Food Chem Protein Exam
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Proteins role in biological systems
Proteins play a central role in biological systems
Complex biological macromolecules
Made up of 20 different amino acids
Partial double amine bond
3D configurations
4 primary elements
• C (50-55%)
• H (6-7%)
• O (20-23%)
• N (12-19%
• May also contain S, P, Fe, Zn, Cu
Proteins are classified based on:
Source
Structure
Composition & Solubility
Biological Function
Animal vs Plant Proteins
Animal Proteins
Higher quality proteins with all essential amino acids
Least variable component – number of muscle fibers fixed at birth
Plant Proteins
Lower-quality proteins with limited essential acids (Met, Lys, Thr and Trp – one or more)
Food Proteins – those that are easily digestible, nontoxic, nutritionally adequate, functionally usable in food products, available in abundance and agriculturally sustainable
What amino acids are in:
Cereal grains/ millets
rice and soybeans
legumes
nuts
sunflower seeds
green leafy vegetables
Lysine, Threonine
Methionine
Methionine, Tryptophan
Methionine, Lysine, Threonine
Lysine
Methionine
Why are milk, eggs and meat a complete protein?
They have all the essential amino acids
Biological Roles and Relationships
Enzymes
Storage proteins
proteins in grains; casein in milk; ovalbumin in egg white
Structural proteins
collagen, elastin, keratin, proteins in cell membrane and cell wall.
Contractile proteins
Myosin and actin in muscle
Transport proteins
Hemoglobin/oxygen; transferrin/iron; serum albumin/fatty acids
Defense proteins
