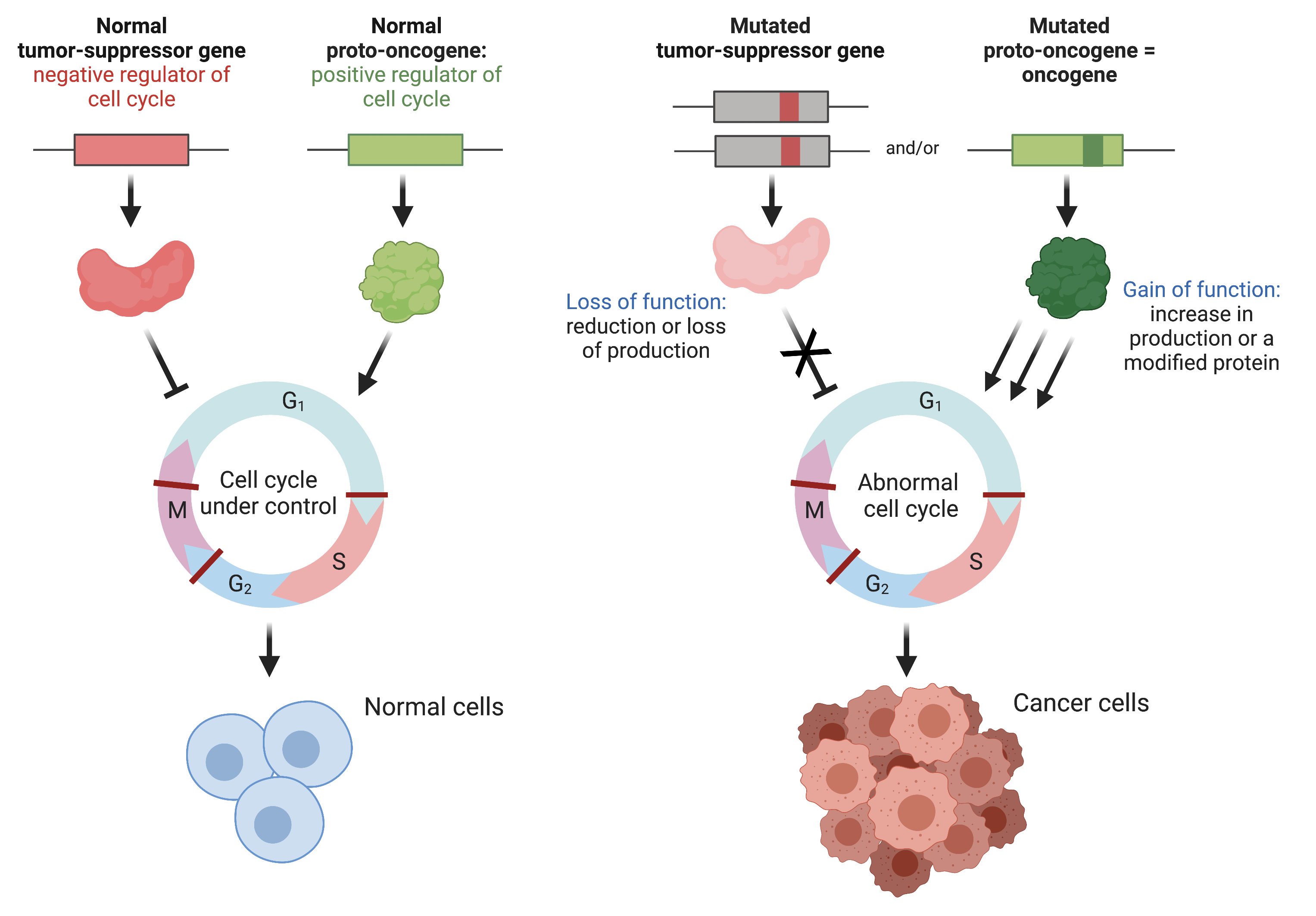
What are some common mechanisms of tumor suppressor gene inactivation? Name 4 tumor suppressors?
Gene deletion - physical loss of gene
Gene mutation - produces protein product (not functional)
Epigenetic inactivation - aberrant, reversible chemical modifications - result in tumor suppressor gene silencing
