Topic 2 Cell Structure and Function
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Microtubules
Hollow tubes (\sim 25 \text{ nm} diameter) made of α- and β-tubulin protofilaments, crucial for cell shape, organelle movement, chromosome segregation, and the structure of cilia/flagella.
Protofilaments
Linear chains of tubulin dimers that assemble to form a microtubule.
Centrosome
The microtubule-organizing center near the nucleus; in animal cells it contains a pair of centrioles and is a major site of microtubule nucleation.
Centriole
One of a pair of cylindrical structures in the centrosome, each with nine triplets of microtubules arranged in a ring.
Spindle apparatus
Microtubule-based structure formed during cell division that organizes and segregates chromosomes
MTOC (microtubule-organizing center)
Sites in the cell where microtubules nucleate and are organized; examples include the centrosome and other cellular locations.
Cilia
Membrane-bound, slender projections extending from a cell; can be non-motile (sensory) or motile; core structure driven by microtubules with a typical 9+2 arrangement in motile cilia.
Flagella
Longer cellular projections used for locomotion; have a similar microtubule-based core to cilia and typically beat with a different motion; commonly found on sperm.
Basal body
A structure that anchors a cilium or flagellum to the cell; derived from a centriole.
9+2 arrangement
Ultrastructure of motile cilia/flagella: nine outer doublets of microtubules surrounding a central pair.
9+0 arrangement
Ultrastructure of a primary (non-motile) cilium: lacks the central pair of microtubules.
Dynein
Motor protein that drives bending movements of cilia and flagella by causing sliding between microtubule doublets.
Kinesin
Motor protein that moves along microtubules (usually toward the plus end) and mediates intracellular transport.
Actin
Globular actin (G-actin) monomers polymerize into filamentous actin (F-actin), forming two intertwined strands; diameter ~7 nm.
Microfilaments
Actin filaments (F-actin) built as a twisted double chain of actin subunits; ~7 nm in diameter; support cell shape, enable movement, participate in muscle contraction and cytokinesis, and drive cytoplasmic streaming.
G-actin
Globular actin monomer that polymerizes to form F-actin.
F-actin
Filamentous actin; polymerized form of actin making up microfilaments, ~7 nm in diameter.
Myosin
Motor protein that interacts with actin to cause muscle contraction and other cellular movements.
Cytoplasmic streaming
Circular flow of cytoplasm within cells, propelled by actin–myosin interactions, aiding distribution of materials.
Muscle
________ contraction results from the interaction between actin and myosin filaments sliding past one another.
Intermediate filaments
Fibrous keratin-family proteins 8–12 nm in diameter that provide mechanical strength, anchor the nucleus, and form the nuclear lamina.
Keratin
Protein subunits of intermediate filaments, diverse by cell type.
Nuclear lamina
A meshwork of intermediate filaments lining the inner surface of the nuclear envelope, providing structural support.
Extracellular matrix (ECM)
Glycoproteins and other macromolecules outside animal cells that provide support, adhesion, movement, and regulation; major components include collagen, fibronectin, and integrins that link to the cytoskeleton.
Collagen
Primary structural protein of the ECM, forming fibrous networks that provide tensile strength.
Fibronectin
ECM glycoprotein that binds to integrins and other ECM components to promote adhesion.
Integrin
Transmembrane receptors that connect the ECM to the cytoskeleton and mediate adhesion and signaling.
Cell wall
Extracellular structure in plants that protects the cell, maintains shape, and limits water uptake; composed mainly of cellulose; may have primary, middle lamella, and secondary layers.
Primary cell wall
Thin, flexible outer wall formed during cell growth.
Middle lamella
Thin layer rich in pectin between primary walls of adjacent plant cells, helping glue cells together.
Secondary cell wall
Additional rigid layer laid between the plasma membrane and the primary cell wall in some cells for extra strength.
Plasmodesmata
Membrane-lined channels that connect plant cells, enabling transport of ions, hormones, and metabolites; establish the symplast (shared cytoplasm).
Symplast
Continued cytoplasm of connected plant cells via plasmodesmata, allowing intercellular transport.
Tight junctions
Junctions that seal neighboring cells at the apical region to prevent leakage of extracellular fluid; involve transmembrane proteins like claudins and JAMs, connected to the actin cytoskeleton by ZO proteins.
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that fasten cells together into strong sheets; composed of desmoglein and desmocollin cadherins linked to intermediate filaments via plakins and catenins.
Gap junctions
Communicating - provide cytoploasmic channels
Intercellular junctions
Connections between cells that include tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions, linking membranes to the cytoskeleton.
Plasma membrane
The phospholipid bilayer that encloses the cell, with embedded proteins, separating cytoplasm from the outside.
Phospholipid bilayer
Two-layer arrangement of phospholipids forming the cell membrane; hydrophobic core restricts movement of water-soluble substances.
Inner leaflet
The cytosolic-facing half of the phospholipid bilayer.
Outer leaflet
The extracellular-facing half of the phospholipid bilayer.
Cytoplasm
All material within the cell membrane, excluding the nucleus (in eukaryotes).
Cytosol
The aqueous component of the cytoplasm containing water, ions, and small molecules.
