602 - Clinical correlations: Opioid epidemic 3/26
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
5 causes of the current opioid epidemic
1. Pain as "fifth vital sign" (no improvement in pain control since)
2. Unrealistic pt expectations regarding chronic pain management (nothing can completely ablate pain)
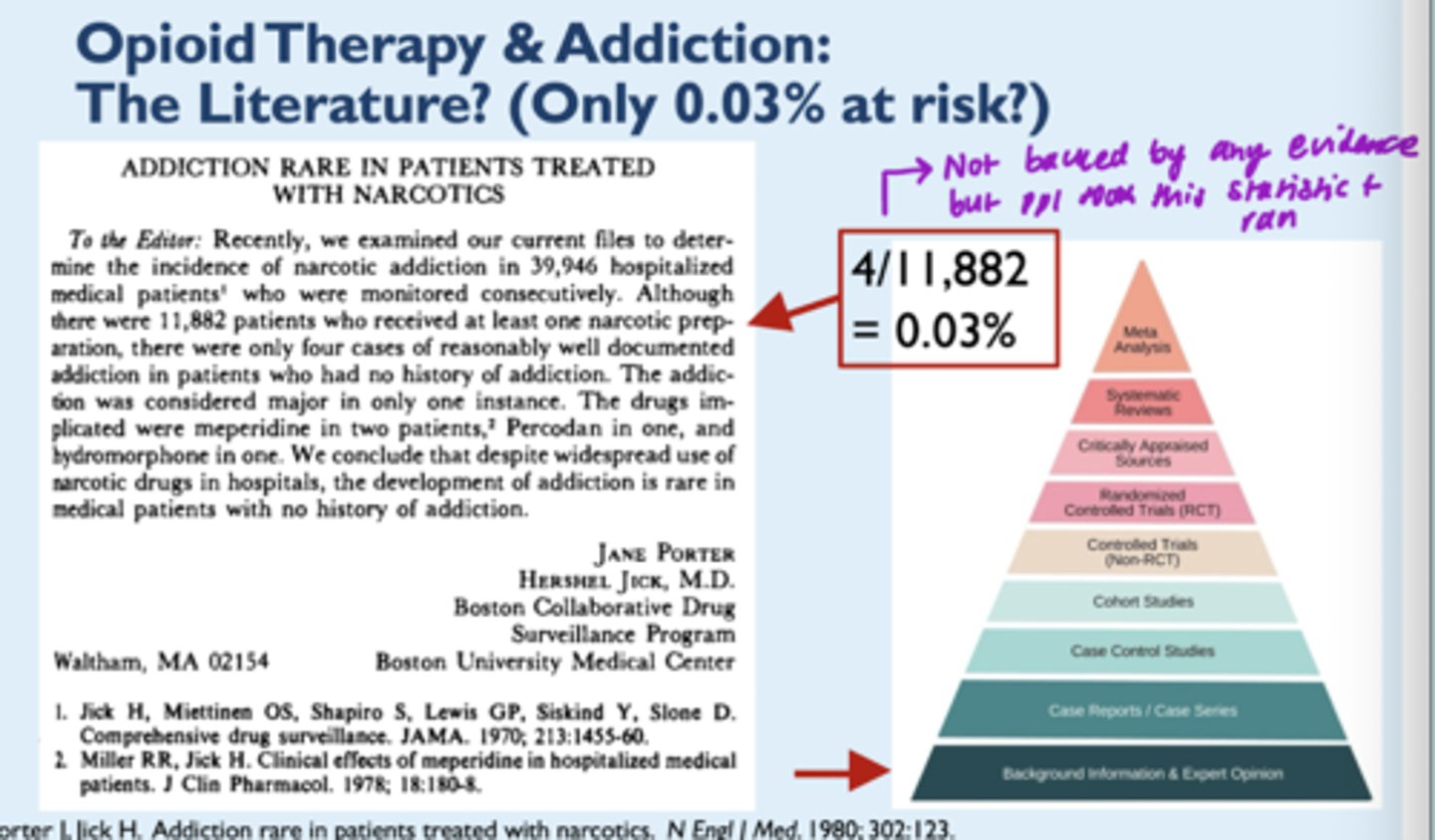
3. Very bad statistics (0.03% dependency rate --> not true)
4. The marketing of OxyContin and Duragesic in the 90's (false assurances of safety)
5. Neuroexcitatory effects of oxycodone, oxymorphone, and hydromorphine
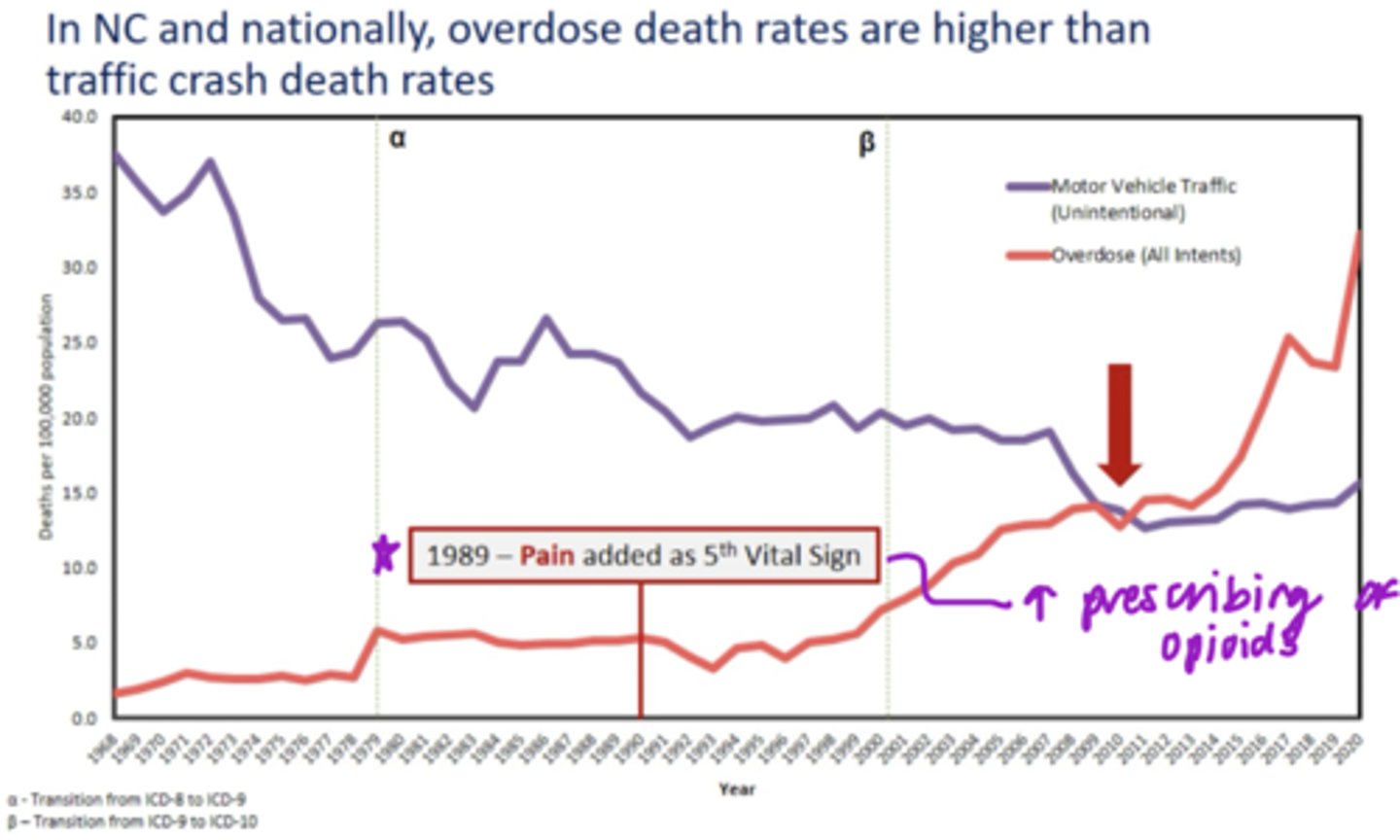
T/F: In NC and nationally, overdose death rates are higher than traffic crash death rates
True
Define misuse
Use of a medication (prescribed for a medical purpose) other than as directed or indicated, whether willfully or unintentionally and whether or not harm results
Define:
- Physical dependence
- Tolerance
- Physical dependence: a state of adaptation that is manifested by a drug-class-specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug or administration of an antagonist
- Tolerance: a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug induces changes that result in the diminished effects of one or more drugs in the body over time
Define:
- Abuse
- Addiction
- Abuse: any use of an illegal drug or the intentional self-administration of a medication for a nonmedical purpose such as altering one's state of consciousness
- Addiction: a primary, chronic, neurobiological disease, with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations; it is characterized by behaviors that include impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm and craving or a combination of these
How did the covid pandemic have an effect on the opioid epidemic?