Tumor suppressors: Rb, p53, BRCA1, p16
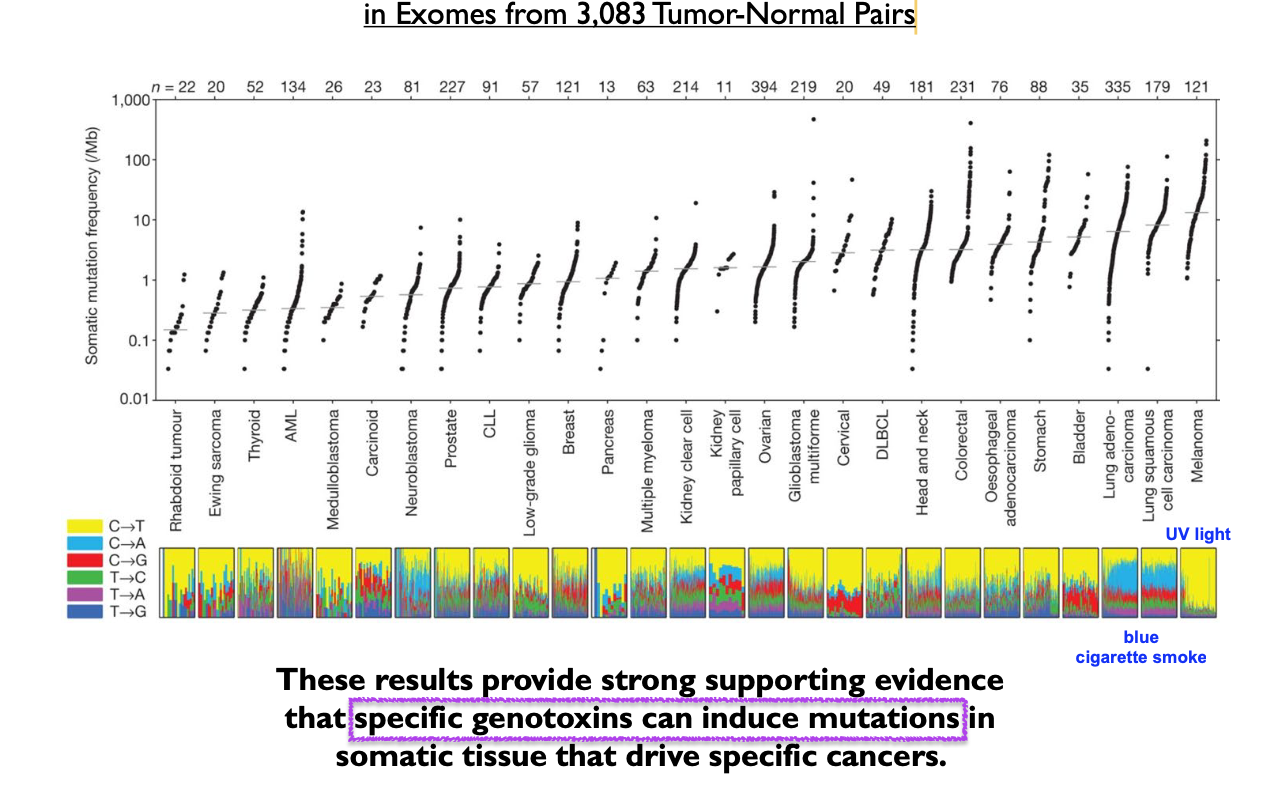
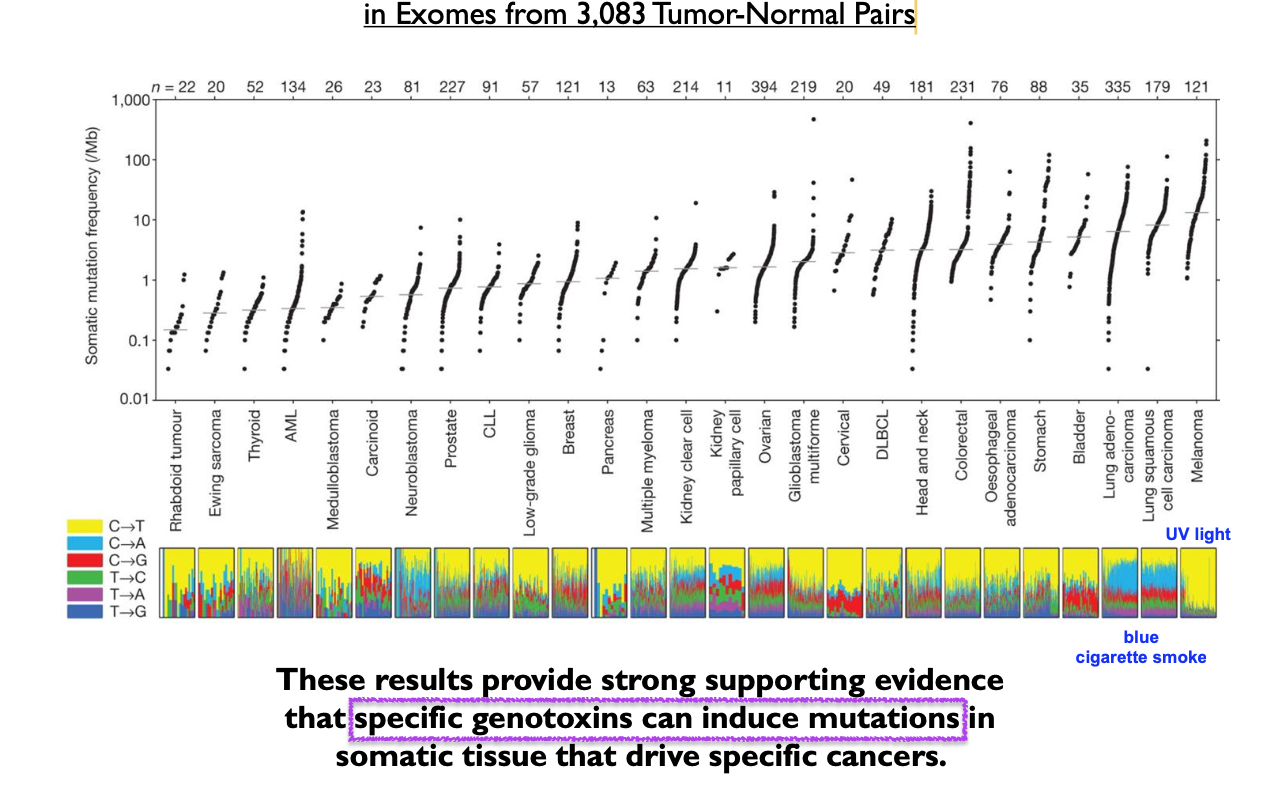
Cancer is a disease of DNA. There is strong evidence that specific _______ can induce mutations in somatic tissue that drive specific cancers
Genotoxins can induce mutations
Cancer can be classified into two heritable properties:
