Cell cycle for eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What occurs during interphase?
Replication of DNA and organelles
Mass of DNA 2x
Mass of cell 2x
Checks the DNA for errors and replicates errors
longest stage of cell cycle
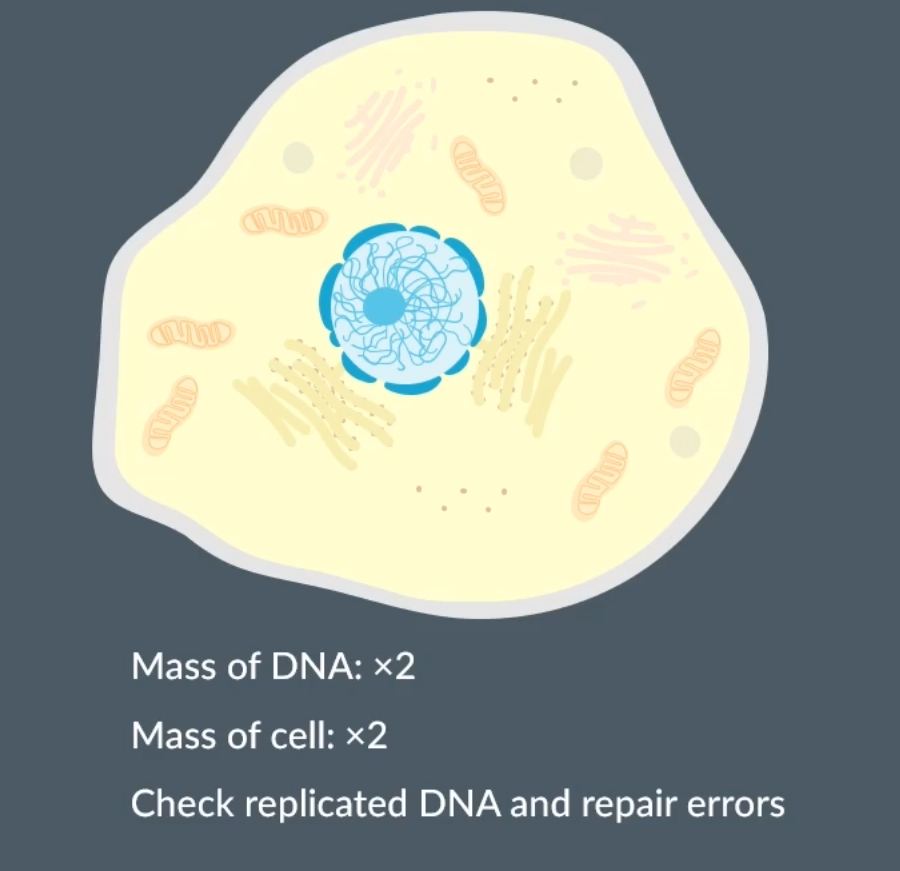
The specific three stages in interphase
The G1 phase where protein synthesis occurs
The S phase where DNA replication
The G2 phase where preparation for mitosis
