AP Psychology: Topic 3.6 - Social-Emotional Development Across the Lifespan
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
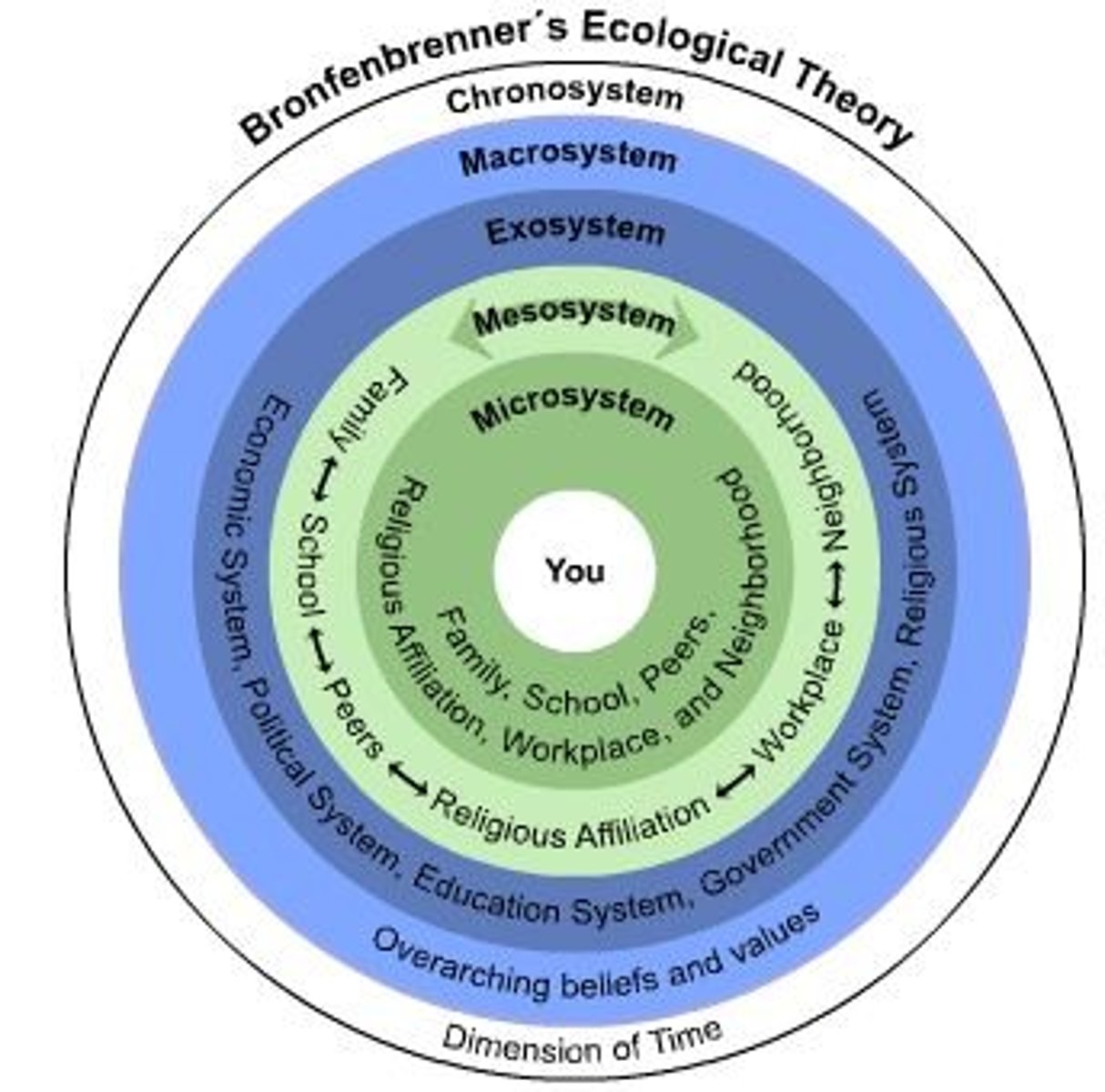
Ecological systems theory
holds that people encounter different environments throughout their lifespan that may influence behavior in varying degrees
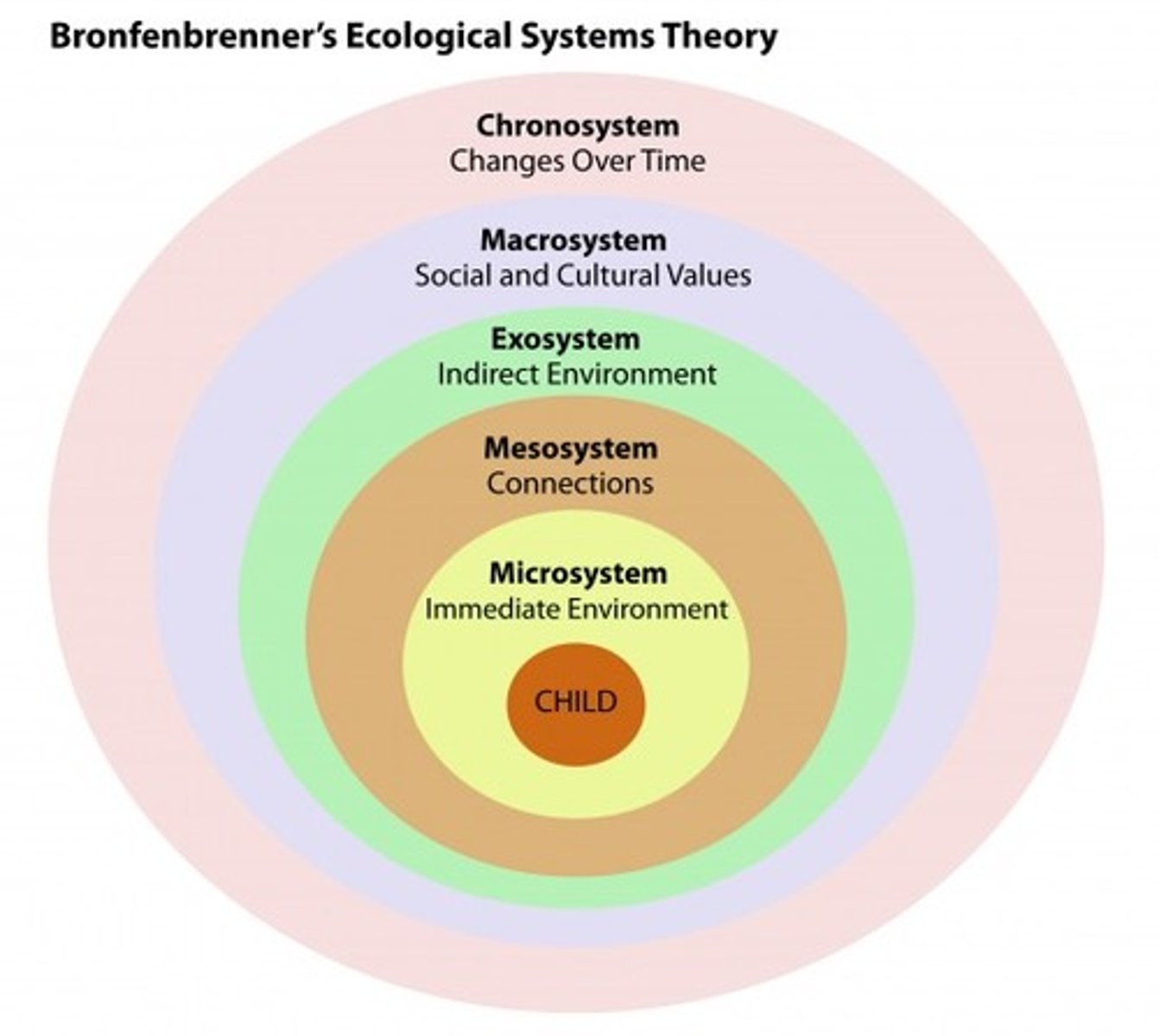
Microsystem
an individual's immediate environment which includes the people the person interacts with daily, having the most direct, immediate impact on the individual