Proliferative capacity that ______________
Ability to invade ___________
Proliferative capacity that no longer responds to normal growth controls
Ability to invade and colonize surrounding tissue, as well as distant sites
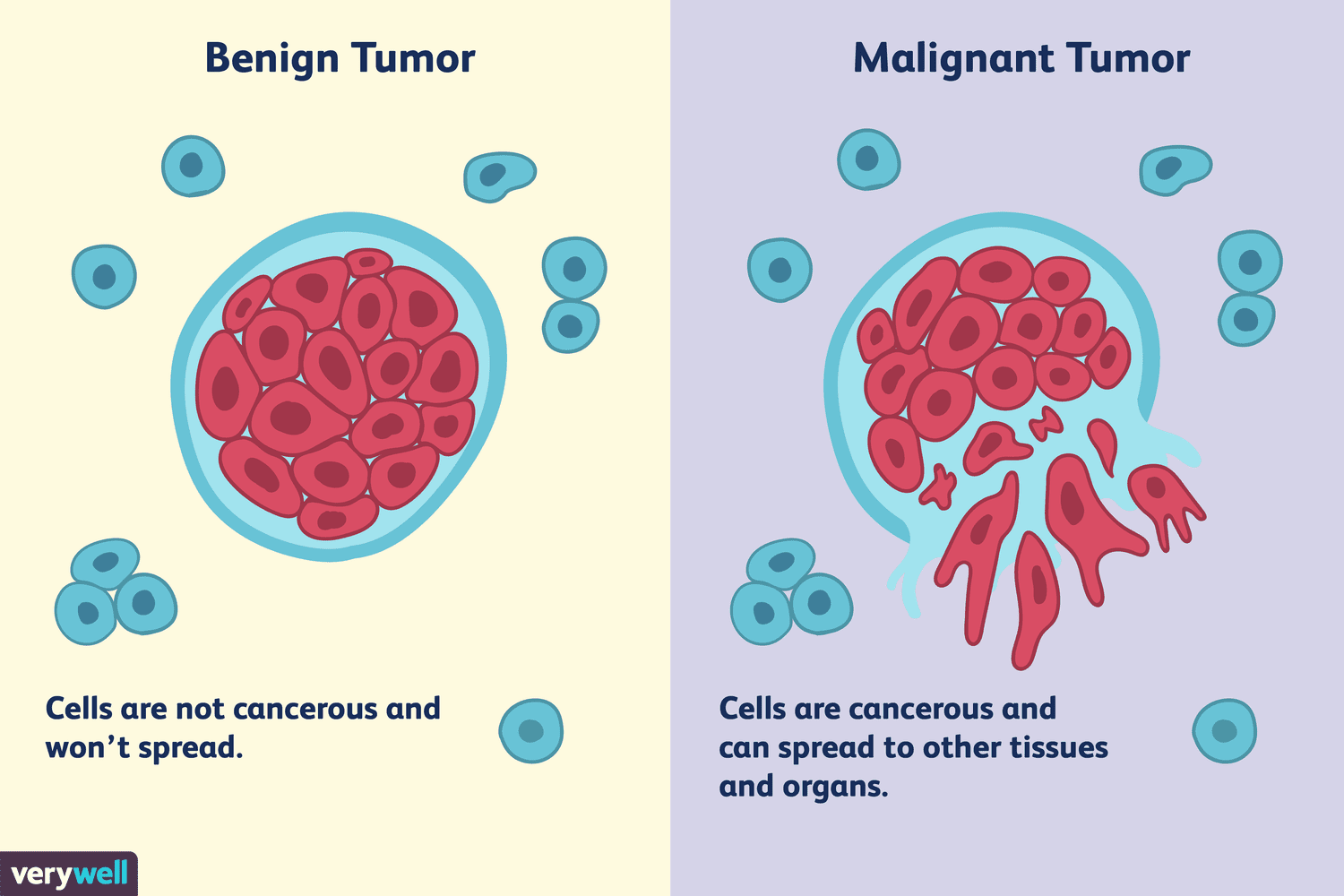
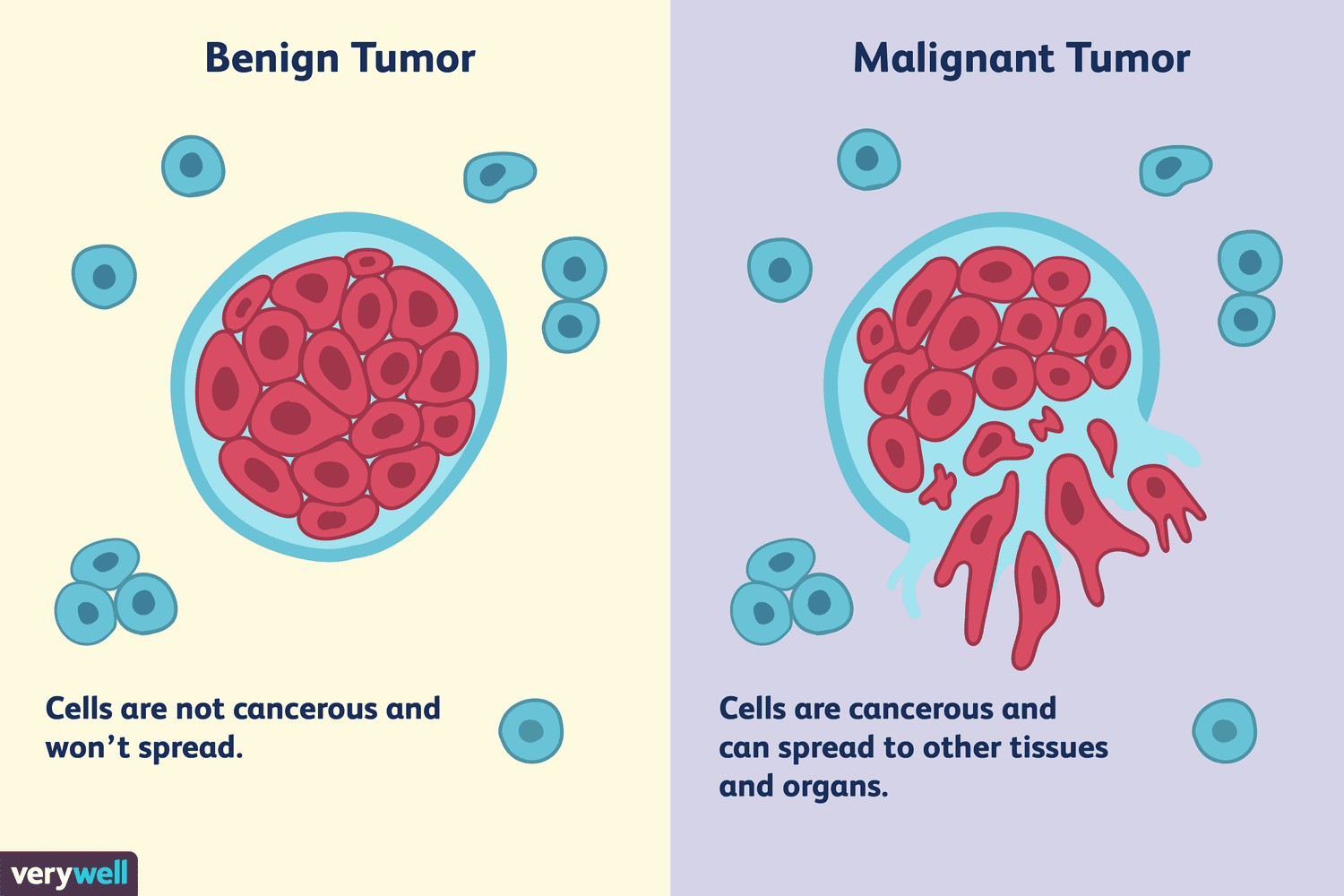
What are benign tumors?
