GI physiology 4: ruminants & hindgut fermenters
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
What are the 2 ways to break down food?
digestive and fermentative
digestive breakdown
digestive enzymes
fermentative breakdown
microbial symbiosis
What microbes are included in the rumen ecosystem?
protozoa
virus
bacteria
fungi archaea
What does the rumen act as?
complex microbial ecosystem facilitating fermentation of plant material
What does microbial fermentation in the rumen unlock?
crucial nutrients and energy sources for the ruminant
What does VFA stand for?
volatile fatty acids
What is the main process of fermentation?
anaerobic bacteria ferment carbohydrates in plant material into short chain fatty acids
What carbohydrates do anaerobic bacteria ferment?
cellulose
hemicellulose
starch
What are products of fermentation?
short chain fatty acids
methane gas
ammonia
B vitamins
Where are short chain fatty acids from fermentation absorbed?
through rumen wall
What provide the main energy source for ruminants?
short chain fatty acids
What do ruminal microbes utilise to synthesise their own protein?
ammonia produced by rumen bacteria
What do ruminal microbes utilise ammonia for?
synthesise own protein
Where do ruminants get proteins from?
microbes when they’re flushed through
Rumen
largest and most important chamber, houses the microbial ecosystem and performs majority of fermentation
Reticulum
has muscular walls that contract and relax, mixing rumen contents and aiding regurgitation for chewing
Omasum
absorbs water and electrolytes
further breaks down feed particles
sorts material for passage to abomasum
Abomasum
true stomach
glandular lining similar to monogastric animals
secretes digestive enzymes acids to digest protein and prepare digesta for further absorption in the SI
What techniques are used to study the motor patterns in ruminants?
endoscopy
balloon manometry
electro-myography
cine-radiography
Why is the motor pattern in ruminants studied extensively?
commercial pressure to understand ruminant
What is the rumen critically dependent on?
ANS - especially vagus nerve
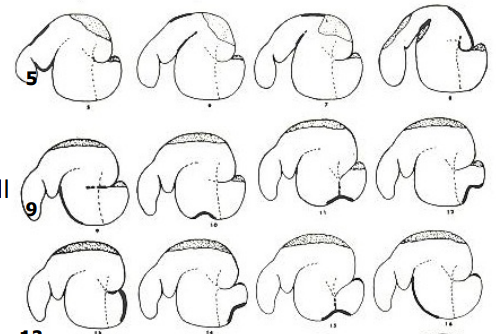
What is the shaded area in the dorsal sac and dorsal blind sac?
gas cap
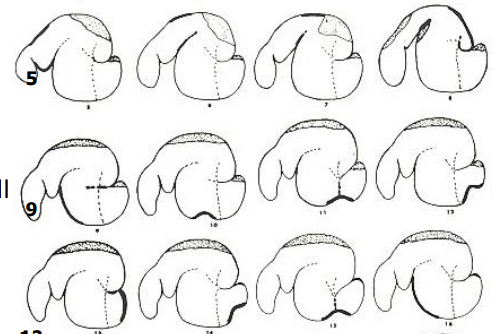
What are the thin dotted lines?
pillars of the rumen
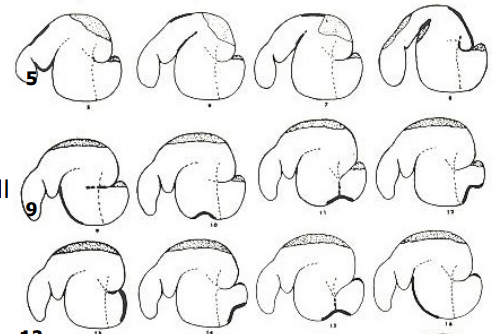
What does the heavy line in each tracing indicate?
actively contracting portion of wall
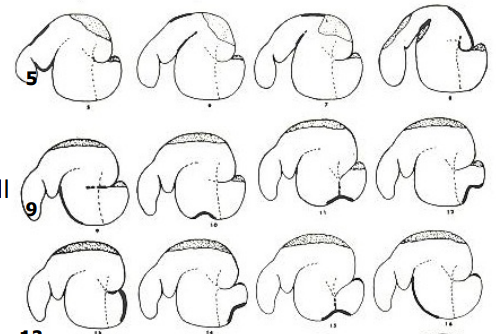
Why is the gas cap clinically significant?
