Vertebral Imaging and Cervical Spine Clearance: Up to Back Pain
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
33
there are ____ vertebrae
7 cervical
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
5 sacral (fused)
4 coccyx (fused)
How many of each vertebrae are there?
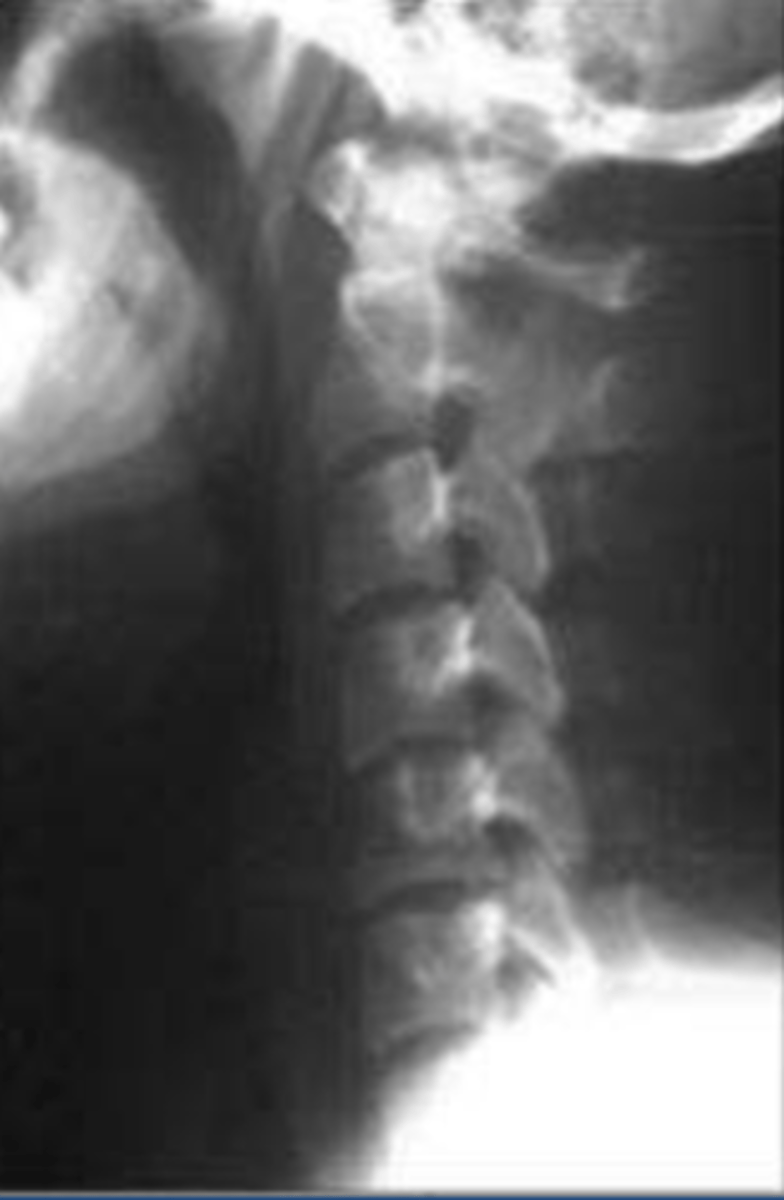
This cervical spine is very straight. This is a position of comfort for a patient with cervical strain or some type of pathology.
What is going on here?
Anterior
the ___ arch (elements) of the vertebral collumn is made up of the vertebral body and disc. Loads 80% of the weight
Posterior
the ____ arch (elements) of the vertebral column include the pedicle, transverse process, superior and inferior articular processes, lamina, vertebral foramen, and spinous process.
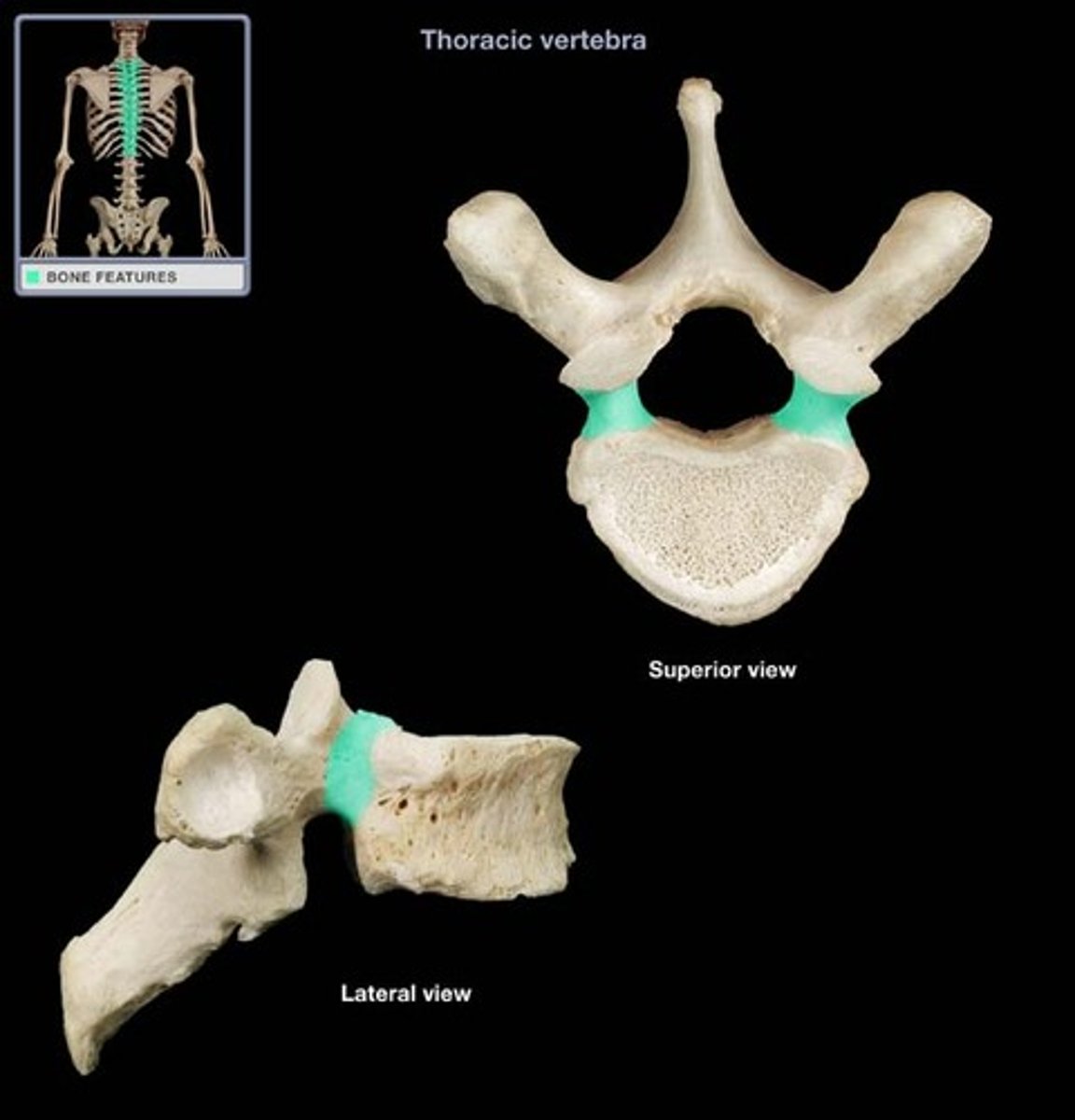
Pedicle
allows for passage of nerve roots, the area between the body and transverse processes.