May arise in ANY TISSUE
Grows locally - does not invade other tissue
Can be surgically removed with no recurrence
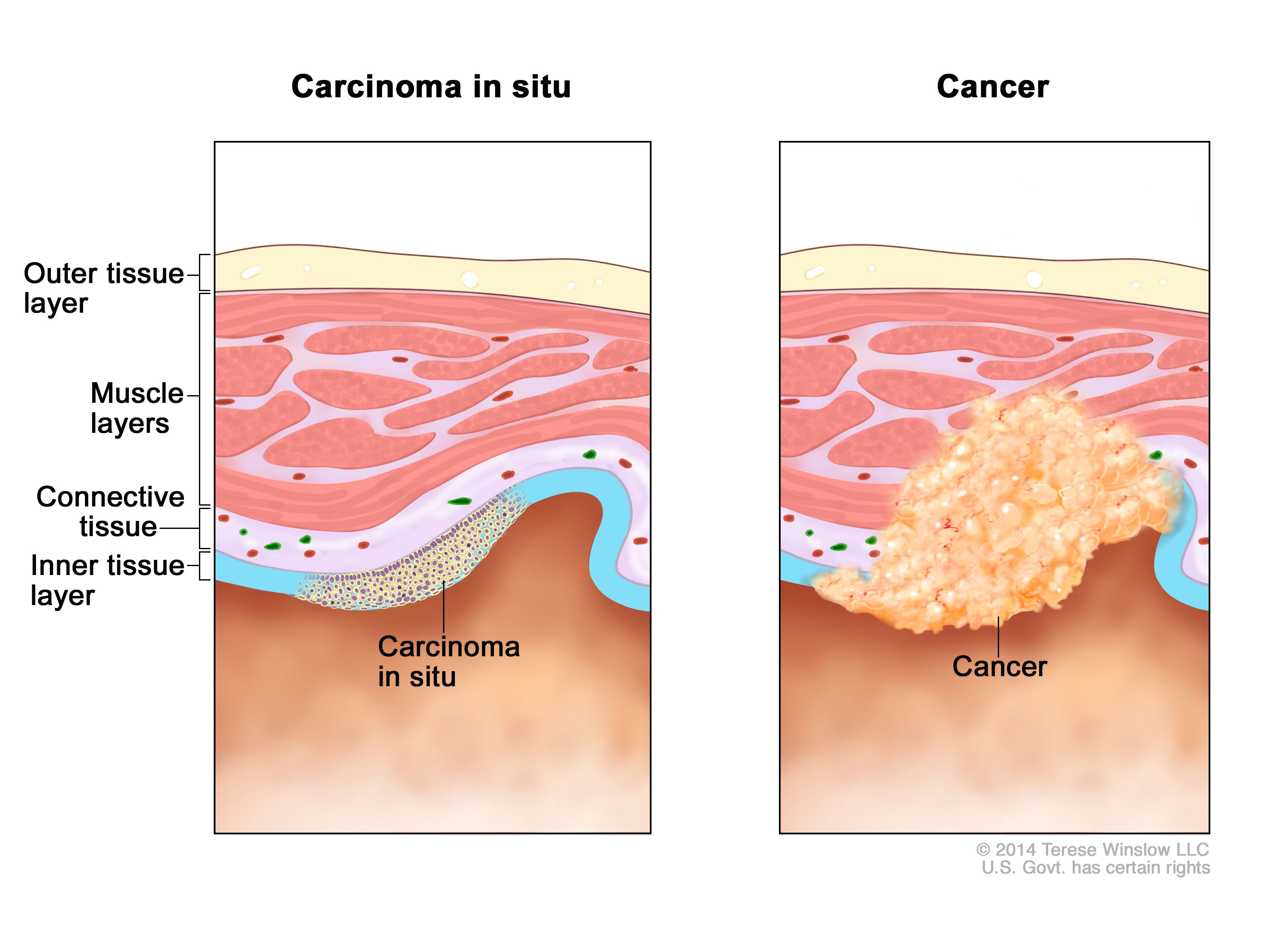
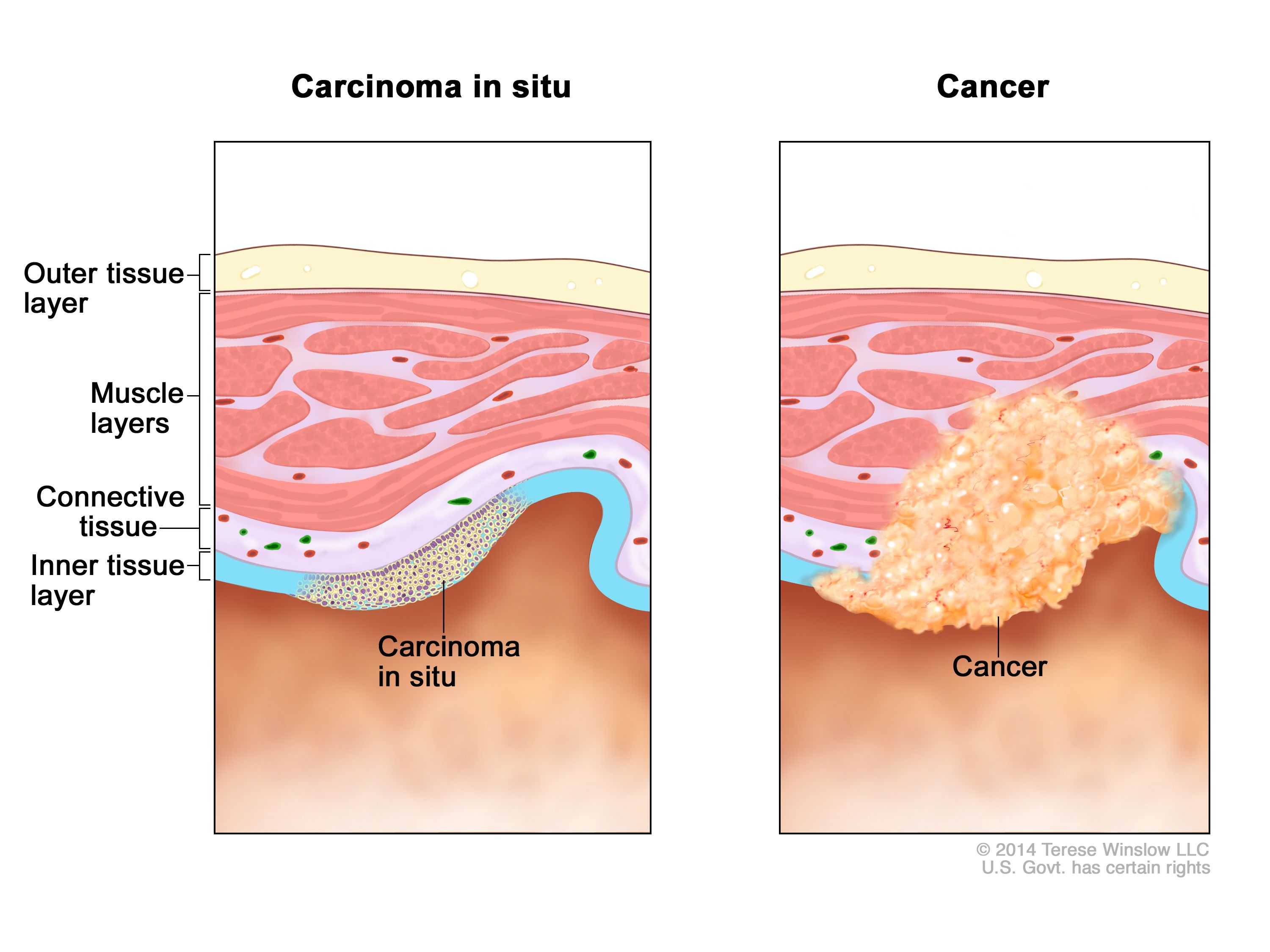
What is carcinoma in situ?