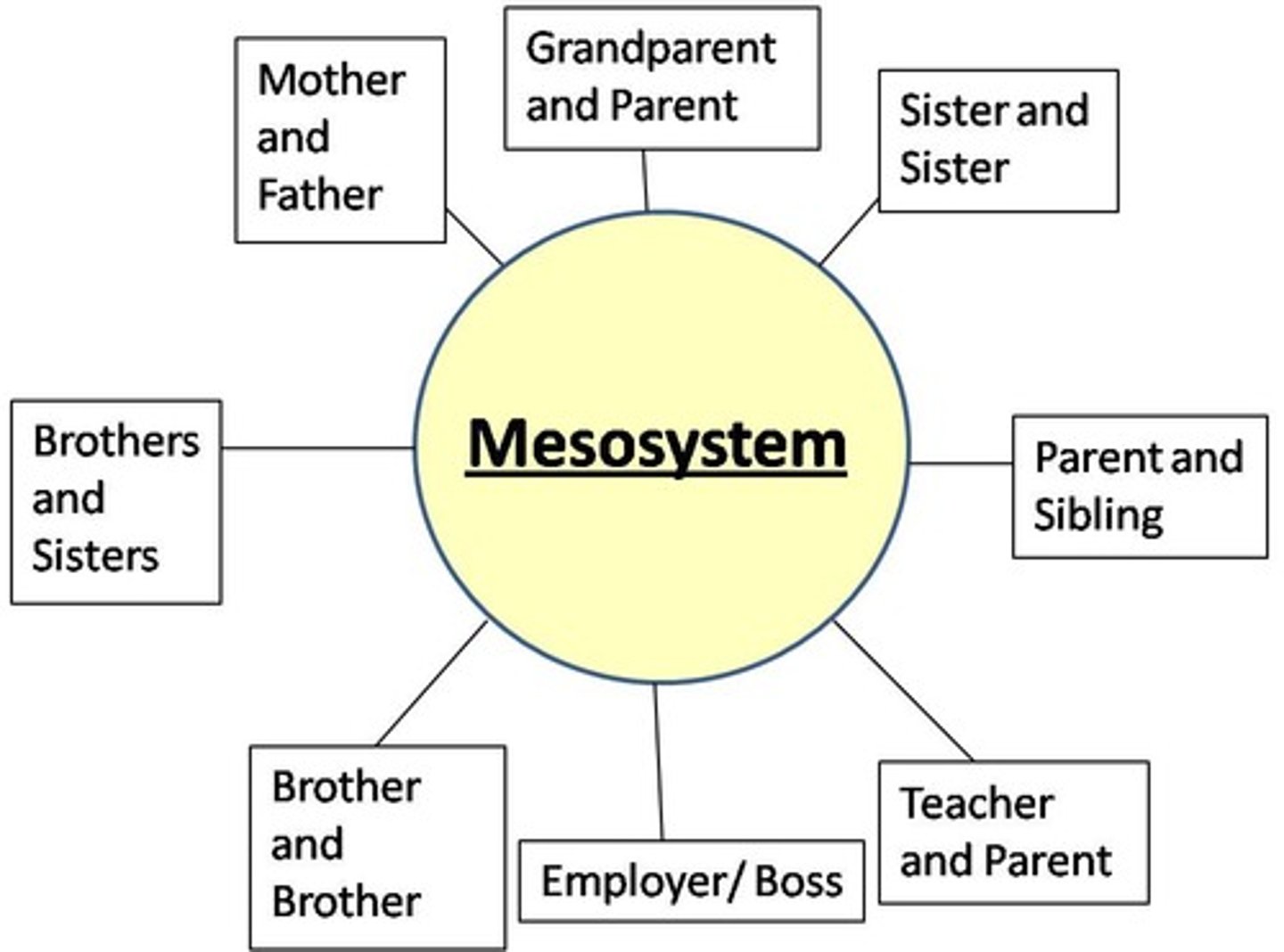
Mesosystem
a connection of two or more microsystems, such as a child's home and school
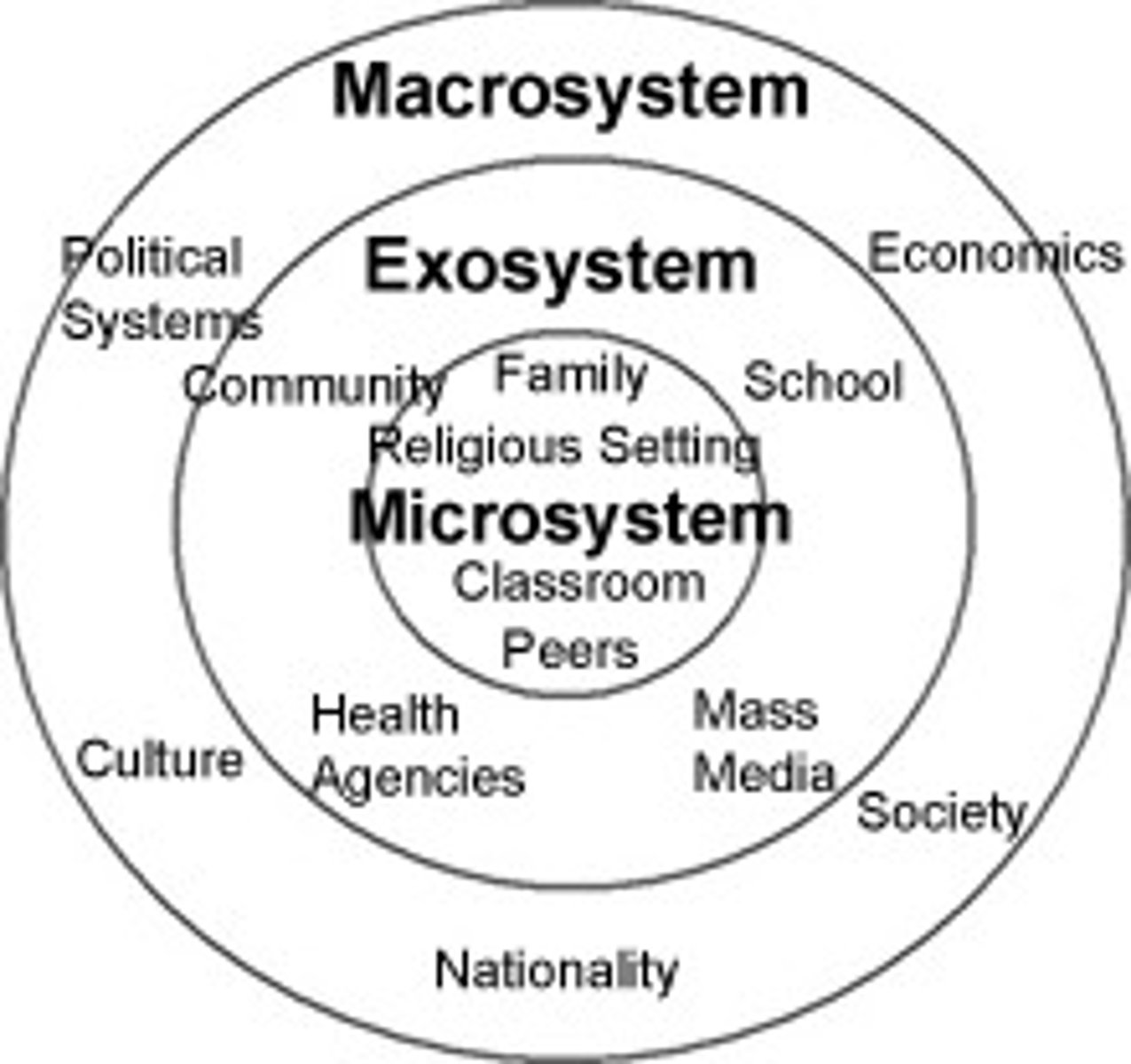
Exosystem
environments in which an individual is not an active participant, yet these still impact the person's development (e.g., mass media or government policies)
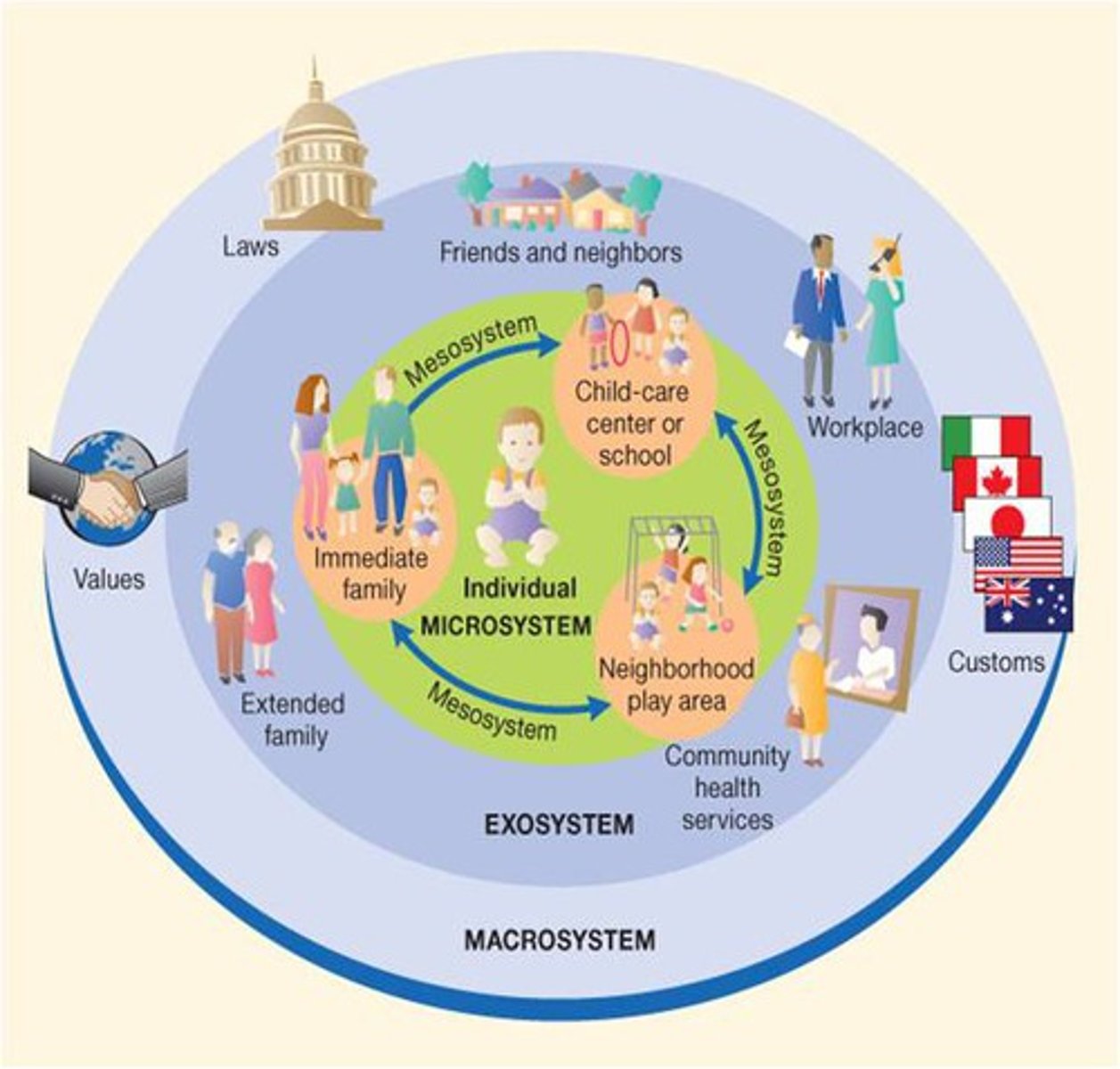
Macrosystem
