Lab 3 Study Materials -- Axial Skeleton
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
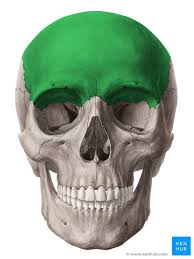
frontal cranial bone
1 bone
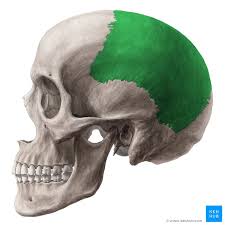
parietal bone
2 bones
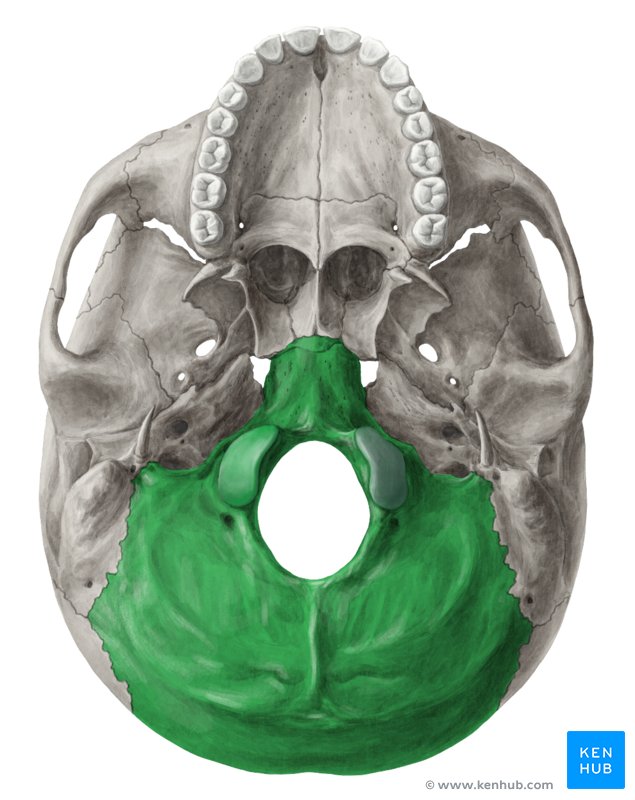
occipital bone
1 bone
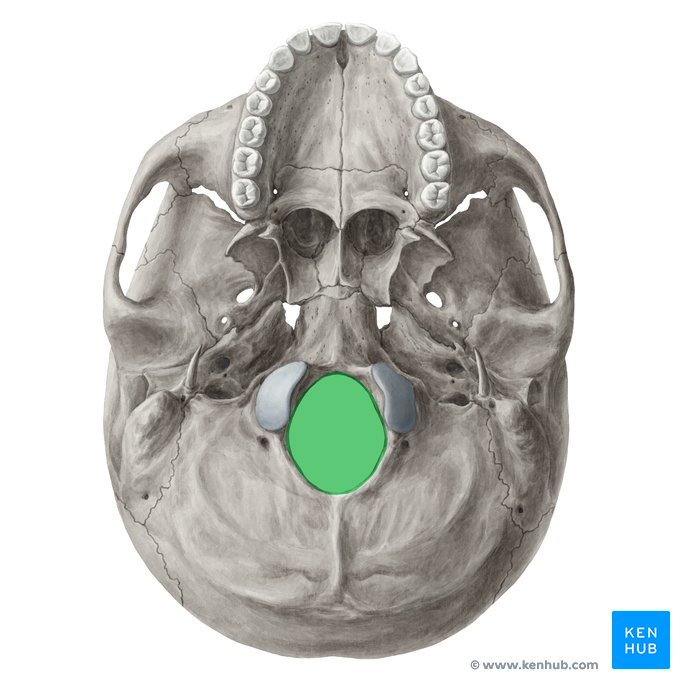
foramen magnum - spinal cord
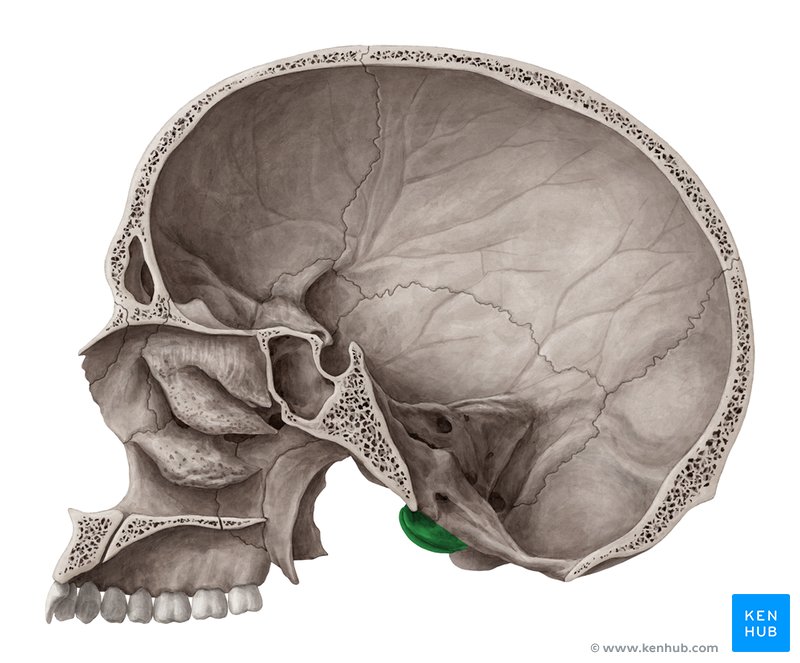
occipital condyles - articulate with atlas
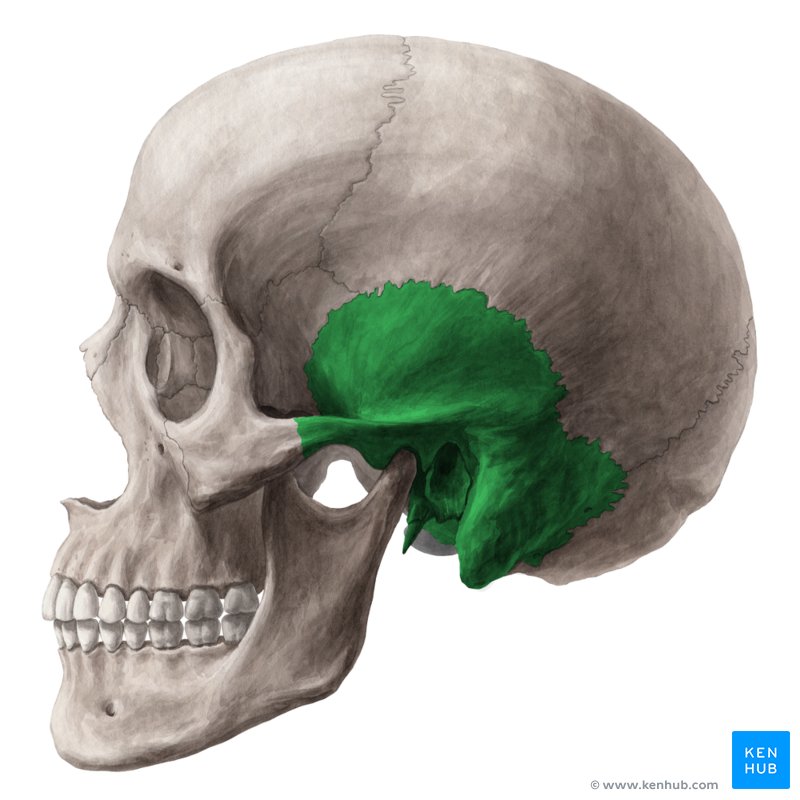
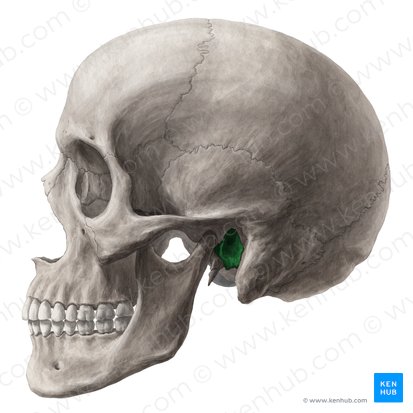
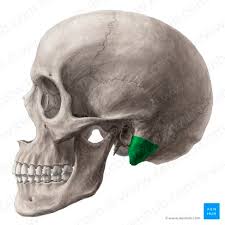
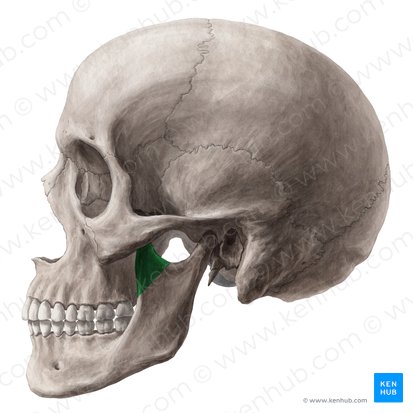
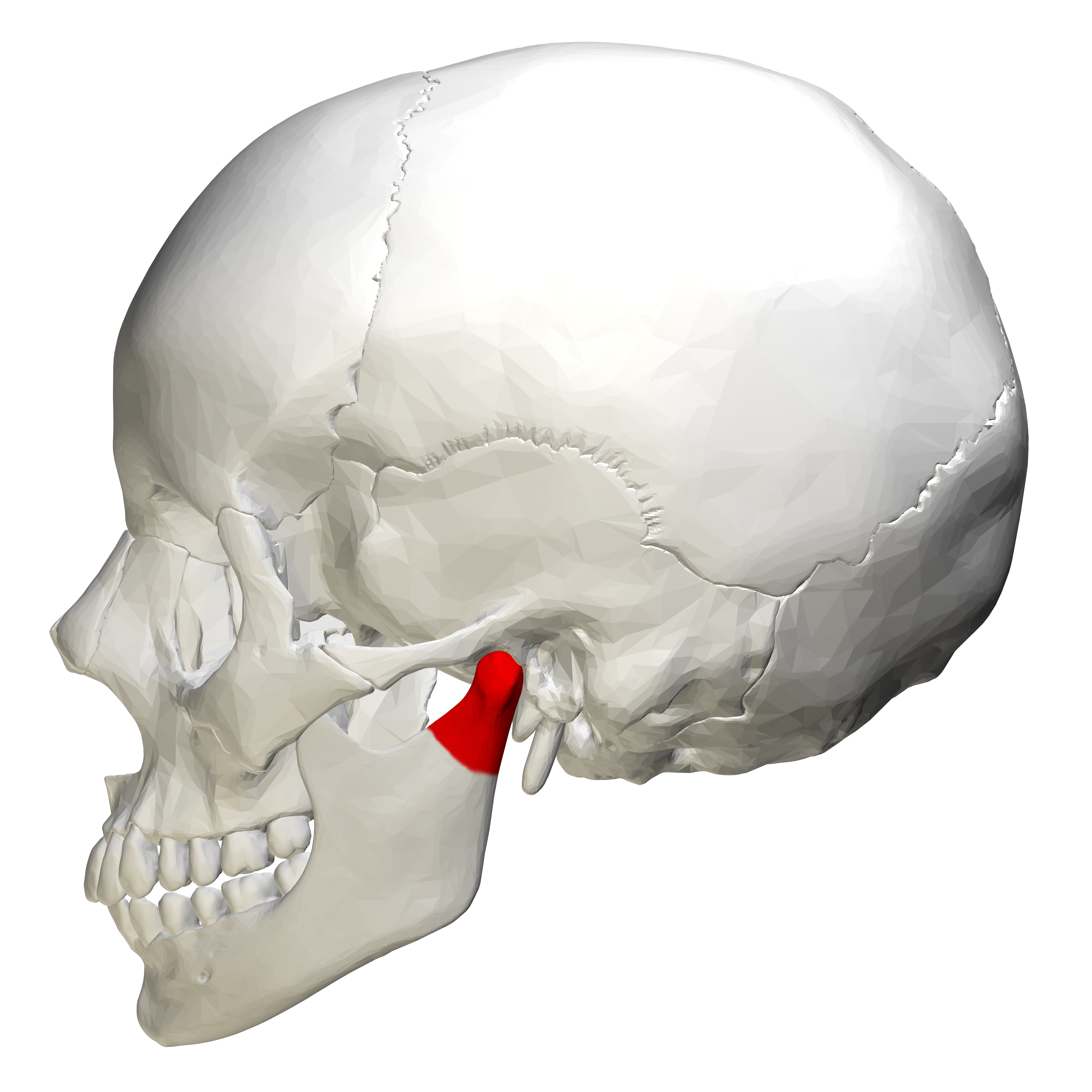
temporal bone
2 bones
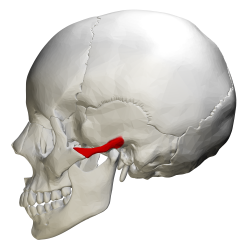