risk of bloat if not removed
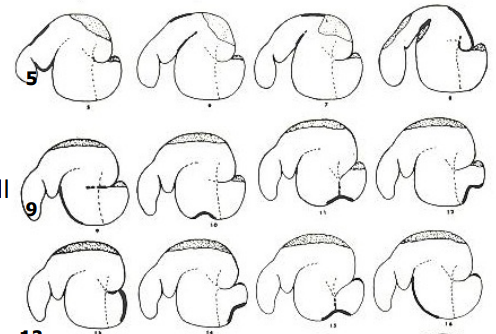
What are these images?
tracings from radiographs
What are the 2 types of contractions of the rumen?
primary and secondary
How frequent are primary contractions (of rumen)?
1-1.5/min in cattle (>in sheep)
What happens to primary contractions if the ruminant is fed more food?
stronger contraction
What is the primary purpose of primary contractions (of rumen)?
mixing
What does the strength of primary contractions (of rumen) correlate with?
rumen fill
Under what circumstances are primary contractions (of rumen) absent?
deep sleep and/or illness
Where do primary contractions begin?
reticulum and sweeps aborally (peristaltic)
What pattern of movement do primary contractions (of rumen) have?
figure of 8 (sweeps fibrous mat from front to back and sets up figure of 8 pattern of movement)
How frequent are secondary contractions (of rumen)?
about half primary contractions followed by secondary contraction
When are primary and secondary contractions (of rumen) 1:1?
high fermentation rate
What is the primary purpose of secondary contractions (of rumen)?
moves gas cap forwards to clear cardia and allow eructation of gas
Are secondary contractions (of rumen) strong or weak?
relatively weak
Where do secondary contractions (of rumen) begin?
caudal sac and moves forwards (anti-peristaltic)
What is motility reduced by?
stress and pain
What does cutting the vagus nerve in a ruminant do?
abolished coordinated reticuloruminal motility
What is rumination a key diagnostic indicator of?
well-being
In a ruminant, when does chewing occur?
during eating (mastication) and rumination
What dictates the ratio of eating to rumination?
diet
Why is mastication & rumination time consuming?
ruminants consume large mass of plant material per day
plant material hard/tough
Why does eating time decrease with increased crude fibre in diet?
higher CF → slower fermentation
longer retention → reduced drive to eat
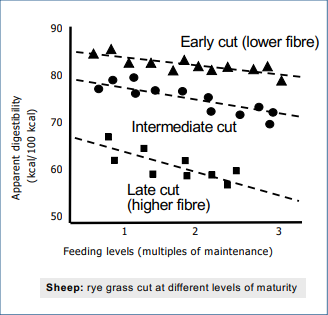
What effect does feeding rate have on digestibility?
increased feeding rate reduces ‘apparent digestibility’
Why does increased feeding rate reduce ‘apparent digestibility’?
as feeding rate increases, time spent in gut reduces
less rumination
less fermentation
less of the energy in food is released
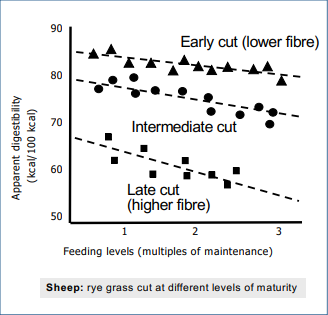
In what food is it more pronounced that increased feeding rate reduces ‘apparent digestibility’?
food that’s harder to digest (e.g. late cut ‘coarse’ grass)
Eructation
voiding of gas from stomach
What gases does fermentation liberate?
CO2 and methane
How many litres/min of CO2 and methane does fermentation liberate in cattle?
1-2 litres per minute
What is the stimulus of the eructation reflex?
distension rumen
What reflex arc is involved in the eructation reflex?
vago-vagal reflex arc
What effect does the eructation reflex have?
stimulation of secondary ruminal wave
What does failure of the eructation reflex mechanism cause?
bloat or ‘ruminal tympony’
What are causes of bloat?
oesophageal block
foamy gas
liquid covering cardia
inhibition of secondary contraction of rumen
What is the composition of the gas that is voided from the stomach during eructation?
