Lecture 12 Key Concepts/Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:35 AM on 11/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Why is "prokaryotes" in quotes?
prokaryotes is in quotes because they are a paraphyletic group, not a single, monophyletic group
2
New cards
why do we only spend one day on 2/3s of the tree of life?
scientists currently estimate we only know 1-10% of archaea and bacteria
until about 300 years ago, no one even knew a prokaryote existed
until about 300 years ago, no one even knew a prokaryote existed
3
New cards
prokaryotes - unicellularity
prokaryotes are typically unicellular
4
New cards
prokaryotes - internal structure
no membrane bounded organelles
5
New cards
prokaryotes - chromosomes
single, circular chromosome
possible plasmids
possible plasmids
6
New cards
prokaryotes - cell division
binary fission
7
New cards
prokaryotes - gene transfer
lateral gene transfer
8
New cards
prokaryotes - flagella
simple, singular fiber
9
New cards
prokaryotes - cell wall
ubiquitous (peptidoglycan or pseudomurein)
10
New cards
prokaryotes - size
typically small
11
New cards
eukaryotes - unicellularity
unicellular or multicellular (most are multi)
12
New cards
eukaryotes - internal structure
highly compartmentalized
many organelles
many organelles
13
New cards
eukaryotes - chromosomes
double membrane bound nucleus with multiple linear chromosomes
14
New cards
eukaryotes - cell division
mitosis
15
New cards
eukaryotes - gene transfer
recombination
16
New cards
eukaryotes - flagella
very complex
9 + 2 structure
9 + 2 structure
17
New cards
eukaryotes - cell wall
in some organisms (no peptidoglycan)
18
New cards
eukaryotes - size
typically larger than prokaryotes
19
New cards
colonial growth
cells aggregate but each performs the same function
20
New cards
filamentous growth
mode of fungal growth
21
New cards
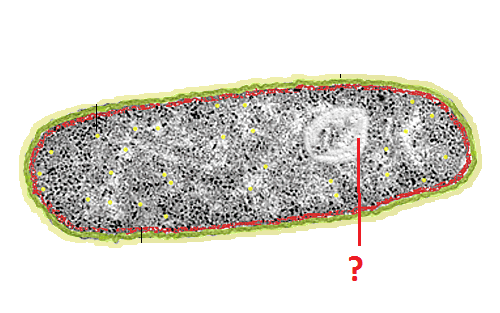
nucleoid region
a non-membrane-enclosed region of the cell where prokaryotic DNA is found
22
New cards
plasmids
small circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the bacterial chromosome
23
New cards
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
24
New cards
bacterial generation time
some bacteria can reproduce very fast (e coli can reproduce every 20 minutes) while some bacteria can take much longer; these varying generation times help us to understand the variability of different bacteria as we classify them
25
New cards
lateral gene transfer
The transfer of genes from one species to another, common among bacteria and archaea.
26
New cards
peptidoglycan
A type of polymer in bacterial cell walls consisting of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides.
27
New cards
Pseudomurein
a substance similar to peptidoglycan that is found in the cell wall of archaea
28
New cards
Gram + bacteria/archaea
envelope absorbs crystal violet stain and appears deep purple
have thick layer of peptidoglycan
have thick layer of peptidoglycan
29
New cards
gram - bacteria/archaea
envelope absorbs safranin and appears pink-red
contain smaller amount of peptidoglycan
contain smaller amount of peptidoglycan
30
New cards
how was bacteria classified before genetic analysis?
shape
metabolism
gram + or -
motile or not
photosynthetic or not
unicellular, colony forming or filamentous
metabolism
gram + or -
motile or not
photosynthetic or not
unicellular, colony forming or filamentous
31
New cards
pre-DNA analysis of bacteria - shape
coccus, bacillus and spirillum
32
New cards
coccus
a spherical bacterium
33
New cards
bacillus
rod-shaped bacterium
34
New cards
spirillum
spiral shaped bacteria
35
New cards
pre-DNA analysis of bacteria - metabolism
anaerobes and aerobes
photoautotrophs and photoheterotrophs
chemoautotrophs and chemoheterotrophs
photoautotrophs and photoheterotrophs
chemoautotrophs and chemoheterotrophs
36
New cards
obligate anaerobes
organisms that cannot live where molecular oxygen is present
37
New cards
obligate aerobes
require oxygen
38
New cards
facultative anaerobes
Can make enough ATP to survive using using fermentation or respiration.
