Financial Markets, Instruments, and Institutions: A Comprehensive Overview
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Financial market
A market in which financial assets (securities) such as stocks and bonds can be purchased or sold.
Liquid securities
Securities that can be easily liquidated without loss of value.
Illiquid securities
Securities that may require a large discount to attract buyers, making them difficult to find.
Treasury securities
Liquid securities due to their frequent issue by the Treasury, attracting numerous investors.
Debt securities
Represent debt (also called credit, or borrowed funds) incurred by the issuer.
Money markets
Facilitate the sale of short-term debt securities by deficit units to surplus units.
Surplus Units
Participants who receive more money than they spend and provide their net savings to the financial markets.
Deficit Units
Participants who spend more money than they receive and access funds from financial markets.
Money market instruments
Low risk instruments that provide lower returns, reflecting their safety and liquidity.
Money market securities
Debt securities traded in the money market that have a maturity of one year or less.
Equity securities
Also called stocks, they represent equity or ownership in the firm.
Capital markets
Facilitate the sale of long-term securities by deficit units to surplus units.
Primary markets
Facilitate the issuance of new securities.
Capital market securities
The securities traded in the capital market.
Secondary markets
Facilitate the trading of existing securities, allowing for a change in ownership.
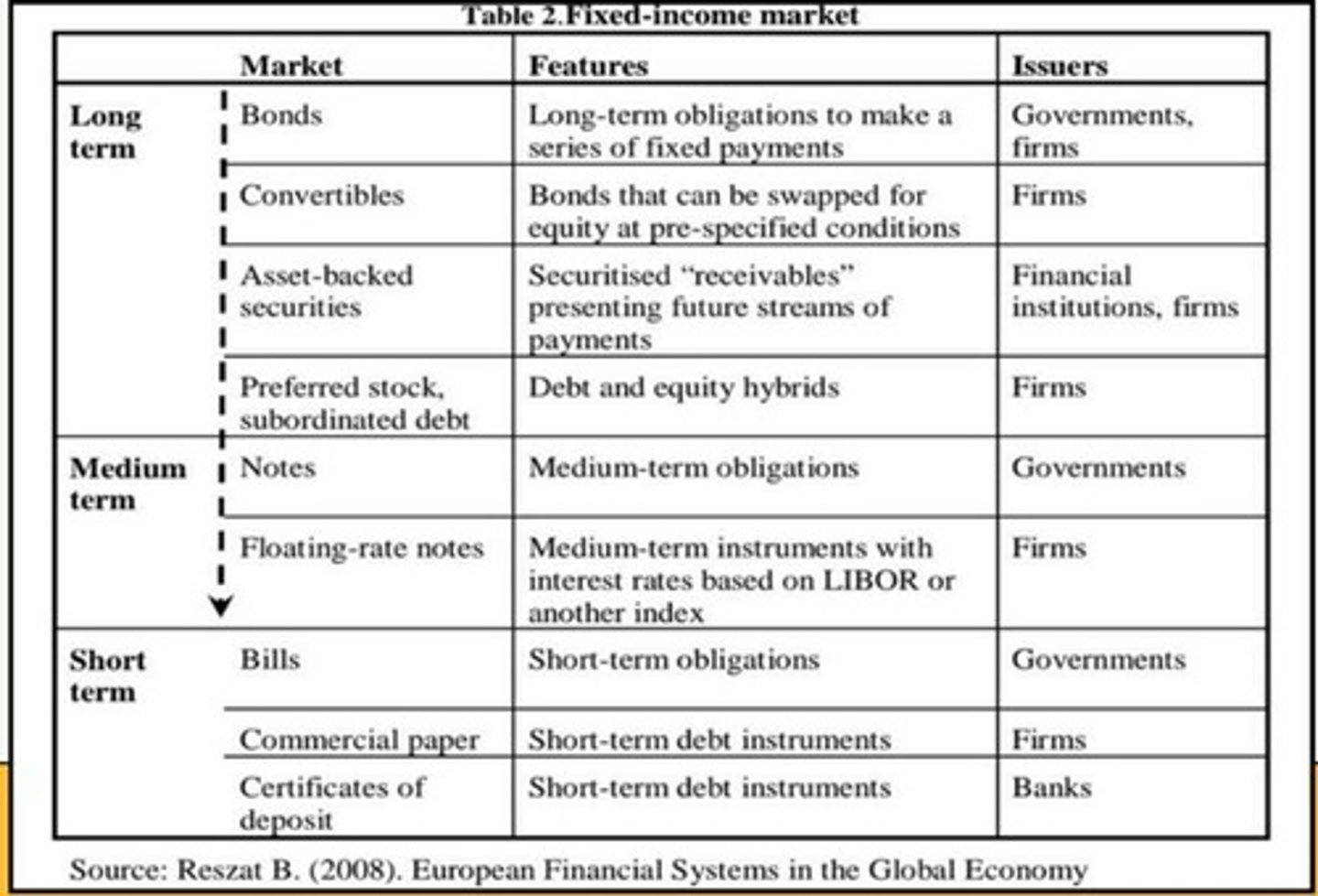
Bonds
Long-term debt securities issued by the Treasury, government agencies, and corporations.
