Microbiology Lab practical: Rapid Microbial Testing & Identification for Gram Positive organisms
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is source specificity?
Refers to what gives the test its ability to detect a specific pathogen or antigen and NOT interact with others
Source Specificity in Rapid Strep
This test detects Group A streptococcus pyogenes
Specificity comes from antibodies on the test strip that bind to Group A carbohydrate antigen present on the bacterial cell well
Source Specificity in Rapid Staph
Identifies staphylococcus aureus
Specificity comes from detection of Protein A and/ or clumping factor (coagulase)
This interactions cause visible agglutination if S. aureus is present (positive result)
Rapid Strep testing process
Tests for presence of Streptococcus pyogenes
Reagents are drops on swab in a tube then a strip is placed in the solution
The flow of the reagent and bacteria solution flow upwards 1st hitting the test line, then the control line
Both lines have to be red for the rapid test to positive
One line on either= negative
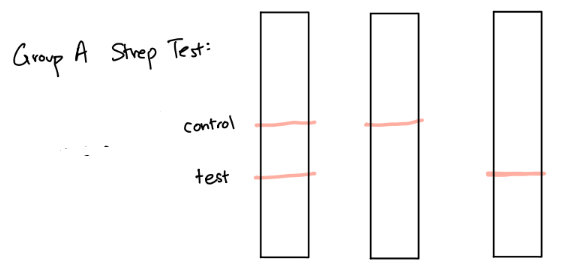
What’s going on here?
1st strip is positive because BOTH the test and control line are red
2nd strip is negative because their is only one red line at the control
3rd strip is invalid because there is a missing control line
Rapid Staph testing process
Tests for presence of Staphylococcus aureus
Identifies Protein A & coagulase
1 drop of Test latex on BOTH circles (sample and (-) control circle’s)
1 drop of (-) control on the control circle
Add culture to sample circle and mix to see results
Agglutination @ Sample circle= POSITIVE
If there is agglutination on the negative control circle, the test is INVALID
Negative control circle should NEVER have agglutination!!!!
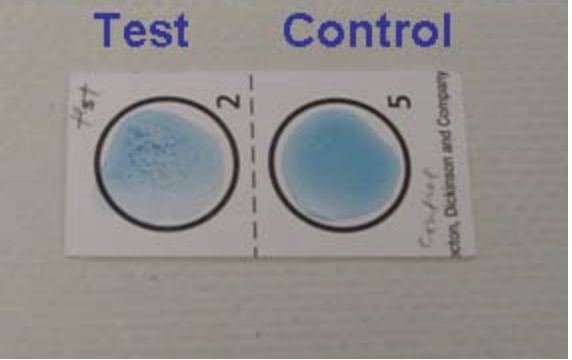
What does this image mean?
The rapid staph test is Positive because there is agglutination on the sample/ test circle
Positive for Staphylococcus aureus
Catalase Test
This test helps identify if the organism will liberate Oxygen gas or not (bubbling or not)
Converts hydrogen peroxide to O2 and H2O
Positive= bubbling occurs→ continue with catalase (+) tests
Negative= NO bubbling occurs→ continue with catalase (-) tests
What tests do the Catalase positive bacteria go through?
Novobiocin Sensitivity and Growth characteristics of MH agar
DNAse agar
MSA agar
PYR test
What tests do the Catalase negative bacteria go through?