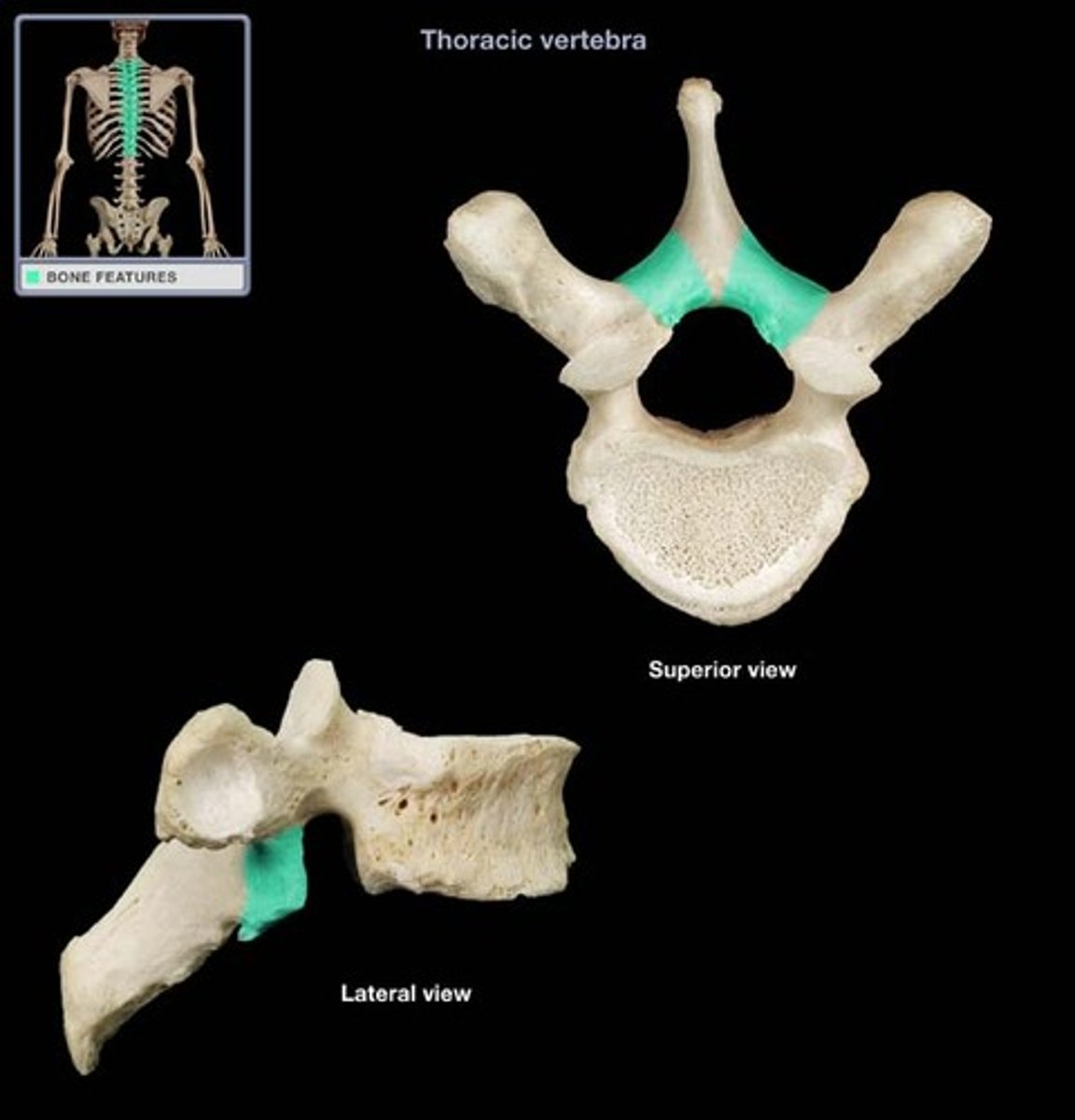
lamina
thin, plate like area between the spinous and transverse processes.
spinal nerve, vasculature and fat
each neural foramina contains...
L1/L2
the spinal cord ends as the conus medularis at the level of
conus medularis
the spinal cord ends as the ____ at the level of L1/L2
cauda equina
the spinal cord ends as the conus medularis and projects as the ____ to the sacrum.
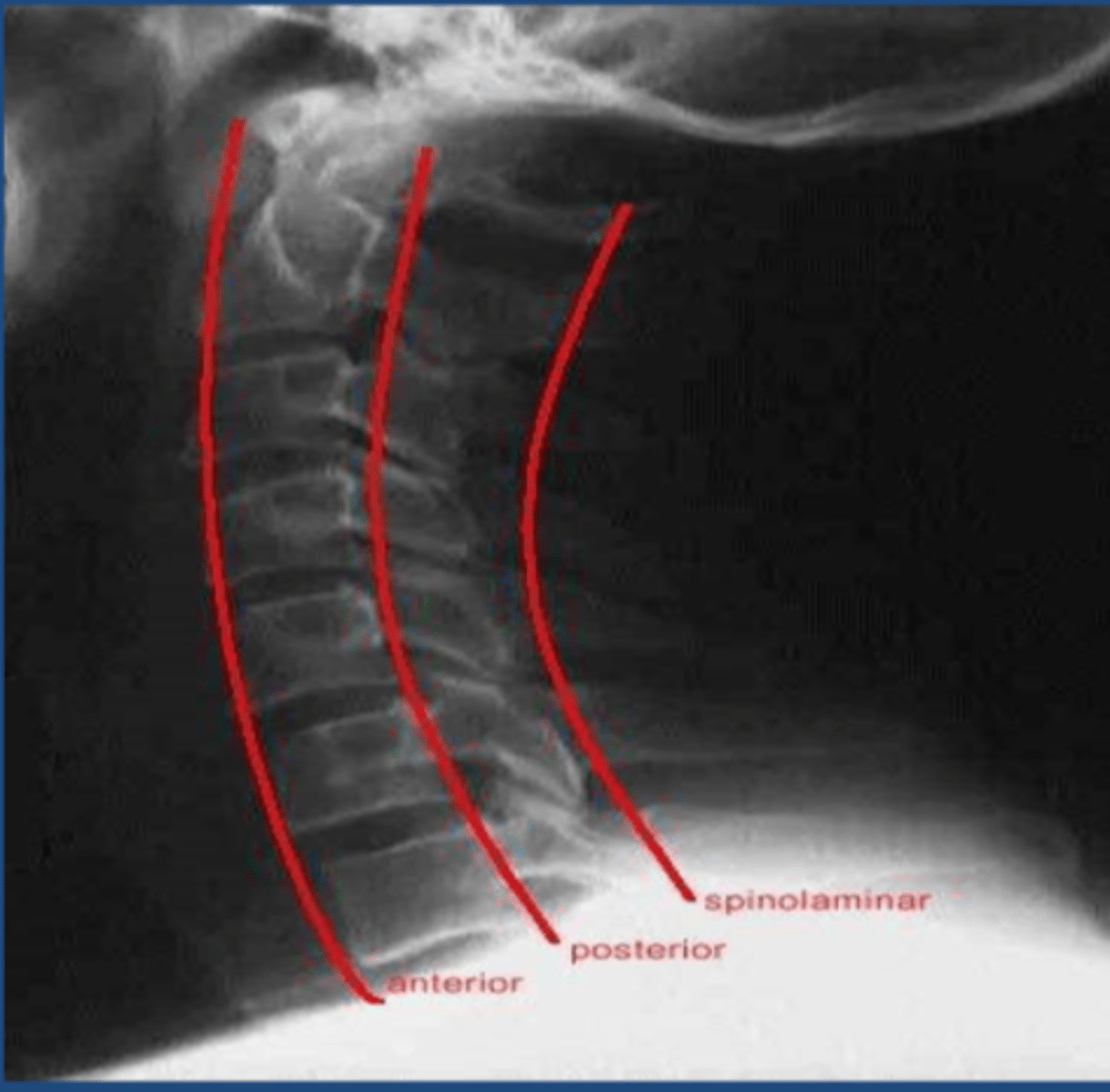
anterior vertebral line
red line
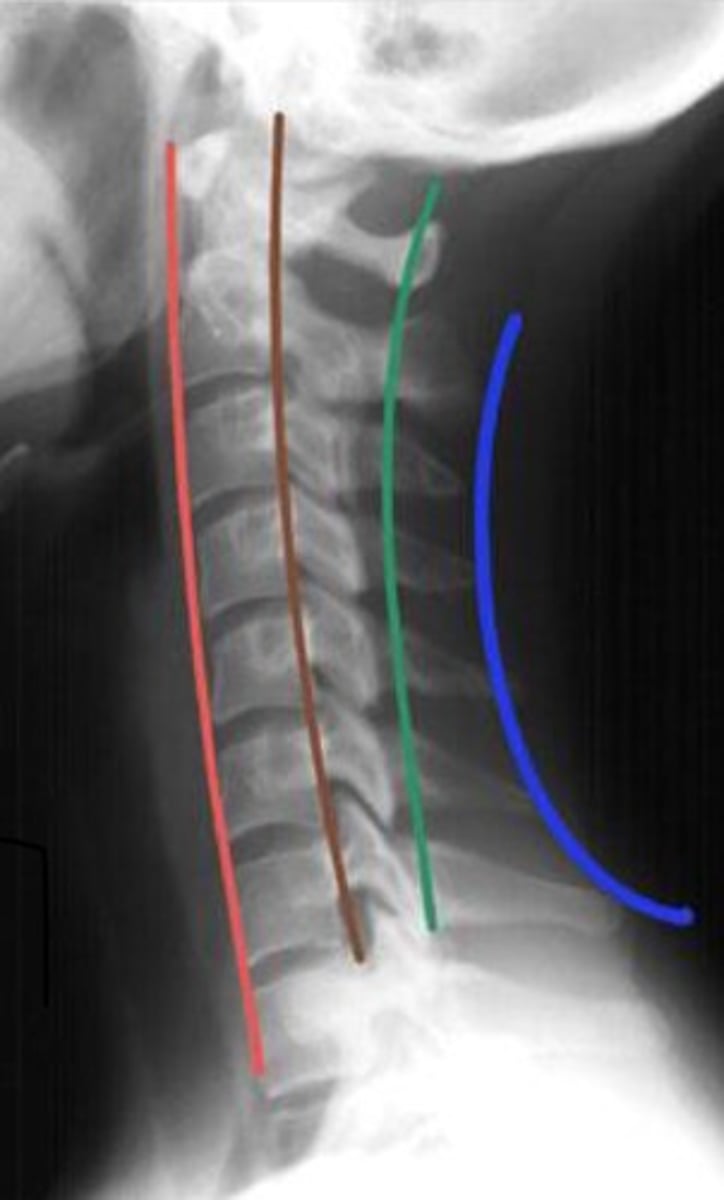
Posterior vertebral line
brown line
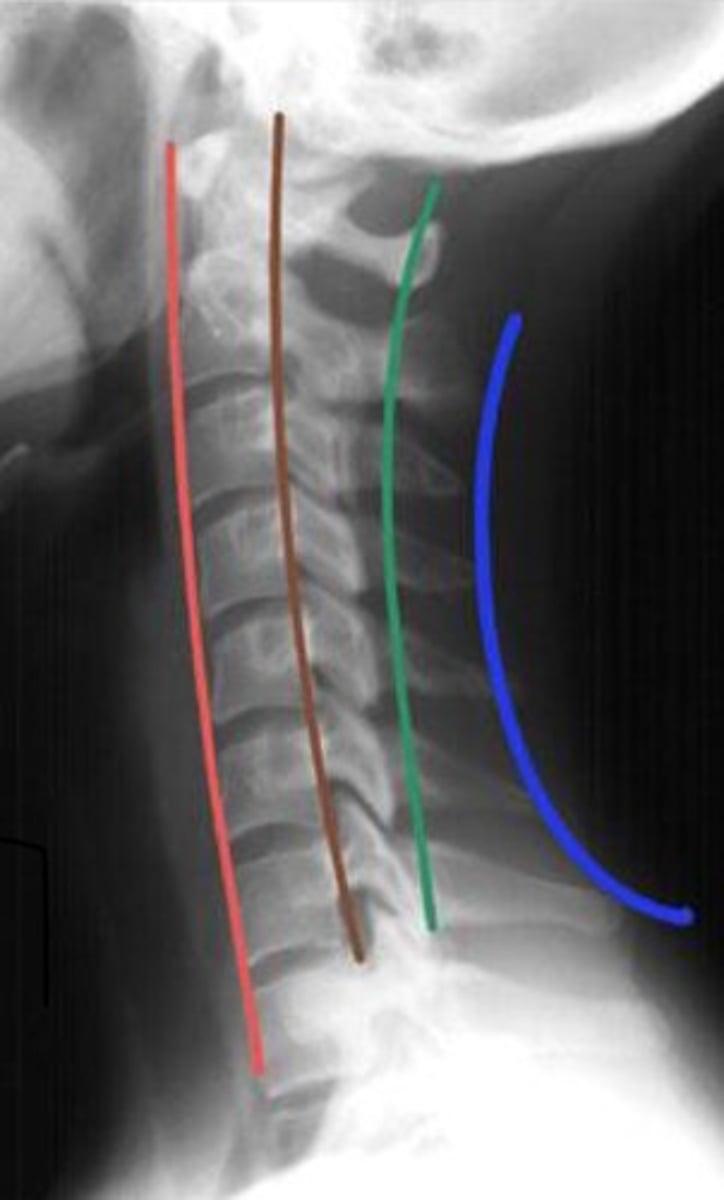
Spinolaminar vertebral line
green line
Odontoid View
Posterior
joints of the spine are lcoated ____ to the vertebral body
Ligamentum flavum
strongest spinal column ligament from the base of the skull to the pelvis. Anterior to and posterior to the lamina. Protects the cord and nerve roots.