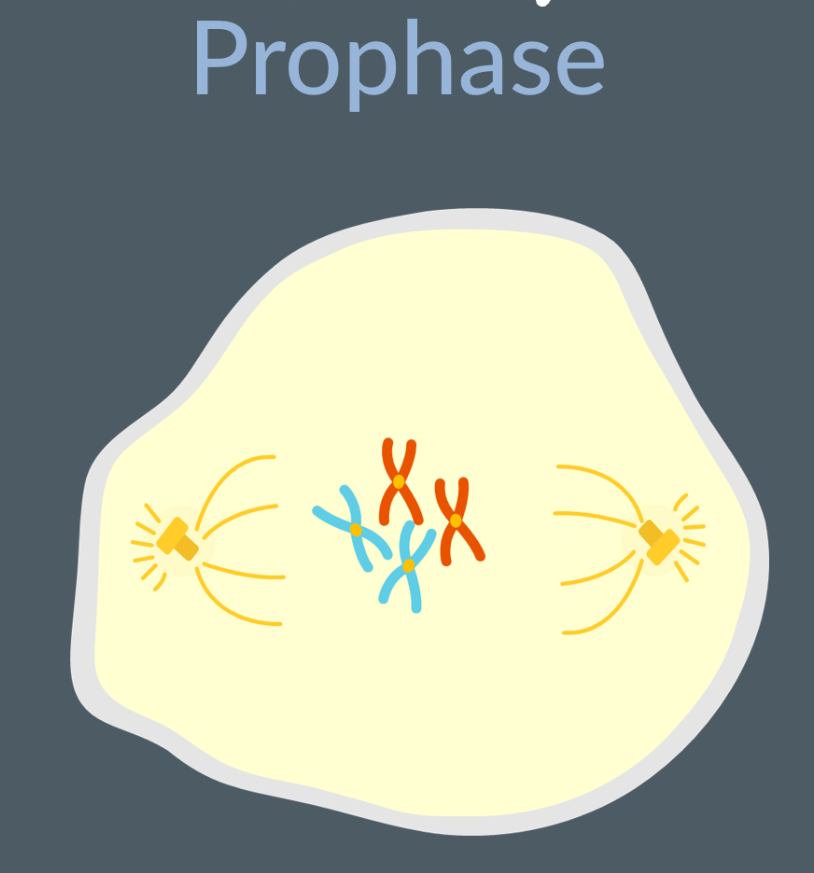
What occurs in prophase?
chromatin condenses into compact chromatin, which are visible. These are arranged as pairs of chromatids with a centromere.
The nucleolus disappears.
The nuclear envelope breaks down.
Spindle fibers form (in animals happens at centrosomes, plants do not have centrosomes, but still form spindle fibres).
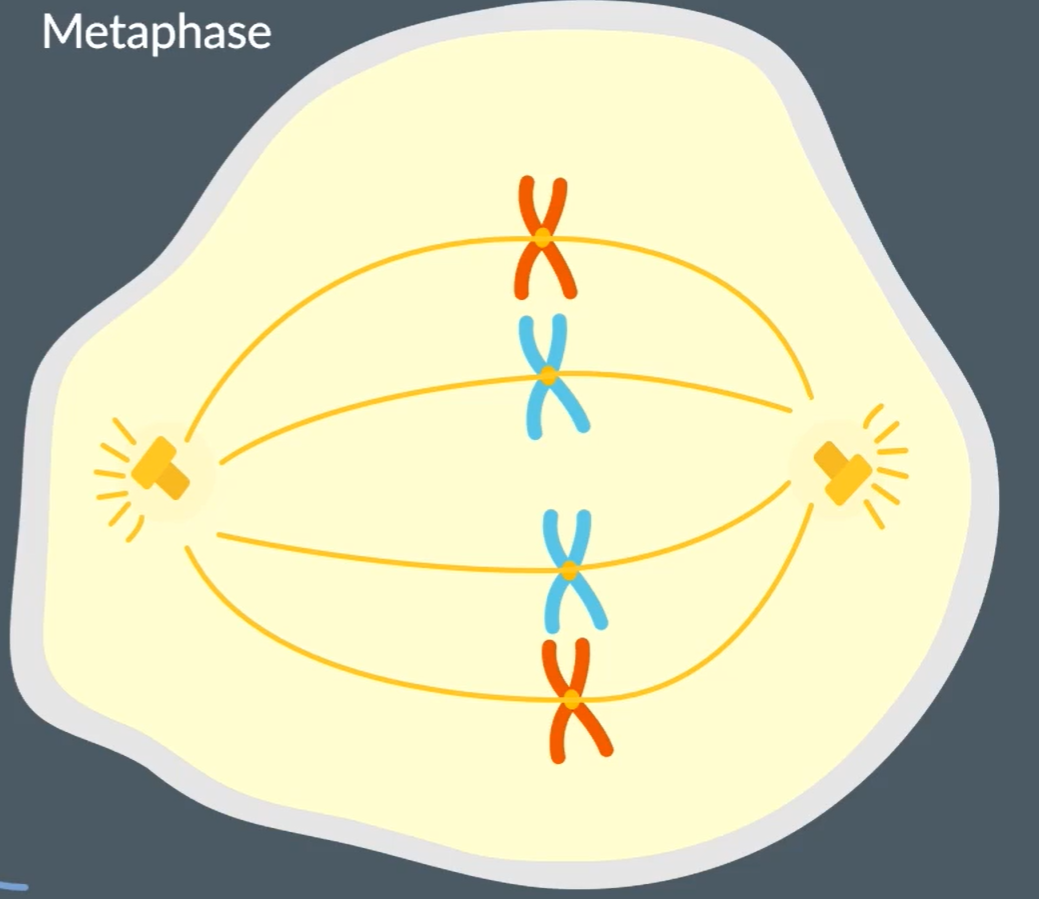
What occurs during Metaphase?