Sensitivity to the antibiotic Bactrim (SXT) and hemolysis (Blood agar and disc)
Esculin Hydrolysis in the presence of bile (BEA Slant)
PYR(Broth) test
Novobiocin Sensitivity (Growth characteristics) of MH agar
Swab culture and put onto the MH plate (one side of plate filled with culture & other side do the streak method)
Put an antibiotic disc on the “streaked” slide
Bacteria growing closer to the disc= Resistant to Novobiocin; larger zone of inhibition
Bacteria growing away from disc= Sensitive to Novobiocin
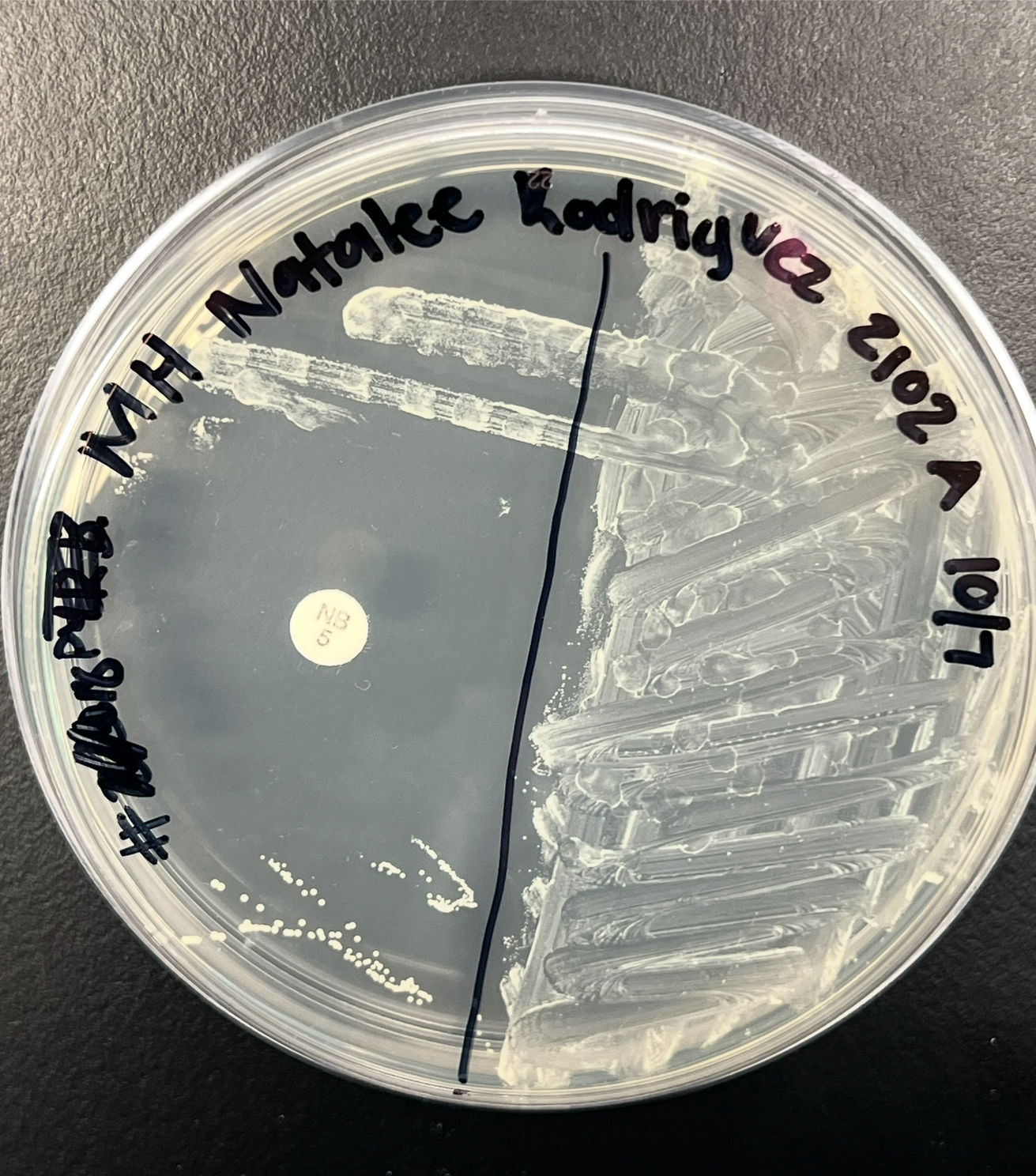
What is going on here?