zygomatic process - articulates with zygomatic bone
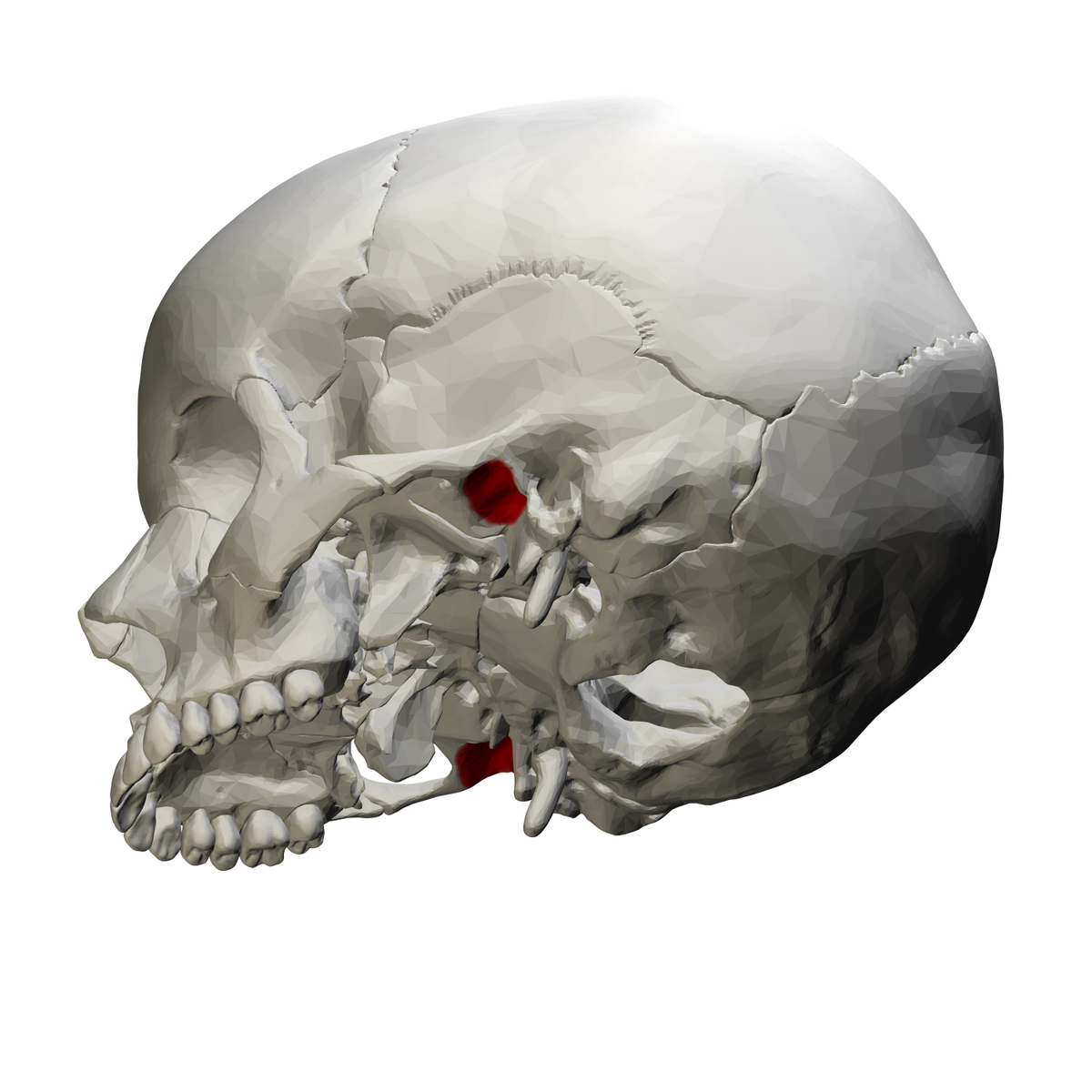
mandibular fossa - forms part of the temporomandibular joint [TMJ]
external acoustic meatus - external ear canal
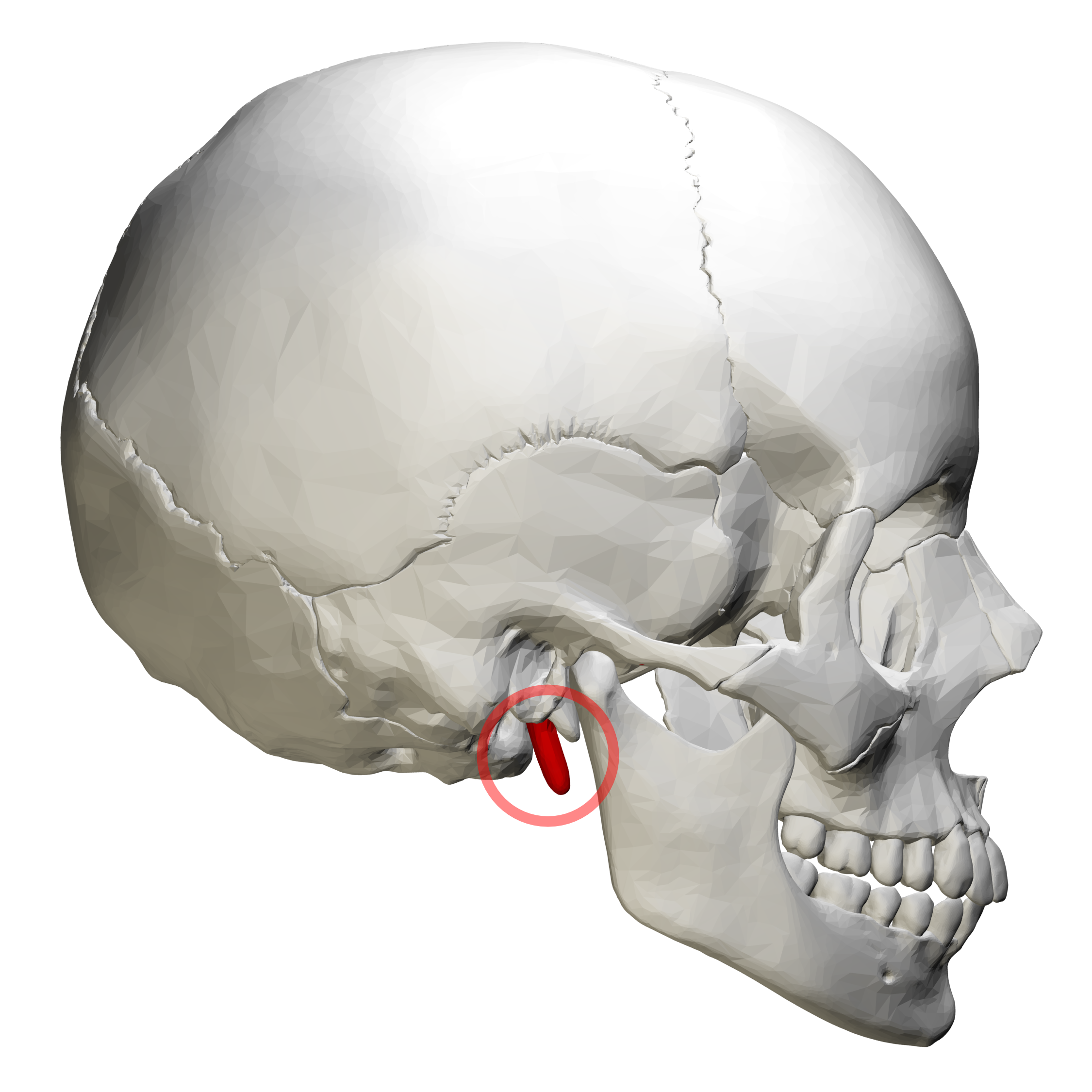
styloid process - attachment for several tongue and neck muscles;
attaches to the ligament of the hyoid bone
mastoid process - attachment site for several neck muscles
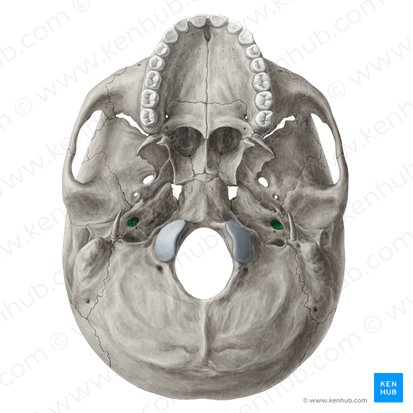
carotid canal - internal carotid artery
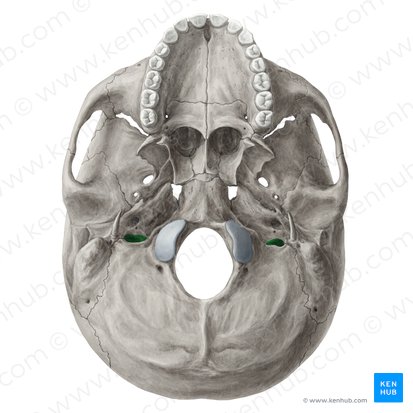
jugular foramen - internal jugular vein, glossopharyngeal, vagus and
accessory nerves
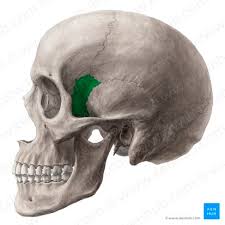
sphenoid bone
1 bone
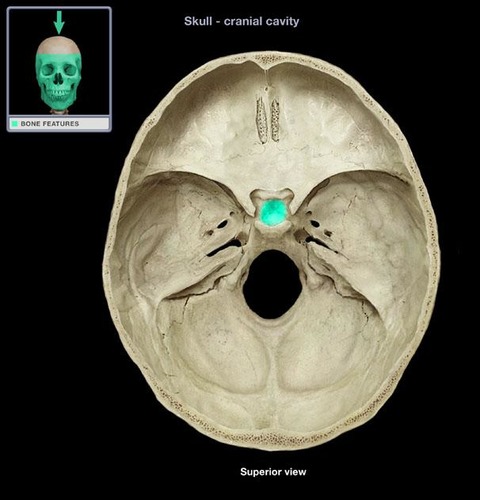
