Sports Med EOPA Review
1/437
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
438 Terms
Coach
Member of the sports medicine team
Responsible for first aid care of athletes in the absence of an athletic trainer.
Athlete
Member of the sports medicine team
Should be well informed about their injury and listen to their body to prevent re-injury.
Parents
Member of the sports medicine team
Important especially with athletes who are minors
Team Physician
Member of the sports medicine team
Assists the athletic trainer in return to play decisions
Athletic Trainer
Member of the sports medicine team
Responsible for all aspects of care of the injured athlete.
Facilitates communication between all members of the sports medicine team.
CSCS (Certified Strength & Conditioning Specialist)
Lead/instruct individuals and groups in exercise activities.
Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialist
"Personal Trainer"
ATC (Certified Athletic Trainer)
Prevent, evaluate, care and rehabilitate injuries.
DC (Doctor of Chiropractic Medicine)
Spine specialists
RD (Registered Dietician)
Promotes healthy eating habits and recommends dietary modifications
Exercise physiologist
Expert in the effect of exercise on the human body
Family Physician
Medical doctor
Diagnose illness, prescribe and administer treatment for people with injury or disease
LMT (Licensed Massage Therapist)
Uses touch to manipulate soft tissues of the body to restore function
OT (Occupational Therapist)
Helps with conditions that limit activities of daily living.
Also has assistants and aides that help within this field.
Orthopedic Surgeon
Medical doctor
Bone/Joint surgeon
DPT (Doctor of Physical Therapy)
Must have a Doctorate degree at an accredited school
Helps restore, maintain physical health by relieving pain and improving mobility.
Also has assistants and aides that help within this field.
PA (Physician Assistant)
Practices medicine under the supervision of physicians and surgeons
Podiatrist
Diagnose and treat issues of the foot and lower leg
Sports Psychologist
Study mental processes and behavior and assists in the mental aspect of sport participation
Collision sport
Athletes use their bodies to deter or punish their opponent.
Examples include football, rugby and hockey.
Contact sport
Contact with the opponent is part of the sport, but is not part of the actual intent of the sport and discouraged by the rules.
Examples include basketball, soccer, and wrestling
Non-contact sport
Players are physically separated from their opponent
Examples include Volleyball, Tennis, and Cross Country running
Assumption of Risk
Athletes recognize that there are some risks inherent in participating in sports and choose to take part anyway.
Battery
Touching someone without their permission
Commission
Doing something extra that a reasonable person would not have done
Omission
Failing to do something that a reasonable person would have done
Failure to Warn
Not informing a participant of potential risks and dangers
HIPAA
Medical information confidentiality law
Informed Consent
Being informed of all procedures and potential risks/benefits of each
Liability
Legal responsibility to act
Malpractice
When an individual commits a negligent act while providing care
Negligence
Failure to use ordinary or reasonable care.
Must prove four things: Duty of care, Breach of duty, Injury/damage, Proximate cause
Standard of Care
Level of care that is expected, based on someone with similar education and experience
ADA
Federal legislation ensuring equal opportunities to Americans with disabilities (American Disability Act)
Scope of Practice
The skills and responsibilities of your level of training.
What you can and cannot do as part of your career.
Title IX
Gender equity law
SOAP
Proper documentation format
Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan
EAP
Plan detailing how to deal with an emergency.
Includes location of equipment and individual responsibilities.
Specific for each sport and venue.
Superior
Closer to the head or higher than another structure
Inferior
Closer to the feet or lower than another structure
Anterior
More in front than another structure
Posterior
More in back than another structure
Medial
Closer to the midline than another structure
Lateral
Farther away from the midline than another structure
Distal
Further from the root of the limb (extremities only)
Proximal
Closer to the root of the limb (extremities only)
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body than another structure
Deep
Closer to the core of the body than another structure
Ventral
Towards the belly/front
Dorsal
Towards the back
Prone
Lying face down
Supine
Lying face up
Unilateral
Pertaining to one side of the body
Bilateral
Pertaining to both sides of the body
Anatomical Position
Standing with the palms facing forward
Sagittal Plane
Divides the body into right and left portions
Frontal Plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
Also called the Coronal Plane
Transverse Plane
Divides the body into upper and lower portions.
Also called the Horizontal Plane
Midline
Divides the body into EQUAL right and left halves.
Also called the Midsagittal Plane
Articulation
The site at which bones meet to form a joint
Bursa
A fluid-filled sac at a joint that prevents friction
Cartilage
Gristle-like padding that lies on or between bones
Ligament
Tissue that connects bone to bone
Tendon
Tissue that connects muscle to bone
Cryotherapy
Treatment by use of cold
Hydrotherapy
Treatment by use of water
Thermotherapy
Treatment by use of heat
Modality
Method or apparatus used for healing an injury
Proprioception
Sense of the body's position in space
Range of Motion
Movement of a joint around a central point (how much motion occurs at a joint)
Reduction
To bring back to the normal position
Valgus
Distal aspect of limb forced away from the midline
Varus
Distal aspect of limb forced toward midline
Indicate
To advise the use of
Contraindicate
To advise against
Acclimatization
The process of the body physiologically adapting to an unfamiliar environment (altitude or temperatures)
Aerobic
Work or exercise requiring oxygen.
