Nervous system development
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Developmental stages in utero
Preembryonic period: conception -2nd week
Embryonic period: 3rd - 8th week
fetal period: 9th - 38th week (birth)
Preembryonic period
~3 days after fetilisation
morula (sphere of cells)
enters the uterus
cavity opens in sphere
now called blastocyst
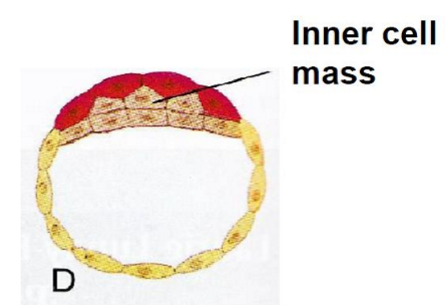
Preembryonic period cont.
blastocyst implants into endometrium (lining of uterus) at end of 1st week
2nd week
blastocyst completely implanted
inner cell mass develops into embryonic disc
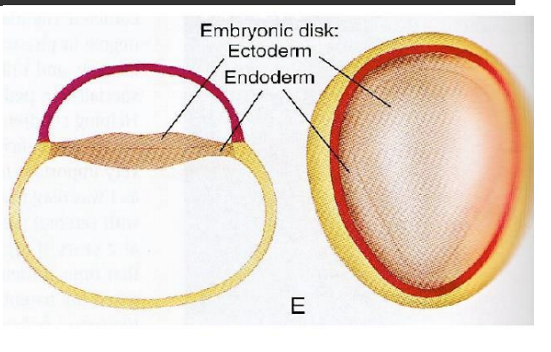
Embryonic disc initially divides into
Ectoderm
Endoderm
2 key phases of embryonic period
neural tube formation
when ends of tube close, brain formation begins
Neural tube formation 1
Embryonic disc becomes trilaminar
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
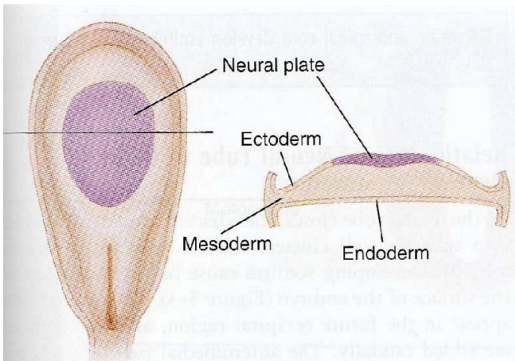
Ectoderm
thickens and forms neural plate
gives rise to nervous system
Mesoderm
gives rise to cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, urinary and reproductive systems
Endoderm
gives rise to respiratory and gastrointestinal system
Neural tube formation 2
About day 18 neural plate forms neural groove
edges of neural plate fold toward each other until they meet and form neural tube
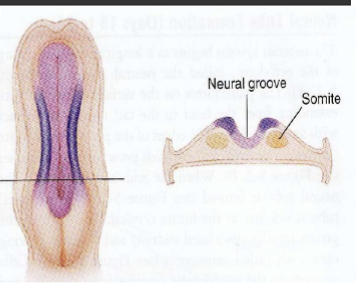
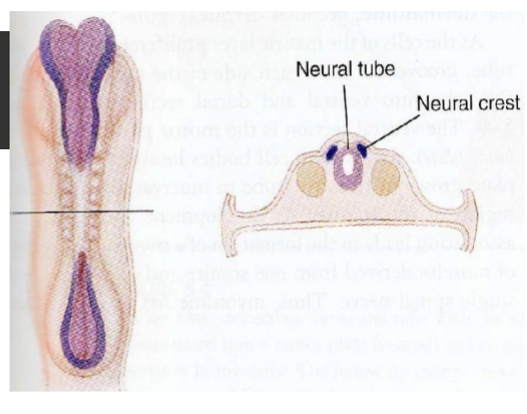
Neural tube
will form brain and spinal cord
2 open ends = neuropores, rostral and caudal
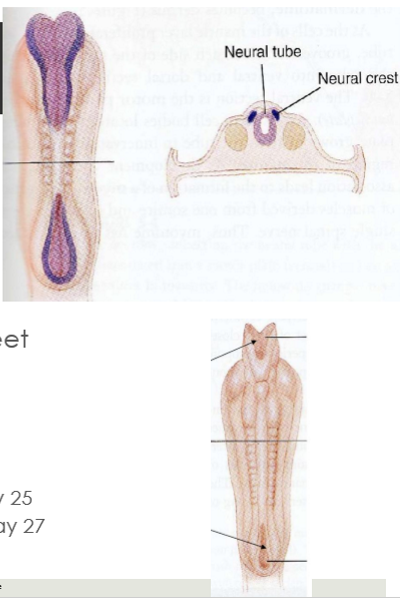
Rostral end of neural tube develops into
The brain
closes about day 25
Caudal end of neural tube develops into
The spinal cord
closes about day 27
Neural crest
cells beside neural tube separate from tube & remaining ectoderm to form neural crest
will form most of PNS
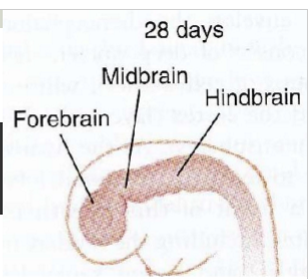
Brain formation during week 4 (after neuropore closure)
enlarged region develops
hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
