Treatment & Rehab Test 3
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What is the load progression for Delorme Protocol?
Set 1: 50% of 10-rep max (10 reps)
Set 2: 75% of 10-rep max (10 reps)
Set 3: 100% of 10-rep max (10 reps)
What is the load progression for Oxford Protocol?
Set 1: 100% of 10-rep max (10 reps)
Set 2: 75% of 10-rep max (10 reps)
Set 3: 50% of 10-rep max (10 reps, or fatigue out a system and increase reps or distance)
What is the load progression for DAPRE Protocol?
Set 1: 50% of 6-rep max (10 reps) → Warm-up
Set 2: 75% of 6-rep max (6 reps) → Warm-up
Set 3: 100% of 6-rep max (as many reps as possible)
Set 4: Adjusted resistance based on Set 3 performance (AMRAP)
What is the key feature of the Delorme Protocol and why would you choose this program?
Delorme is best for gradually building strength while preventing early fatigue. Used to build pure strength and good for beginners, post-surgical rehab, controlled progressive loading.
What is the key feature of the Oxford Protocol and why would you choose this program?
Oxford is rehab-friendly, considering muscle fatigue by reducing load each set. Used to build muscle endurance and fatigue resistance.
What is the key feature of the DAPRE Protocol and why would you choose this program?
DAPRE is the most adaptive, allowing daily weight adjustments based on actual performance. You could use this in prehab, advanced rehab, athletes, and dynamic strength training where progressive overload needs fine-tuning.
Describe the sliding filament theory:
Muscle contraction occurs as actin & myosin filaments slide past each other.
Nerve impulse triggers the release of acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine causes the release of calcium.
Calcium (Ca²⁺) binds to troponin, shifting tropomyosin to expose myosin-binding sites.
Myosin heads form cross-bridges with actin and pull (power stroke).
ATP breaks the cross-bridge, allowing myosin to reset and repeat.
Contraction continues with Ca²⁺ & ATP; relaxation occurs when Ca²⁺ is removed.
Describe the all or none principle:
When the motor neuron receives sufficient stimulus, all muscle fibers in the unit will contract.
Muscle fiber types:
Type I – slow-twitch fibers, slow oxidative fibers
Type IIa – intermediate fibers, fast-oxidative glycolytic fibers
Type IIb – fast-twitch fibers, fast-glycolytic fibers
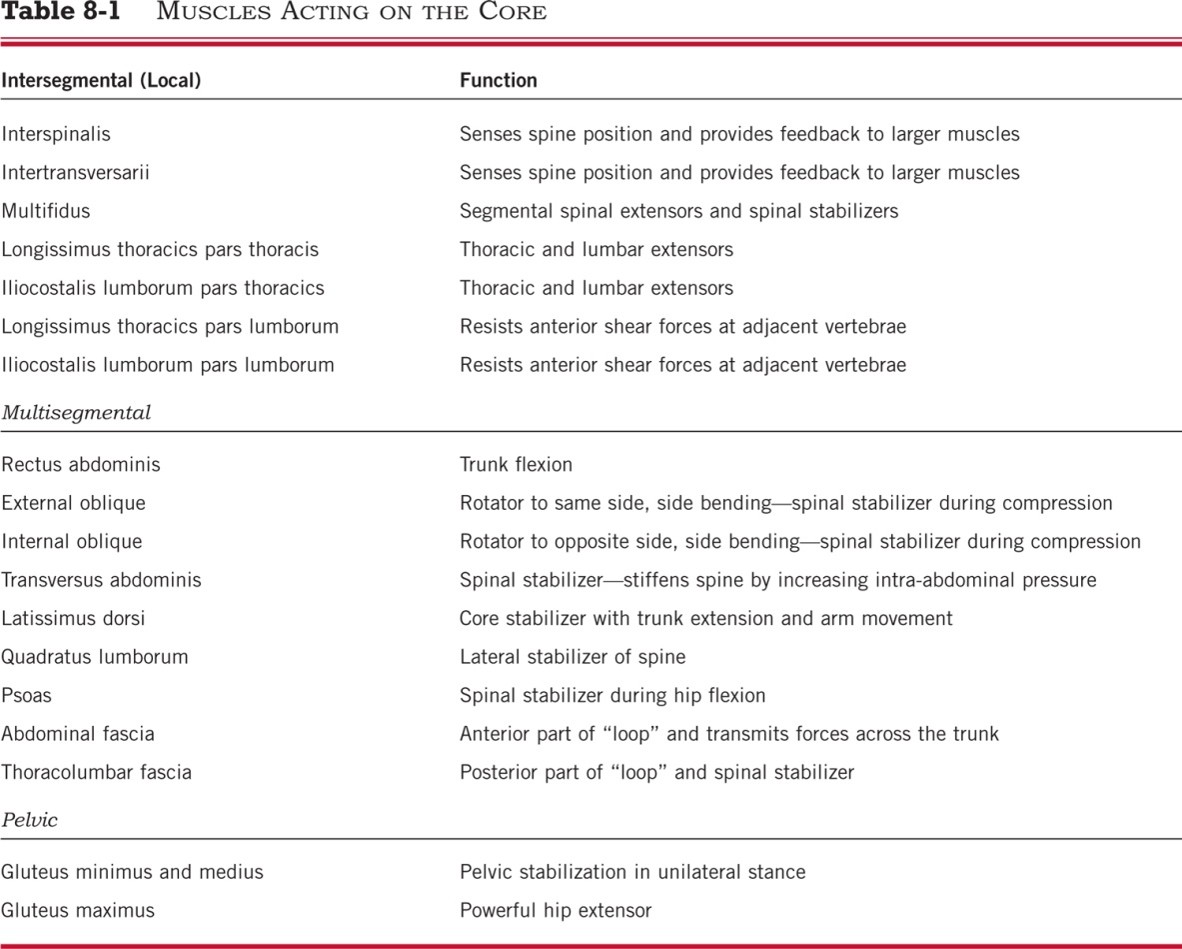