Novobiocin Sensitivity: An antibiotic disc is place here to see if the bacteria is susceptible or resistant to the disc
There’s a large zone of inhibition
Growth away from disc
Result= Resistant
DNAse agar
This plate differentiates b/w organisms ability to secrete exoenzyme DNAse
Positive result= clear zone and does contain the exoenzyme DNAse
Negative result= no clear zone and bacteria doesn’t contail DNAse
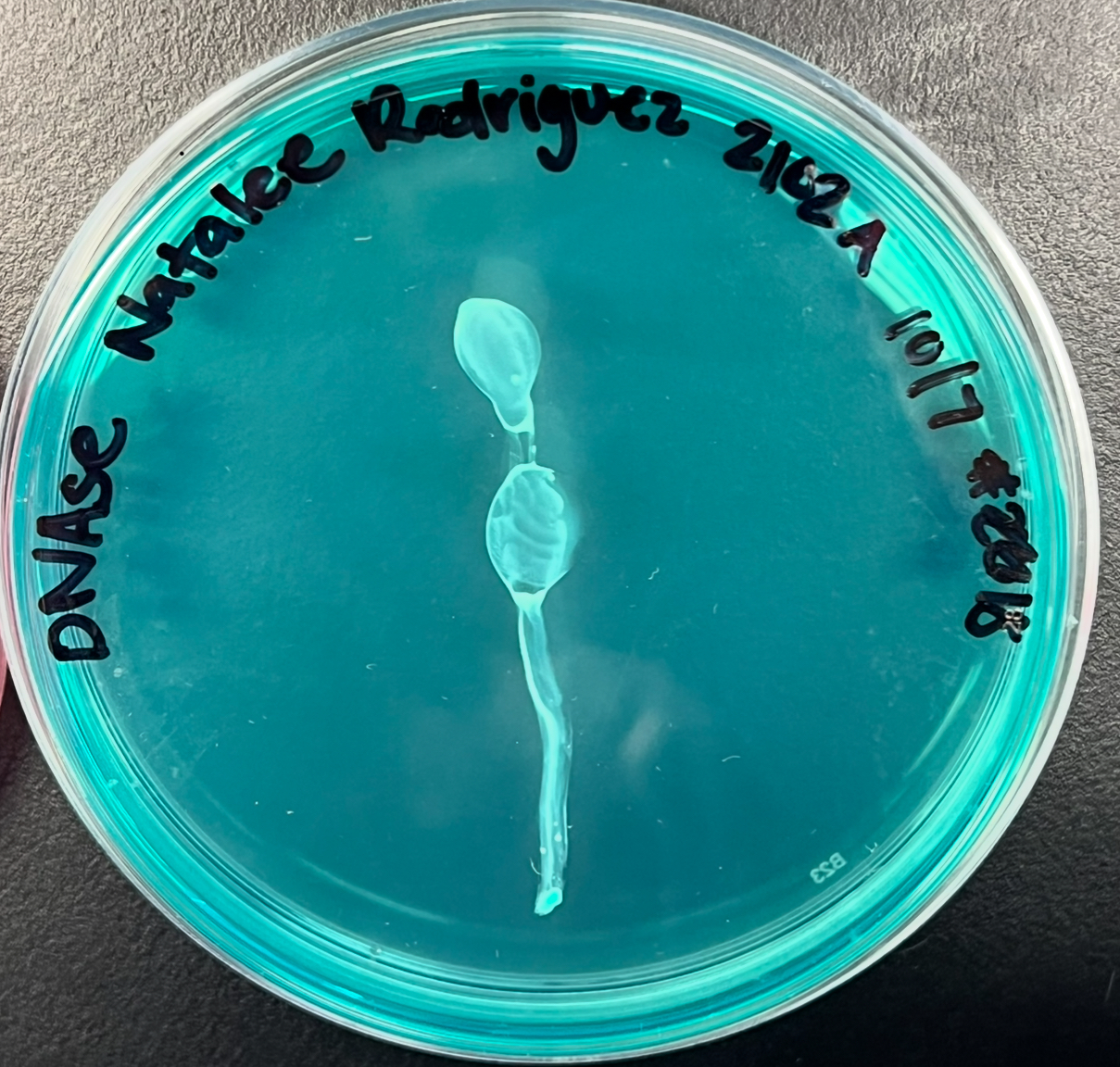
What does this mean?