midbrain (mesencephalon)
forebrain (prosencephalon)
Central canal of neural tube becomes ventricular system
choroid plexus develops for production of CSF
Rhombencephalon divides into
myelencephalon (medulla)
metencephalon (pons and cerebellum)
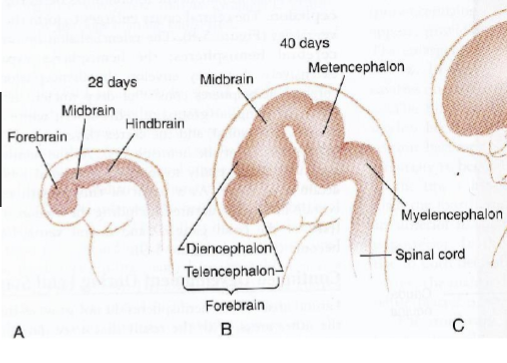
Mesencephalon
Midbrain
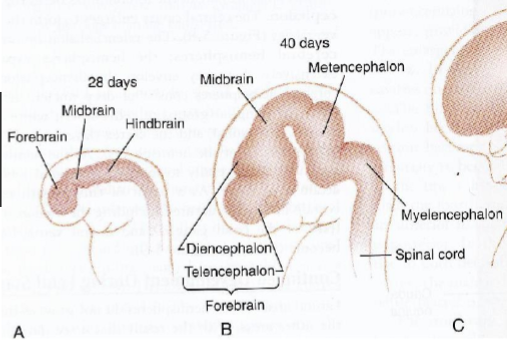
Prosencephalon divides into
diencephalon (inc. thalamus & hypothalamus)
telencephalon (inc. cerebral hemispheres)
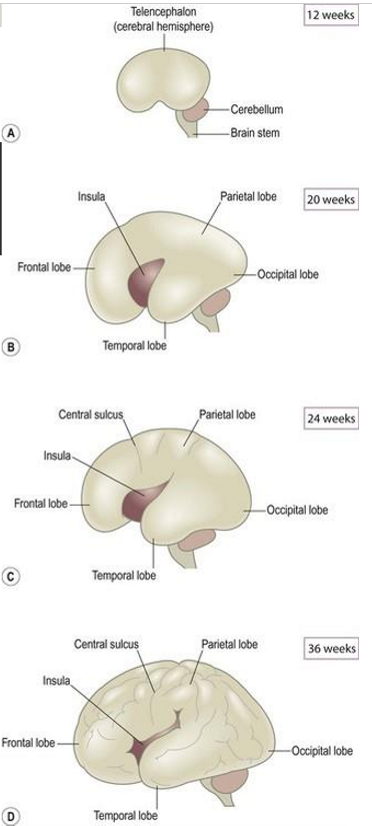
Fetal period
nervous system develops more fully
4th month - few years after birth: myelination
20 weeks: brain begins to convolute from smooth cortex
24 weeks: gyri and sulci formed
After birth
most rapid brain growth (0-2 years)
myelination continues during first few years
pruning (removing synapses that are no longer helpful)
Fluid-filled cavity of neural tube evolves into
Ventricular system
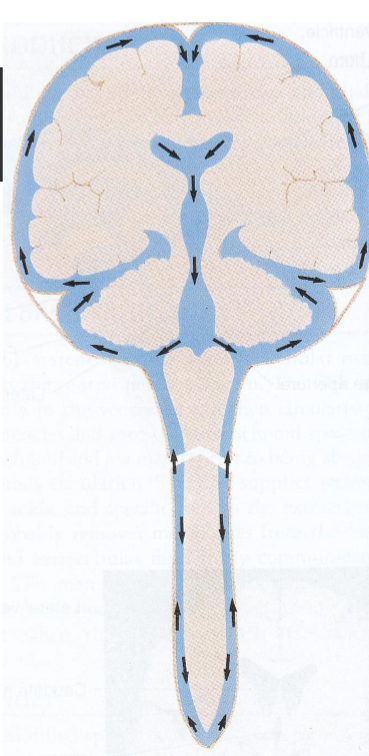
Ventricular system
Contains CSF
Provides buoyancy and protection to the brain
clear colourless fluid
circulates through nervous system
continually produced and reabsorbed within the brain
replaced up to 4x/day
produced by choroid plexus
Cerebral ventricles
Interconnected system of 4 cavities:
2 lateral ventricles
1 in each hemisphere
largest, courses through all 4 lobes
3rd ventricle
behind lateral ventricles, top of brainstem
4th ventricle
between cerebellum & pons
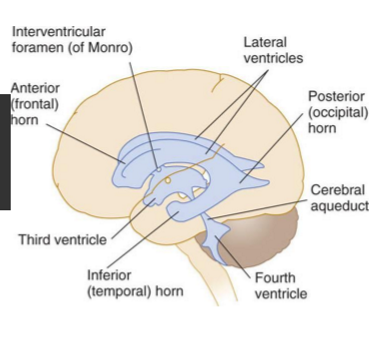
Lateral and 3rd ventricle connected by
intra-ventricular foramen
3rd and 4th ventricle connected by
cerebral acqueduct
Flow of CSF
Flows in 1 direction over brain surfaces
lateral ventricles >
3rd ventricle >
4th ventricle >
foramina (openings) >
subarachnoid space >
circulates around brain and spinal cord >
reabsorbed through arachnoid villi/granulations (project into venous sinuses)
Causes of congenital abnormalities
genetic factors affecting development including chromosomal abnormalities
environmental teratogens (e.g. drugs, chemicals) that cause developmental defects