the collection of broad systems that surround an individual such as cultural values, laws, and social customs
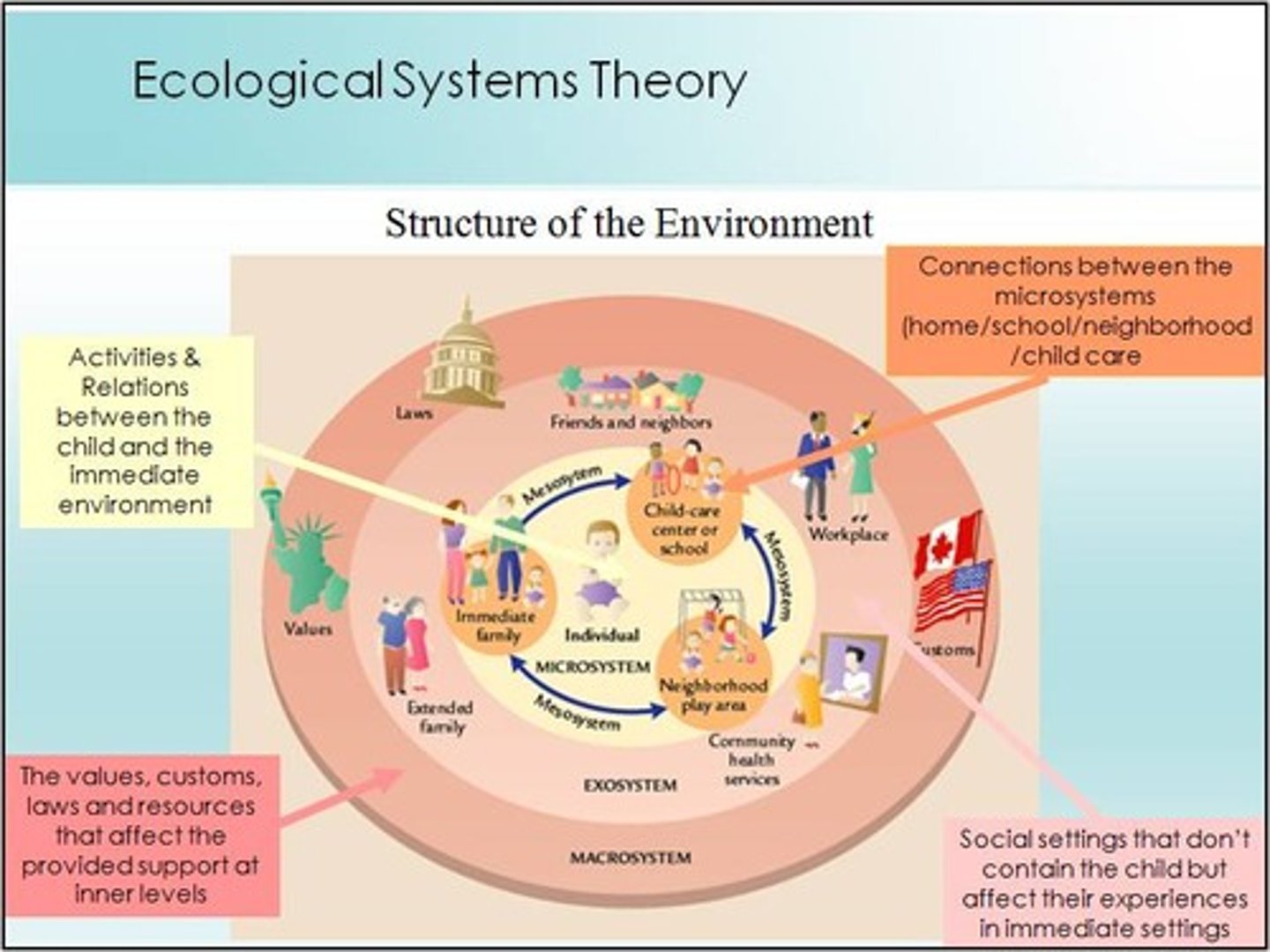
Chronosystem
all of the experiences a person has had during their lifetime, including environmental events, major life transitions, and historical events
Authoritarian parenting
a style of parenting in which a parent is rigid and overly strict, showing little warmth to the child
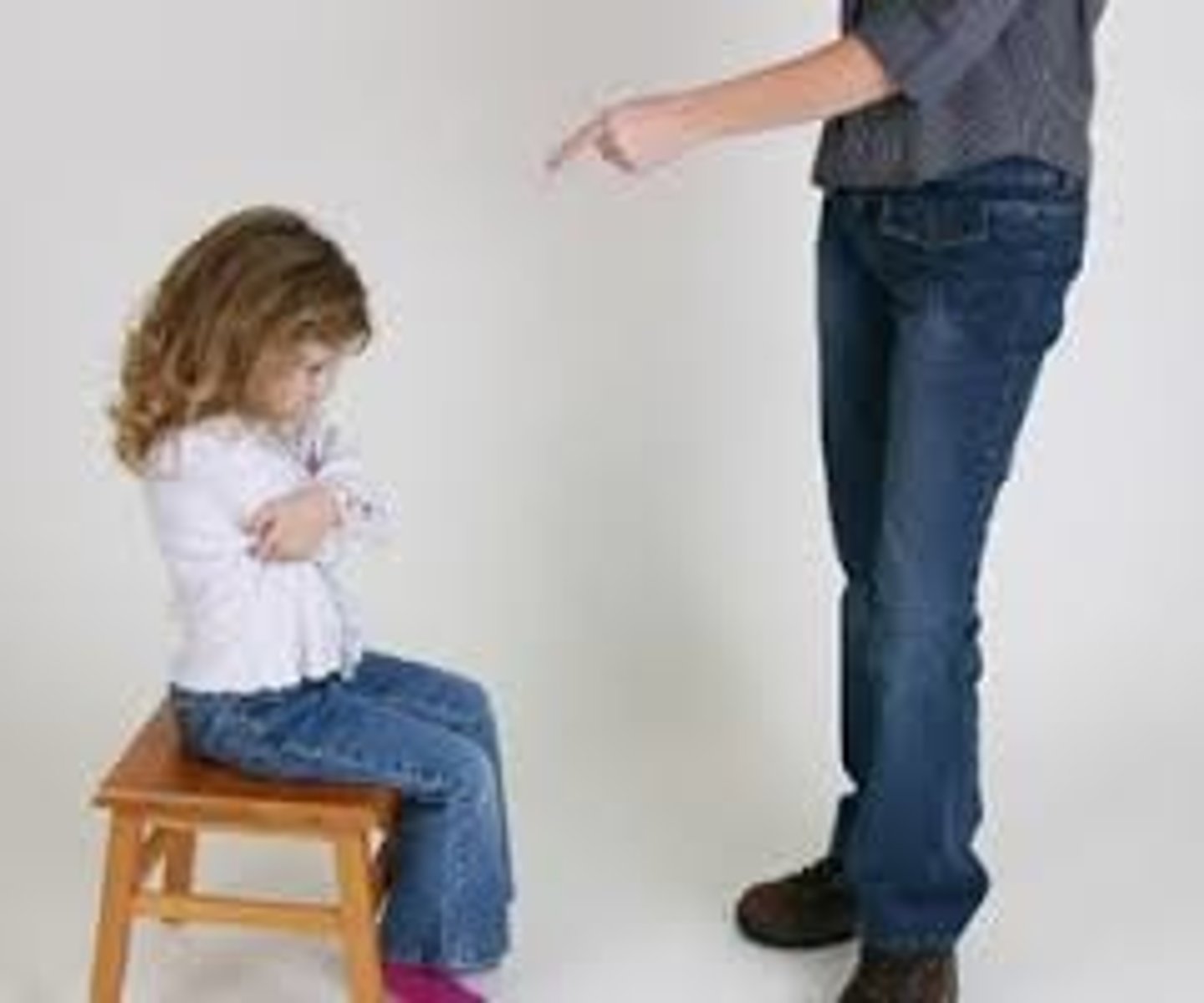