Anterior longitudinal ligament
spinal column ligament that runs from the occiput to the sacrum. Anterior vertebral body to annulus fibrosis
Posterior longitudinal ligament
spinal column ligament that runs from the occiput to the sacrum. Posterior vertebral body to annulus fibrosis
Interspinous ligament
spinal column ligament that attaches to ligamentum flavum, which runs into the cord
Supraspinous ligament
spinal column ligament that attaches tip of each spinous process to the next.
Just Review the three lines
Just Review the three lines
flexion and rotation
____ mechanism of injury causes Unifacet Dislocation
30
only ___% of patients with Unifacet Dislocation have neuro deficit.
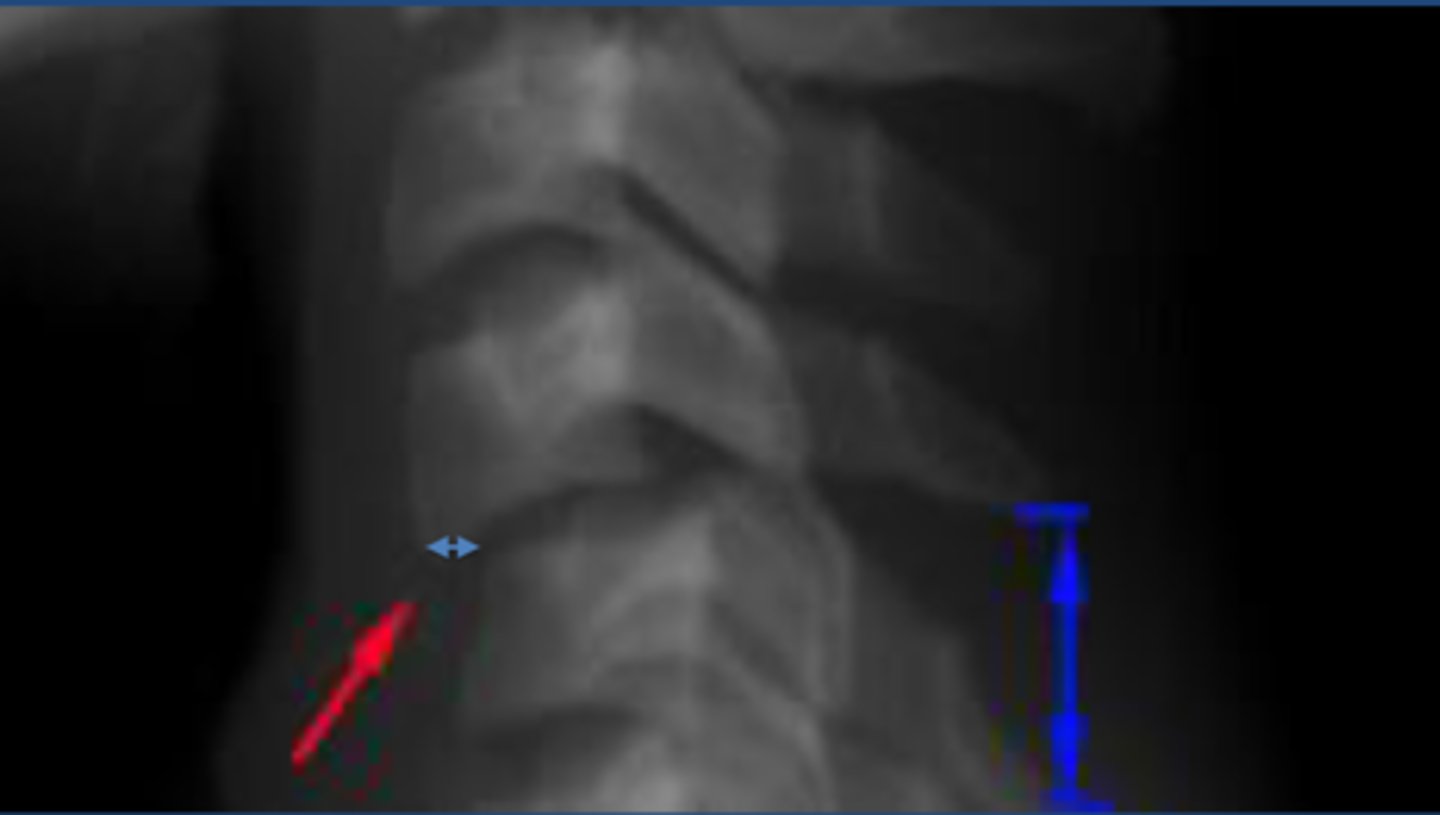
Unifacet Dislocation
vertebral body subluxes but less than 25% of width of the VB. Inferior artic facet of superior VB locked in front of superior artic facet of the inferior VB, on 1 side.