Spindle fibers attach to the centromeres of the chromosomes and allign the chromosomes at the equator of the cell.
Each sister chromatid is attached to the opposite pole
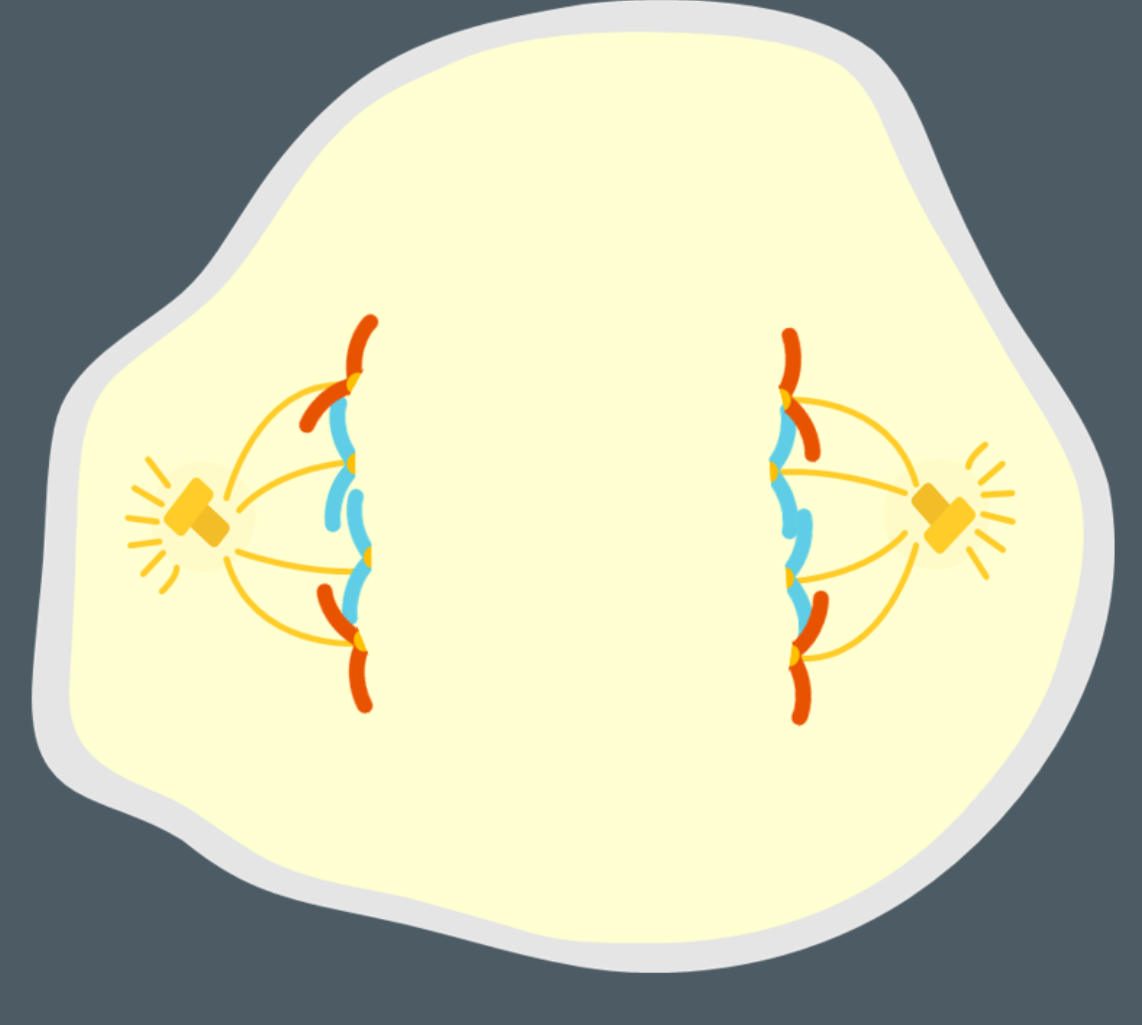
What occurs during Anaphase?
