4.2 Relearning Activity #2 (Practice Test) biology cp
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Genetic variability
is the measure of the differences among individuals within a population.
Meiosis
when sex gametes reproduce and it produces 4 gametes
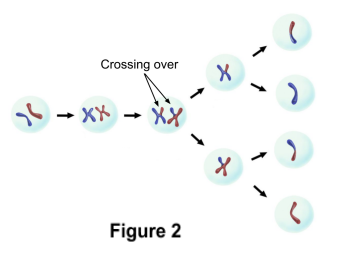
Crossing Over
During crossing over, certain proteins break sections
of chromosomes, and these sections switch with
the other chromosome, as shown in figure 2.
This, in effect, ensures that the offspring will
inherit a unique mixture of the parents’
chromosomes.
Genetic variation
the difference in DNA among individuals or the differences between populations among the same species.
Ways Genetic Variation Can Occur
Mutations - they can change the gene expression or not
Meiosis - has genetic variation because of the crossing over that occurs
Environmental factors - can cause mutation due to mutagens
Mutations
a change in the DNA sequence of an organism
Genetics
the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms
mutation
a change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
punnet square
a table in which all of the possible outcomes for a genetic cross between two individuals with known genotypes are given
How do mutations occur
Offspring, parents, random chance,
How Inherited genetic variation resulting from meiosis, environmental factors, and error in replication
Inherited genetic variation resulting from meiosis, environmental factors, and errors in replication is fundamental to the diversity of life. Meiosis introduces genetic diversity by shuffling and recombining parental genetic material, ensuring unique combinations of genes in offspring. Environmental factors such as radiation and toxins can induce mutations, leading to new traits and driving evolution. Additionally, errors in DNA replication during cell division can result in mutations, further contributing to genetic diversity within populations.