C4-C5 and C5-C6
most common levels for a unifacet dislocation.
unifacet dislocation
Bilateral facet dislocation
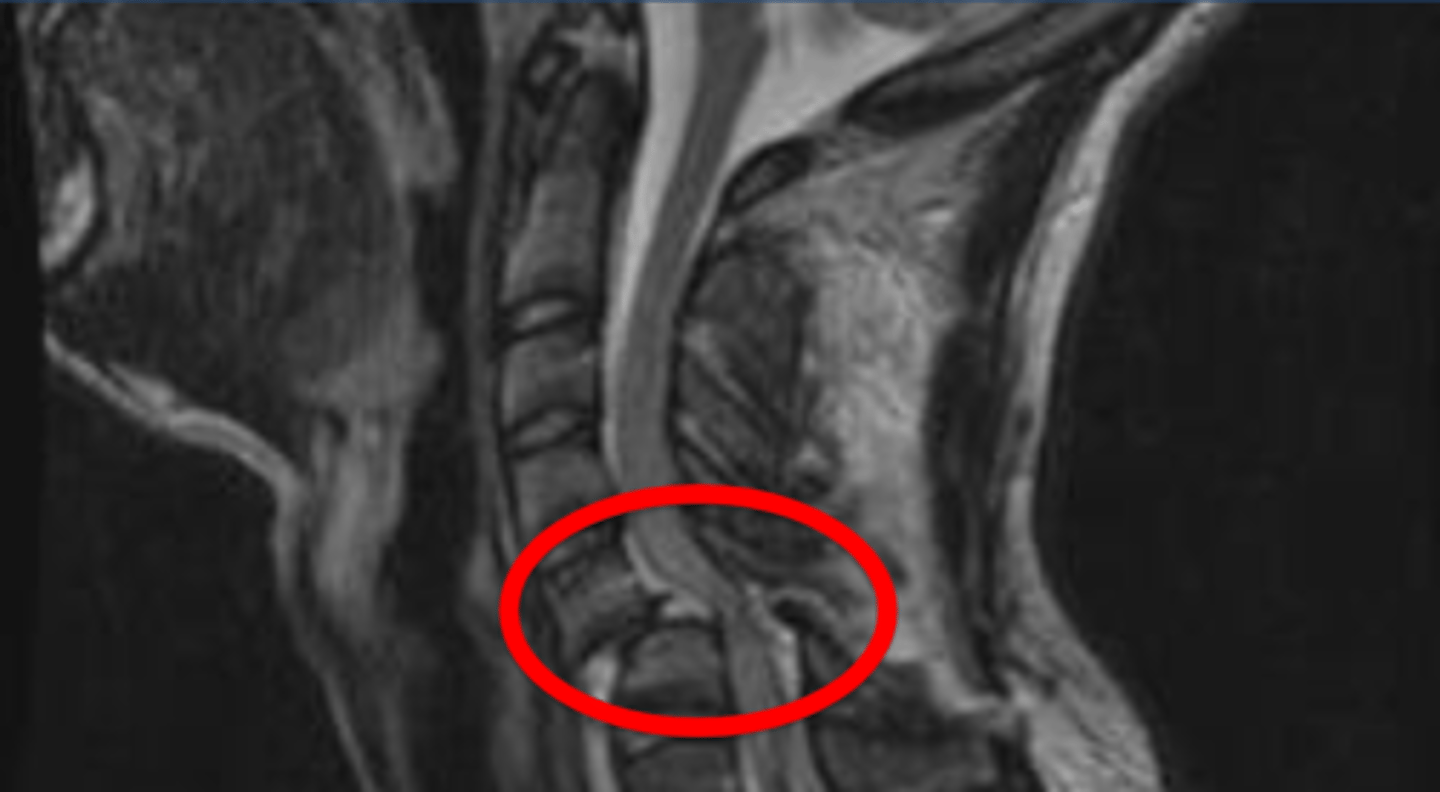
"Locked" facets, "Naked facet sign" on CT. Anterior longitudinal ligament and posterior longitudinal ligament often injured/disrupted. Superior VB subluxes over inferior VB by greater than 50% of width of VB.
lower cervical region
most common region for Bilateral facet dislocation
lamina and vertebral arch
Bilateral facet dislocations are often associated with fractures of the _____
85
___% of patients with bilateral facet dislocation have neuro deficits
less
decompression of cord
If posterior elements fracture in a bilateral facet dislocation there is ____ chance of quadriplegia
bilateral facet dislocation
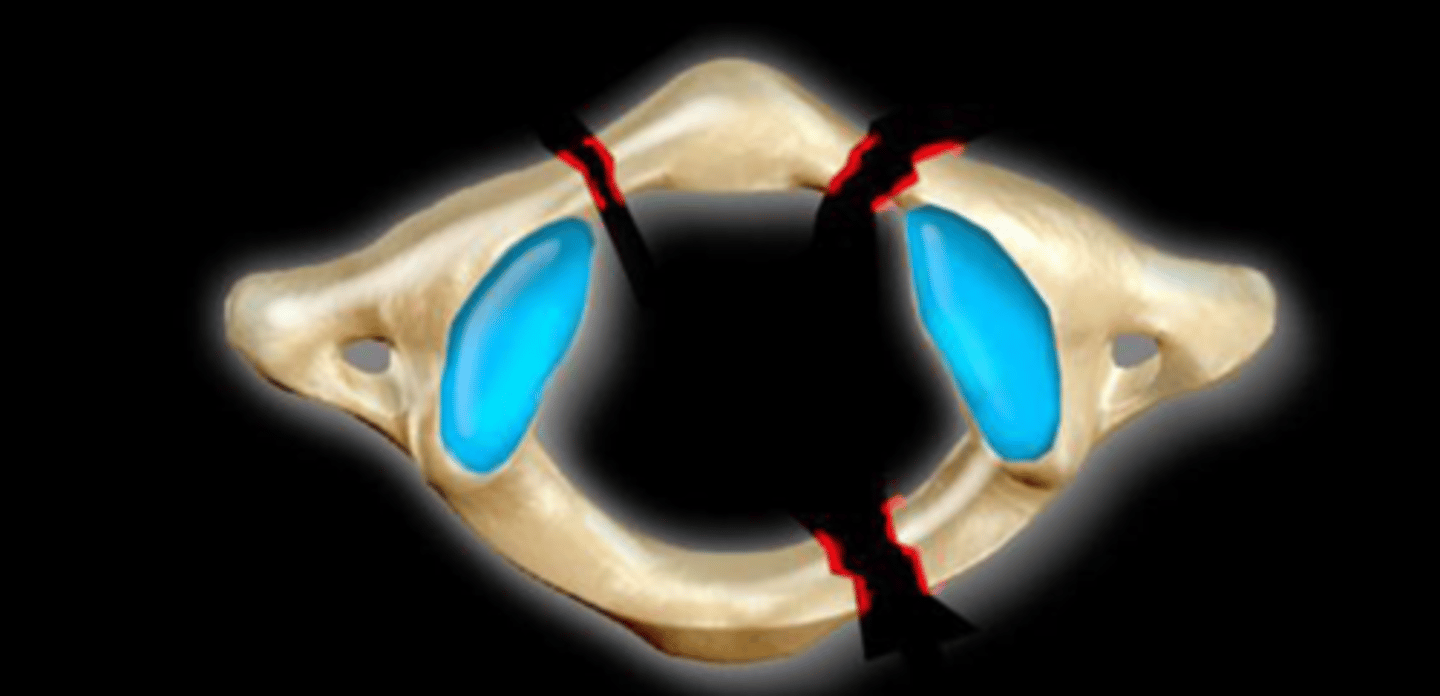
Jefferson fracture
fracture of the anterior/posterior arches of C1. Usually bilateral (4 fractures), but does not have to be.
Axial
___ load mechanisms is the typical cause of a Jefferson Fracture
Lateral offset of C1 lateral masses
Hallmark sign of Jefferson fracture
no
due to complete decompression of canal
Do neuro deficits typically accompany a Jefferson fracture.