Antibodies, fibrinogen and thrombin – blood clotting
regulatory proteins
Insulin, growth hormones
ATP - regulates chemical reactions
Toxic proteins
Clostridium botulinum toxin, ricin in plants
Allergens
Proteins are maid of:
Amino Acids
20 for protein construction
9 essential (isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, valine)
Histidine for children
PVT TIM HLL
Stereochemistry of Amino Acids
α-L-amino acids are the most commonly found
L – “Levo” or Left
D – “Dextro” or Right
α- refers to the position of N in relation to the carboxyl group
All naturally occurring amino acids in proteins are of the L-configuration (except glycine, which doesn’t have a stereocenter)
D-amino acid L-amino acid
Chiral= four different functional groups that have two mirror forms
what does alpha mean in alpha amino acid
the amine group is attached directly to the carbon and is next to the carboxyl group
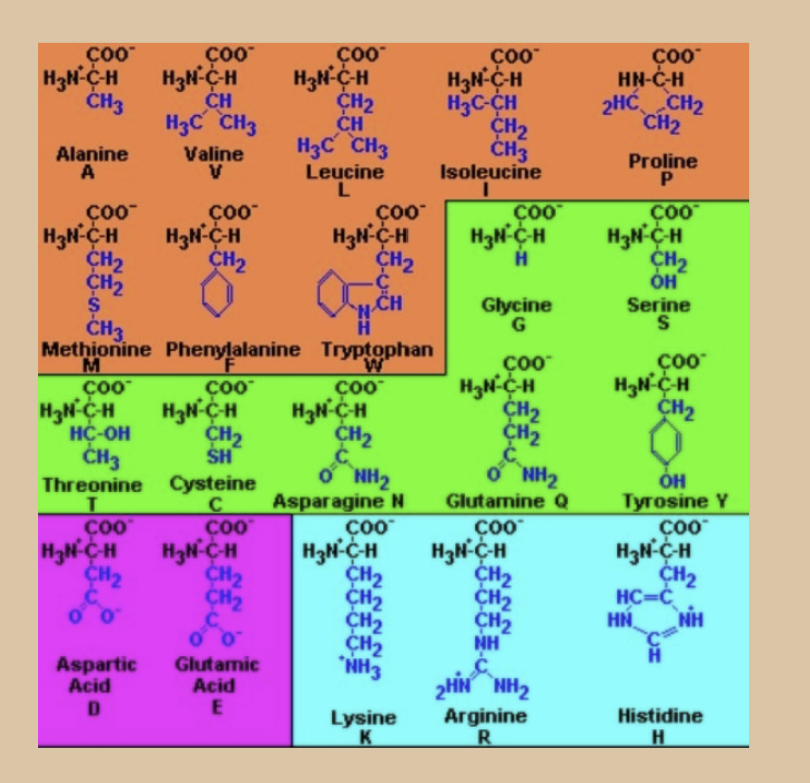
What is the orange group
Orange = Non polar/ hydrophobic
Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine,
Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Methionine,
Proline
• R-Groups contain only C & H
• Except Methionine with S atom
• Normally found inside protein structures, away
from water
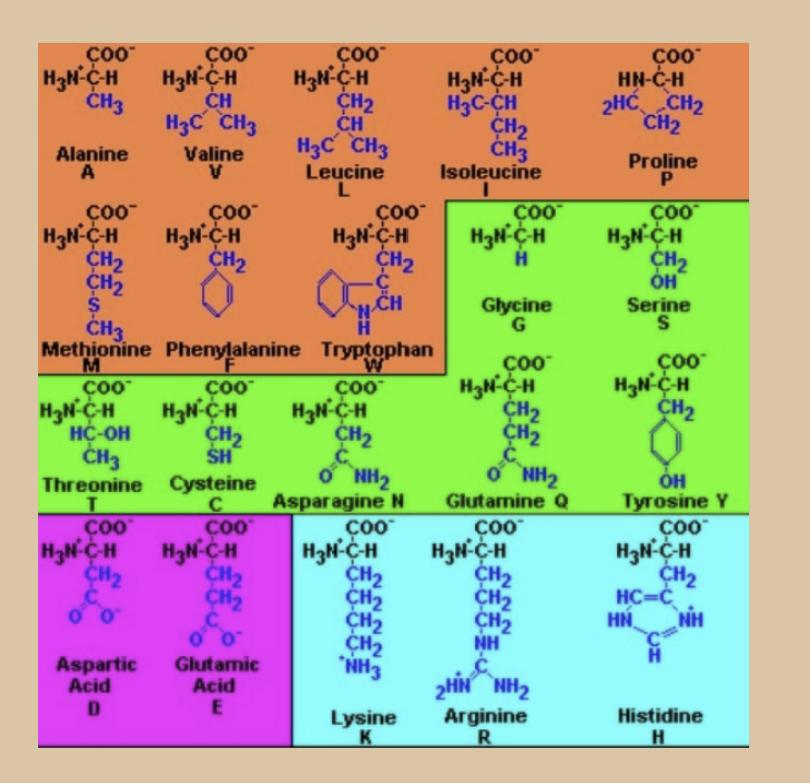
what is the green group?
Polar / Uncharged
Glycine, Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Tyrosine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Have groups with O and N which can participate in hydrogen bonding - as proton donors or acceptors
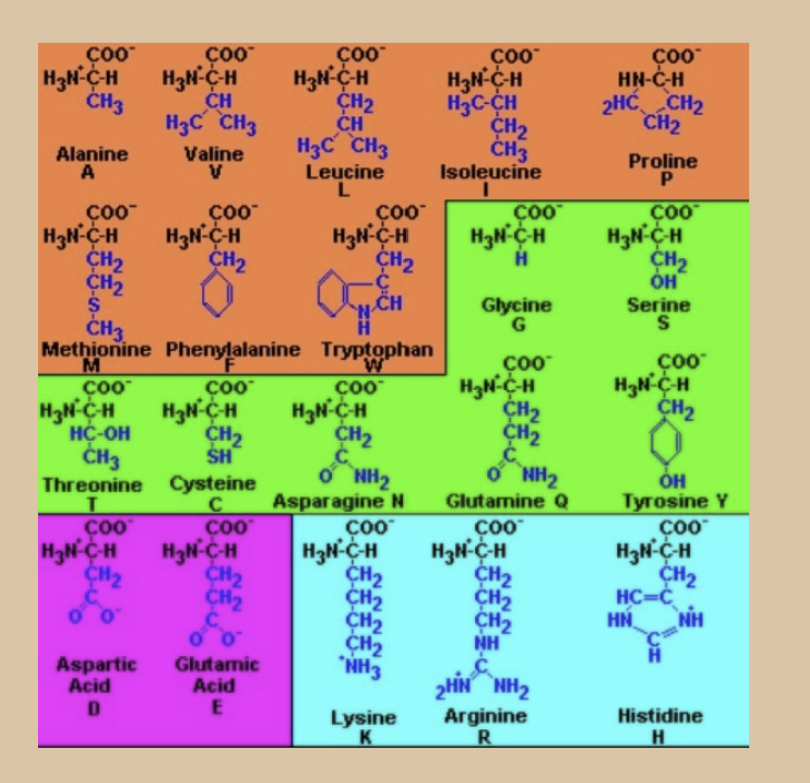
what is blue and purple?