(Endurance, long in duration yet low in intensity)
Anaerobic
Work or exercise not requiring oxygen
(Sprints, short in duration and high in intensity)
Analgesic
An agent for producing insensibility to pain
Constriction
State of being pinched off or smaller than normal
Dilation
State of being enlarged
Contralateral
On the opposite side
Diagnosis
The name of the disease or condition a person is believed to have
Prognosis
Prediction of the course and end of a disease or eventual outcome of an injury
Innervate
To supply with nerves
Palpation
Examination by touch
Vasoconstrictor
An agent causing the constriction or closing of blood vessels
Vasodilator
An agent causing the dilation or opening of blood vessels
Abrasion
Minor wound in which the skin's surface is rubbed or scraped
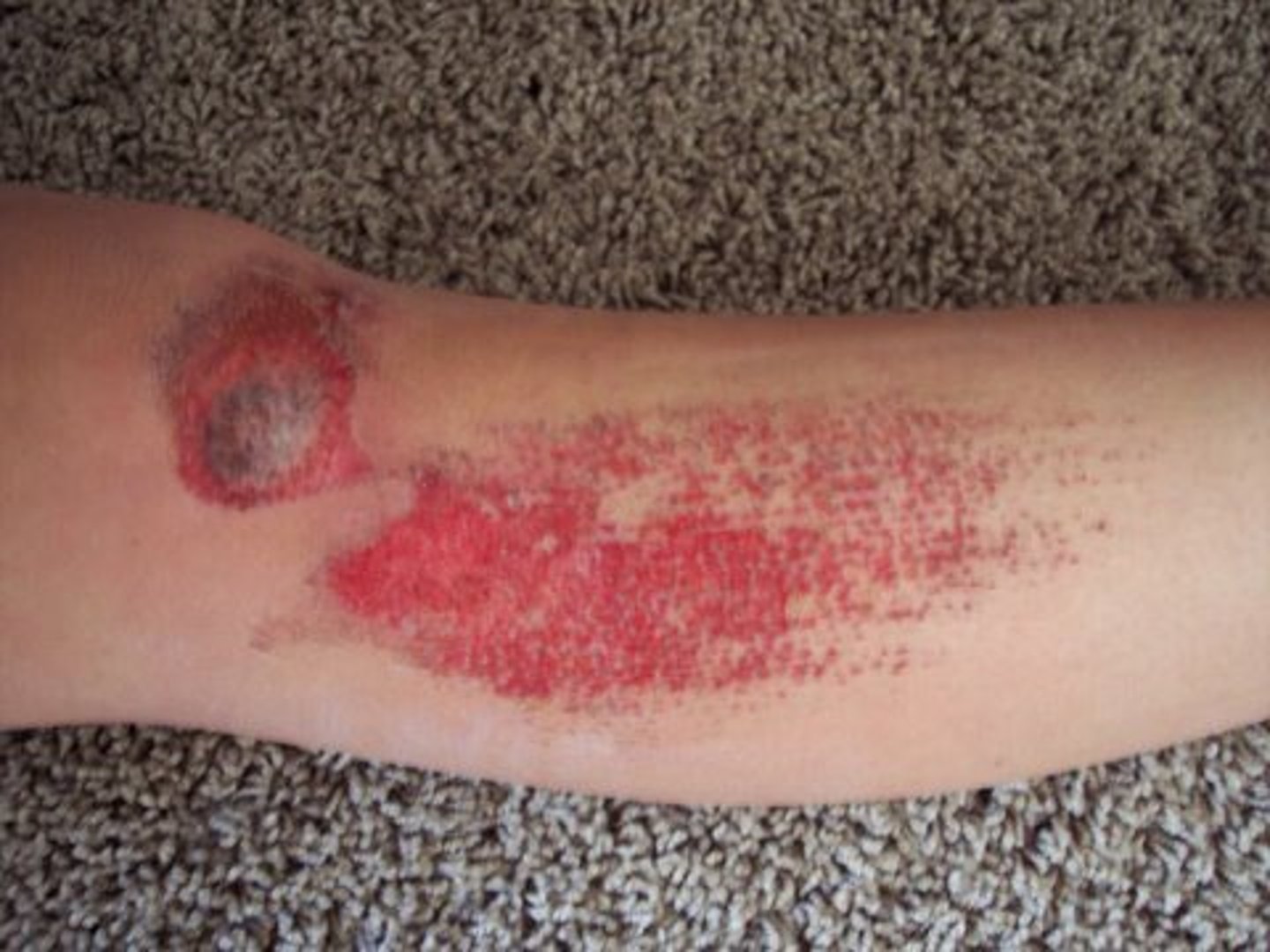
Avulsion
Tearing or pulling away or a part of a structure
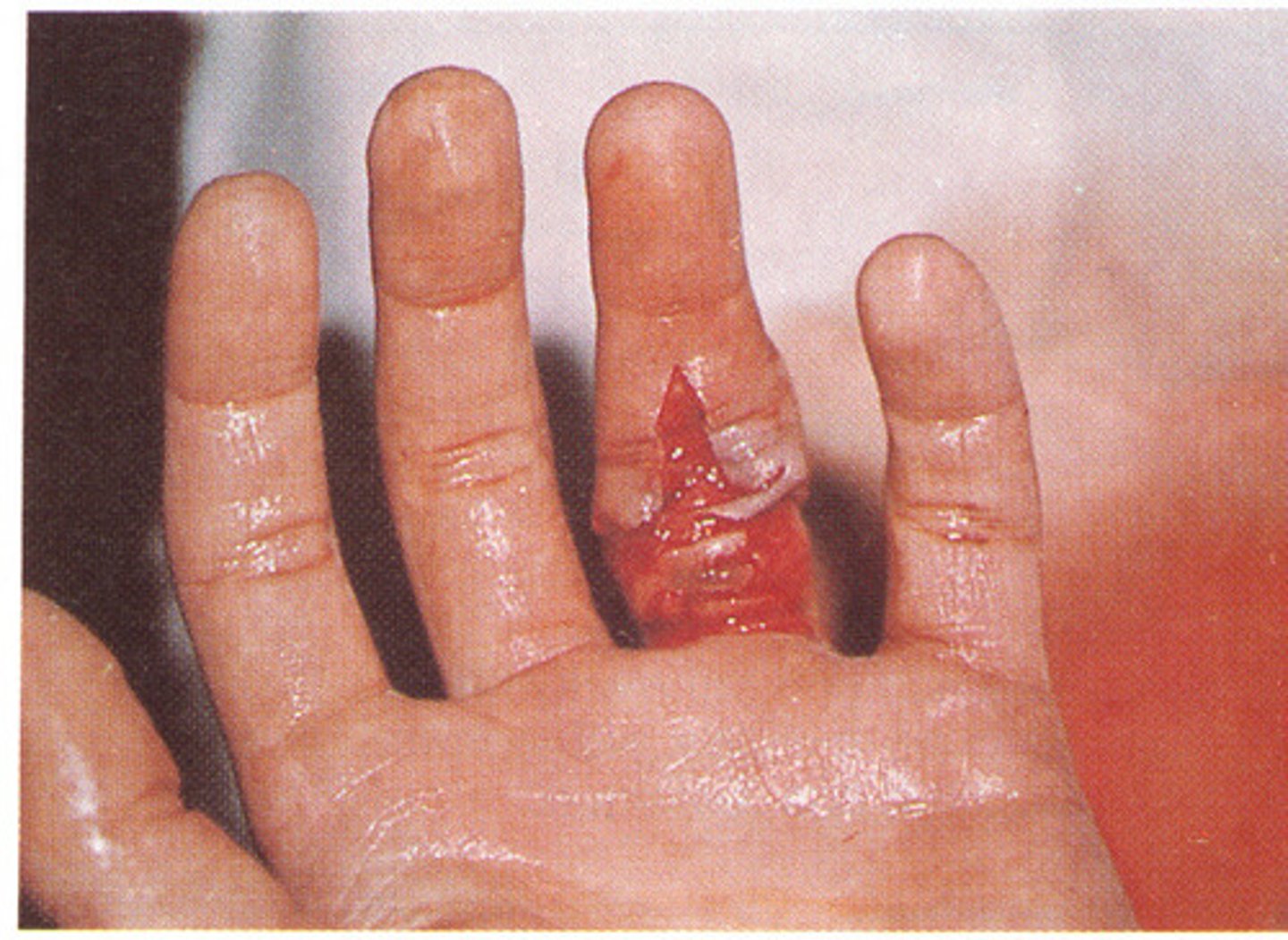
Bursitis
Inflammation of a bursa
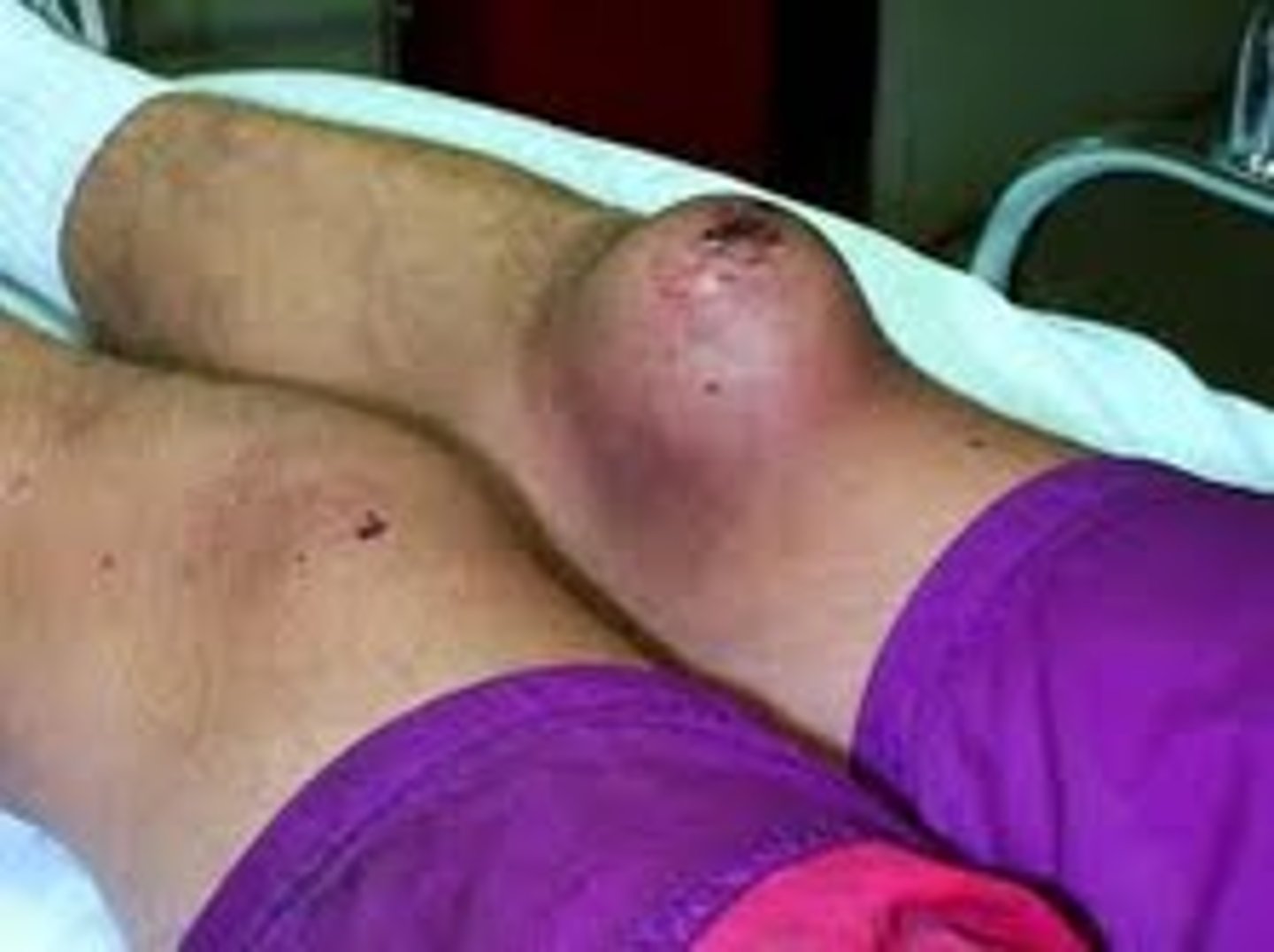
Contusion
A bruise to a bone or muscle, caused by an outside force resulting in tissue damage and internal bleeding.