Epithelial in origin
Morphologically similar to cancer
Non-invasive (premalignant lesion)
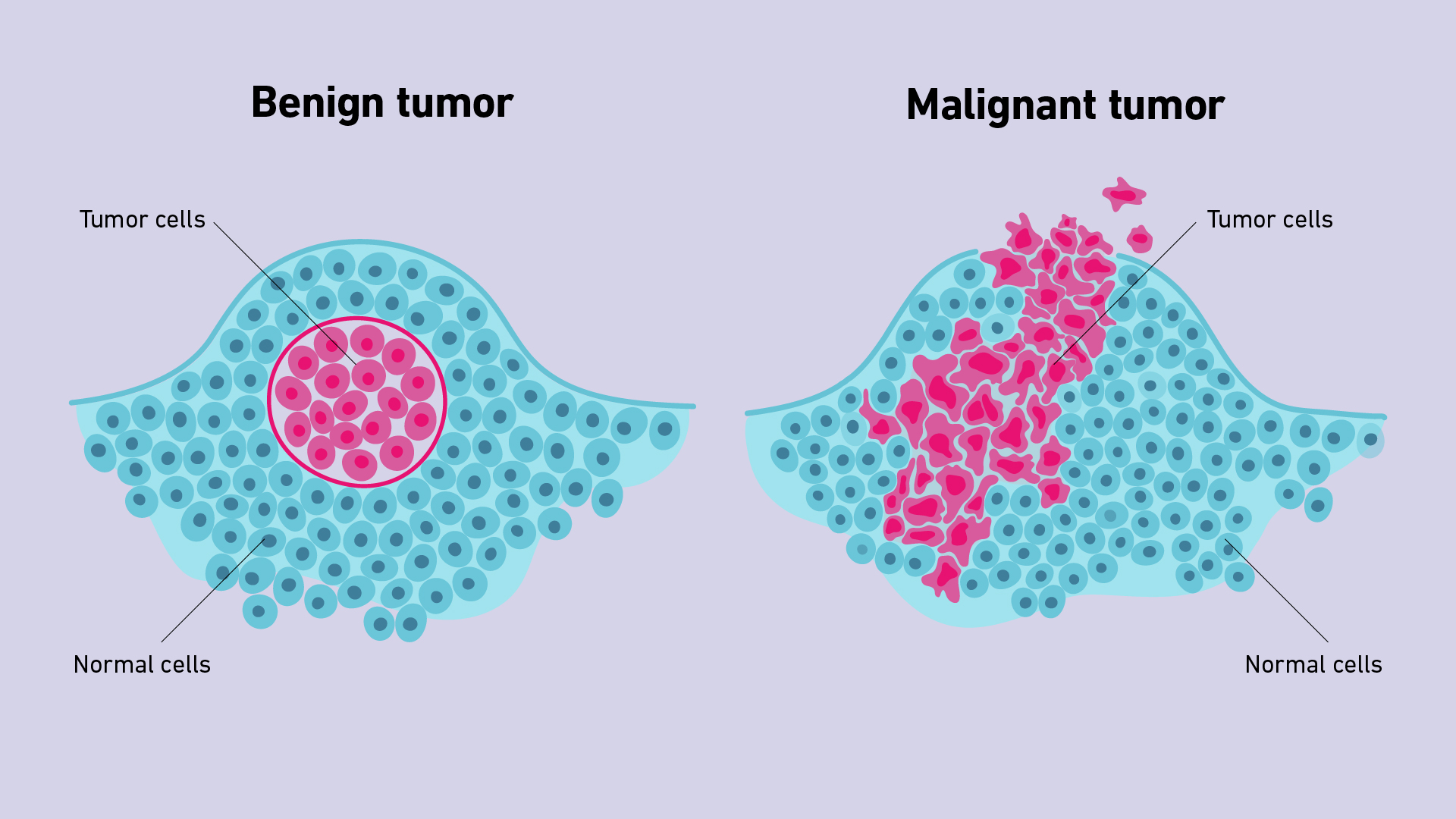
What are malignant tumors?
