L6 - Secondary glass processing
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Toughened glass & Laminated glass - how they break. Coatings and colourants. Principal glass types
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the finishing processes done to glass?
Toughening or tempering
coating
How is toughened or tempered glass made?
Stronger than ordinary window glass
By introducing stress through rapid heating & cooling of glass surface
Resistant to breaking under stress
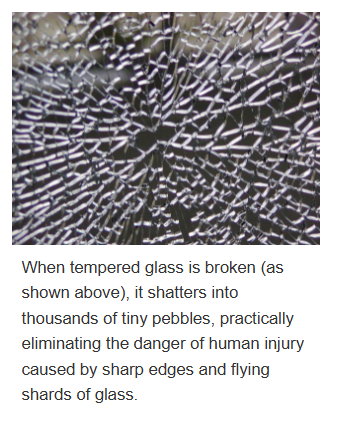
How does tempered glass break?
does not shatter
fragments into small squares
with little splintering
= small blunt pieces reduces risk of serious injury
What is laminated glass?
One layer of plastic
Sandwiched between two layers of glass permanently bonded with a tough, clear polymer interlayer, such as PVB.
Used in automotive windshields
How does laminated glass break?
it cracks in a "spiderweb" pattern, with the broken glass shards remaining stuck to the inner polymer layer.
the outer layers of glass break but are held together by the strong, adhesive plastic interlayer (PVB)
No sharp shards = safety
Continued cracking: Over time, the cracks can spread further as more stress is applied to the damaged glass.

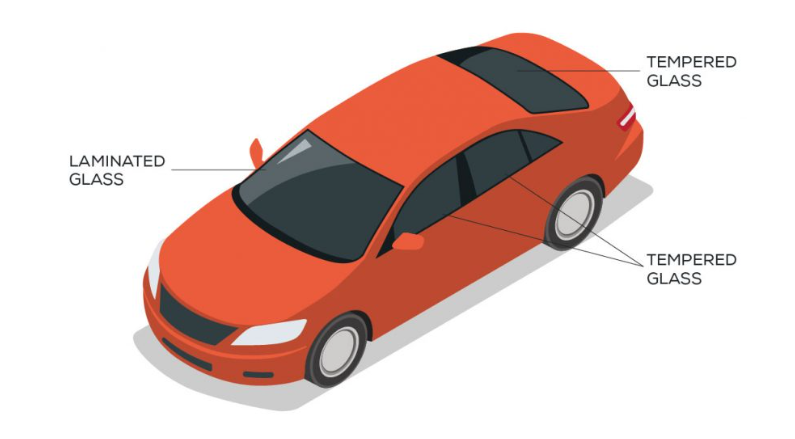
Where is toughened glass used in automotives?
Rear & side windows
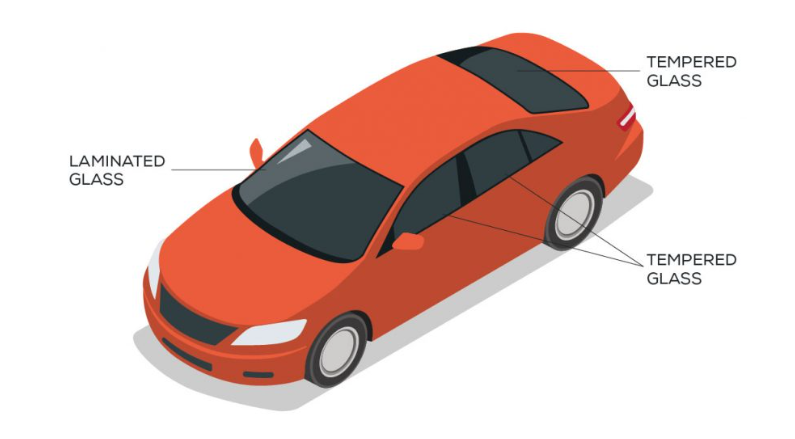
Where is laminated glass used in automotives?
Windscreens
Why is coating used for glass?
Decoration
Protection
Strengthening
How is coating applied ?
= 2 stages
Hot end coatings
Cold end coatings
When is hot end coatings applied?
Applied just after the glass has left forming machine
Compounds of tin or titanium
When is cold end coatings applied?
Applied just before the annealed glass leaves lehr
Organic waxes, polyethylene emulsions, polyethylene glycols, fatty acid esters, fatty acids
What is the natural colour of glass?
Unless raw materials (silica etc.) very pure
Resultant glass normally has green tint
Primarily caused by iron oxide
Has effect in 1 in 1000 part
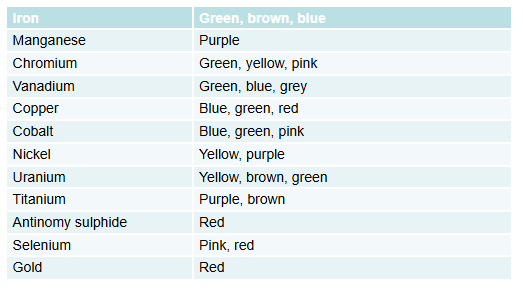
What are the colourants used in glass?
What are the principal glass types?
Fused Silica
Soda lime silicate glasses
Borate silicate glasses
Lead glass
Aluminosilicate glasses
Alkali barium silicate glasses
Borate glass
Phosphate glass
What is fused silica glass?
Silica can be melted and cooled to form glass
Very high processing temperatures
Products
Good temperature resistance
Low thermal expansion
Hence good resistance to thermal shock
Excellent chemical durability
What is soda lime silicate glass?
Silica (SiO2) Soda (Na2O) & lime (CaO)
Used in wide range of applications
Containers, flat, domestic glassware
Greatest tonnage for containers (bottles and jars)
Container glass is made in three colours:
White (also known as flint)
Green
Amber
What is borate silicate glass?
Mainly silica and boric oxide (B2O3) + smaller amounts of alkalis and aluminium oxide
Good chemical stability
Low thermal expansion
Good resistance to thermal shock
Used in kitchenware, laboratory glassware
What is lead glass?
Lead oxide (PbO)
Excellent hand-working and optical properties
Used in manufacture crystal glass
Over 24% PbO can be described as Lead Crystal [European Directive 69/493]
What is insulating lead glass?
Good insulating and dielectric properties
Lead oxide + potassium and sodium oxides
What is optical glass?
Lead imparts high refractive index without colouring glass
What is Aluminosilicate glasse?
Small but important group of glasses
Contain 20% aluminium oxide (alumina Al2O3)
Often include calcium and magnesium oxides
small amounts of boric oxide
Very small amounts of soda or potash
Able to withstand high temperatures with good resistance to thermal shock
Applications: combustion tubes, gauge glasses for high pressure steam boilers, envelopes of halogen-tungsten lamps (operate as high as 750oC
What is Alkali barium silicate glass?
Used to shield X-rays (e.g. cathode-ray tubes)
Contain heavy metal oxides
Lead
Barium
Strontium