Dislocation
Complete displacement of a bone from its normal position in a joint.
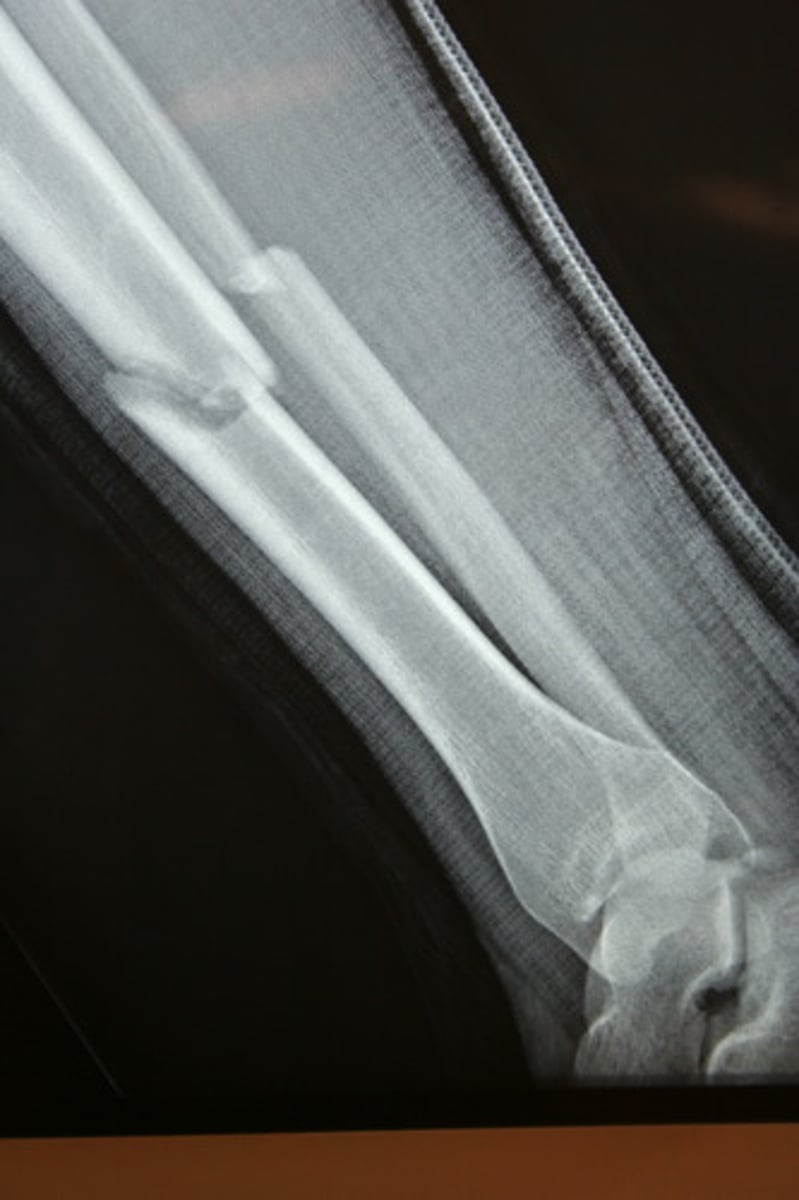
Fracture
A break or crack in a bone
Hematoma
Swelling composed of blood.
Internal bleeding associated with a contusion.