Mortgages
Long-term debt obligations created to finance the purchase of real estate.
Subprime mortgages
Mortgages offered to borrowers who do not have sufficient income to qualify for prime mortgages.
Secondary Market
A market where investors can sell securities they purchased in the primary market before maturity.
Liquidity
A crucial characteristic of securities traded in secondary markets, allowing them to be easily bought or sold.
Commercial Mortgages
Long-term debt obligations created to finance the purchase of commercial property.
Mortgage-Backed Securities
Debt obligations representing claims on a package of mortgages.
Stocks (Equity Securities)
Represent partial ownership in corporations and serve as a long-term source of funds without maturity.
Derivative Securities
Financial contracts whose values are derived from the values of underlying assets, such as debt or equity securities.
Nondepository Financial Institutions
Institutions that generate funds from sources other than deposits and play a major role in financial intermediation.
Finance Companies
Obtain funds by issuing securities and lend them to individuals and small businesses.
Mutual Funds
Sell shares to surplus units and use the funds to purchase a portfolio of securities.
Speculation
The act of investing in derivative securities to speculate on underlying asset value movements without purchasing them.
Risk Management
Using derivative securities as a tool to adjust the risk of investments, potentially offsetting losses on bonds.
Behavioral Finance
The application of psychology to make financial decisions, explaining why markets are not always efficient.
Depository Institutions
Accept deposits from surplus units and provide credit to deficit units through loans and purchases of securities.
Commercial Banks
The most dominant depository institution, offering a variety of deposit accounts and transferring funds to deficit units.
Federal Funds Market
Facilitates the flow of funds between depository institutions, including banks.
Savings Institutions
Also known as thrift institutions, including savings and loan associations and savings banks, focusing on residential mortgage loans.
Credit Unions
Nonprofit institutions that restrict their business to credit union members.
Securities Firms
Perform various functions in financial markets, including acting as brokers, dealers, underwriting, and advising.
Brokers
Execute securities transactions, with fees reflected in the difference between bid and ask quotes.
Dealers
Maintain an inventory of securities and earn income from the performance of their portfolio.
Investment Banking
Services provided by securities firms, including underwriting and advising.
Advisory Services
Services provided by securities firms on mergers and corporate restructuring.
Insurance Companies
Companies that offer policies to reduce financial burdens from death, illness, and property damage, charging premiums and investing funds in stocks or bonds.
Pension Funds
Financial intermediaries that manage contributions from employees and employers to corporations and government agencies, providing a retirement savings method.
Systemic Risk
The spread of financial problems among financial institutions and across financial markets that could cause a collapse in the financial system.
Financial Institutions
Entities that accept savings and transfer them to those that need funds.
Financial Markets
Organized forums in which suppliers and demanders of various types of funds can make transactions.
Private Placement
An unstructured nature of liquidity that provides an opportunity for investors to sell a financial instrument.
Transaction Costs
Costs charged and/or borne by financial market participants when trading a financial instrument.
Financial Instrument
Monetary contracts between parties that can be created, traded, modified, and settled.
Fixed Income Instrument
Debt investments, such as bonds and certificates of deposit, where the issuer promises to pay a fixed rate of interest and return the principal at a specified maturity date.
Individuals
Net suppliers of funds because they save more than they borrow.
Businesses
Net demanders of funds because they borrow more than they save.
Government
Net demanders of funds because they borrow more than they save.
Investment Banks
Institutions that assist companies in raising capital and advise firms on major transactions such as mergers or financial restructurings.
Glass-Steagall Act
An act of Congress in 1933 that created the federal deposit insurance program and separated the activities of commercial and investment banks.
Shadow Banking System
A group of institutions that engage in lending activities like traditional banks but do not accept deposits and are not subject to the same regulations.
Price Discovery
The process where transactions between buyers and sellers of financial instruments determine the price of the traded asset.