CO2 = 60%
CH4 = 40%
What are the steps of eructation?
secondary ruminal wave
oesophagus fills
rapid antiperistalsis
voided through nares
What percentage of eructated gas is inhaled by cows?
50%
What can cows inhaling 50% of eructated gas lead to?
milk taint
What are the 2 types of carbohydrates digested?
alpha-bonded - starch
beta-bonded - cellulose
What type of carbohydrate makes up the bulk of plant carbohydrate?
beta-bonded ‘structural carbohydrate’
Name examples of beta-bonded ‘structural carbohydrates’ found in plants?
cellulose
hemicellulose
pectin
What do anaerobic microbes hydrolyse beta-bonds by?
fermentation
Can mammalian enzymes hydrolyse beta-bonds?
NO
What is glucose found as in tissues?
CO2
glycogen
fatty acids
triacylglycerol
What tissues is CO2 found in?
muscles, etc
What tissues is glycogen found in?
liver, muscle
What tissues are triacylglycerols found in?
liver, fat
What are examples of short chain fatty acids (VFA) in blood?
acetate
propionate
butyrate
ketone bodies
What is acetate converted into in tissues?
triacylglycerol
CO2
What process is propionate converted into glucose and glycogen via?
gluconeogenesis
What is propionate converted into to be found as in tissues?
glucose
glycogen
What are butyrate and ketone bodies found as in tissues?
triacylglycerol
CO2
How many carbons does acetate have?
2
How many carbons does propionate have?
3
How many carbons does butyrate have?
4
What 3 factors influence fermentation?
substrates
microbes
conditions
What substrates influence fermentation?
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins
What microbes (bacteria, protozoa & fungi) influence fermentation?
substrate preferences
tolerance to conditions
What are the conditions that influence fermentation?
pH
substrate concentrations
Are beta-linked carbohydrates soluble or insoluble in rumen fluid?
insoluble
Are starches soluble or insoluble in rumen fluid?
soluble
What are starches found highly in?
cereals
What are starches found low in?
grasses
What is the pH of the rumen?
5.5-7
How can changes in diet alter conditions for fermentation?
alters substrates
change in balance of microbes
alters end products, substrates, pH, etc
What does relative abundance of bacteria reflect? (conditions for fermentation)
rate of growth/division
What can change the stability of the complex network of inter-dependency with & ratios of bacteria and protozoa?
food type

What does this equation show?
methanogenesis
In the USA, what are antibiotics against methogenic bacteria used for?
reduce loss via methane in beef production
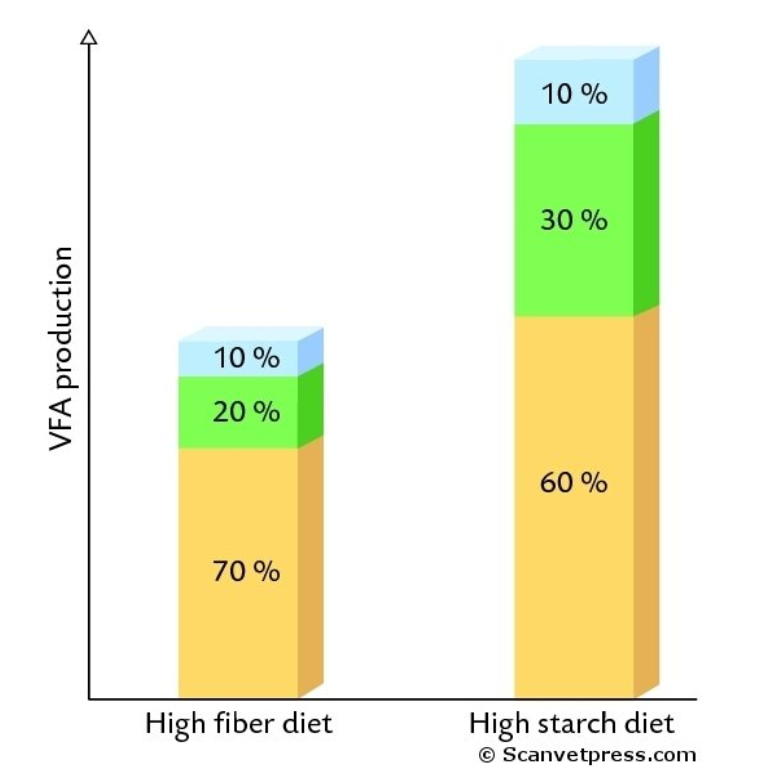
What does the blue represent?