Generally more serious than benign tumors
Potentially life threatening
Can be surgically removed, able to invade surrounding tissue/blood
Can damage local and distant tissues/organs
Forms secondary tumors (metastases)
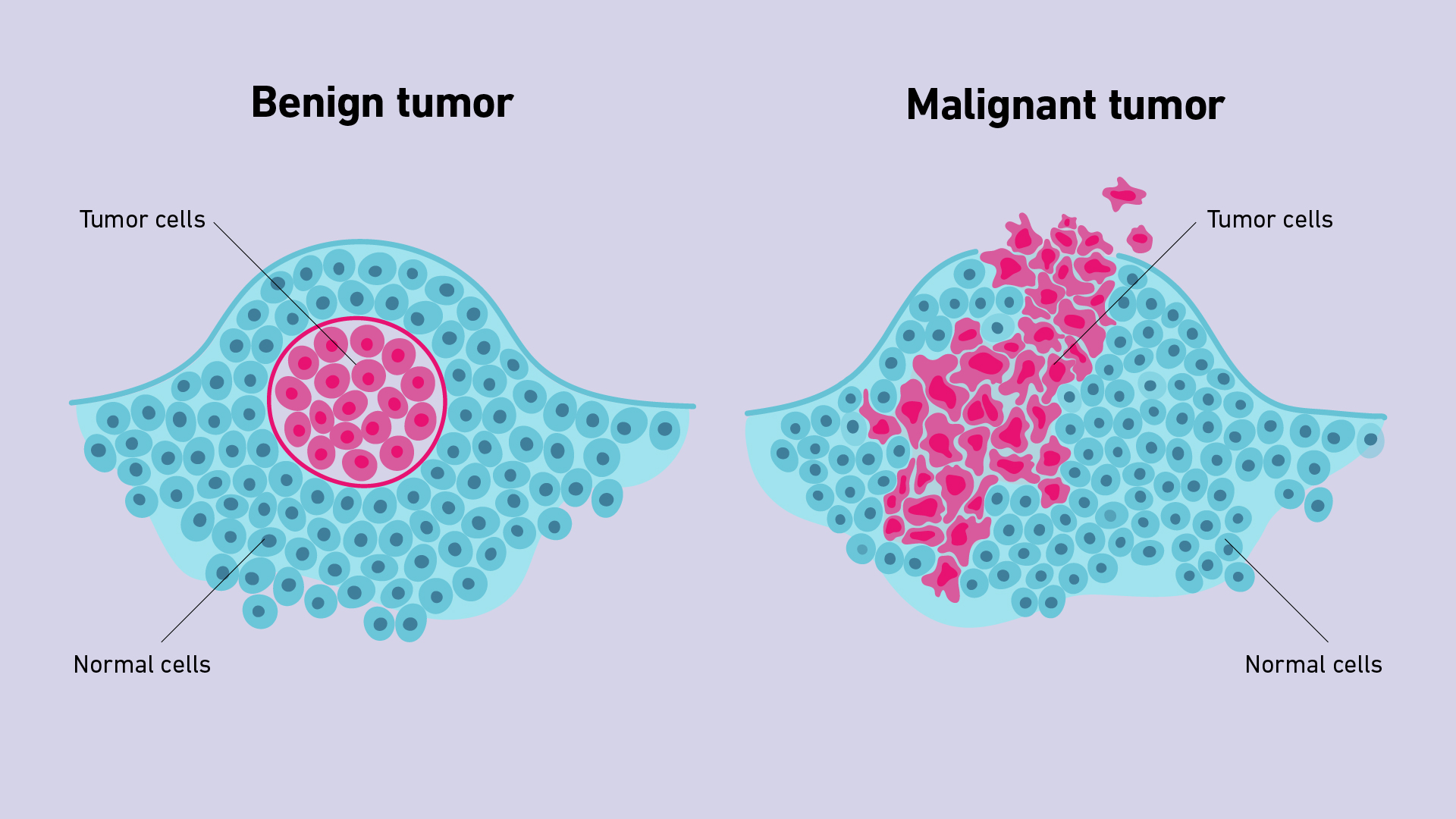

Describe cancer nomenclature…
-oma = tumor
Epithelial benign tumors = papilloma, adenoma
Malignant epithelial tumors = Carcinoma
Mesenchymal benign cancers = osteoma, fibroma
Malignant mesenchymal tumors = Sarcoma

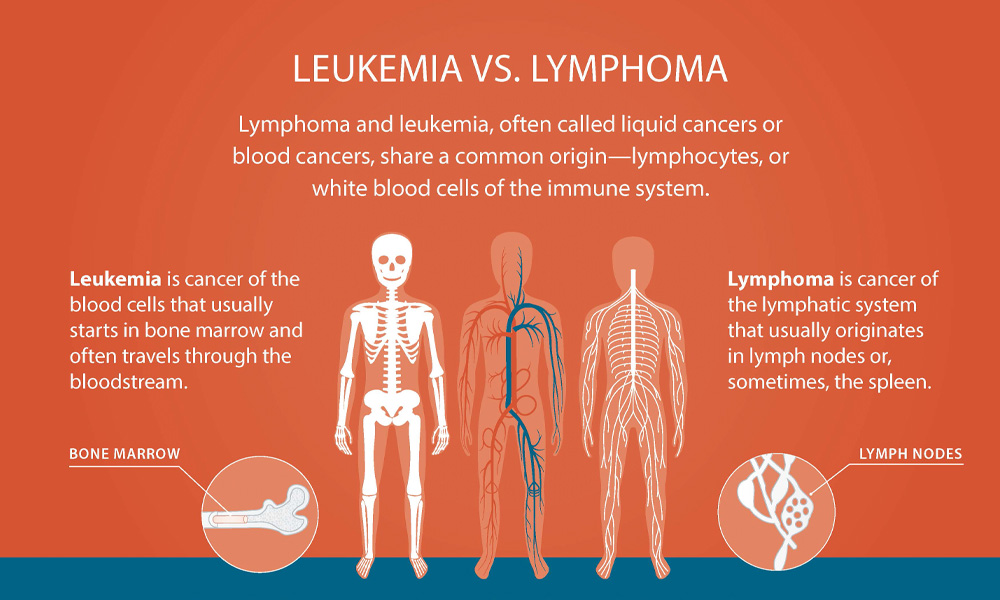
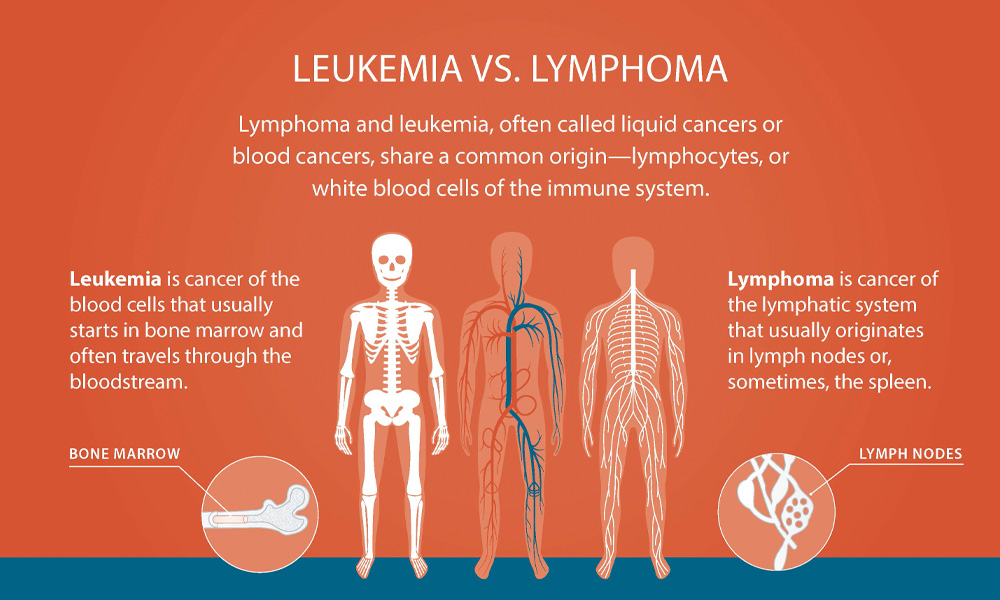
Hematopoietic system: Cell lineage of origin, divided into what two categories?