- Social isolation increases risk for addiction
- Isolation may increase the risk of overdose deaths
Post-pandemic issues:
- trauma era
- following those who regressed
- access to recovery
T/F: we are seeing a decrease in overdose deaths
True
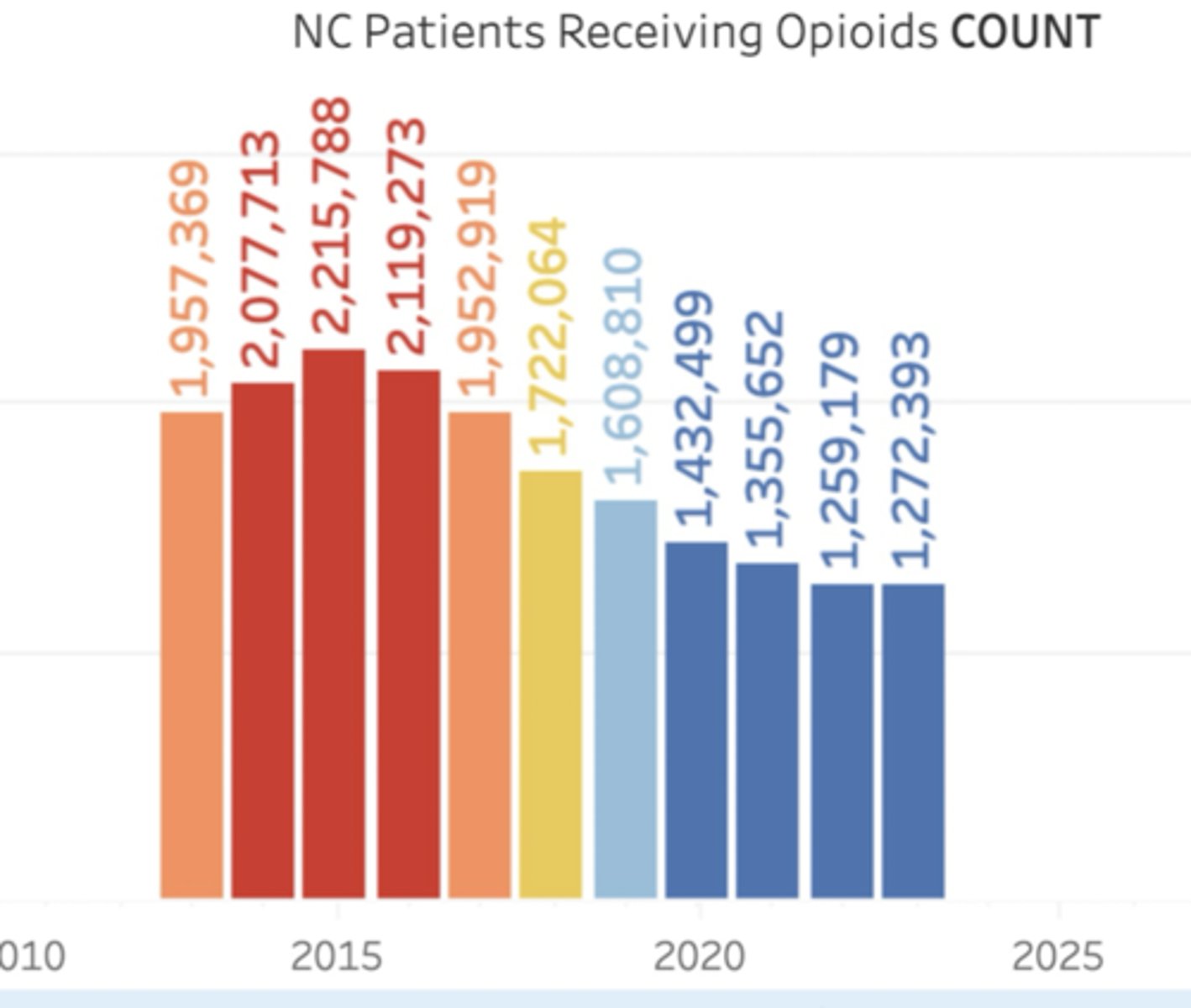
The patients receiving opioids rate in NC was _________ %of residents in 2023
11.9
- going down - ppl becoming aware
T/F: There has been a general increasing trend in opioid prescribing in dentistry over past 10 years
False - decrease (45% decrease)
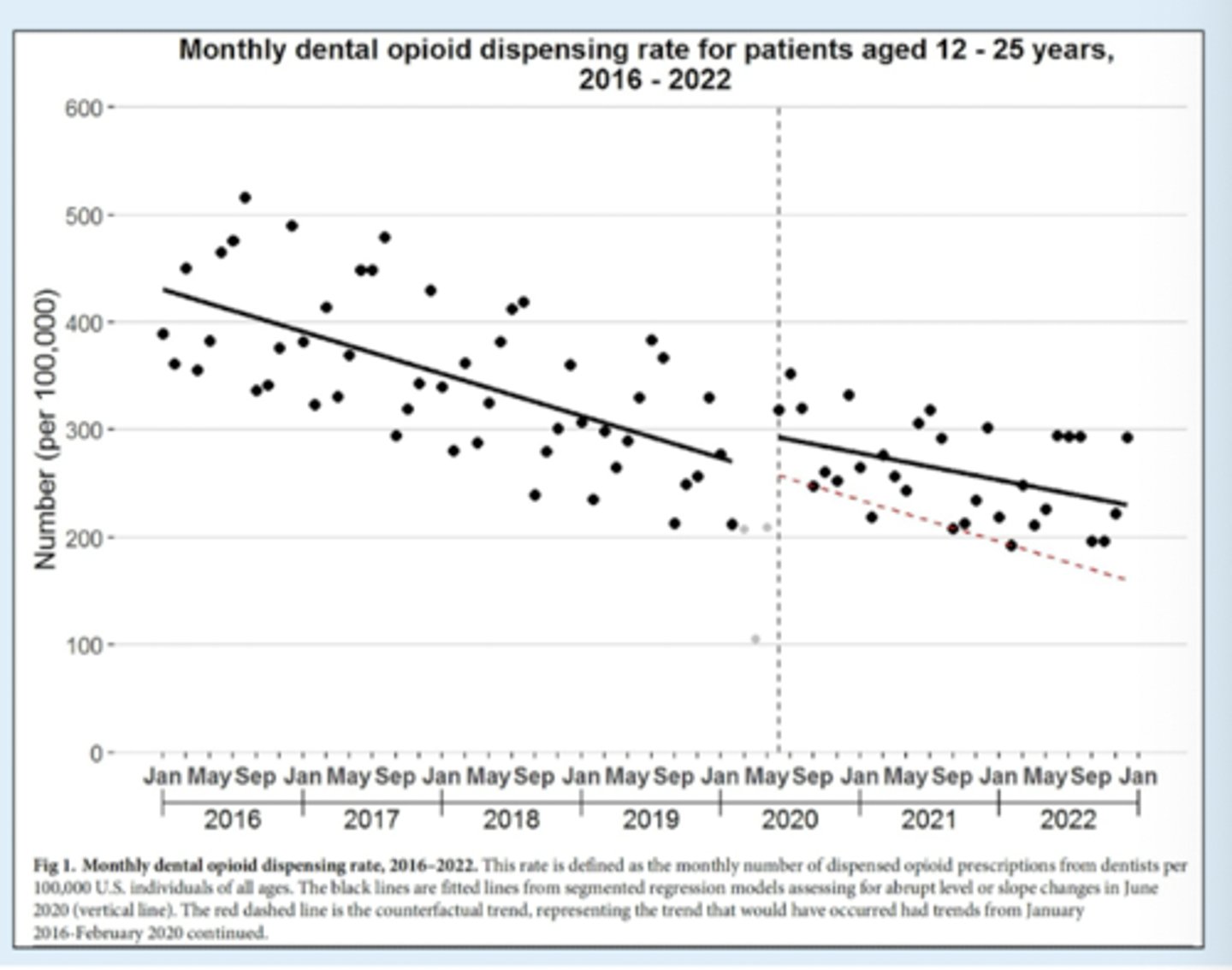
Dependence risks from excess opioids
- Excess supply of prescription opioids after surgical procedures
- 5-15% of opioid-naiive pts develop dependence
Post-surgical pts receiving opiates for pain control are particularly vulnerable to dependence due to: (3)
- excessive post-procedural prescribing of opioids
- gaps in follow-up
- inadequate disposal of unused excess supply
Overdose rates are ~_______x higher among pts who filled an opioid prescription after dental procedure vs pts who did not
2.5
- overdose rates also higher among family members of such pts
Groups at higher risk of overdose (2)
- Diagnosed mental health condition
- Substance use disorder
Which procedures in dentistry account for the highest proportions of US dental opioid prescriptions?