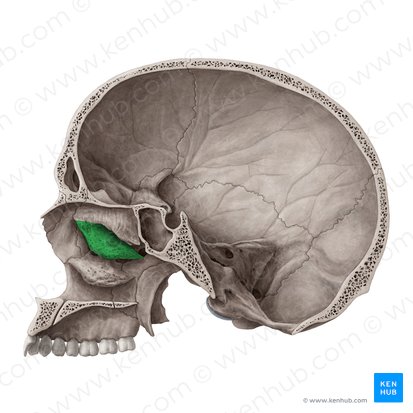
sella turcica/hypophyseal foss - houses/protects = pituitary gland
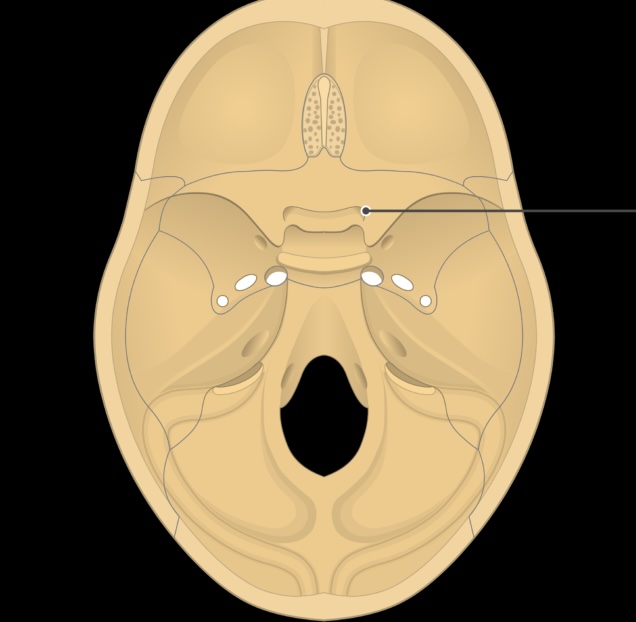
optic canal - optic nerve and artery pass through
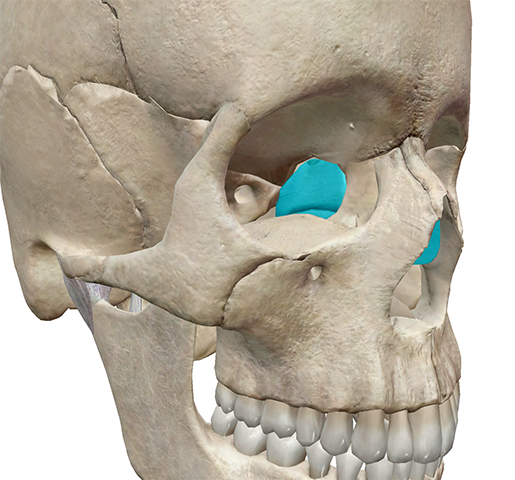
ethmoid bone
1 bone
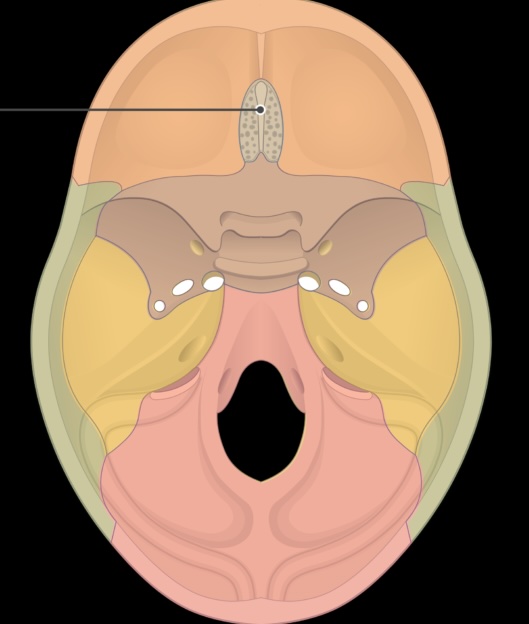
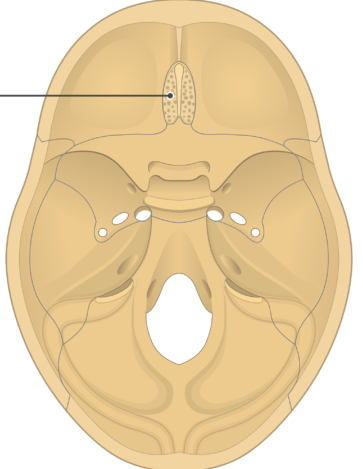
crista galli - anchors part of the dura mater
cribriform plate - passage of olfactory nerves
middle nasal concha
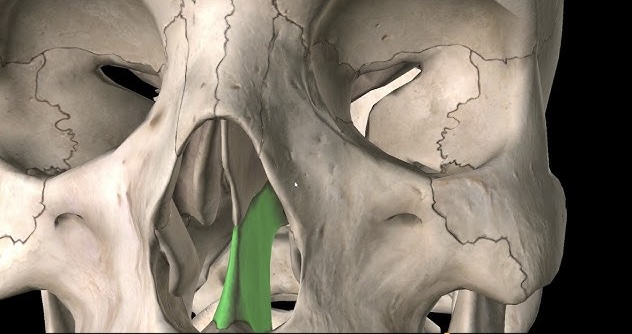
perpendicular plate - part of the bony nasal septum
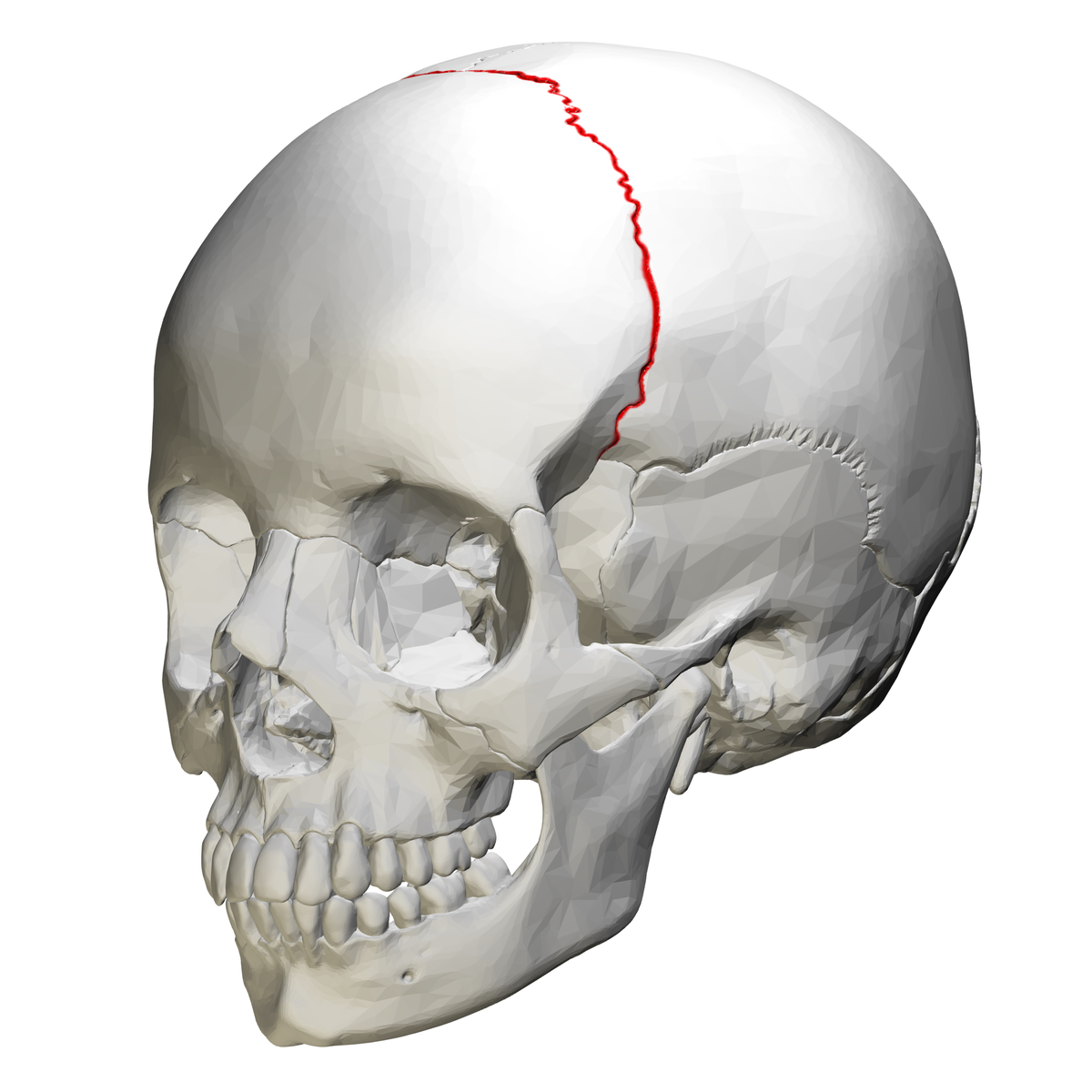
coronal suture
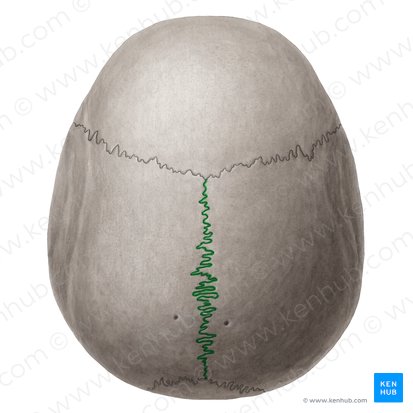
sagittal suture
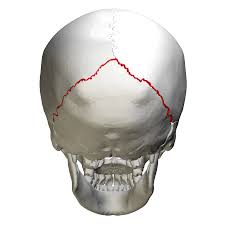