39
New cards
aerotolerant anaerobes
do not utilize oxygen but can survive and grow in its presence
40
New cards
photoautotrophs
organisms that use light and carbon dioxide as their source of energy
some bacteria and some eukaryotes
chlorophyll
very similar to photosynthesis
some bacteria and some eukaryotes
chlorophyll
very similar to photosynthesis
41
New cards
photoheterotrophs
organisms that use light and organic compounds as their source of energy
bacteriochlorophyll
makes elemental sulfur
some bacteria
bacteriochlorophyll
makes elemental sulfur
some bacteria
42
New cards
chemoautotrophs
organisms that use inorganic substances and carbon dioxide as their energy source
use chemical bonds
some bacteria, many archaea
use chemical bonds
some bacteria, many archaea
43
New cards
chemoheterotrophs (heterotrophs)
organisms that usually use organic compounds (sometimes use inorganic compounds) as their energy source
some bacteria, some archaea, most eukaryotes
some bacteria, some archaea, most eukaryotes
44
New cards
hadobacteria
thermophiles that can withstand extremely high temperatures approaching water's boiling point
gram -
gram -
45
New cards
hyperthermic bacteria
heat loving bacteria; similar to hadobacteria
gram -
gram -
46
New cards
firmicutes
gram-positive cell walls that are thick and strong
some have lost their cell walls
some can form endospores
some have lost their cell walls
some can form endospores
47
New cards
actinobacteria
gram +
filamentous
many make antibodies
bacteria that attack other bacteria
filamentous
many make antibodies
bacteria that attack other bacteria
48
New cards
cyanobacteria
photoautotrophic
can be unicellular, filamentous or colonial
gram -
*photosynthesis *
can be unicellular, filamentous or colonial
gram -
*photosynthesis *
49
New cards
spirochets
have axial filaments
mobile
gram -
heterotrophs
common pathogens
mobile
gram -
heterotrophs
common pathogens
50
New cards
chlamydias
very small
parasitic
cocci
gram -
two-cell-type life cycles
cannot live long without a host
parasitic
cocci
gram -
two-cell-type life cycles
cannot live long without a host
51
New cards
proteobacteria
most diverse bacterial lineage
gram -
only known species group with all four types of metabolism
gram -
only known species group with all four types of metabolism
52
New cards
metagenomics
DNA from a group of species is collected from an environmental sample and sequenced
53
New cards
Lokiarchaeota
A clade of deep-sea archaea
Have eukaryotic-like genes including cell shape, cytoskeleton formation and cell membrane functioning
Have eukaryotic-like genes including cell shape, cytoskeleton formation and cell membrane functioning
54
New cards
Crenarchaeota
most are extremophiles
thermophilic, cryophilic and acidophilic
maintain internal pH
thermophilic, cryophilic and acidophilic
maintain internal pH
55
New cards
thermophilic
heat loving
56
New cards
cryophilic
thriving at low temperatures
57
New cards
halophilic
salt loving
58
New cards
acidophilic
acid loving
59
New cards
Euryarchaeota
methanogens, halophiles and extreme thermophiles
methane producing bacteria found in animal intestines
methane producing bacteria found in animal intestines
60
New cards
methanogens
A group of archaebacteria that produce methane as a by product of their metabolism.
61
New cards
Thermotoga maritima
20% of genes are archaean in origin, even though they are a bacteria; shows that prokaryotes pass genes through lateral transfer between species
62
New cards
Bacillus anthracis
firmicute; causes anthrax
63
New cards
Clostridium botulinum
causes botulism (food poisoning)
forms endospores
firmicute
forms endospores
firmicute
64
New cards
mycoplasmas
small and lack cell walls
firmicute
firmicute
65
New cards
streptomyces
actinobacteria
produces streptomycin and other antibiotics
produces streptomycin and other antibiotics
66
New cards
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
causes tuberculosis
actinobacteria
actinobacteria
67
New cards
actinomyces
breaks down organic soil
responsible for the "after rain" smell and composting
responsible for the "after rain" smell and composting
68
New cards
Treponema pallidum
causes syphilis
spirochete
spirochete
69
New cards
Berrelia burgdorferi
causes lyme disease
spirochete
spirochete
70
New cards
Escherichia coli
E. coli
proteobacteria
proteobacteria
71
New cards
chlamydia causes what
eye infections and STIs
72
New cards
salmonella
proteobacteria
73
New cards
Vibrio cholerae
causes cholera and plague
proteobacteria
proteobacteria
74
New cards
Methanopyrus
deep sea thermal vents
euryarchaeota
thermophile
euryarchaeota
thermophile