Jefferson fracture
Jefferson fracture
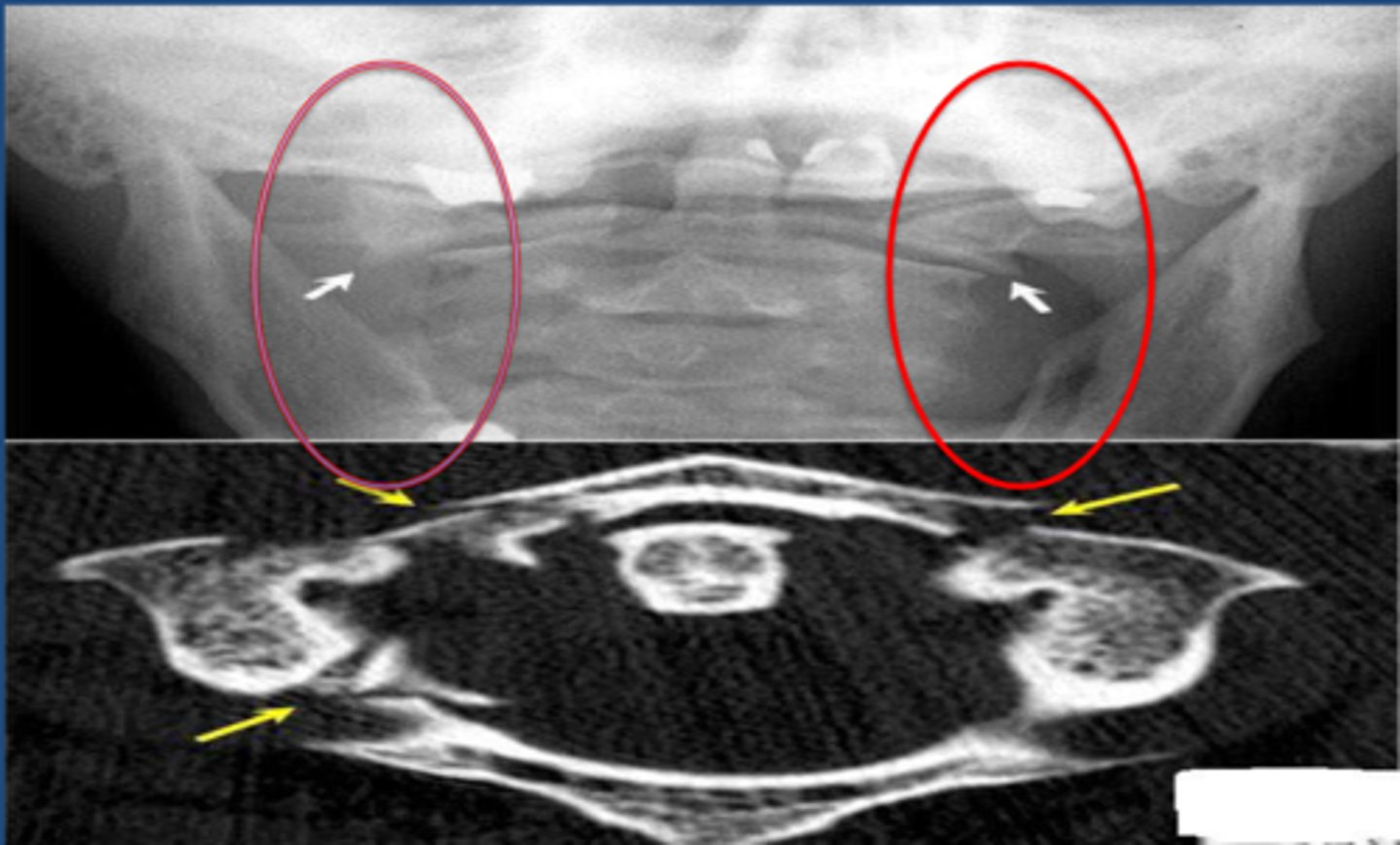
Hangman's fracture
fracture of C2 vertebral body posterior elements separate from anterior VB. VB of C2 subluxes over C3 VB.
Hyperextension/compression
Unrestrained occupant in motor vehicle crash with head into windshield/rearview mirror
Mechanism of Injury for Hangman's fracture
No
due to spinal canal decompression
Is a Hangman's fracture typically accompanied by neuro deficit?
Hangman's fracture
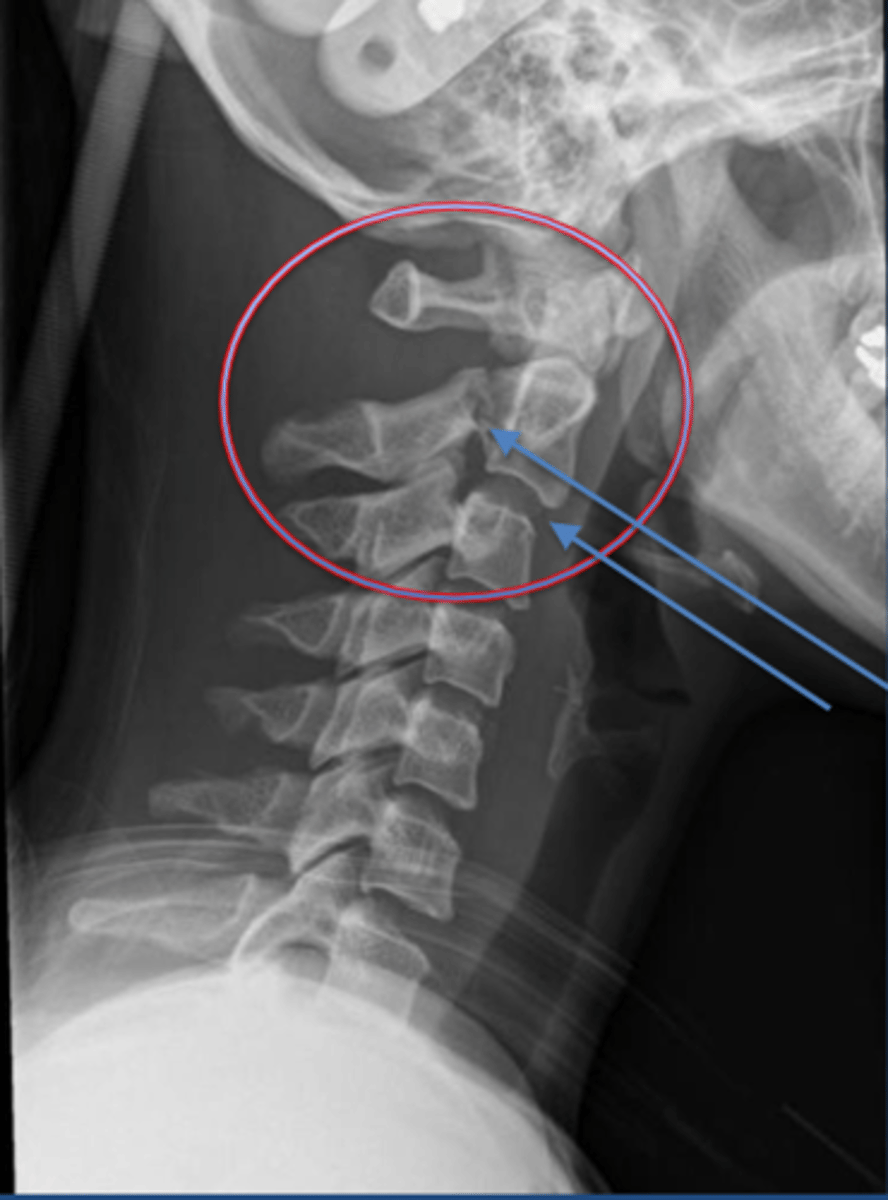
Hangman's fracture
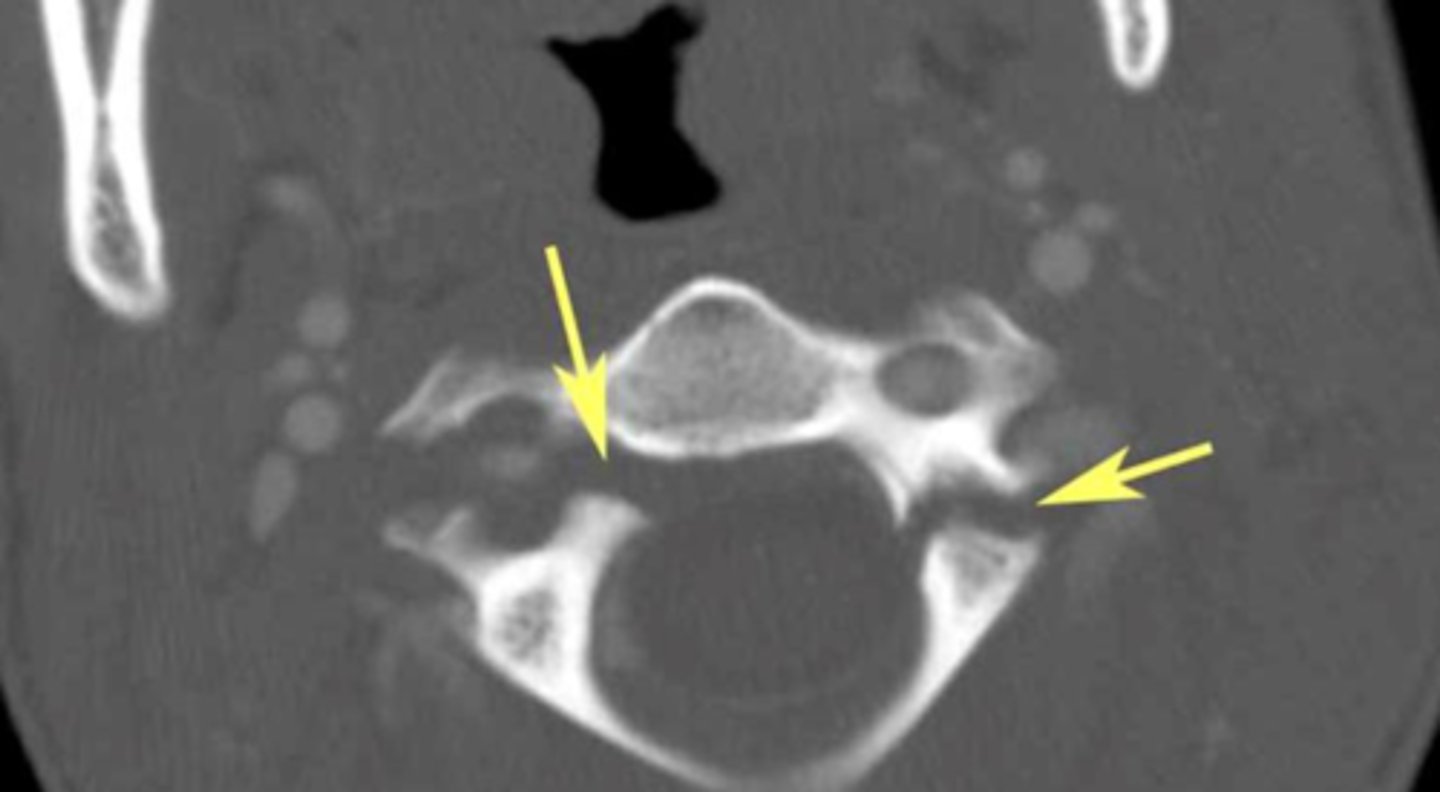
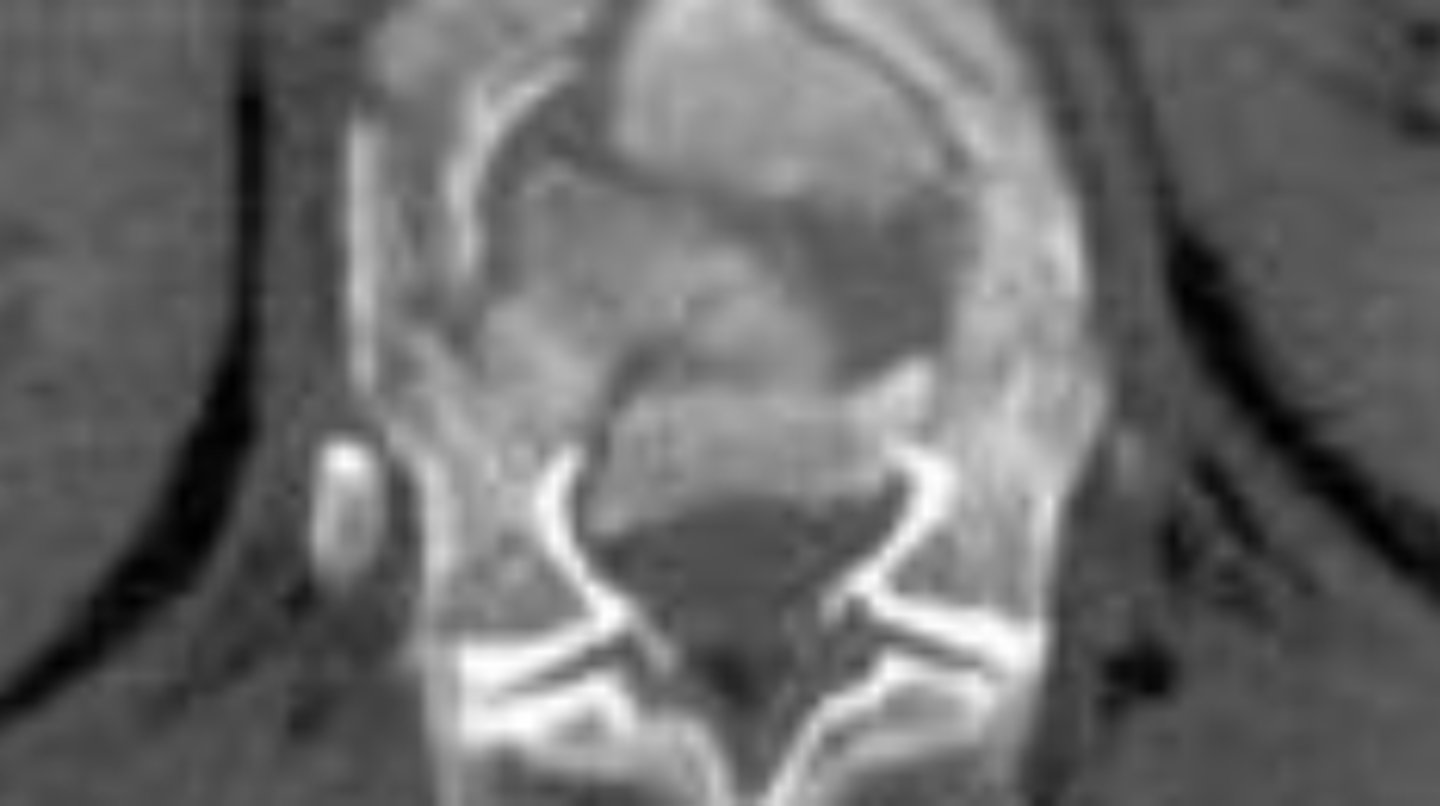