What muscles are involved in global stability and why it it important for the core?
Prime movers: Rectus abdominis, paraspinals, obliques. (Muscles that are larger, more superficial, and generate greater force.) These are important for dynamic stability.
What muscles are involved in local stability and why is it important for the core?
Segmental stability muscles: Transverse abdominis, multifidus. (Muscles that are deep, small, and close to the joints) These are important for static stability.
Muscles acting on the core:
Describe the phases of plyometrics using the example of a jump.
Eccentric/down phase: Quad are performing an eccentric contraction, going down into a squat
Amortization/transition phase: Quads are briefly in an isometric contraction, transitioning into moving upward
Concentric/up phase: Quads perform a concentric contraction as knees extend
Before starting plyometrics, the clinician must have knowledge of patient levels for:
Strength and range of motion (ROM)
Balance and neuromuscular control (mostly subjective, visual or observatory: looking for point of summation)
What are two strength guidelines for screening preparatory plyometrics in the lower extremity?
Parallel single-leg step up
5 parallel single-leg squats in 8 seconds
What is a strength guideline for screening preparatory plyometrics in the upper extremity?
10 push-ups (elbows at 90-degree angle) in 15 seconds
What should you evaluate in the technique of plyometrics?
Coordination, stability, timing of movement, proper landing technique, postural control, biomechanics
What are some biomechanics in technique of plyometrics?
Shoulders over knees
COG between base of support
Feet shoulder-width apart
No valgus motion at knee, especially upon landing
Knee in line with foot
Soft landing, no stiff knee (listening to noise, treadmill)
How should you progress in plyometrics?
Preparatory phase
Submaximal phase
Maximal phase
Progress from areas of safety
1.Jump (land on two legs) in place
2.Jump forward - sagittal plane
3.Jump side to side - frontal plane
4.Jump twist - transverse plane
5.Hops (land on single leg)
What are two characteristics of resistance in isokinetic exercise?
Is accommodating based on the patient’s effort
Can be maximal throughout the entire range of motion (ROM)
Strength can be measured in:
Force (straight plane) or torque (rotational motion)
What is peak torque?