The spindle fibers shorten causing the sister chromatids to pull to opposite sides of the cell.
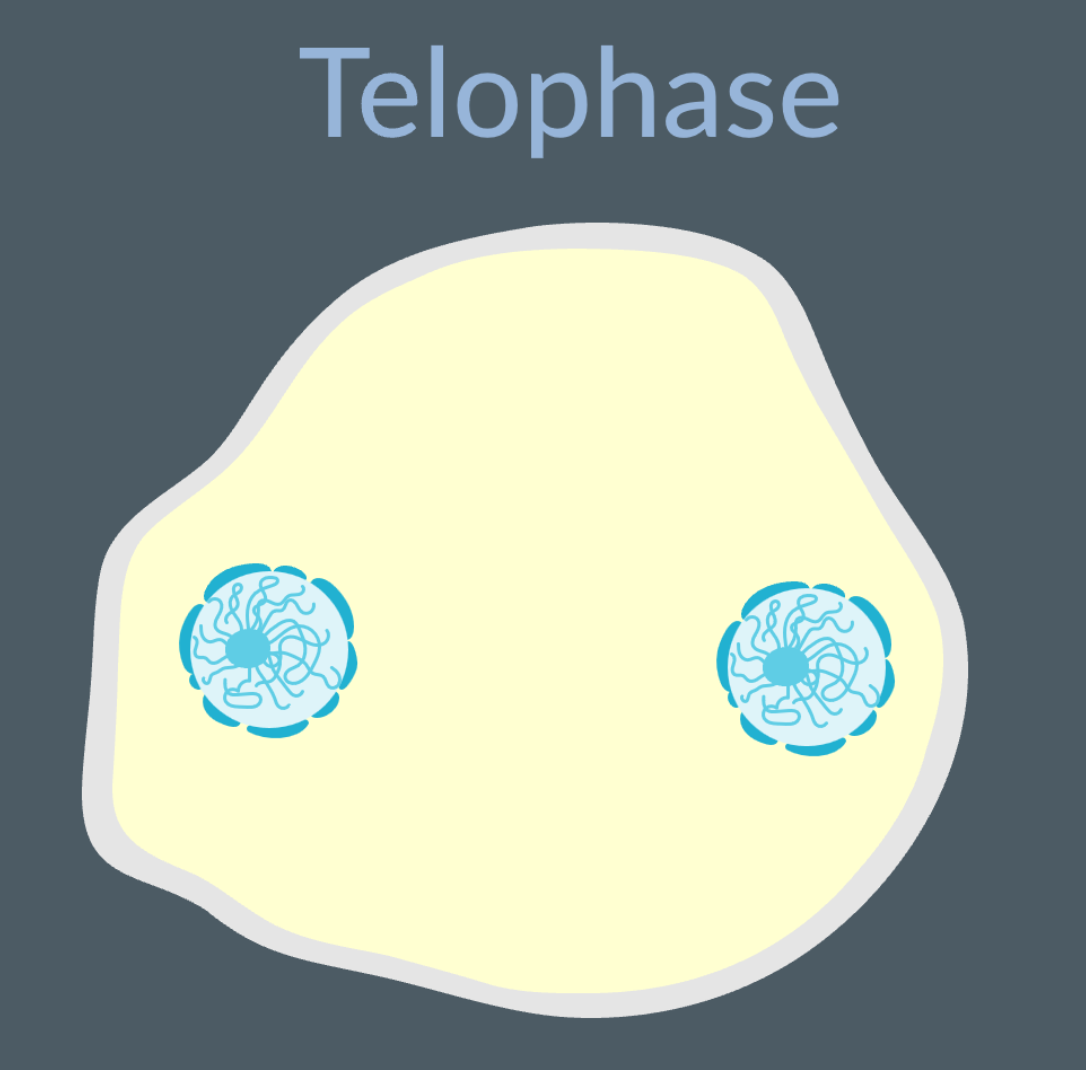
What occrus during telophase?