Burst fractures
fracture in which VB ruptures and fragments of bone and likely disc can be retropulsed into canal. Patients could have neuro findings.
C-spine, T-spine, and upper L-spine
most common spinal levels for Burst Fractures
axial load
MOI for Burst Fractues
Yes, patient could have Neuro deficits
Do patients typically have neuro deficits with Burst Fractures?
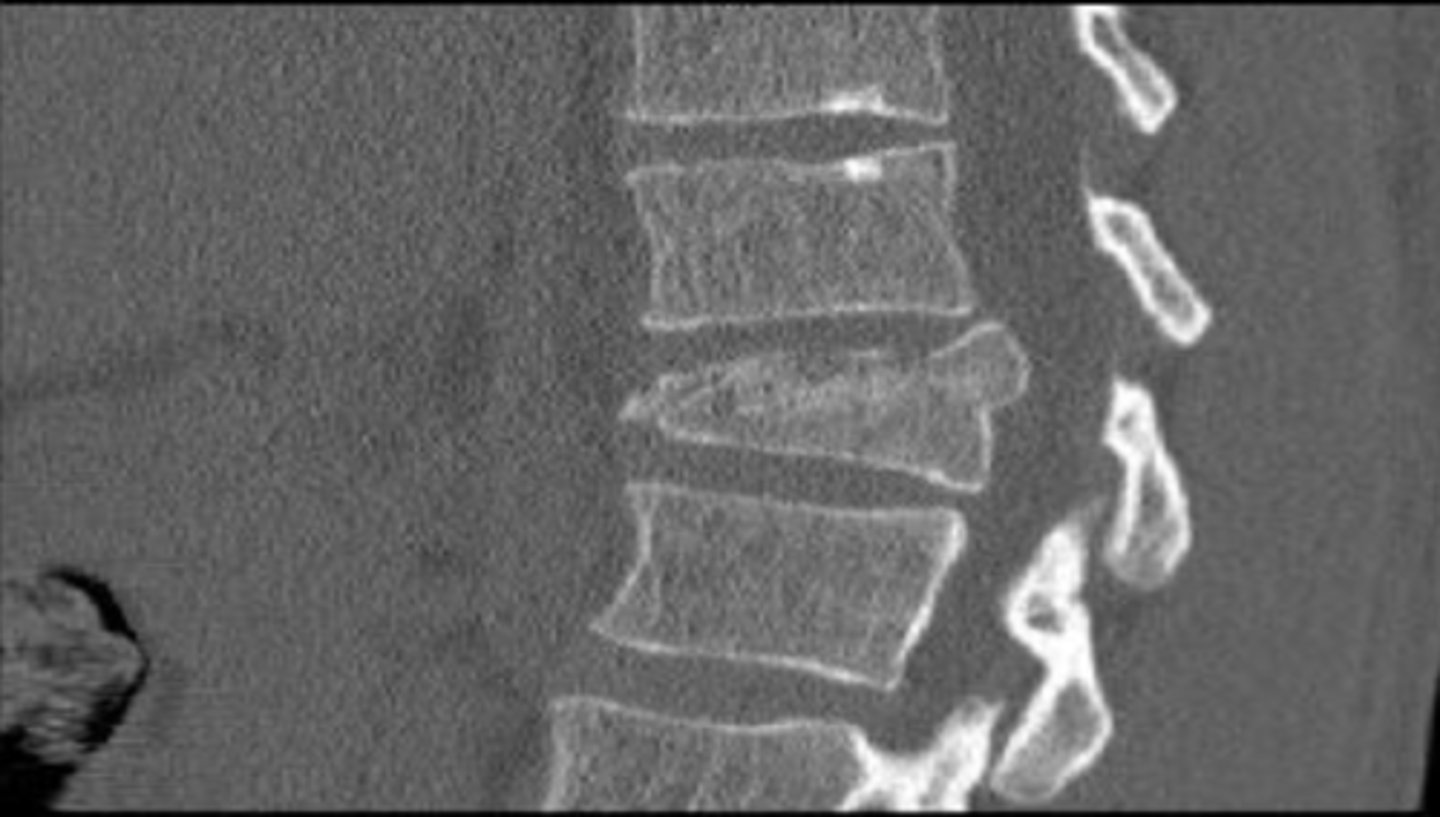
T12 Burst Fracture
T12 Burst Fracture
Type 1
Odontoid fracture involving the Tip, rare
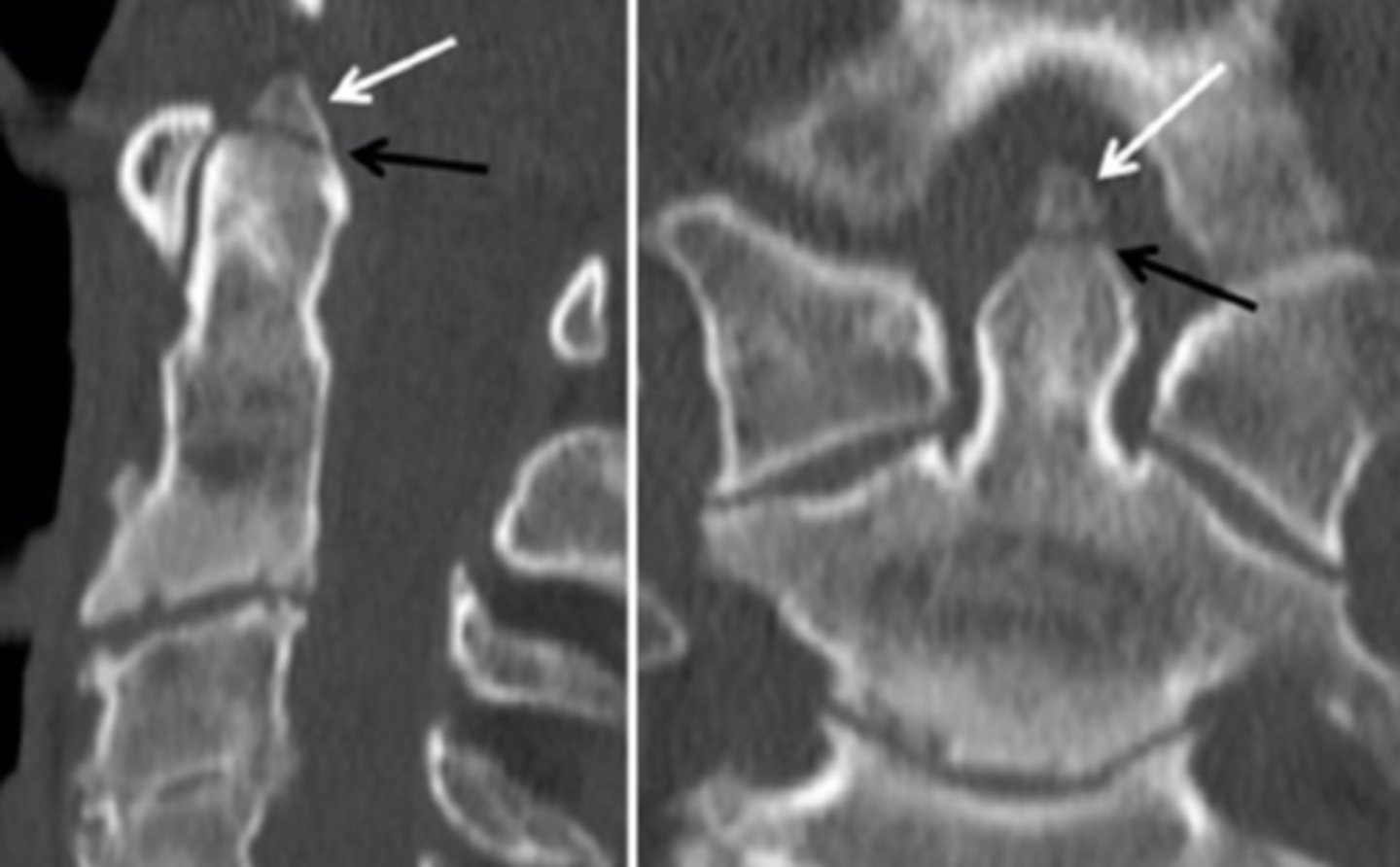
Type II
odontoid fracture involving the body of the odontoid process, most common
Type III