butyrate
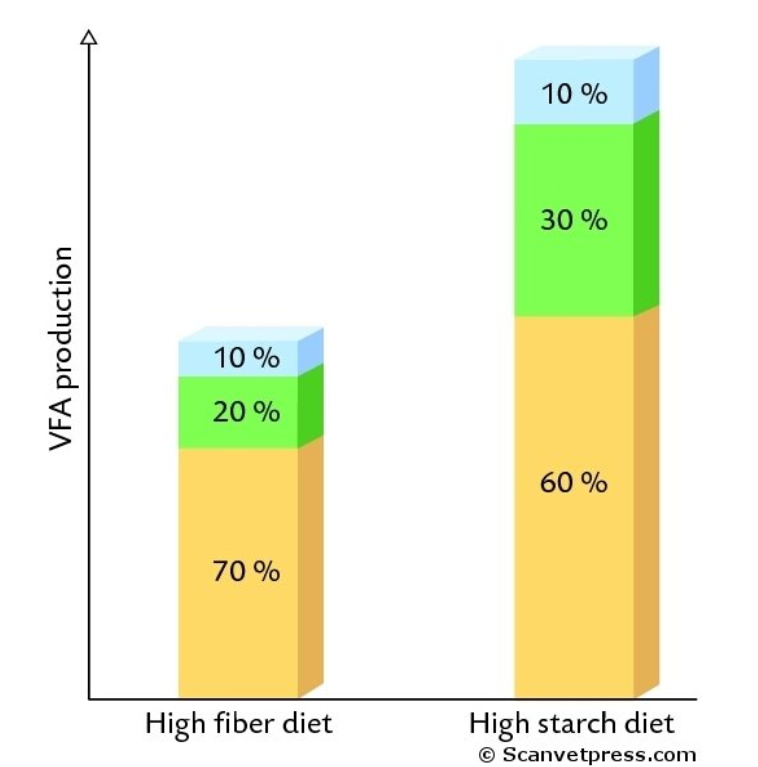
What does the green represent?
propionate
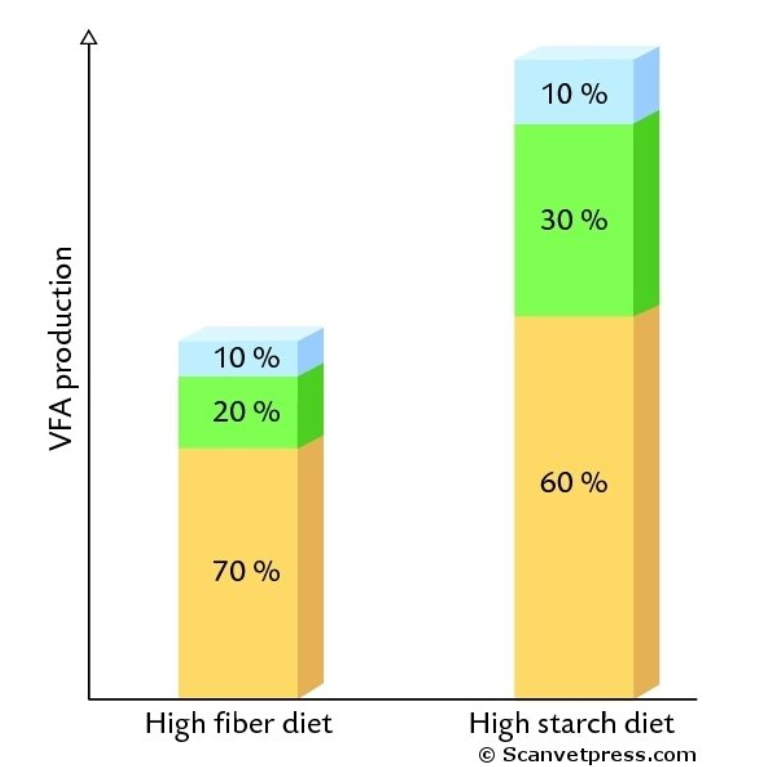
What does the orange represent?