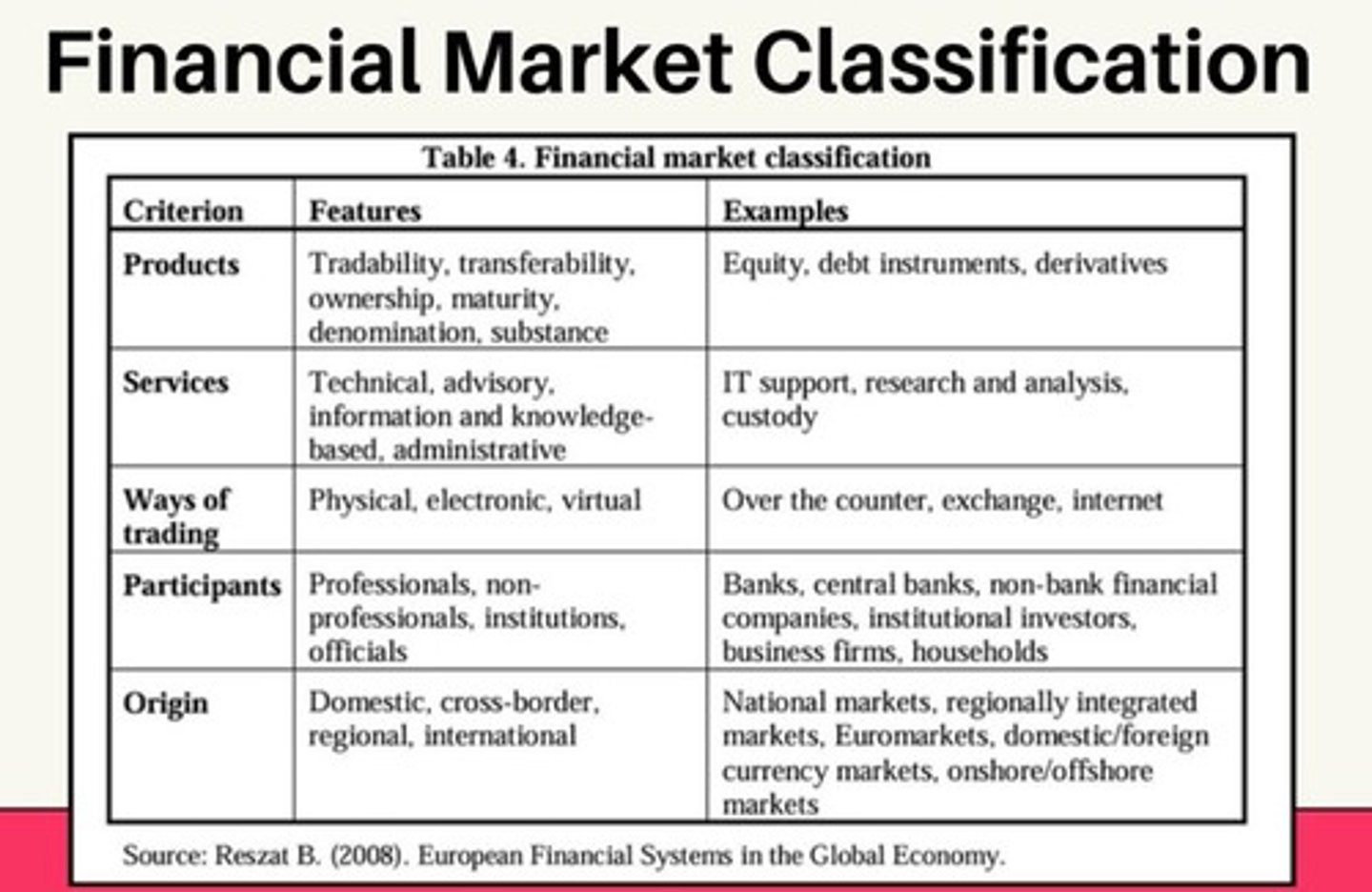
Information & Knowledge-Based Services
Services that provide data, research, and market analysis so investors can make informed decisions.
Administrative Services
Services that handle the record-keeping, settlement, and safekeeping of financial assets.
Physical Trading
Trading that happens face-to-face in a physical location.
Electronic Trading
Trading that happens through computerized systems or online platforms.
Virtual / Internet Trading
Trading that happens through the internet or apps, accessible to individual investors directly.
Equity Instrument
Represents ownership in a company.
Tradability
Easily tradable in stock exchanges.
Transferability
Can be transferred from one investor to another.
Maturity
No fixed maturity date; you own it as long as the company exists or until you sell.
Denomination
Usually in shares.
Substance
Ownership security.
Debt Instrument
A financial instrument representing a loan made by an investor to a borrower.
Professionals
People who are trained and licensed to work in financial markets.
Non-Professionals
Ordinary people or households who invest their own money.
Institutions
Large organizations that handle huge amounts of money.
Ownership in Debt Instruments
No ownership rights; you are a lender, not an owner.
Maturity in Debt Instruments
Has a fixed maturity date.
Substance in Debt Instruments
Borrowing/lending contract.
Derivatives
Contracts whose value is derived from another asset (stock, commodity, currency).
Domestic Markets
All transactions happen within one country.
Cross-Border Markets
Transactions that involve two countries.
Regional Markets
Markets that connect or integrate countries in a specific region.
International Markets
Trading happens on a global scale without borders.
Technical Services
Services that provide specialized knowledge and expertise to support the effective use, maintenance, and improvement of technology and technical systems.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation
An agency created by the Glass-Steagall Act that provides insurance for deposits at banks and monitors financial institutions to ensure their safety and soundness.
Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
A law that allows business combinations—such as mergers—between commercial banks, investment banks, and insurance companies.
Securities Act of 1933
A law that regulates the sale of securities to the public through the primary market, ensuring transparency and investor protection during initial offerings.
Securities Exchange Act of 1934
A law that governs the trading of securities—such as stocks and bonds—in the secondary market, focusing on fair practices and disclosure requirements.
Securities and Exchange Commission
The primary government agency responsible for enforcing federal securities laws and overseeing the integrity of financial markets in the United States.