Abnormal embryonic development
anencephaly
spina bifida
hydrocephalus
chromosomal abnormalities - Down Syndrome and Fragile X Syndrome
Critical period for brain development
3 -16 weeks gestation
particularly when neural tube and neural crest form
Anencephaly
defective fusion of neural tube
cranial (rostral) end of neural tube remains open and forebrain doesn’t develop
most die before birth, almost none survive more than 1 week after birth
causes: e.g. maternal nutritional deficiencies (folic acid), chromosomal abnormalities
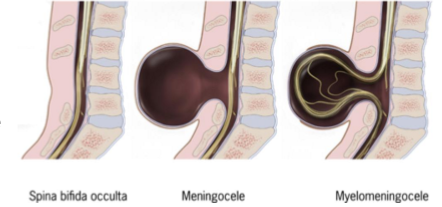
Spina bifida
defective fusion of neural tube
caudal end of neural tube remains open > results in malformation of lower spinal cord
variable severity: asymptomatic (occulta - no visible sign) > paralysis of lower limbs
folic acid supplements reduce incidence of neural tube defects by about 70%
Hydrocephalus
enlargement of ventricles due to CSF accumulation
raised intracranial pressure > progressive brain damage
Types:
obstructive hydrocephalus
communicating hydrocephalus
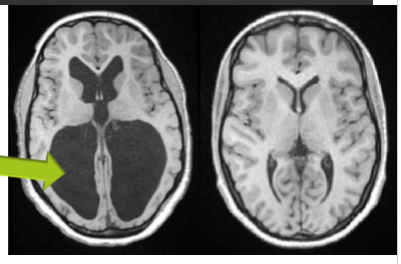
Obstructive hydrocephalus
Occlusion of CSF drainage channel > dilation above blockage
Communicating hydrocephalus
Inadequate reabsorption of CSF or excessive CSF production > dilation of entire ventricular system
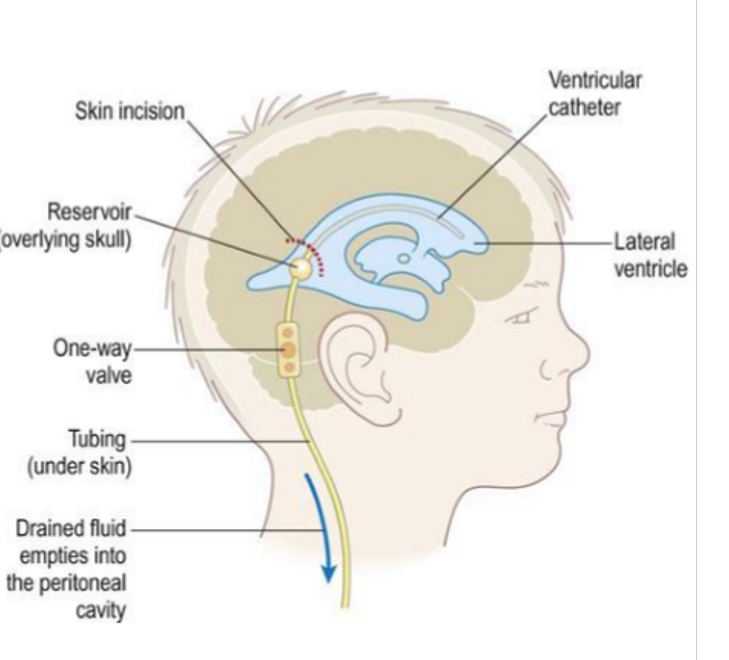
Hydrocephalus treatment
shunt (one-way valve) in ventricle, excessive CSF drained to abdominal area, needs frequent replacement
Down Syndrome (trisomy 21)
Extra copy of chromosome 21
Characteristics may include:
cognitive impairment
small, flattened skull
short and flat nose
short fingers
small oral cavity, large tongue, low tone of tongue and lips - language development or speech production can be affected
Fragile X Syndrome
X-linked recessive syndrome
expressed much more frequently in males
characteristics include:
cognitive impairment
long and narrow face with large ears
high-arched palate - can affect speech and language development