acetate
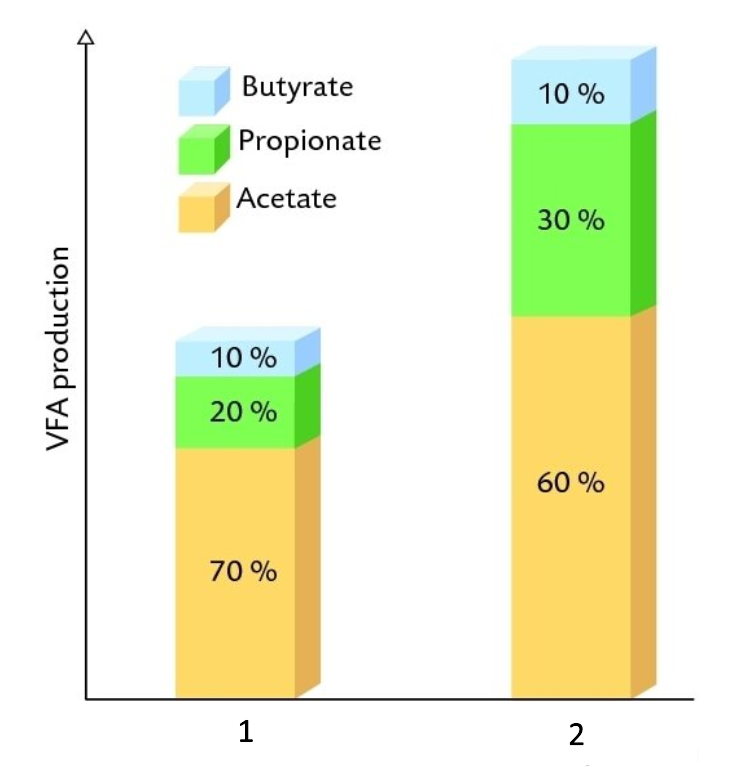
What kind of diet is 1?
high fibre diet
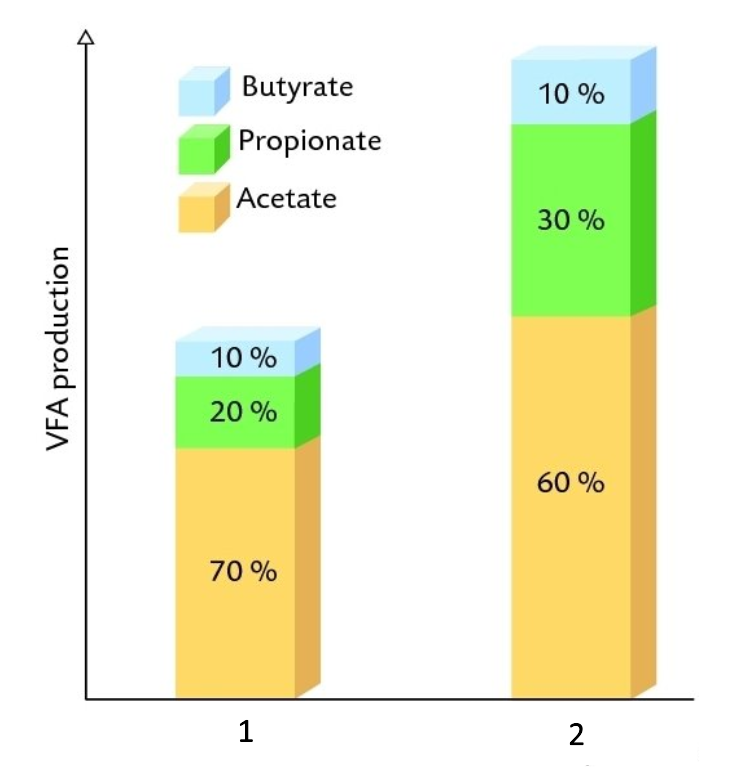
What kind of diet is 2?
high starch diet
What is ammonia produced during?
breakdown of amino acids (from dietary protein and fermentation of urea)
What is ammonia produced by?
rumen bacteria