Incision
A cut made surgically with a sharp knife
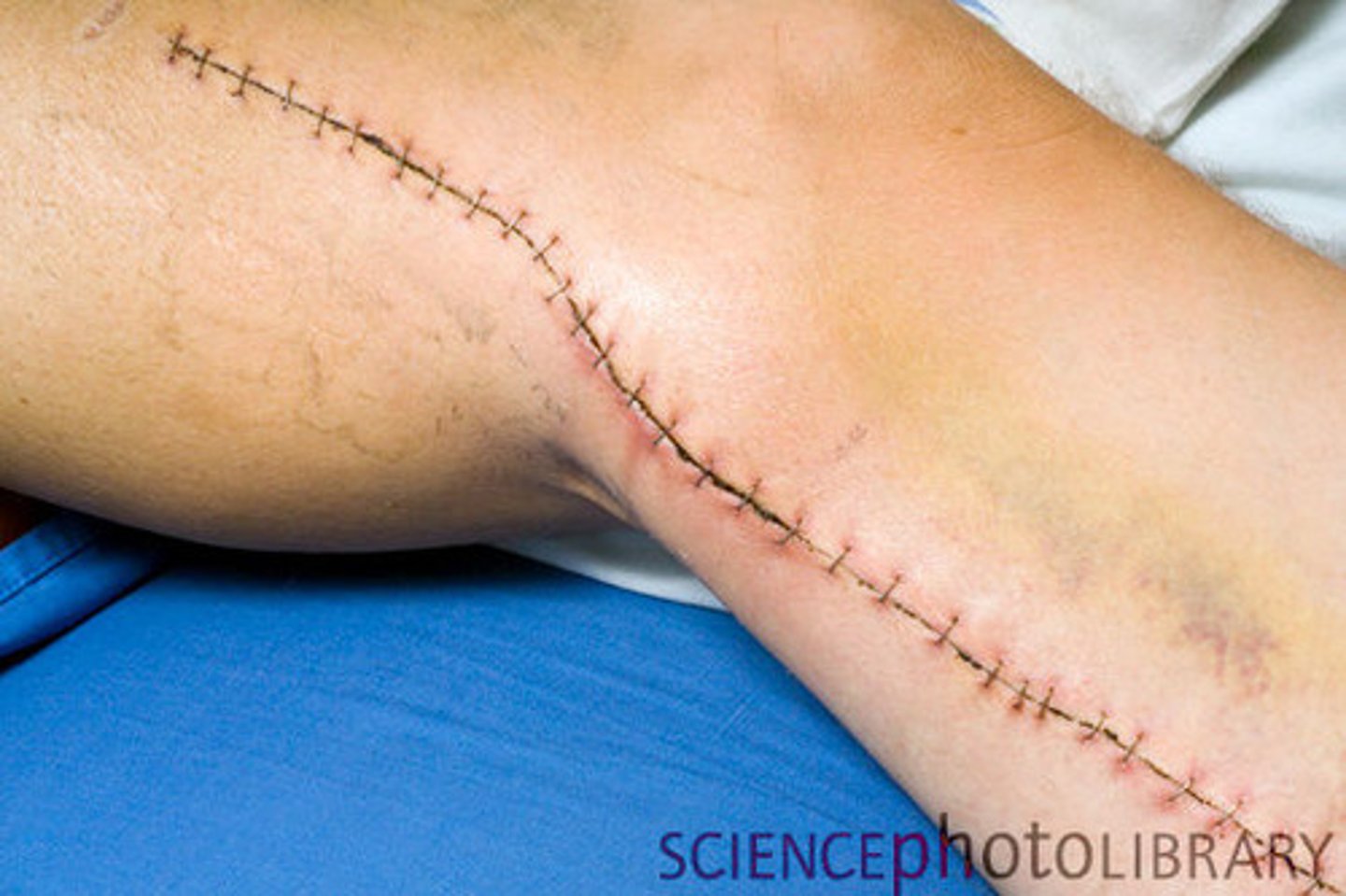
Laceration
A jagged cut or tear in the skin