Defined as the maximum rotational force production for a single point in the single best repetition of the set. (At midrange)
Exercises for preparatory phase of plyometrics (lower extremity):
Hopping in place:
40 reps in 30 seconds, 2-4 sets
Jump rope:
20-60 seconds 3-5 sets
Hop and holds:
5-10 reps (hold landing for 2-3 seconds) in 10-20 seconds, 2-3 sets
Exercises for submaximal phase of plyometrics (lower extremity):
Jumps: (multidirectional)
6-12 reps in 15-30 seconds, 3-5 sets
Ladder drills: 2-4 passes through the ladder in 10-20 seconds, 3-5 sets
Power skips: 8-12 reps per leg in 10-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Exercises for maximal phase of plyometrics (lower extremity):
Depth jumps:
4-6 reps in 10-15 seconds, 3-5 sets
Box jumps:
6-10 reps in 15-25 seconds, 3-4 sets
Split squat jumps:
4-6 reps per leg in 10-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Exercises for preparatory phase of plyometrics (upper extremity):
Wall push-ups:
10-20 reps in 15-30 seconds, 2-4 sets
Incline push-ups:
8-15 reps in 15-30 seconds, 2-4 sets
Med-ball partner pass:
8-10 passes in 10-20 seconds, 3-5 sets
Exercises for submaximal phase of plyometrics (upper extremity):
Overhead soccer throw (med ball):
6-12 reps in 10-20 seconds, 3-5 sets
Deceleration Baseball Throw:
6-10 reps per arm in 20-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Push-Up with Clap or Lateral Movement:
6-12 reps in 10-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Exercises for maximal phase of plyometrics (upper extremity):
Power drop:
4-6 reps in 8-15 seconds, 3-5 sets
Exercise Ball Push-Up:
6-12 reps in 10-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Medicine Ball Push-Up
6-12 reps in 10-20 seconds, 3-4 sets
Instruct an abdominal bracing session using SLR slides as stability guides:
Instruct on brace and breathe (sphygmomanometer)
Instruct on stable pelvis-heel slides from hook
Instruct on stable pelvis-heel slide-SLR
Instruct a William’s flexion protocol:
a. Static posterior pelvic tilts: Hold 5-10 sec, 10-20 reps, 2-3 sets
b. Single knee-to-chest: Hold 10-30 sec per leg, 2-3 sets
c. Double knee-to-chest: Hold 10-30 sec, 2-3 sets
d. Abdominal crunch: Hold 2-5 sec at top, 10 reps, 2-3 sets
Instruct a McKinzie Extension protocol:
Prone Lying: 20-30 sec work up to 1 minute, 3 sets
Prone on Elbows: 20-30 sec work up to 1 minute, 3 sets
Cobra: Hold 20-30 sec, 3 sets
Cat/Cow: Hold 2-5 sec, 10-15 reps, 3 sets
List exercises with parameters that you could do with an exercise ball to strengthen the core:
Plank: 20-60 seconds, 3-4 sets
Walk outs: 6-12 reps in 20-30 sec, 3-4 sets
Bridges: 10-15 reps with 10-20 sec hold at top, 3-4 sets
How can you progress shoulder strengthening with a series of isometric contractions?
Progress 30 degrees in isometric contractions: 30, 60, 90, 120,…
What are types of exercises, equipment, and parameters you can use for shoulder strengthening?
Tension bands, dumbbells, body weight
Tension Band Exercise: External Rotations
10-20 reps 3 sets
Dumbbell Exercise: Dumbbell Shoulder Press
8-10 reps, 3-4 sets
Bodyweight Exercise: Push-Ups
10-20 reps, 3-4 sets
What are types of exercises, equipment, and parameters you can use for shoulder endurance?
Tension Band Exercise: Band Lateral Raises
15-25 reps, 4-5 sets
Dumbbell Exercise: Dumbbell Shoulder Press
15-20 reps, 4-5 sets
Bodyweight Exercise: Plank to Downward Dog
30-60 sec, 4-5 sets
You are working at a PT facility that has a KIN COM unit. List 5 reasons you love it:
Objective data collection
Controlled resistance
Isolates specific muscles
Biofeedback for patient
Customizable programs
You are working at a PT facility that has a KIN COM unit. List 5 reasons you hate it:
Lengthy set up
Expensive
Takes up space
Difficult communicating instructions to patients
Difficult to learn how to use