Complete Economic methodology and the economic problem
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Normative statements
Statements that involve a value added judgement
positive statements
Objective statements that can be tested
How to remember positive and normative statements
Positive statements → can be true or false → positive or negative → can be tested
Normative → emotive → value judgement
How is economics similar to a science
Economists write statements, test these and evaluate government intervention
How is economics different to a science
In economics it is hard to test hypothesis in the real world. Whereas scientists can conduct experiments to determine the validity of their assumptions. They also have the ability to control and alter individual variables precisely to establish causality.
Economists cannot replicate the complexity of the world economic system in a controlled environment. Therefore we instead rely on models which focus of the changing of an individual variable by keeping all other variables constant (ceteris paribus assumption).
Economics relies on human nature, which is often unpredictable, so economists can only make predictions rather than positive statements.
Conclusions derived from economic phenomena will change over time, whereas scientific conclusions are more static and repeatable.
How thinking as an economist may differ from other sciences
Economists may have normative goals, whereas scientists do not.
What are peoples views concerning the best option often influenced by
The positive consequences of different decisions and moral and political judgements
ceteris paribus
all other things being equal
another word for free market
laissez-faire
laissez-faire
abstention by governments from interfering in the workings of the free market
People’s views concerning the best option is influenced by
The positive consequences of different decisions
Moral and political judgments
what is the “central purpose of economic activity“
the production of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants
What are the key economic descisions
What to produce?
How to produce?
Who is to benifit from the goods and services produce?
Key economic descions short form
What/How/For whom to produce
needs
anything required for human survival eg food. water, shelter
wants
anything that someone desires or would like to have
economic reasorces acronym
CELL
economic resources
capital, enterprise, land and labour
capital
a man made resource used in the production of a good or service
examples of capital