Polar / (+) or (-) charged
(+): Lysine, Arginine, Histidine — blue
(-): Aspartic Acid, Glutamic Acid — purple
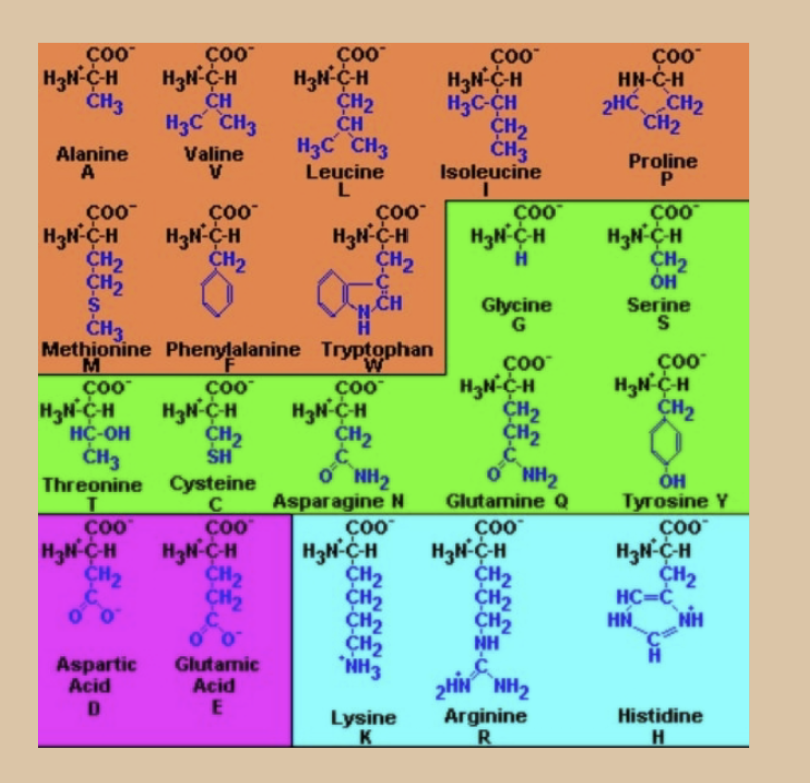
Groups for each
Aliphatic hydrocarbons: glycine, alanine, valine, isoleucine, leucine, proline
R-containing aromatic ring : phenylalanine, tryptophan,
tyrosineR-containing aliphatic –OH group: serine, threonine
R-containing amide group (-CO-NH2): asparagine, glutamine
Sulfur containing: cysteine, methionine
Acid group (-COOH): aspartic acid, glutamic acid
Basic group (-NH2): arginine, lysine , histidine
Four levels of protein structure
Primary
.Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
• Classification of proteins is based on tertiary structure
Primary Structure
Single strands of ordered amino acids bonded by peptide bonds
Peptide Bonds: α-carboxylic (1st AA) joined to α-amino group (2nd AA)
“Amine Bond”
The chain length and sequence act as the code for formation of secondary and tertiary structures
Also determines protein physiochemical, structural and biological functionality of the protei
Secondary Structure
Strands fold on each other to form:
• α-helices:
• β-sheets:
• Stabilized by hydrogen bonds in the peptide backbone
Tertiary Structure
Helices and sheets further fold on themselves through disulfide
bonding
Disulfide bridges = covalent bonds between cysteine residues
Each Cysteine has a –SH (thiol) group
When two cysteines are close together in a folded protein, they can be oxidized to form a bond
-S-S- = Disulfide Bridge
Two ways to classify proteins based on tertiary structure
Fibrous
Rod shaped molecules containing twisted linear polypeptide chains
Collagens (bone, teeth, skin)
Elastins (ligaments)
collagen and elastin = texture of meat/ food
Keratins (hair, wool, nails)
Myosin + Actin (contractile muscles)
Fibrin (blood clot)
Globular
Spherical or ellipsoidal shapes