____ categories or schedules for controlled substances
- based on?
5
Based on:
- the drug's acceptable medical use
- the drug's abuse or dependency potential
Schedule ______ drugs represent the least potential for abuse
V
Schedule II drugs
- refills allowed?
- transmitted how?
- does prescription expire?
- Refills NOT permitted
- Transmitted via electronic transmission or fax
- Prescription expires 6 months after prescribed date
Schedule I-V drugs
- which has greatest potential for abuse?
- refills?
- exs?
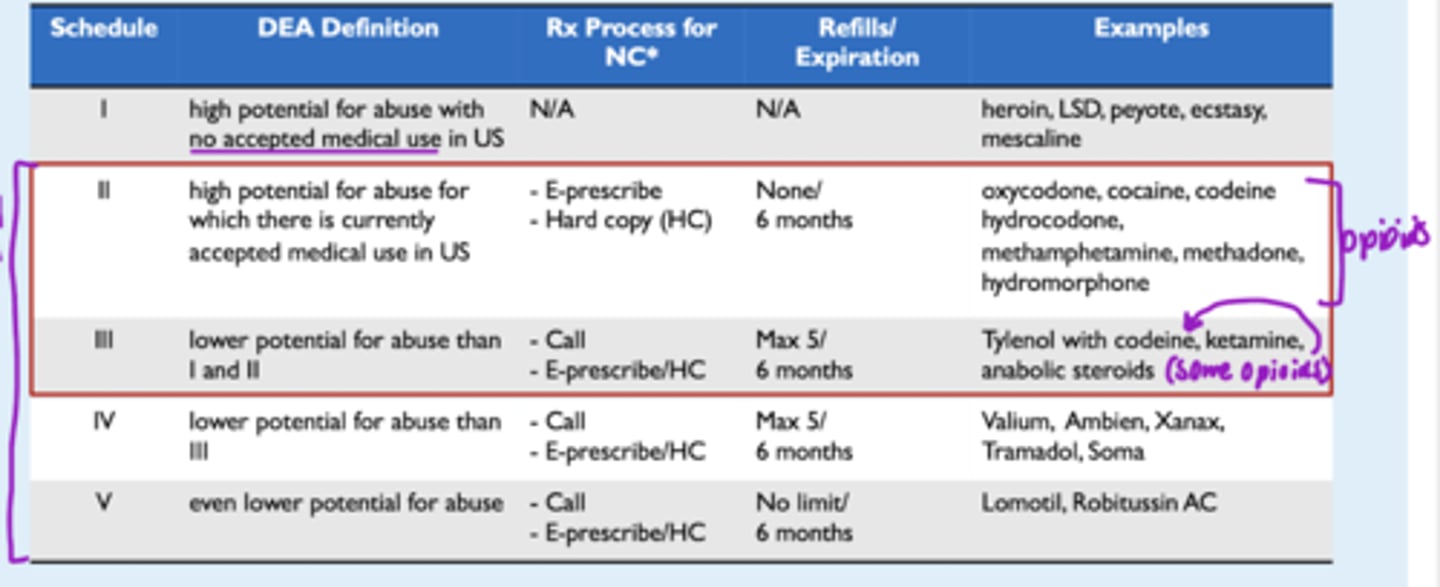
What is the NC Board of Pharmacy Controlled Substances Pocket Card?
- Rules and regulations
- Refill requirements
- How you can send it in
- Breaks down schedule
- etc

The ADA 2023/2034 Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Pain looks at 4 outcomes as critical decision making:
- pain relief
- globe efficacy rating
- use of rescue analgesia
- serious opioid-specific adverse effects
The ADA 2023/2034 Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Pain looks at 4 adverse effects for decision making:
- GI adverse effects
- CNS adverse effects
- Proportion of pts with >50% maximum pain relief
- Sum of pain intensity difference
Effectiveness of opioid and nonopioid analgesics on simple and surgical tooth ext
- NSAID monotherapy or in combo w acetaminophen are more effective in reducing post-op pain than opioids
- opioids increase risk of dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting
Effectiveness of opioid and nonopioid analgesics on toothache
- lack of evidence
- should be same mechanism as pain for ext --> NSAIDs
Effectiveness of corticosteroids on simple and surgical tooth ext and toothache?