Authoritative parenting
a style of parenting characterized by emotional warmth, high standards for behavior, explanation and consistent enforcement of rules, and inclusion of children in decision making
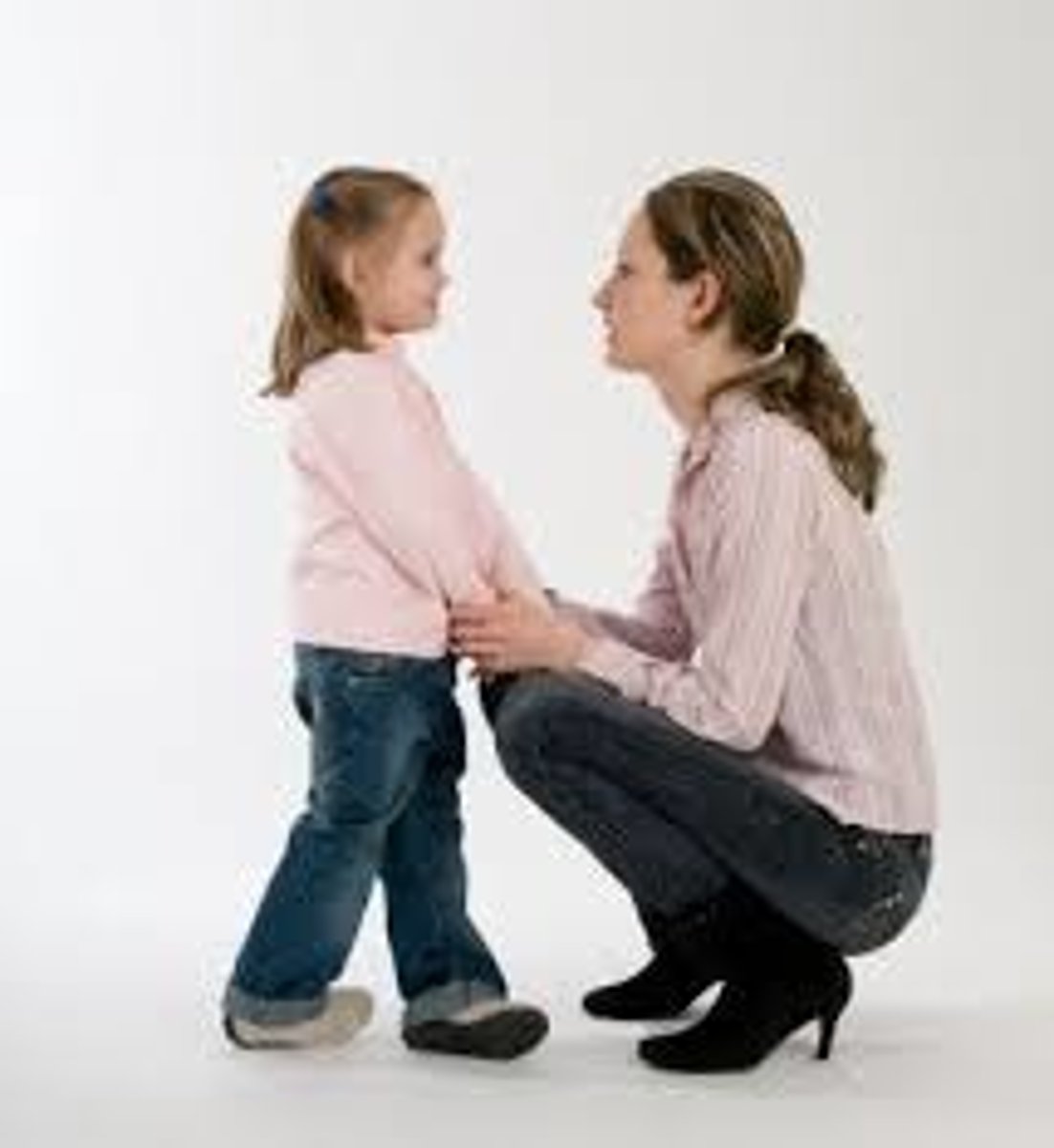