lambdoid suture
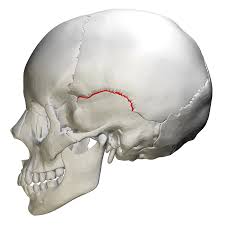
squamous suture
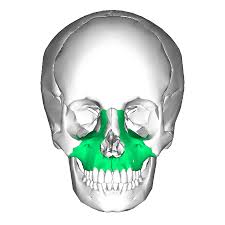
maxilla
palatine
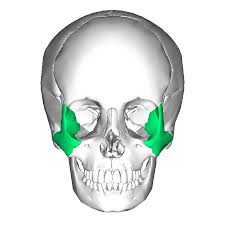
zygomatic
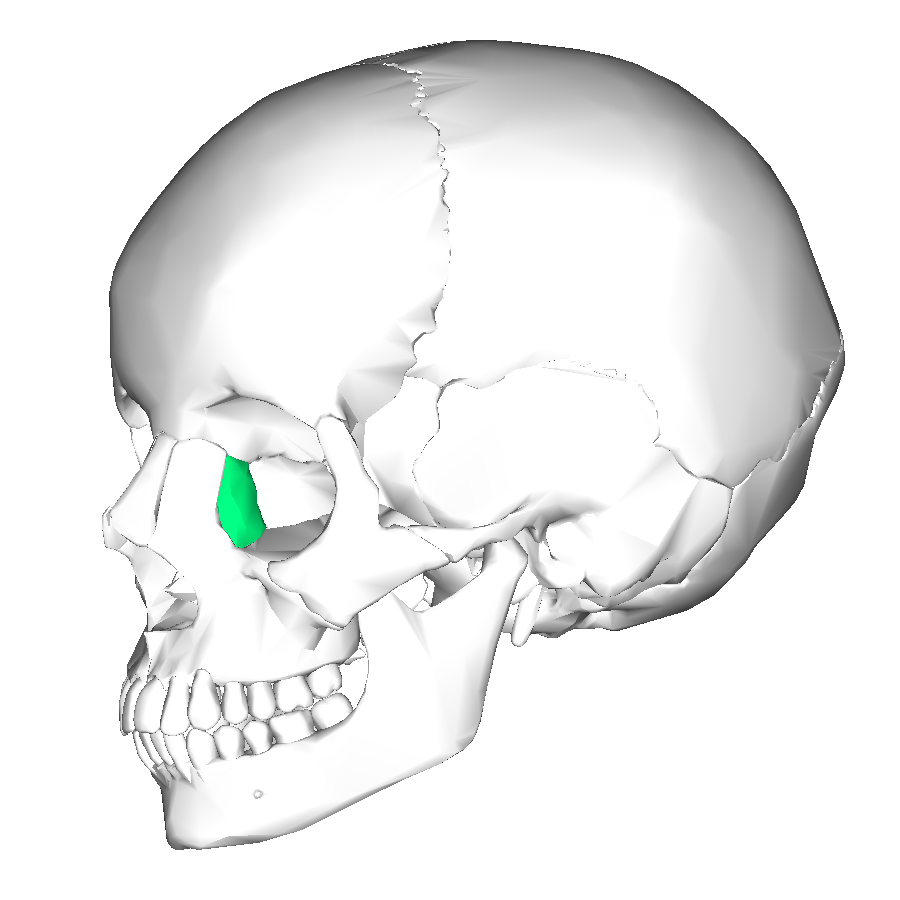
lacrimal
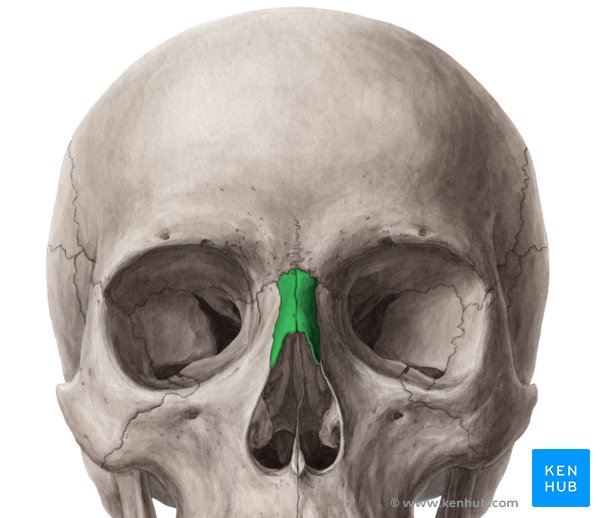
nasal
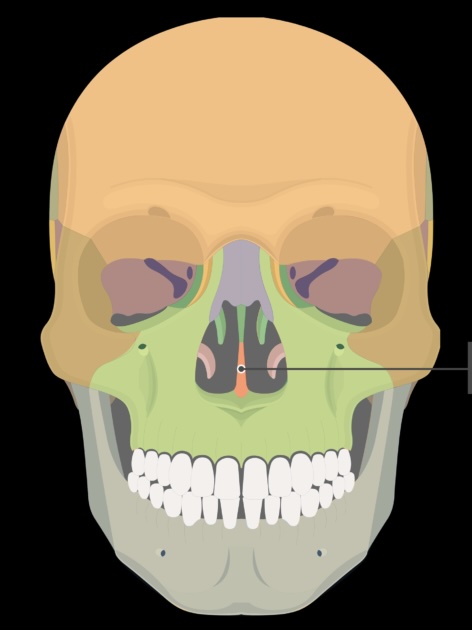
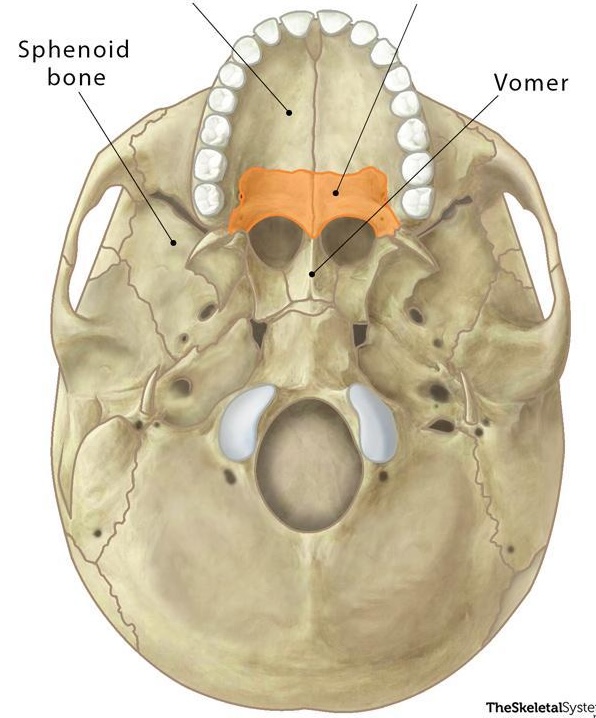
vomer bone
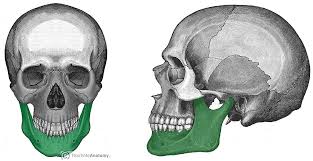
the mandible
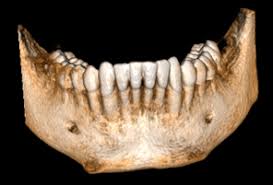
mental foramen
coronoid process
condylar proces
malleus
“hammer” 2 of them and it’s one of the auditory ossicles
incus
“anvil” 2 of them and it’s one of the auditory ossicles
stapes
“stirrup” 2 of them and it’s one of the auditory ossicles