There is no zone of clearance therefore this organism does NOT secrete the exoenzyme DNAse= NEGATIVE
MSA agar
Selective for halotolerant organisms (media contains 7.5% NaCl)
Differential is organisms can ferment mannitol or not
Yellow color change= organism can ferment mannitol (a type of carbohydrate substrate) LOWer pH
No color change= bacteria is a non-mannitol fermenter (takes on color of media)
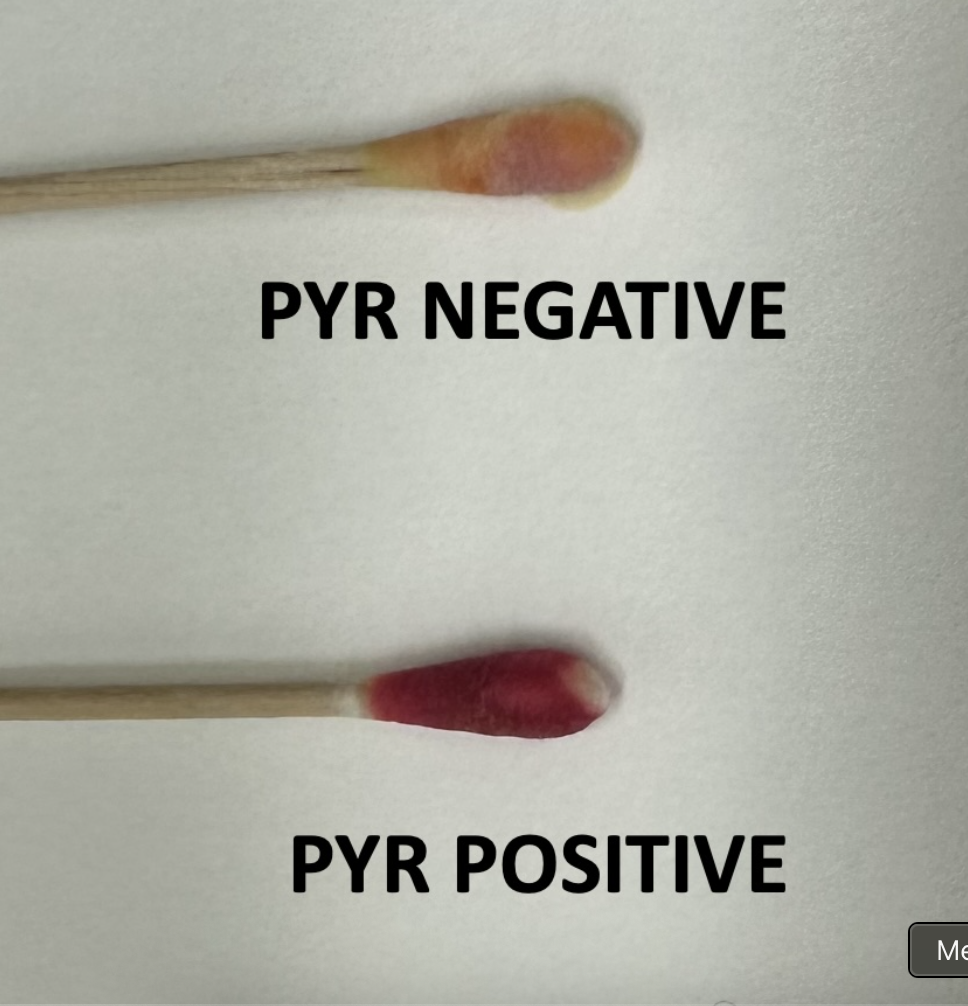
PYR test
Checks to see whether bacteria produce the enzyme pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYRase) by dropping the PYR reagent onto the swab with the culture
Red/pink= contains the PRYase enzyme
Yellow= Doesn’t contain the PYRase enzyme
SXT sensitivity and hemolysis
Only done if the catalase test was negative
is bacteria sensitivity to the antibiotic Bactrium (SXT)?