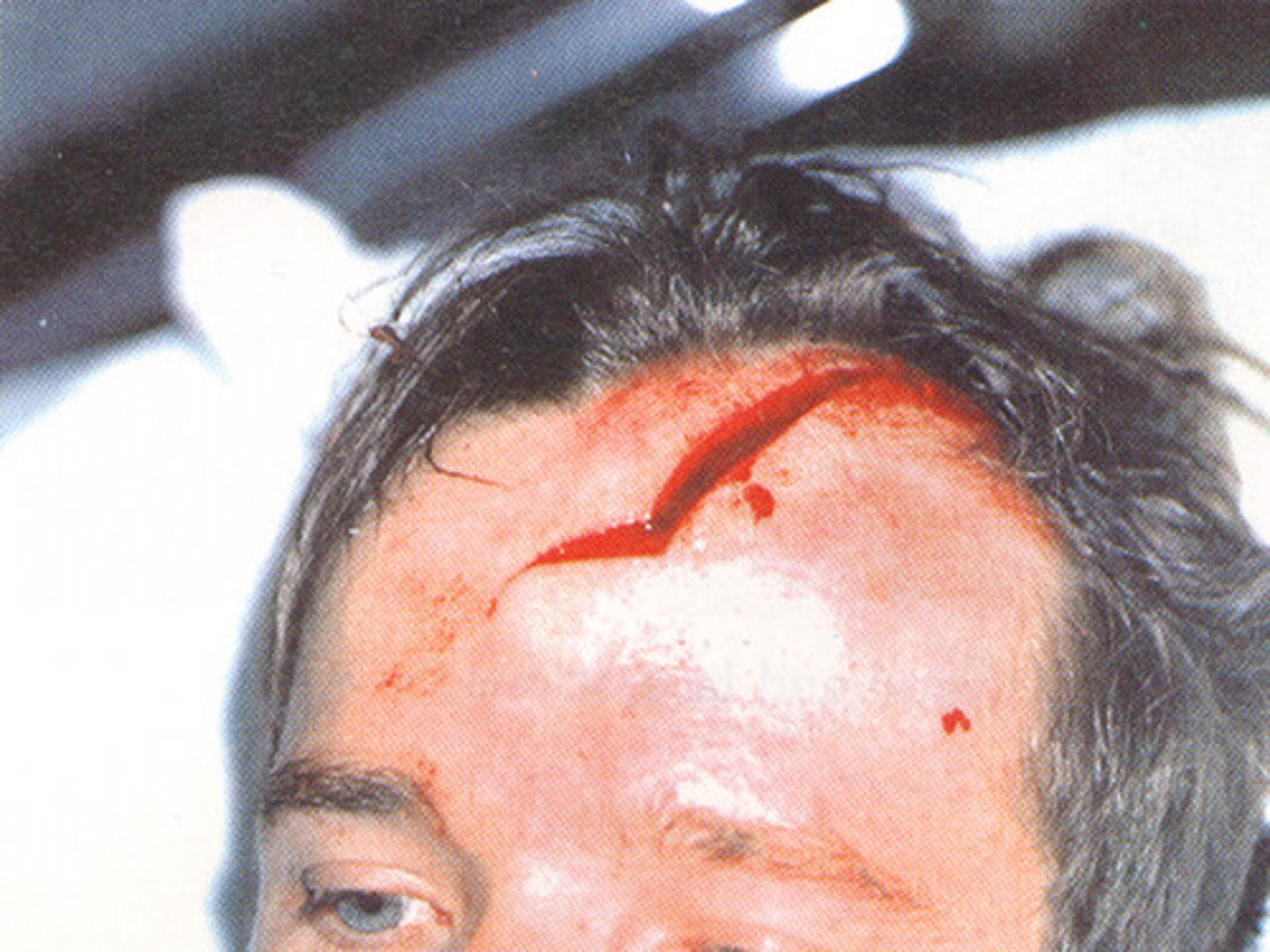
Separation
Pulling apart of a generally non-movable joint
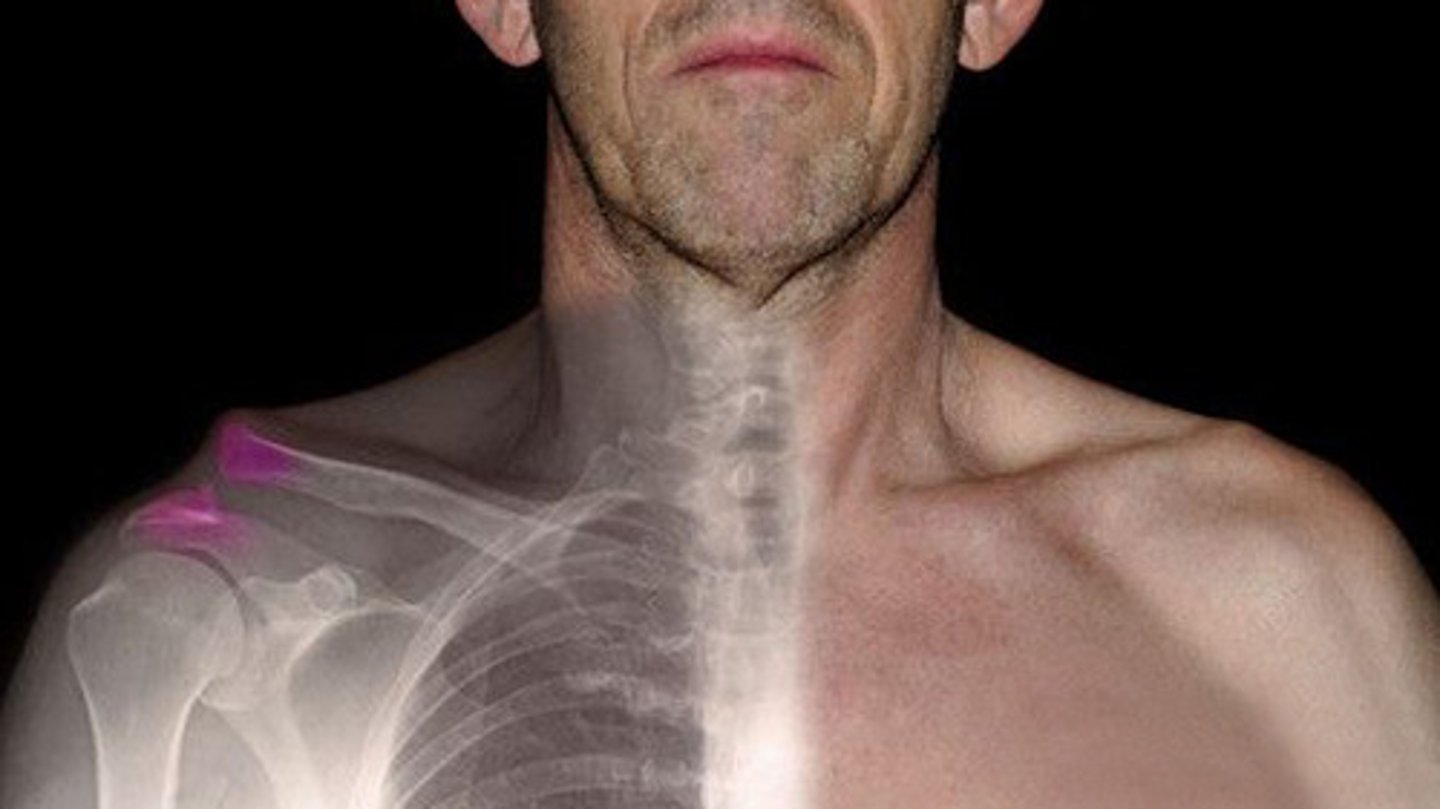