Leukemias = myeloid
Lymphomas = lymphoid
Tumors of neurons (nervous system) occur when?
These include neuroblastoma or retinoblastoma
Appear only shortly after birth
Among the most common form of brain tumors seen in adulthood, all other arise from supporting ______ cells. Name an example.
Glial cells
Astrocytes
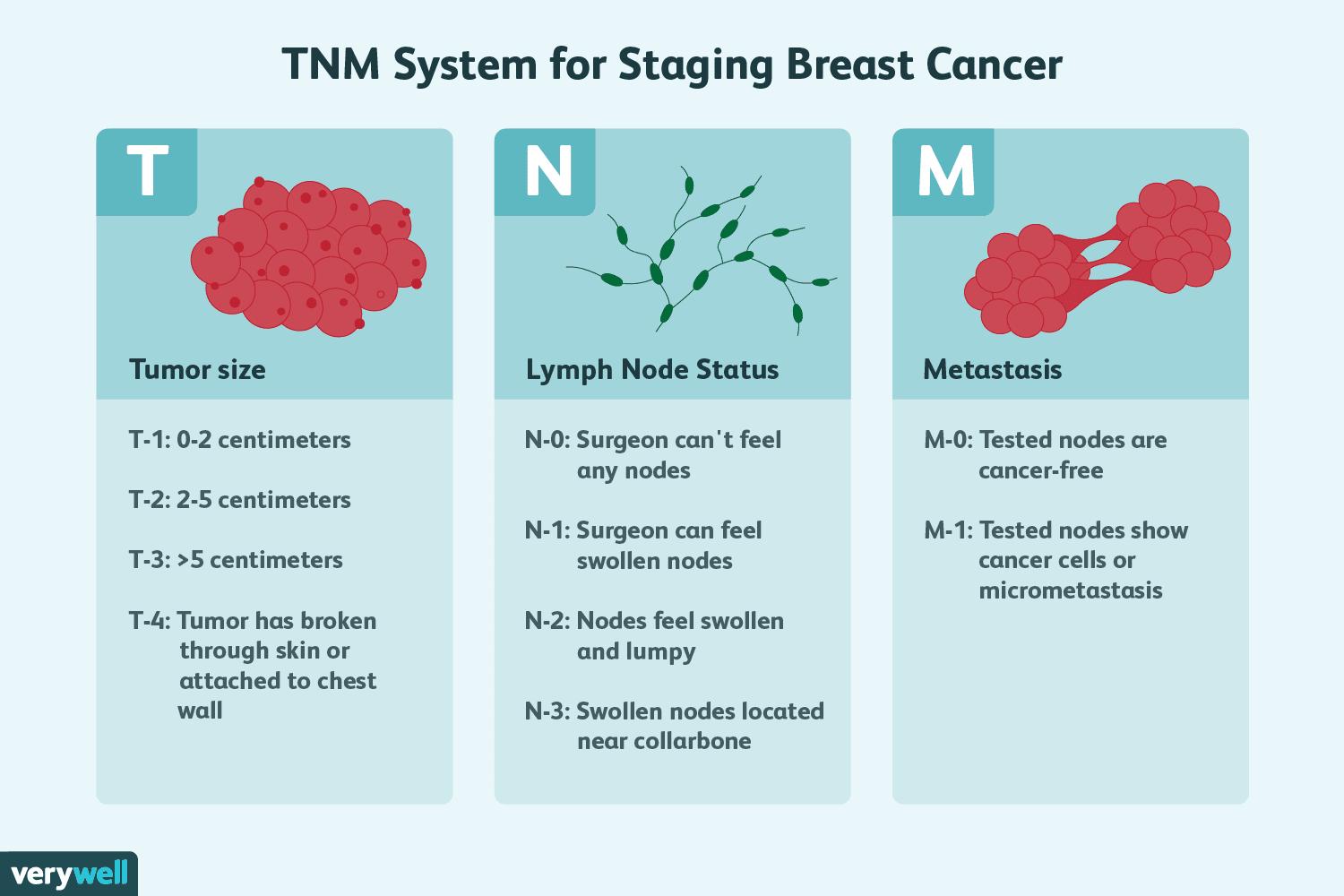
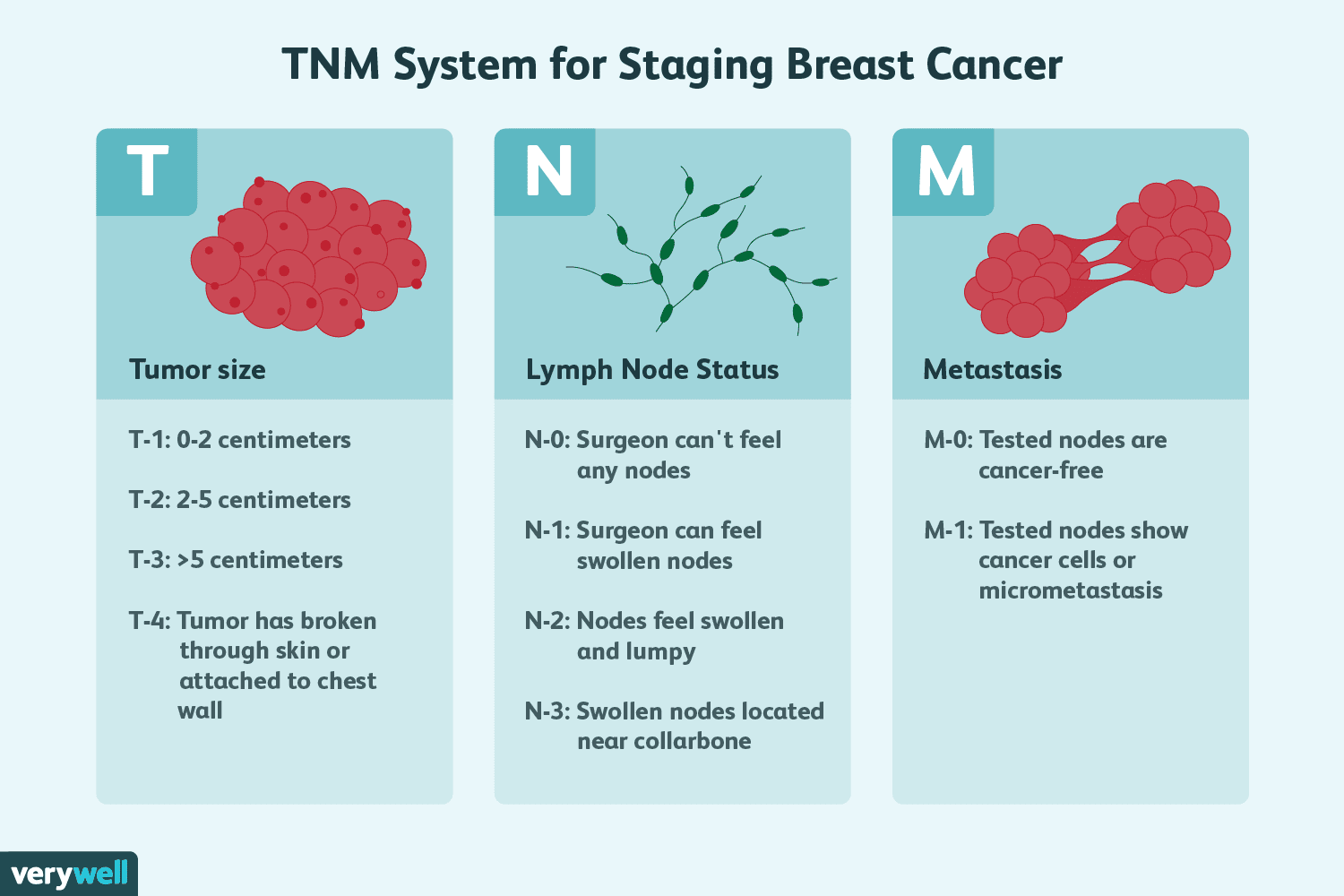
What is the TNM system?
Assessment of primary Tumor
Assessment of regional lymph Nodes