Blood agar is used here (enriched and differential among streptococcus species)
Types of hemolysis
S or R
BEA slant
Selective and differential medium
Can organism hydrolyze carbohydrate esculin
Positive for esculin hydrolysis= black color within slant (more than 50%)
Negative=less than 50% of slant is back, or there’s no black
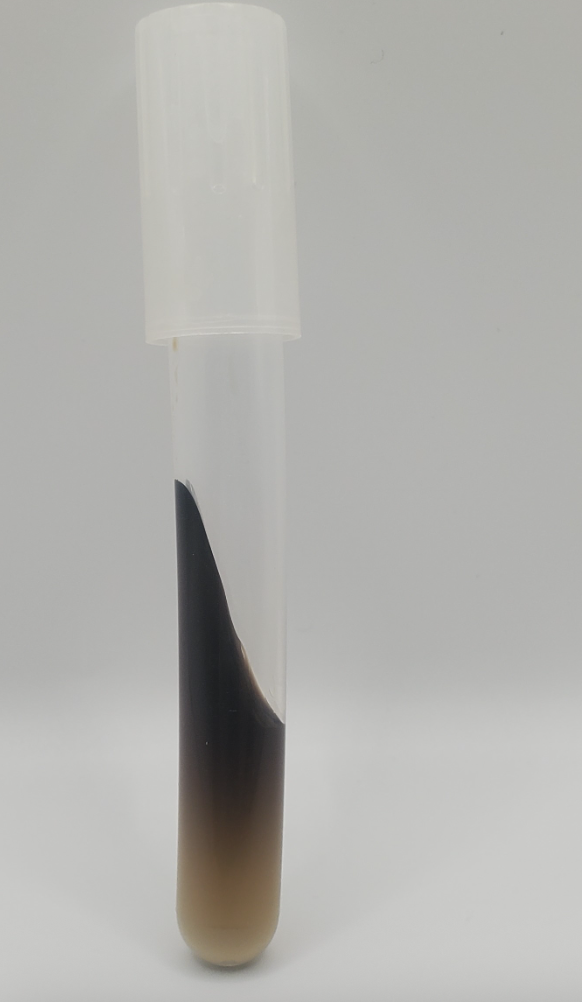

What does this slant mean?
This is a BEA slant
Black color= able to hydrolyze esculin
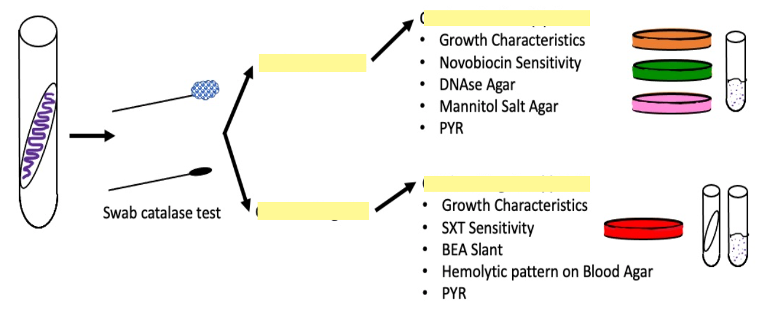
What are the blanks?
Positive or Negative for Catalase test
Positive for catalase test is the top
Negative or Catalase test is the bottom