Chromosome
The DNA molecule that stores hereditary information.
Ribosome
Ribonucleoprotein particle that carries out protein synthesis; can be free in cytosol or bound to membranes.
Cytoskeleton
Protein filament network that maintains cell shape, anchors organelles, and aids in movement.
Prokaryote
A cell type lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (Bacteria and Archaea).
Eukaryote
A cell type with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Nucleoid
Region where prokaryotic DNA is located, not enclosed by a membrane.
Nucleus
Membrane-bound organelle containing most of the cell's DNA; site of transcription; enclosed by a nuclear envelope with pores.
Nuclear envelope
Double-membrane barrier surrounding the nucleus, with nuclear pores.
Nuclear pore
Protein-lined channel regulating traffic between nucleus and cytoplasm.
Nucleolus
Nuclear substructure where ribosome assembly begins.
Chromatin
DNA-protein complex that forms chromosomes within the nucleus.
Glycocalyx
Sugar-rich coating on cell surfaces; in bacteria includes slime layer or capsule depending on attachment to the cell.
Slime layer
Loosely attached glycocalyx; a non-tight protective layer.
Capsule
Firmly attached glycocalyx; protective layer around some bacteria.
Pili
Hairlike appendages that mediate attachment and genetic exchange in bacteria.
Flagellum
Long whip-like tail used for propulsion by rotation.
Bacterial cell wall
Rigid outside layer of bacteria providing shape and protection, typically containing peptidoglycan.
Endomembrane system
Interconnected membranes (ER, Golgi, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane) that modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins; does not include mitochondria or plastids.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membrane-bound tubules and sacs; continuous with the nuclear envelope; two forms: rough (with ribosomes) and smooth (without).
Rough ER
ER region studded with ribosomes; synthesizes proteins and membranes; products move to the Golgi.
Smooth ER
ER region lacking ribosomes; synthesizes lipids, detoxifies compounds, and stores calcium.
Golgi apparatus
Stack of flattened membranes that modifies, sorts, and ships proteins and lipids via vesicles; cis, medial, and trans cisternae.
Cis face
Golgi’s receiving side facing the ER.
Trans face
Golgi’s shipping side where vesicles depart.
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound sacs that transport cargo between organelles or to the plasma membrane.
Lysosome
Membrane-bound organelle with hydrolytic enzymes for digestion and autophagy; acidic interior.
Phagocytosis
Cellular process of engulfing large particles into a phagosome that fuses with a lysosome.
Autophagy
Lysosome-dependent degradation and recycling of cellular components.
Mitophagy
Autophagy of mitochondria.
Vacuole
Membrane-bound sac with varied functions; in plants central vacuole; in animals lysosomal/storage vacuoles.
Central vacuole
Large plant cell vacuole for storage and turgor; surrounded by tonoplast.
Tonoplast
Membrane surrounding the central vacuole.
Mitochondria
Organelle for cellular respiration; produces ATP; double membrane; contains its own DNA and ribosomes.
Cristae
Folds of the inner mitochondrial membrane increasing surface area for enzymes.
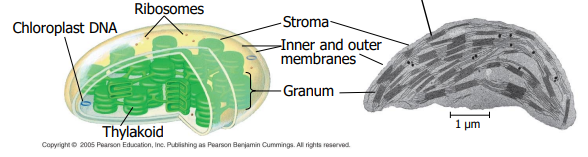
Chloroplast (plastids)
Site of photosynthesis in plants/algae; double membrane; contains thylakoids, granum, and stroma; contains its own DNA.
Thylakoid
Flattened membrane sacs within chloroplasts where light reactions occur.
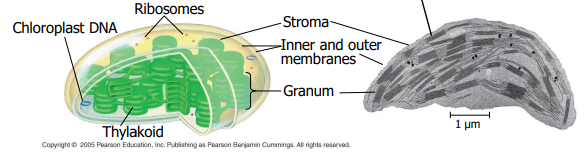
Granum
Stack of thylakoids within a chloroplast.
Stroma
Fluid inside chloroplast surrounding thylakoids; site of the Calvin cycle.
Peroxisome
Oxidative organelle; contains enzymes to break down fatty acids and detoxify; produces hydrogen peroxide and converts it to water and oxygen.
Glyoxysome
Specialized peroxisome in plants/molds converting stored lipids into carbohydrates.
Endosymbiosis
Theory that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as free-living prokaryotes engulfed by a host cell.
Mitochondrial DNA
Circular DNA present in mitochondria, separate from nuclear DNA.
Double membrane
Two phospholipid bilayers enclosing organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Desmosome
Anchoring junction that mechanically links adjacent cells in tissues.
Plasmodesmata
Channels through plant cell walls that connect cytoplasm of neighboring cells.
Cell wall (plants)
Rigid layer outside the plasma membrane; in plants primarily cellulose; provides support and protection.
Cytoskeleton components
Network of protein filaments (microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments) that supports the cell, enables movement, and organizes organelles.
Semiautonomous
organelles that can grow and divide independently within a cell, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts.
Which locations in the cell do not contain DNA?
Ribosomes