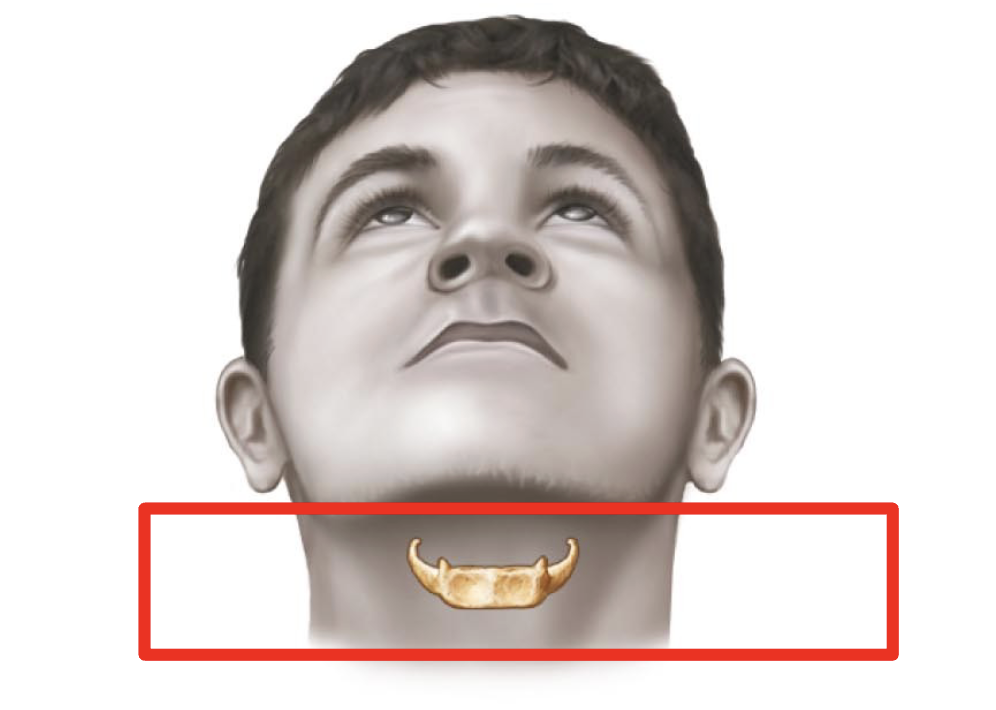
hyoid bone
cranial bones
frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid, and ethmoid
cranial sutures
coronal, sagittal, lambdoid, and squamous
facial bones
maxilla, palatine, zygomatic, lacrimal, nasal, vomer, inferior nasal concha, mandible
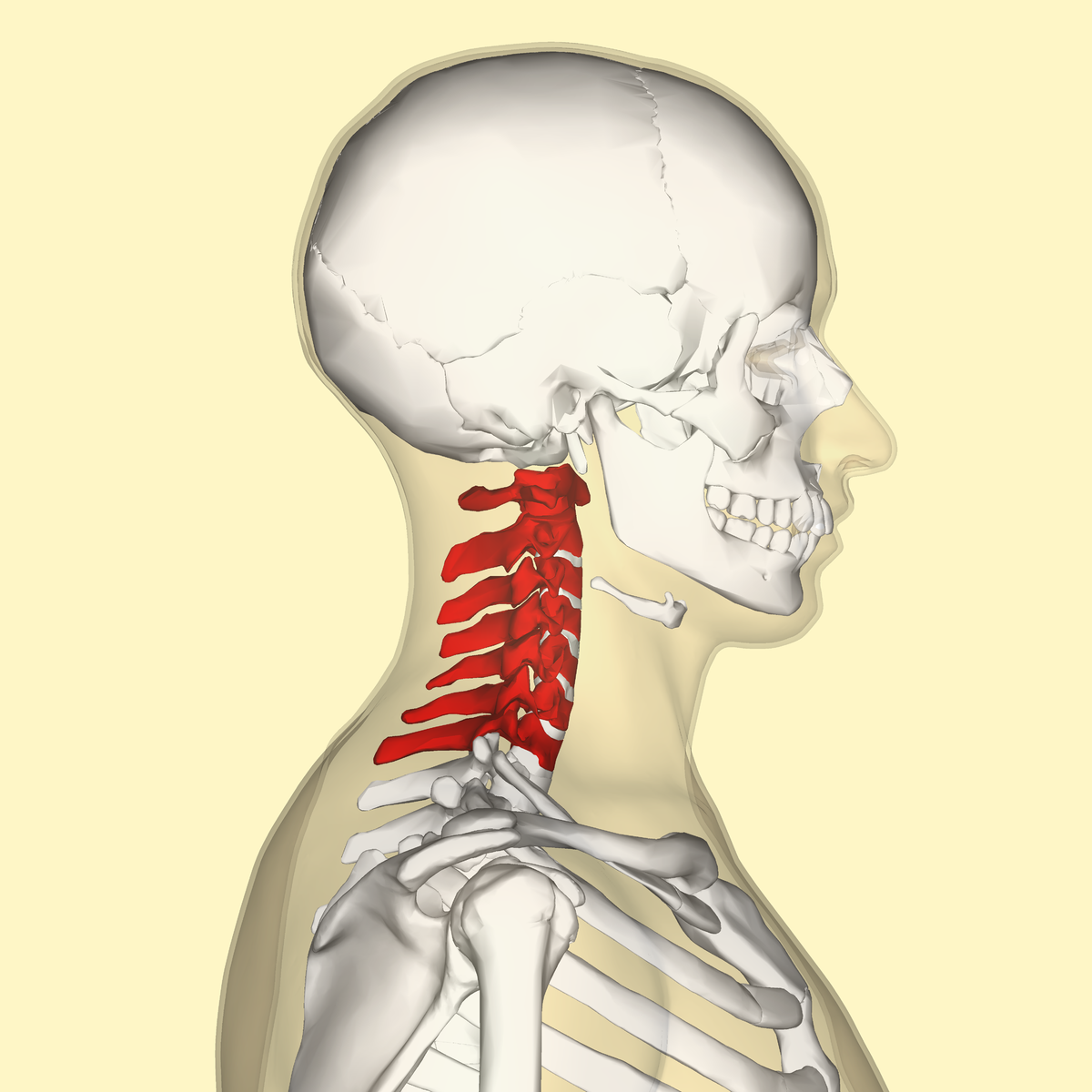
cervical vertebrae, first 7 bones in the neck that make up the cervical spine
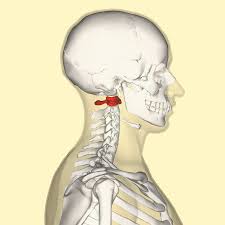
C1 the atlas. it has no body or spinous process and is only comprised of two bony arches with two bony masses laterally. it articulates with the occiput above and C2 (the axis) below. this part rotates
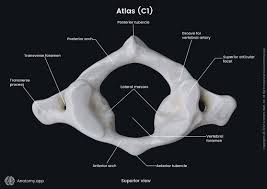