Sprain
Stretching or tearing of ligaments
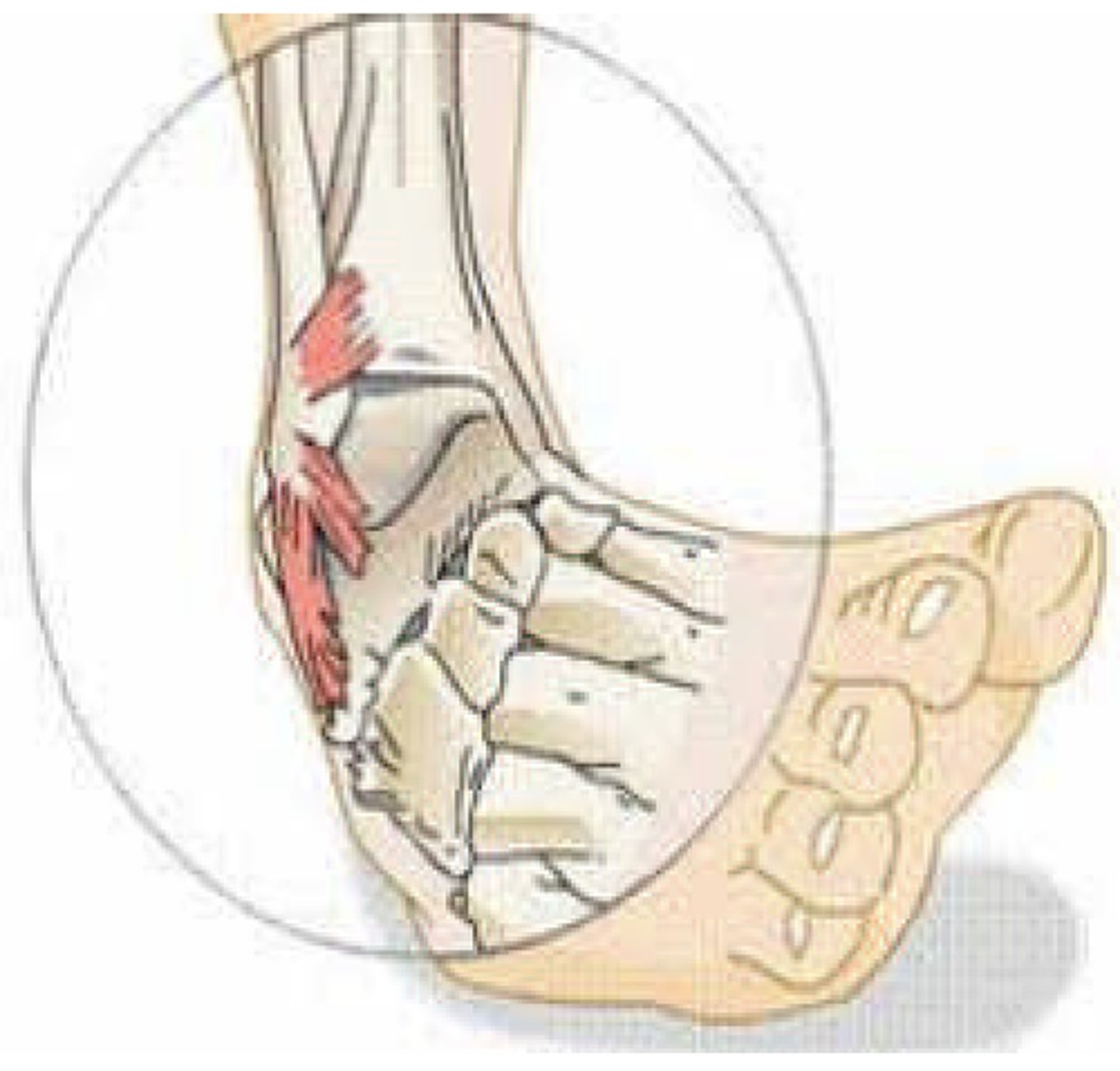
Strain
Stretching or tearing of muscle or tendon