Permissive parenting
a style of parenting in which few, if any, demands are made on a child's behavior

Attachment styles
a theory about the early bonds between infants and their parents/caregivers with the idea that babies need to form a close relationship with at least one primary caregiver to ensure their survival
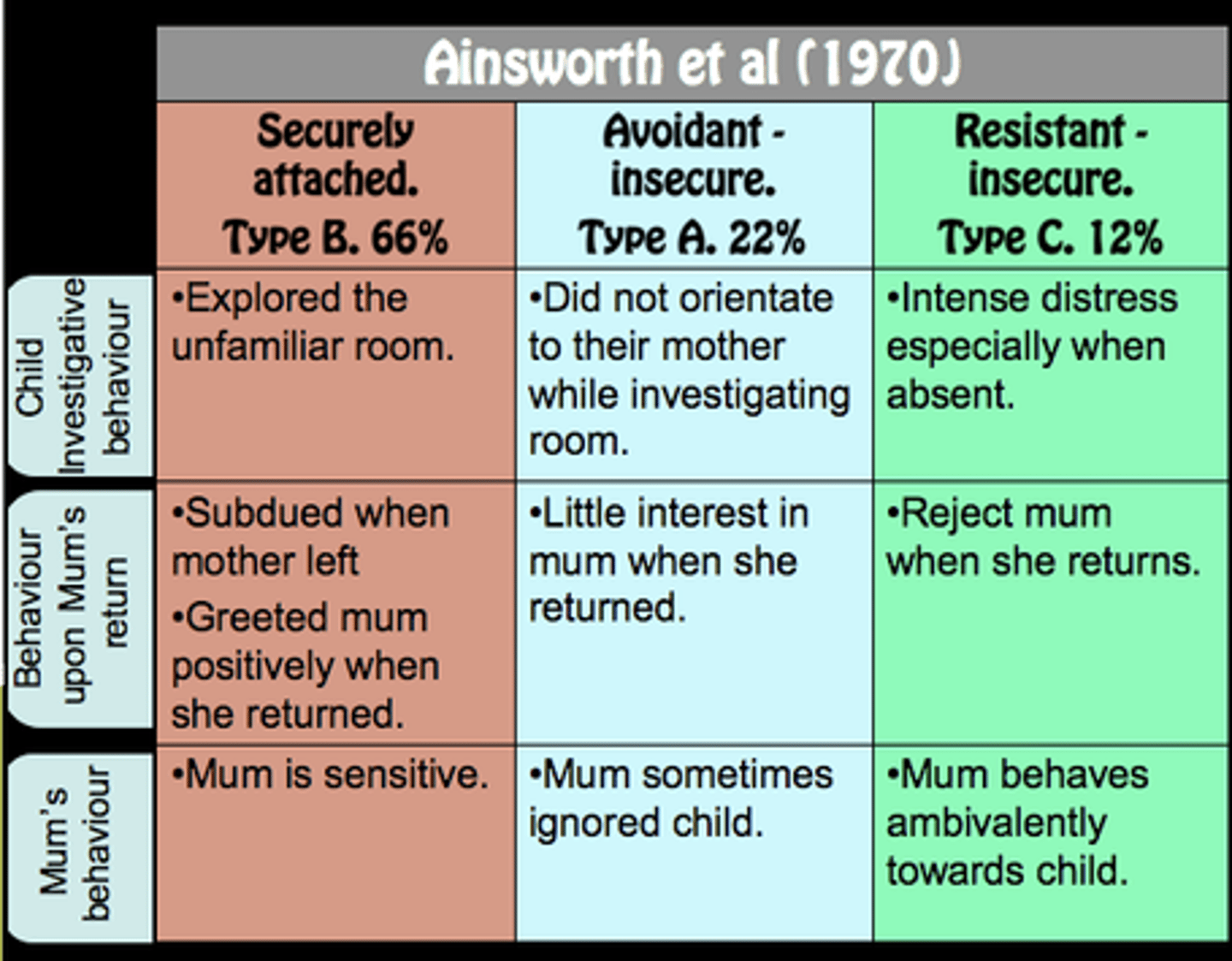
Secure attachment
a relationship in which an infant obtains both comfort and confidence from the presence of his or her caregiver