Presence or absence of Metastases
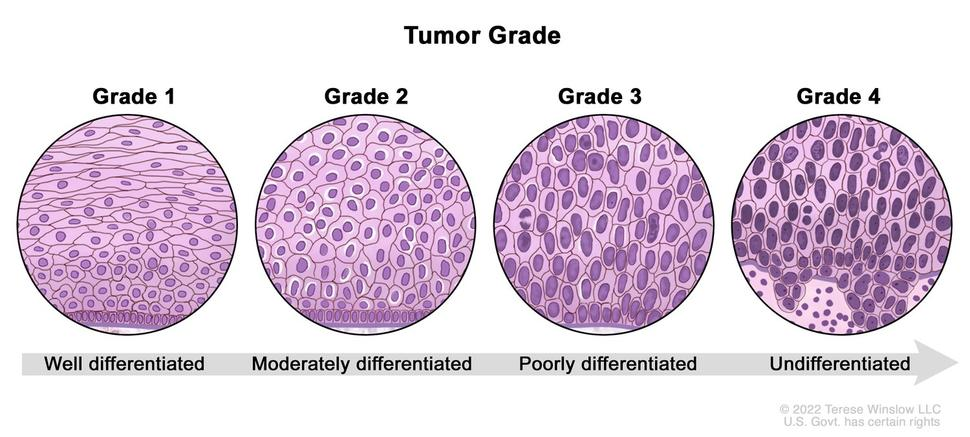
What are the 3 tumor grades?
Grade 1: well differentiated
Grade 2: medium differentiation
Grade 3: poorly differentiated
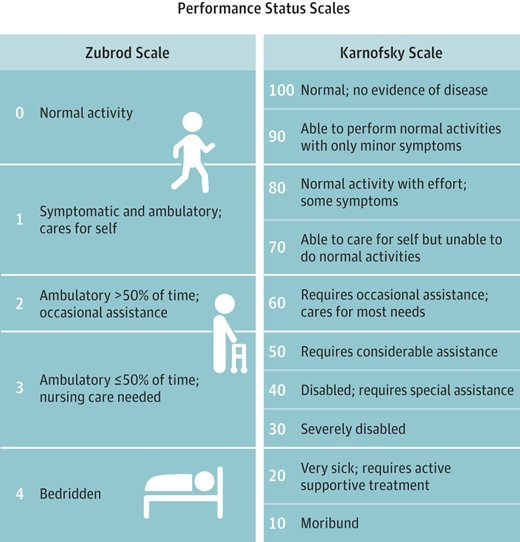
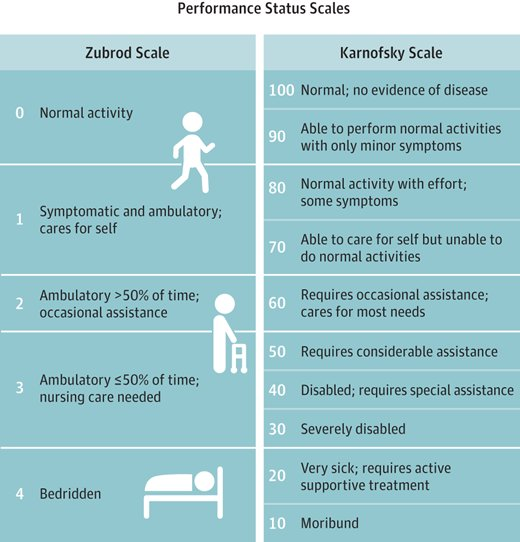
What Patient Staging tool is a standard way of measuring the ability of cancer patients to perform ordinary tasks?
Karnofsky Performance Status
Range from 0-100
Higher score - can better carry out daily activities