tractor, machineary, tools
Factors of production are _____ to produce ….
inputs to produce the output of goods and services
the environment is a _______ resource
scarce
which FoP are environmental reasources a part of
Land
renewable resources are
resources that will replenish faster than depleted
Human capital
The value human labour brings to the production process
productive efficiency is a point
anywhere on the PPF curve
allocativly efficient
a specific point on the PPF
If a point is _____ efficient then it must be ______
If a point is allocatively efficient then it must be productively efficient
why is the ppf curved
The law of diminishing returns
as you increase units of one resource and keep other factors constant the marginal benefit from the extra units will eventually start to decline in the short run
how does the ppf show opportunity cost
For points on the curve to produce more of good y the opportunity cost is good x (in the photo opportunity cost of A to B is 50 units of good x)
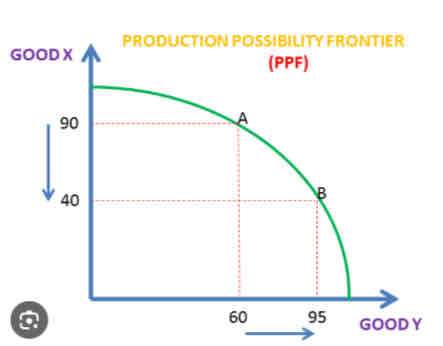
how does the ppf show unemployment of economic reasources
Any point inside the ppf as there is spare capacity
how does the ppf show economic growth
Outward shift because the productive capacity of the economy has increased
what is on the y axis of a ppf
consumer goods/good y
what is on the x axis of a ppf
capital goods/good x
what does a point outside the ppf curve show
unabtainable
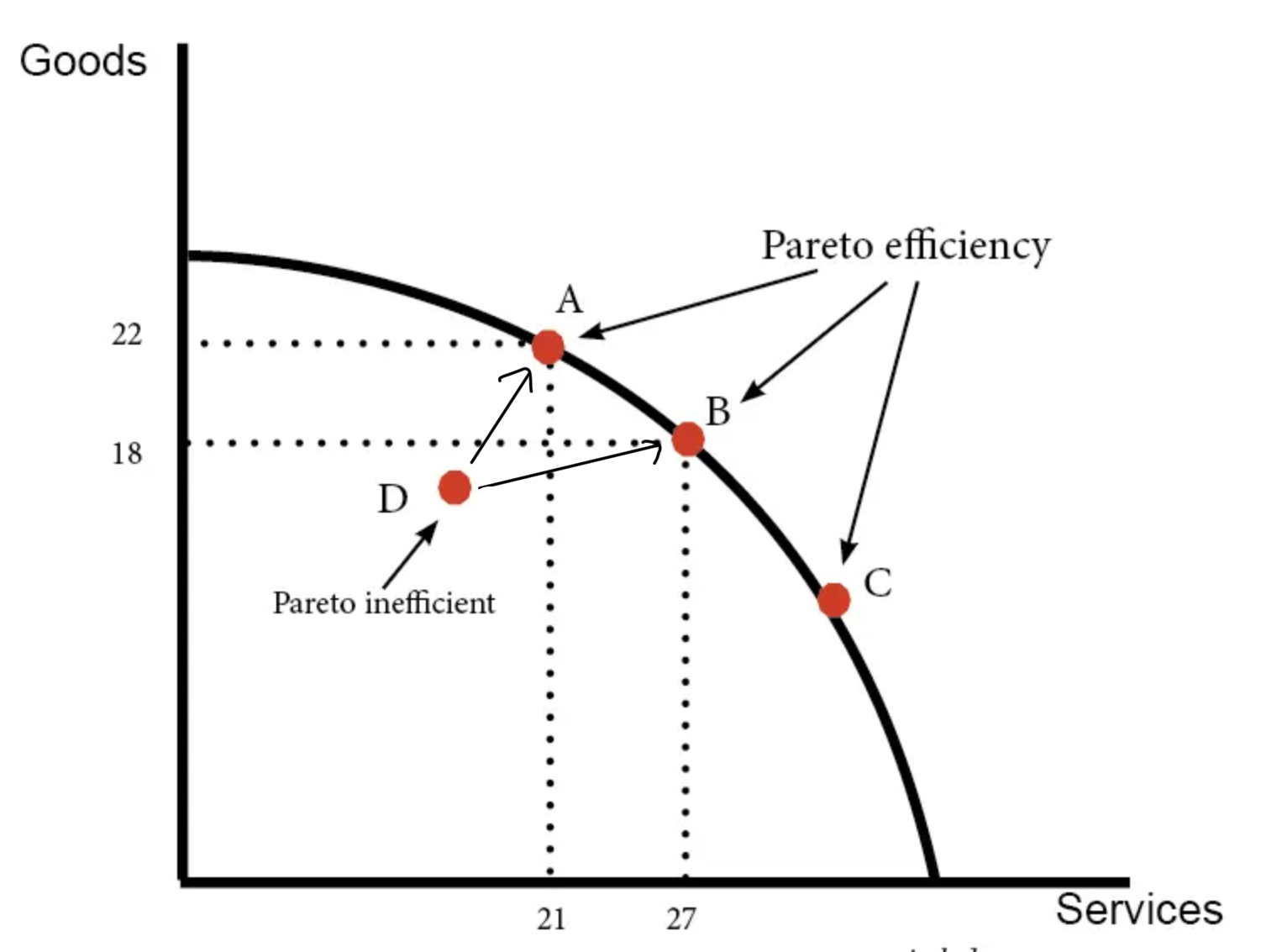
pareto efficiency is where on the ppf diagram
any point that lies on the production posibility curve and for example it is not possible to increase the quantity of consumer goods without sacrificing capital goods
What is a Pareto improvement
A change in output where no one is worse off (D to A or B)
what is the economic problem
scarcity resulting from limited resources to satisfy unlimited wants
scarcity means that
Choices have to be made about how scarce resources are allocated between different uses
resources are _____ and wants are ______
limited
unlimited
opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative forgone when a descision is made
In some cases opportunity cost excedes…
The monetary cost/price
Example of where opportunity cost excedes monetary value
Attending university
Opportunity cost = price of university + lost potential earnings
Issues with opportunity cost
1) not all factors have alternatives
2) some alternatives are unknown
3) Agents may lack information on alternatives to assign a monetary value
4) can be difficult to switch some factors to another use