Insecure attachment
characterized by lack of trust, such as avoiding contact with the caregiver, or by alternating between approach and avoidance behaviors; results from trauma, neglect, or abuse

Avoidant attachment
characterized by physical and emotional independence from a caregiver; results from a caregiver who does not show nurturing other than providing necessities such as food and shelter

Anxious attachment
characterized by insecurity, fear of abandonment, and mistrust; results from a caregiver who fails to give attention and show affection in a dependable way

Disorganized attachment
characterized by conflicting feelings of wanting to be cared for while simultaneously being intensely afraid of such a relationship; results from a parent who repeatedly causes a state of fear in a child

Separation anxiety
excessive fear or distress about separation from a caregiver

Temperament
an individual's basic emotional style that appears early in development and is largely genetic in origin rather than learned
Parallel play
activity in which children play side by side with similar toys without interacting

Imaginary audience
a common adolescent belief that they are under constant, close observation by peers, family, and even strangers

Personal fable
a common adolescent belief that they are unique, so none of life's dangers or difficulties will affect them regardless of their behavior
Social clock
the cultural timeline set by a society on what should happen at given stages of life (e.g., marriage, parenthood, and retirement)

Emerging adulthood
a period from about age 18 to 25 when adolescents gradually rely less on parents and develop adult level commitments toward romantic relationships and work

Stage theory of psychosocial development
Erikson's theory that personality is shaped in a sequence of eight stages that occur over time and through the influence of other people
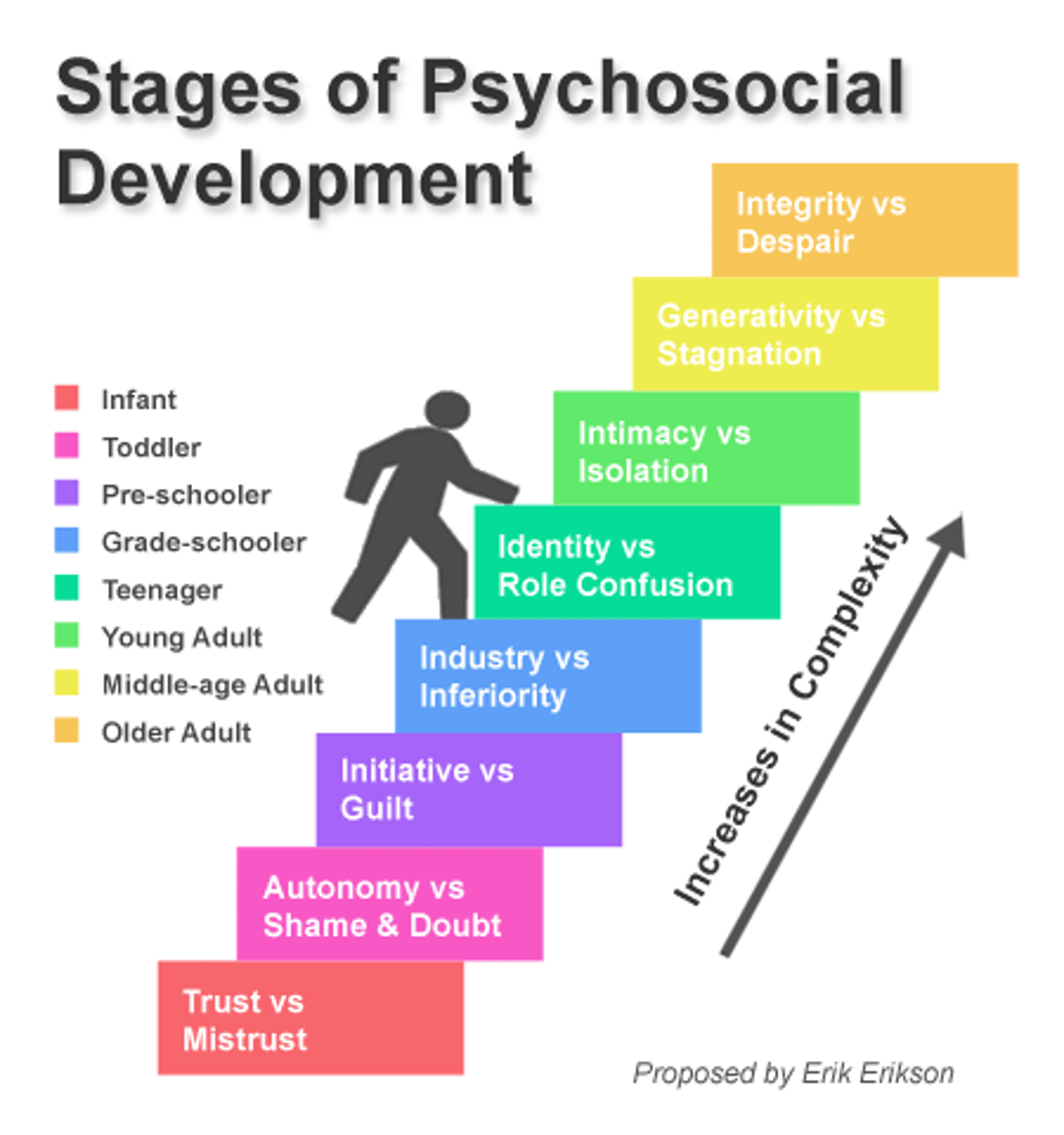
Trust vs. mistrust stage
the period during which infants develop a sense of trust or mistrust, largely depending on how well their needs are met by their caregivers