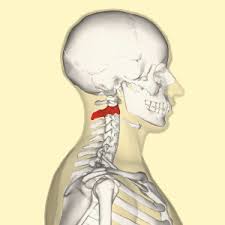
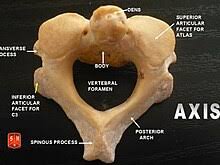
C2 the axis. the primary weight-bearing bone of the upper cervical region. it helps the atlas in rotation.
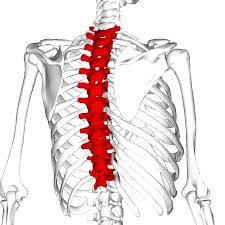
T1-T12. the thoracic vertebrae. In between the neck and the bottom of the ribs.
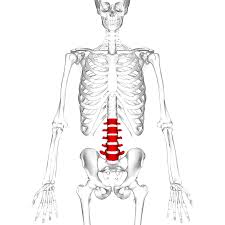
L1-L5. the lumbar vertebrae. the five bones that make up the lower back. these are the largest of your entire spine. located below your 12 chest (thoracic) vertebrae
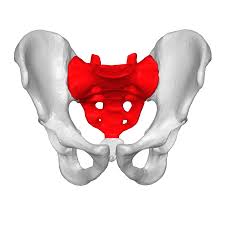
the sacrum. a shield-shaped bony structure that is located at the base of the lumbar vertebrae and is connected to the pelvis.
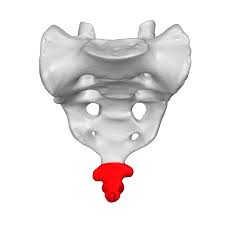