The chromotids reach at the poles of the cell, and decondense into chromatin.
Nucleoulous reforms
nuclear envelope reforms
The spindle fibres breakdown
Two genetically identical nucleus
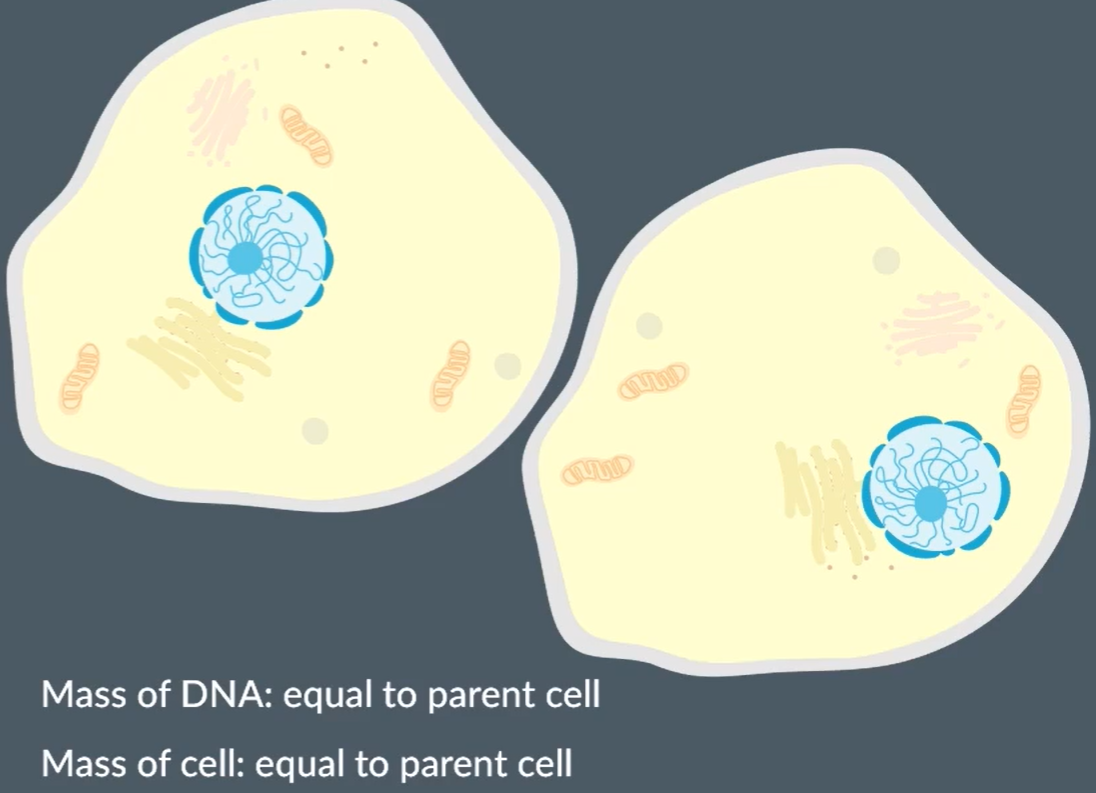
What is cytokenesis?