Autonomy vs. shame & doubt stage
the period during which toddlers develop independence and autonomy if they are allowed the freedom to explore, or shame and self-doubt if they are restricted and overprotected

Initiative vs. guilt stage
the period during which children experience conflict between independent actions and the sometimes negative results of their actions

Industry vs. inferiority stage
the period from age 6 to 12 when children develop confidence in their own efforts and are able to respond to feedback from adults about their efforts

Identity vs. role confusion stage
a period when adolescents explore their independence and develop a sense of self and what makes them unique
Intimacy vs. isolation stage
a period during early adulthood when individuals engage with the challenges of close relationships

Generativity vs. stagnation stage
a time of adulthood when individuals engage with the challenges of making a positive contribution to the world while dealing with being unproductive or lacking a sense of purpose

Integrity vs. despair stage
when older individuals reflect on their life and come away with a sense of fulfillment (a life well-lived) or a sense of regret (a life misspent)

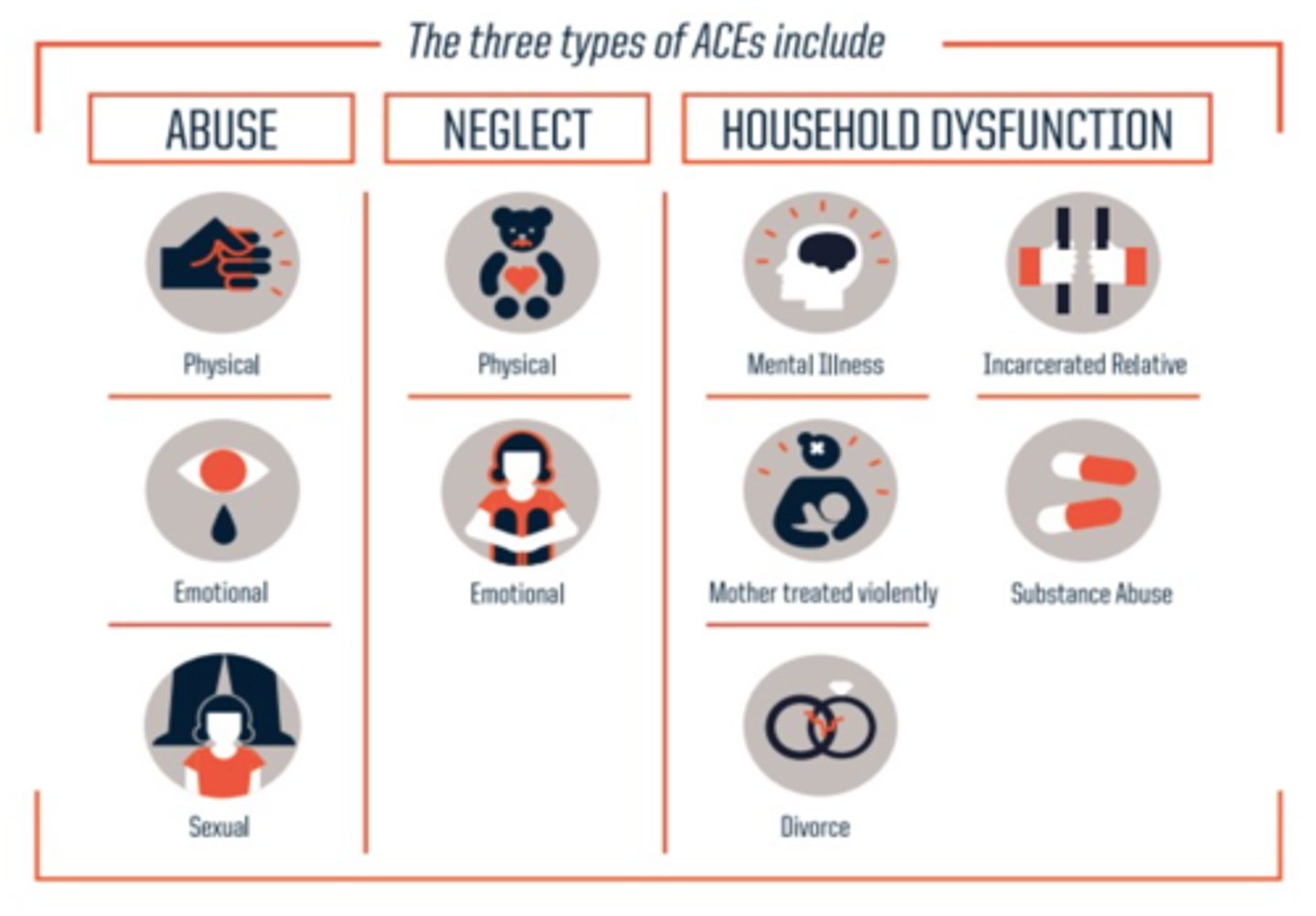
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
traumatic childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, violence exposure, or death of a parent, that are linked to mental and physical health problems later in life
Achievement
the status of adolescents who commit to a particular identity following a period of crisis during which they consider various alternatives
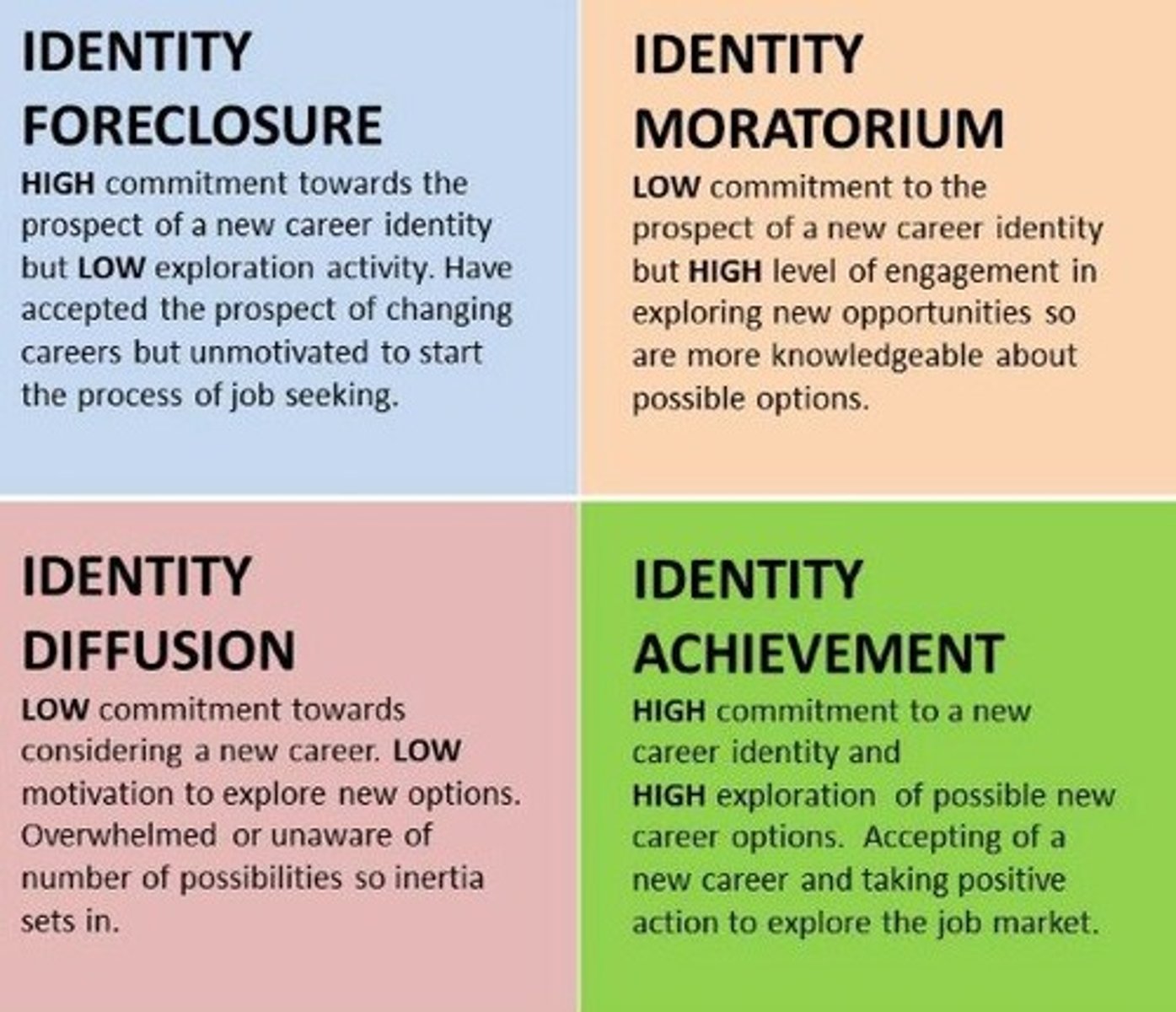
Diffusion
when an adolescent has not yet developed a firm identity, or their identity is in a state of crisis and they haven't committed to a resolution