odontoid fracture in which the body of C2 is involved
Type 3 Odontoid fracture
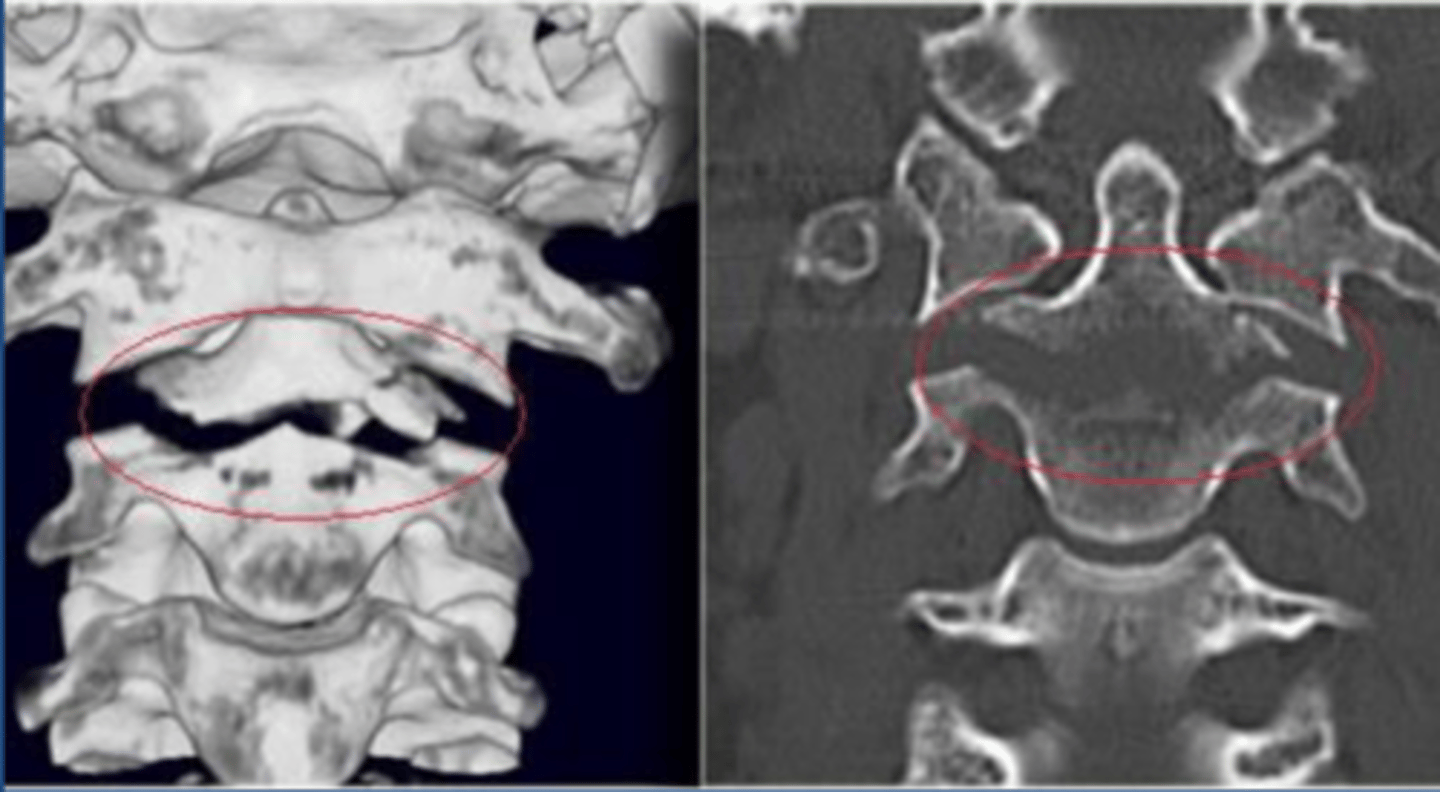
Type 2 Odontoid Fracture
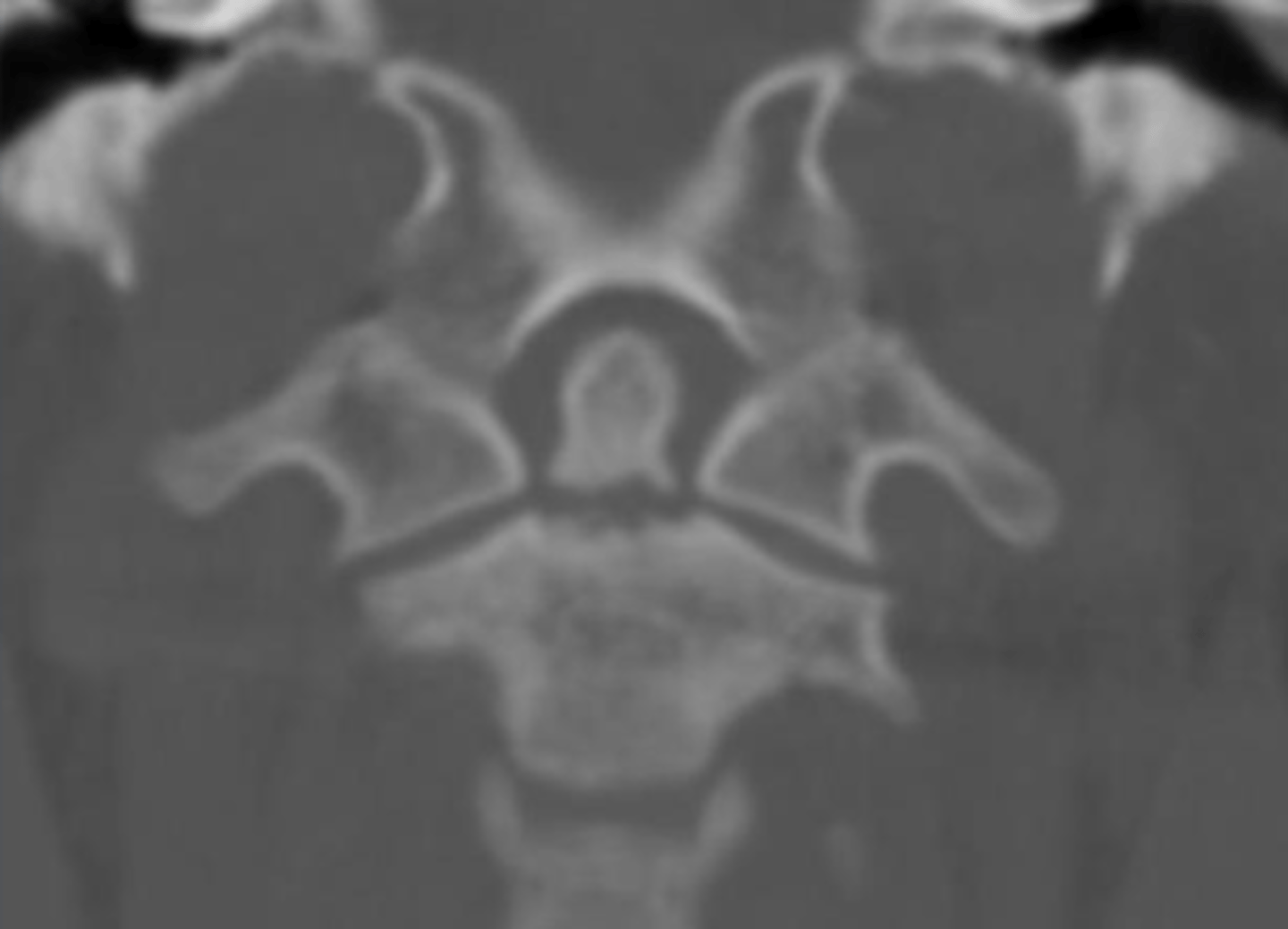
Type I Odontoid Fracture
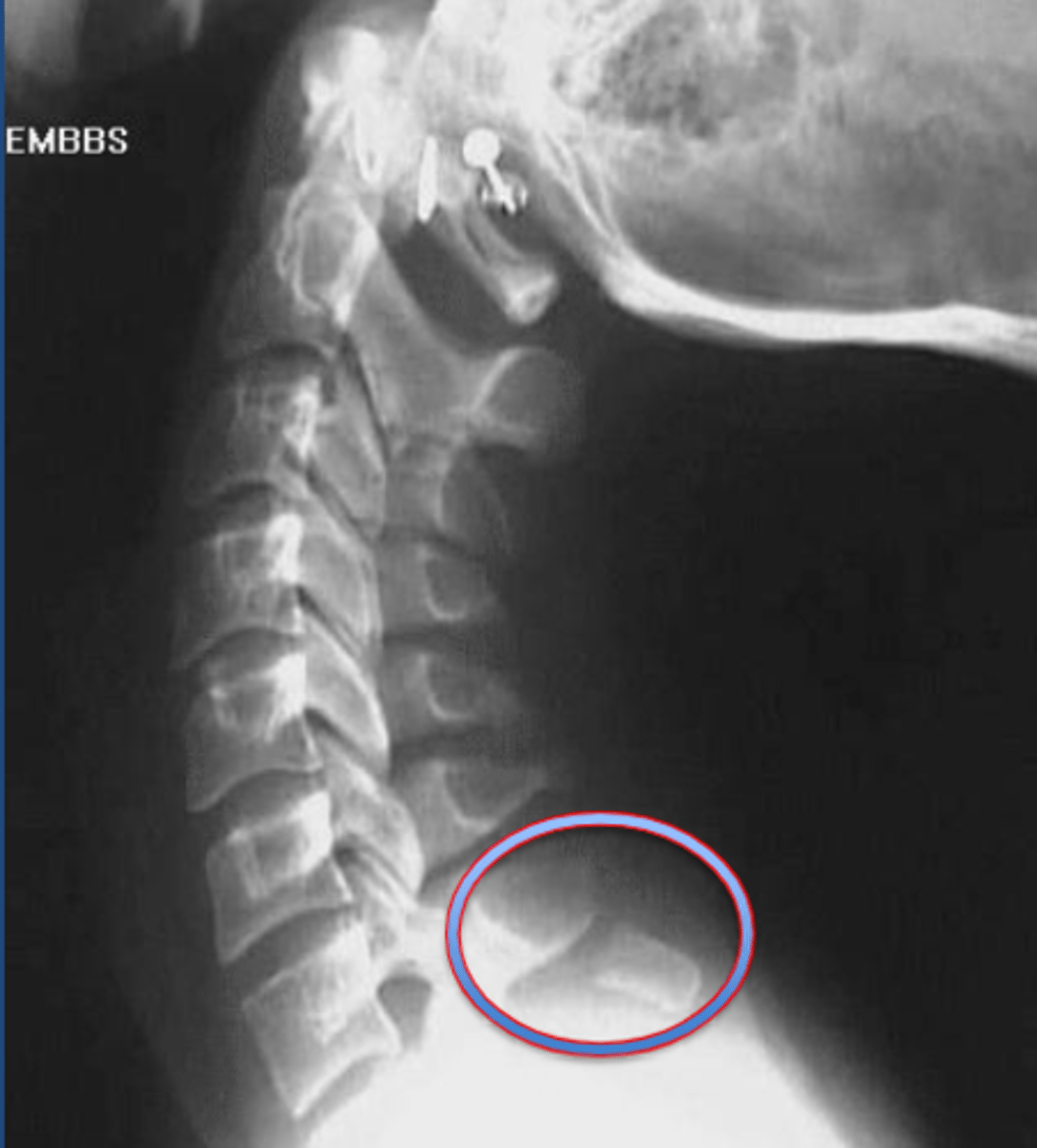
Clay-shovler's fracture
oblique fracture of the spinous processes of the lower C-spine.
C6 or C7
most common spinal level for Clay-shoveler's fracture
Hyperflexion
mechanism of injury for Clay-shoveler's fracture
no
Is Clay Shoveler's fracture typically associated with neuro deficits?
Clay-shoveler's fracture
Axial skeleton
spine, pelvis, skull, ribs
most common location for bony mets
posterior VB
more common area for axial mets ebcause of increased blood supply.
anterior VB
osteoporosis more commonly affects the ____
Mets
Compression of Posterior VB is typically ____
osteoporosis
Compression of anterior VB is typically ____.
compression fracture
______ are common due to bony destruction from Mets
osteolytic or osteoblastic
metastatic lesions can be...
osteoblastic
metastatic lesions that are more dense
Prostate
Osteoblastic lesions are related to mets from _____ CA
Osteolytic
metastatic lesions that are less dense
lung
Osteolytic lesions are related to primary Cancer in the ____