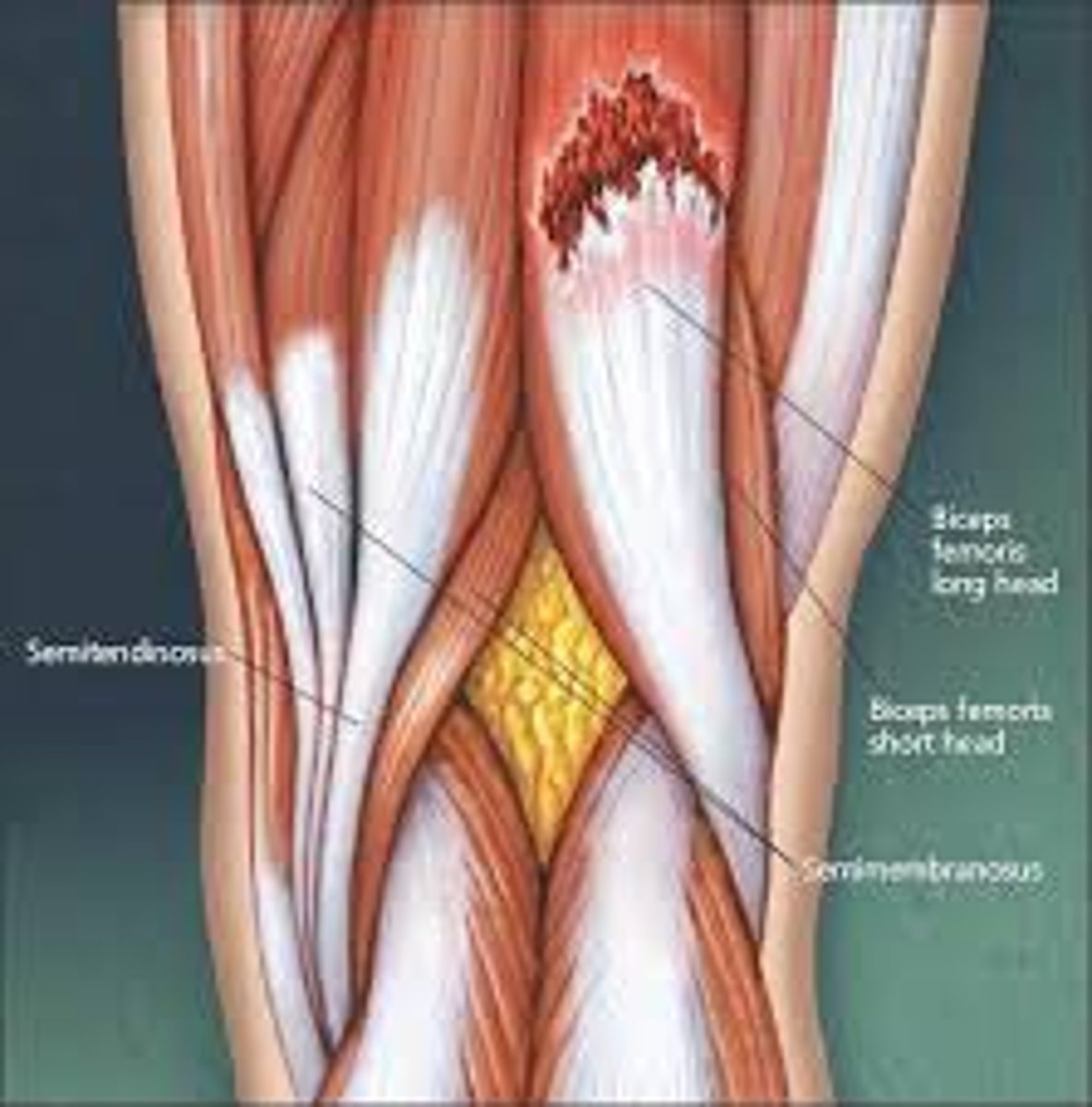
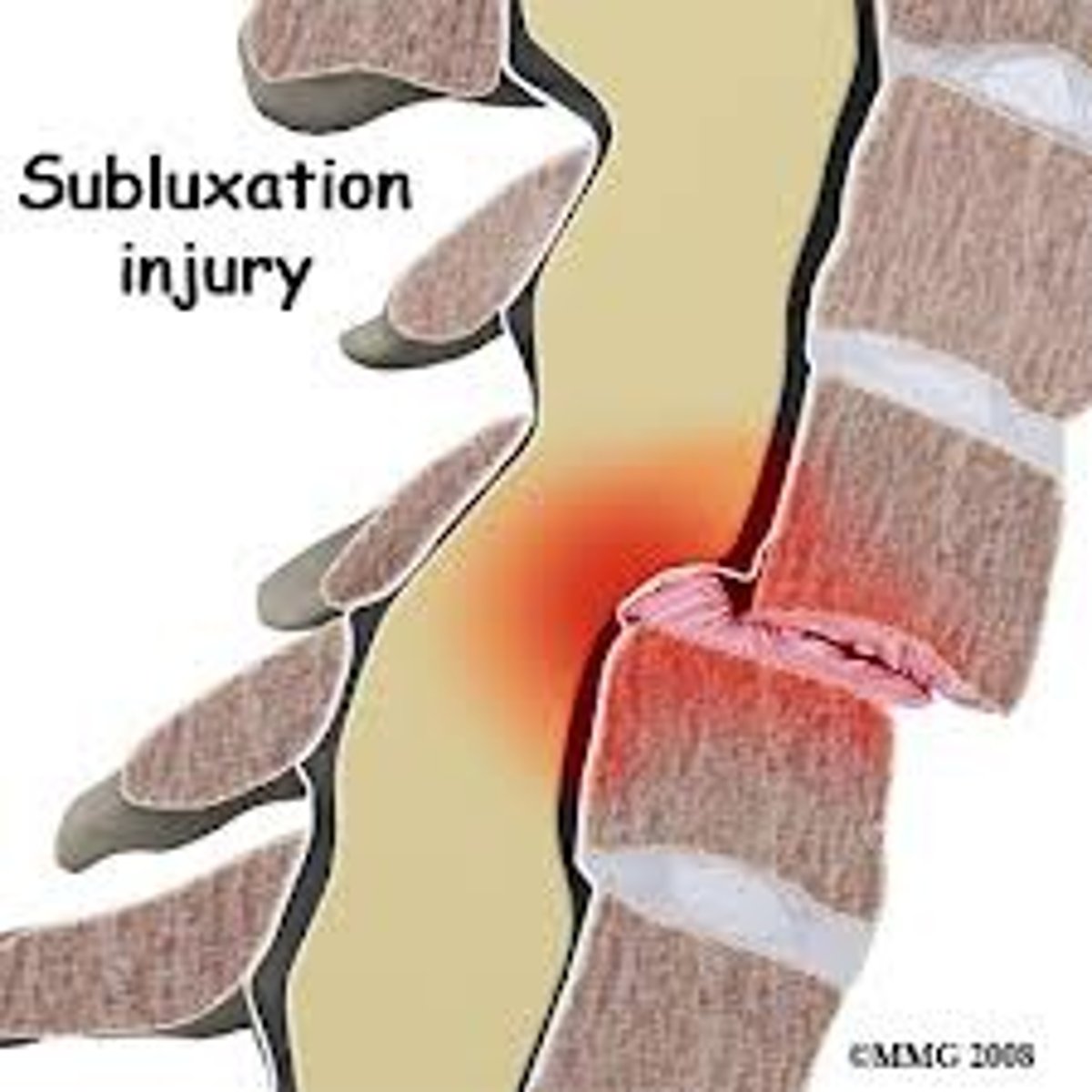
Subluxation
Incomplete or partial dislocation of a joint