Foreclosure
when an adolescent has not explored other identities, but is committed to one or more choices
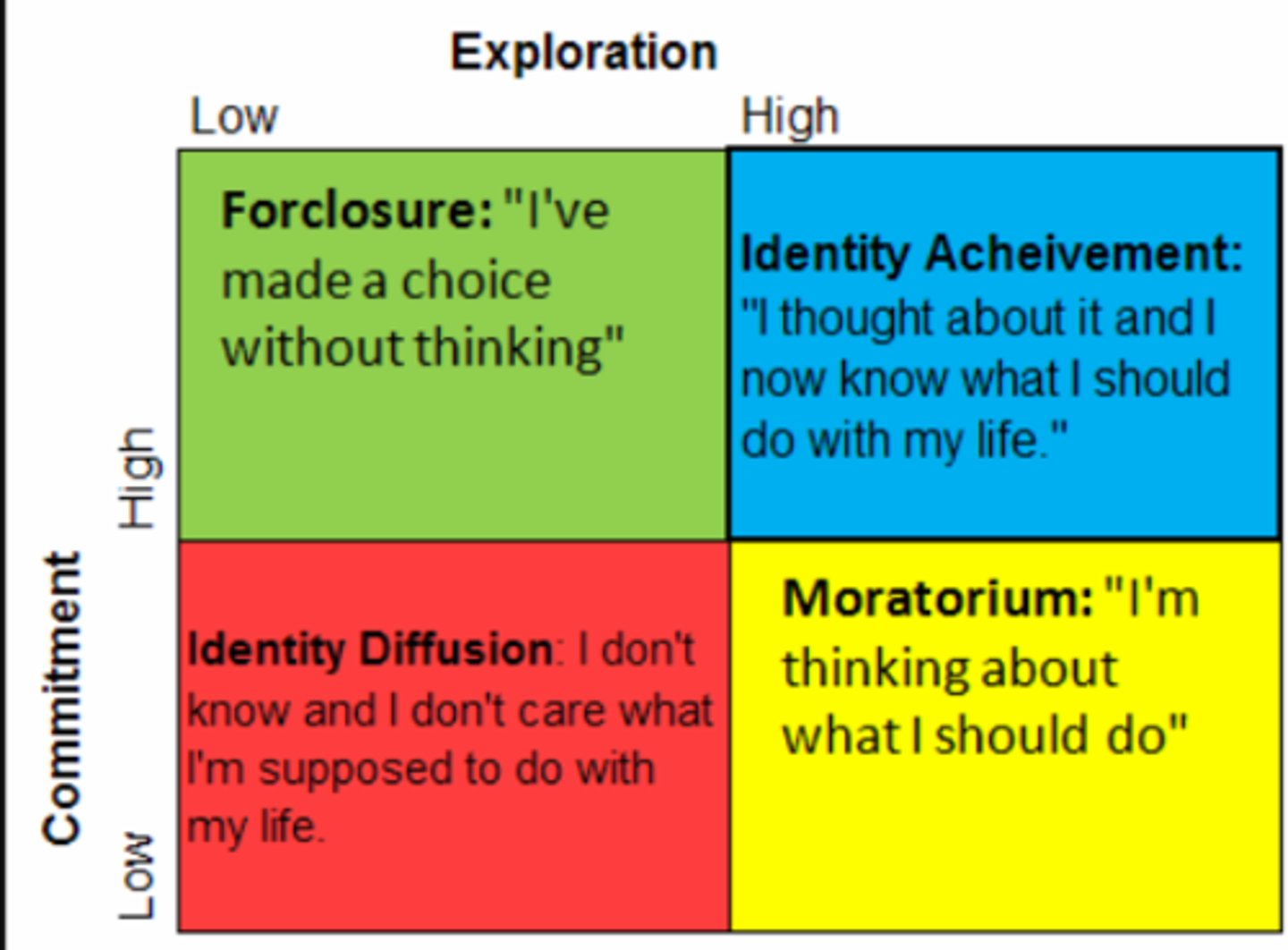
Moratorium
when an adolescent is actively exploring their identity but has yet to make a commitment

Racial/ethnic identity
the sense of membership in a racial or ethnic group and the feelings that are associated with that membership

Sexual orientation
a person's sexual identity in relation to the gender to which they are attracted
Religious identity
the sense of group membership in a religion and the importance of this membership as it pertains to one's self-concept

Occupational identity
the conscious awareness of oneself as a worker and how you feel about your occupation

Familial identity
a sense of group membership in a family and the importance of this group membership as it pertains to one's self-concept

Possible selves
individuals' ideas of what they might become, what they would like to become, and what they are afraid of becoming