coccyx/tailbone
body
bears weight of upper body, protects spinal cord
spinous process
site attachment for muscles and ligaments; can be palpitated
lamina
protects spinal cord
pedicle
form intervertebral foramina allowing spinal nerves to pass laterally
vertebral foramen
passage of spinal cord
intervertebral foramen
passage of spinal nerves
transverse process
attachment of muscles and ligaments; thoracic transverse
process articulate with ribs
superior and inferior articular facets
allows adjacent vertebrae to articulate; the inferior facets of a superior vertebrae articulate with the superior facets of an inferior vertebra
vertebral column
26 bones. cervical C1-C7, thoracic T1-T12, lumbar L1-L5, sacrum, and coccyx
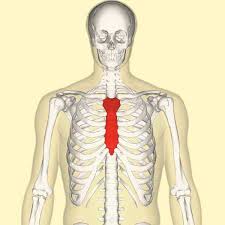
the sternum/breastbone. located in the center of the chest wall. consists of manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
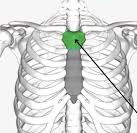
manubrium
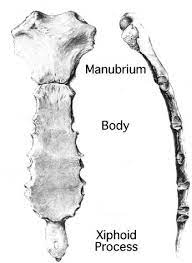
body
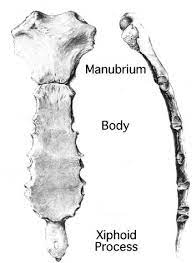
xiphoid process
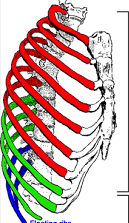
red
true ribs 1-7. have their own costal cartilage
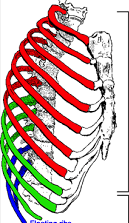
green
false ribs 8-12. their costal cartilage attaches to the costal cartilage of rib 7.
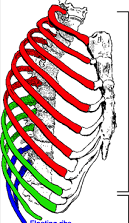
blue
floating ribs 11-12. do not have costal cartilage therefore no connection to the sternum