Building Therapeutic Relationships
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
nurse-client relationship
A relationship between the nurse and client that is founded upon trust, respect, and professionalism.
theory of Interpersonal Relationships
pre-interaction:
self- evaluate of needs, beliefs and behaviors before interaction
orientation
build trust/ rapport
place boundaries
collect data, assess, works w/ client for goals, and identify barriers
account for health literacy
working
progress towards the goal
help pt have a plan to solve the problem → sense of autonomy
termination phase
goals have been met → new goals developed
building trust and rapport
rapport build up when pt feels understood, and tx is transparent
employ honesty, fidelity, respect, understanding
barriers: socioeconomic status, education, cultural and racial differences, language backgrounds, and gender.
transference
client experiences feelings or emotions from a person or object and displaces those feelings or emotions toward the nurse.
if negative→ talk to supervisor
countertransference
The unconscious effort on behalf of the nurse to redirect their previously experienced feelings or emotions toward the client.
motivational interviewing
A communication strategy that assists clients in developing motivation to resolve insecurities and ambivalent feelings toward behavior change.
congruence
When a client’s expressed mood matches their affect.
SOLER
therapeutic non verbal communication
S: Sit squarely to the client
O: Open posture
L: Lean forward
E: Eye contact
R: Relax
SURETY
therapeutic non verbal communication
sit at an angle
sitting across might appear like confrontation
uncross legs and arms
relax,
eye contact,
touch:
hand, lower arm, sholder
your intuition.
non verbal cues
Affect: frowning; lack of expression; grimacing; pursed lips; raised or lowered eyebrows; biting, licking, smacking lips; nose scrunching
Appearance: sudden disrobing; clothing that is incongruent to current temperature; disheveled grooming
Autonomic Response: visible brow or palm perspiration; pupil dilation; facial flushing or paleness; increased respirations
Body Behaviors: gait; posture; hand clenching; rocking; psychomotor agitation
Eye Movement: suspicious; squinting; open with minimal blinking
open ended
“ tell me more ….”
affirmations
used when the nurse feels like the client is making real progress in conversation or treatment.
state what the pt did and then affirm
If the nurse does not feel genuine about the affirmation, they should not say it. The nurse’s body language and the tone of their voice are cues when they do not feel genuine about what they are saying.
simple reflection
uses some element of what the client said.
complex reflection
taking educated guess on how the pt is feeling
“So you are saying...,” “It sounds like…,” or “I get the impression that you….”
summaries
restate major key concepts in a conversation about change
OARS
Open-ended
Affirmations
Reflections
Summaries
non therapeutic communication
giving advice or opinions
health literacy: avoid jargon
disagreeing: confrontation, makes pt defensive
primary language
reassuring: will minimize how the pt is feeling
why questions: pt feel the need to defend ideass
disapproval
anxiety, pain, and physical discomfort:
pharmacological and non pharmacological interventions
Socratic questioning types
Clarification: “Tell me more about your current thought.”
Questions about the question: “How were you feeling when you asked that question?”
Probe assumptions: “I wonder how someone would explain this belief?”
Probe reasons: “What do you think causes this to happen?”
Probe viewpoints: “What are the strengths and weaknesses for...”
Probe implications: “What might be the consequences of…”
Active listening
look interested
respond
stay on task
respond by summarizing
evaluate message
neutralize feeling: w/o judgment
LISTEN
Look interested
Involve
Stay on task
Test
Evaluate
Neutralize
transtheoretical model of change
integrative, biopsychosocial model to conceptualize the process of intentional behavior change.
precontemplation,
contemplation,
preparation,
action, and
maintenance
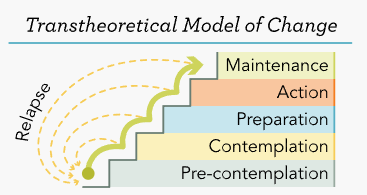
Precontemplation
pt lacks insight or demonstrates defense mechanism of denial.
The client does not recognize the benefit of change or may have previously attempted change and failed to maintain healthy behaviors.
Contemplation
ambivalence
see themselves making a change or understand the change’s importance.
→ aim to explore the positives and negatives of current and proposed behavior changes.
Preparation
pt demonstrate adjustments or minor changes to their current habits.
may have yet to fully commit to a changed lifestyle or is having difficulties overcoming barriers to change.
→ aim to identify the client's current coping skills and possible support systems.
action
by the client experiencing changed behaviors.
behavior: changed when the previous behavior has not been experienced for more than 180 days.
→ identify positive outcomes of making the behavior change and develop contingencies if planned coping or support systems fail.
maintenance
the change is second nature and actively working to prevent relapse.
behavior for more than six months and no longer feels like change is necessary.
→ aim to help the client identify triggers for relapses like people, places, or objects that are associated with the old behavior.
therapeutic window
psychological state in which therapeutic interventions are believed to be most beneficial.
need to be culturally considerate
culturally competent care (6)
awareness
self-reflection
knowledge:
life-long learning and actively seeking knowledge
sensitivity:
skill:
Giger and Davidhizar Transcultural Assessment Model: cultural differences in communication, space, time, social organization, environmental control, and biological variations.
proficiency
dynamicity
Transcultural Nursing Theory
Madeleine Leininger
pt culture develops their values and beliefs that can impact their health and lifestyle decisions.
whole body approach + autonomy
maintenance
cultural preservations: Care considerations to retain the client’s core cultural beliefs and values related to health care.
negotiation
cultural accommodations: help the client adapt or negotiate with other cultures while in treatment
cultural repatterning
supports the client who is changing a culturally related behavior in an effort to improve health outcomes.
cultural formulation interview
cultural def of the problem
cultural perceptions of cause, context, support
cultural factors that affect self-cope and past help-seek
cultural factors affecting current help-seek
organizational culture
the values, attitudes, beliefs, psychology, and experiences that influence daily operation.
DEI
Diversity: refers to the qualities of a client that differs from that of the nurse.
equity: ensures that the client has an equal opportunity to initiate and continue fair treatment.
inclusion: the ability of all care team members, including the client, to voice their concerns with treatment and influence the decision-making process.
Bias free language
avoid generalization
be specific
if unsure how to address pt, ask for pronouns
don’t use “normal”
telehealth
cost-effective and increasingly accessible in rural areas
motivational interview process
engaging: allow pt to discuss their concern and major importance in life
helps build trust and rapport while supporting client autonomy
focus: identify unhealthy behaviors → analyze alternatives
expert trap: when a clinician prescribes advice without consent or solicitation from the client.
always ask for consent
evoke:
importance, or confidence, ruler statements: statement designed to evoke motivation by focusing on the client’s strengths.
plan: works with the client to develop a plan for behavior change.
SMART
goal plan
Specific:
Measurable:
Achievable:
Realistic:
Time:
occupational role of nurse
The occupational role of a nurse includes education, group facilitation, and care management.