Albumins (eggs)
Globulins (muscle foods)
Quaternary Structure
2+ polypeptide chains united by non-covalent bonds
3D arrangement that assembles into ONE functional proteins
Unraveled = Independent Proteins
Myoglobin = stores oxygen
Hemoglobin = transports oxygen
Simple Proteins (homoproteins): ONLY amino acid
1. Albumins –
2. Globulins –
3. Glutelin –
4. Prolamines –
5. Scleroproteins
know examples of these
Conjugated Proteins (heteroproteins): protein + prosthetic group
1. Metalloproteins –
2. Glycoproteins/mucoproteins –
3. Lipoproteins –
4. Nucleoproteins –
5. Phosphoproteins –
6. Chromoproteins –
know examples of these
Milk Proteins
Milk contains 30-36 g/L total protein
Major classes:
• Casein
• Whey
• Serum (blood) proteins
Caseins
Represent about 80% of total proteins in milk
Main Types:
αs1-casein, αs2-casein, β-casein, K-casein, γ-casein
Each Globular with hydrophobic regions
High ratios of polar amino acids
Valine, leucine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, and proline
Uniquely heat stable – up to 140°C
Renitt = makes milk coagulate
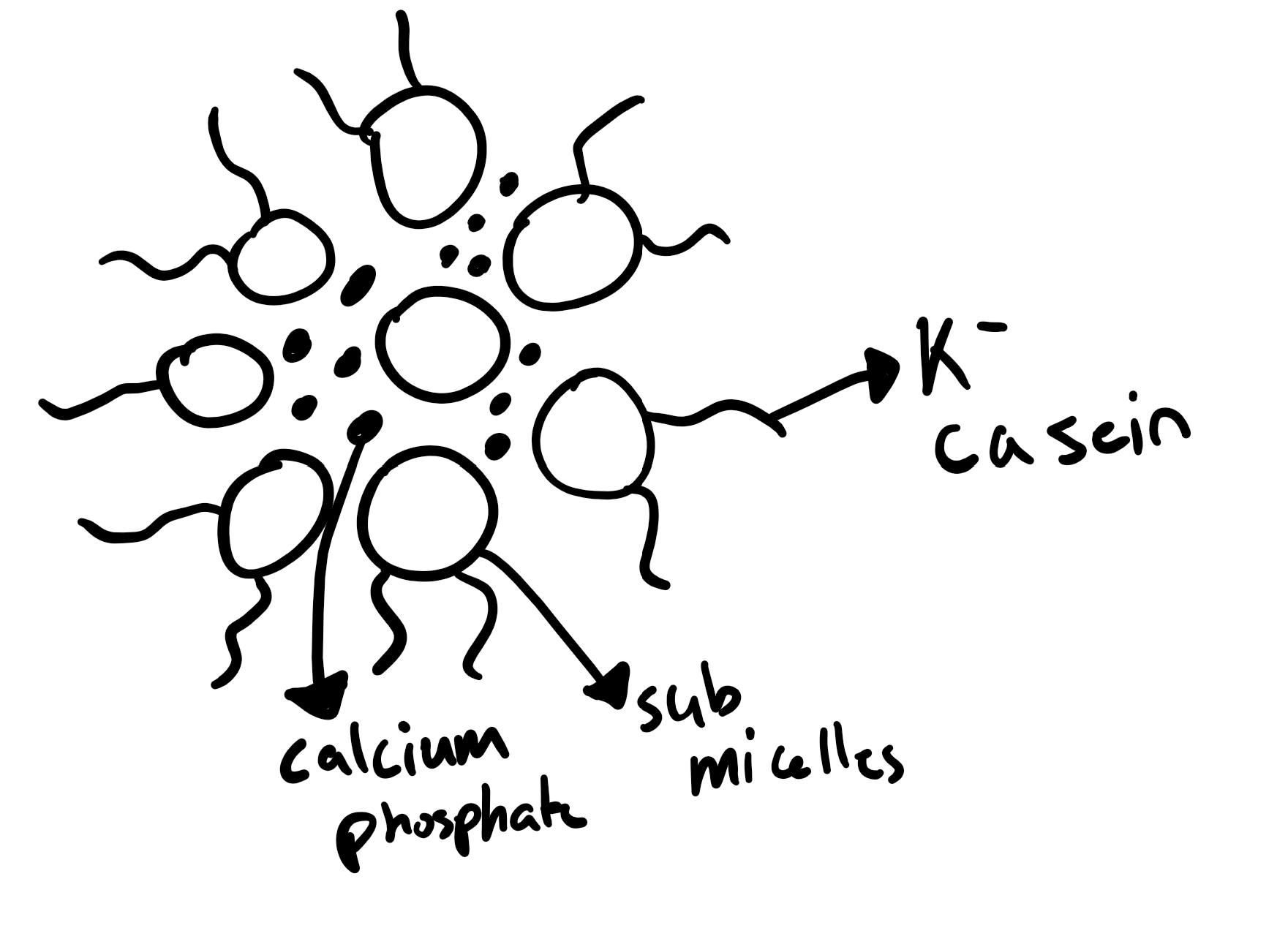
Casein Micelles
Micelle = casing + calcium phosphate
Contain majority of casein proteins
95%
Plus some calcium
Size varies 80 – 1,000 nm in diameter
Average is 250 nm in bovine milk
Made up of submiclles (12-15 nm)
α- and β-casein concentrated in middle of submicelles
K-casein on surface
Hydrophilic protruding chain extends from surface
”Hairy Layer”
Micelles carry calcium
Draw Milk
Whey Proteins
Hydrophobic, globular proteins
Well-developed secondary, tertiary and quaternary structures
Poor heat stability
Denature at 75 C
2 Primary proteins
α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin
Others include
Proteose peptones
Derived from hydrolysis of β-casein
Considered whey protein because they elute in the whey fraction