When the cytoplasm divides to form two genetically identical daughter cells.
The mass of both of these cells are the same
What is the order of the stages in cell cycle?
Interphase
G1
S
G2
Mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokenesis
The importance of mitosis
Growth: responsible to form a multicellular organism from a single zygote
Repair: to replace damaged cells from genetically identical cells
Reproduction: It is a form of asexual reproduction
Immune system: Production in large numbers of white blood cells
What is mitotic index?
The total number of cells undergoing mitosis (so only in the prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) divided by the total number of cells in sample.
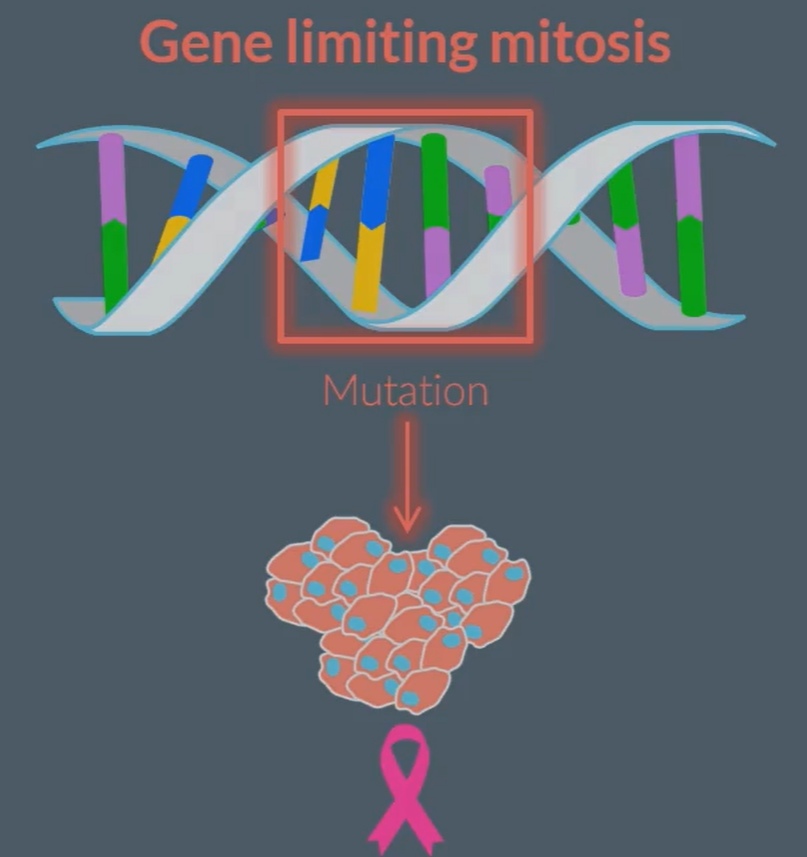
The role of mitosis in cancer:
Rate of mitosis is controlled by certain genes, if these cells mutate then this can cause cell division to be uncontrolled leading to tumors and possibly cancer.
Treatments of cancer:
chemotherapy drugs can effect the interphase, preventing the DNA from replicating, or distrupt prophase to prevent spindle fiber formation.
However, it can distrupt normal cells as well.
Since, cancer cells divide much faster than normal cells this treatment is still effective
can cause side effects
How do bacteria undergo binary fission?
Prokaryotics single circular DNA is replicated. Additionally, if there are any plasmids present they are also replicated.
The cytoplasm divides, forming two genetically identical prokaryotes. They may have different number of plasmids, but the same circular DNA.
How do viruses replicate?
Trick question!!
Viruses are particles, not cells, so they do not undergo cell division.
They instead inject nucleaic acid into the hosts cell, and rely on the infected host to replicate the particle.