Extractions
- lack of evidence, uncertain
Toothache
- not indicated
Effectiveness of local anesthetics on simple and surgical tooth ext
- Low certainty evidence suggests bupivicaine administered before discharge could reduce need for rescue analgesia 8-48 hours postoperatively
- Moderate certainty there is negligable difference between bupivicaine and short-acting local anesthetics
- no diff btwn 3% bupivicaine and 4% articaine

Effectiveness of local anesthetics on toothache
- failed to find direct evidence , utilized indirect evidence from post-operative pain
T/F: There is a lack of evidence that bupivicaine may decrease use of rescue analgesia (NSAIDs, APAP, opioids)
False - there is evidence
- may be superior to lido w/ epi and mepivicaine
- con: expense
- has prolonged analgesic effect well beyond its duration of action

Effectiveness of topical anesthetics on simple and surgical tooth ext
- Not indicated for exts
- Toothache: low certainty evidence suggests substantial pain reduction in pain intensity 20-30 mins compared to placebo
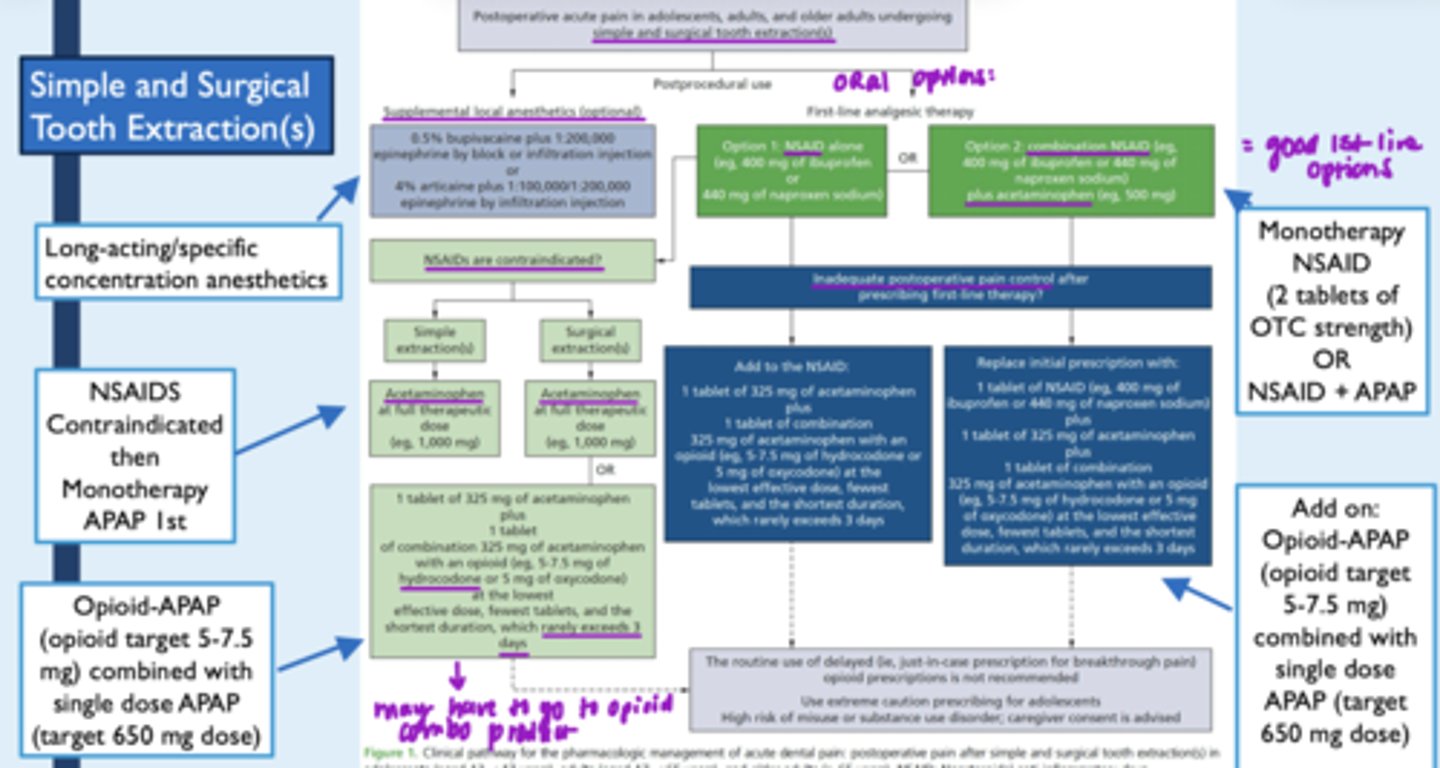
Pain reduction txt for simple and surgical exts
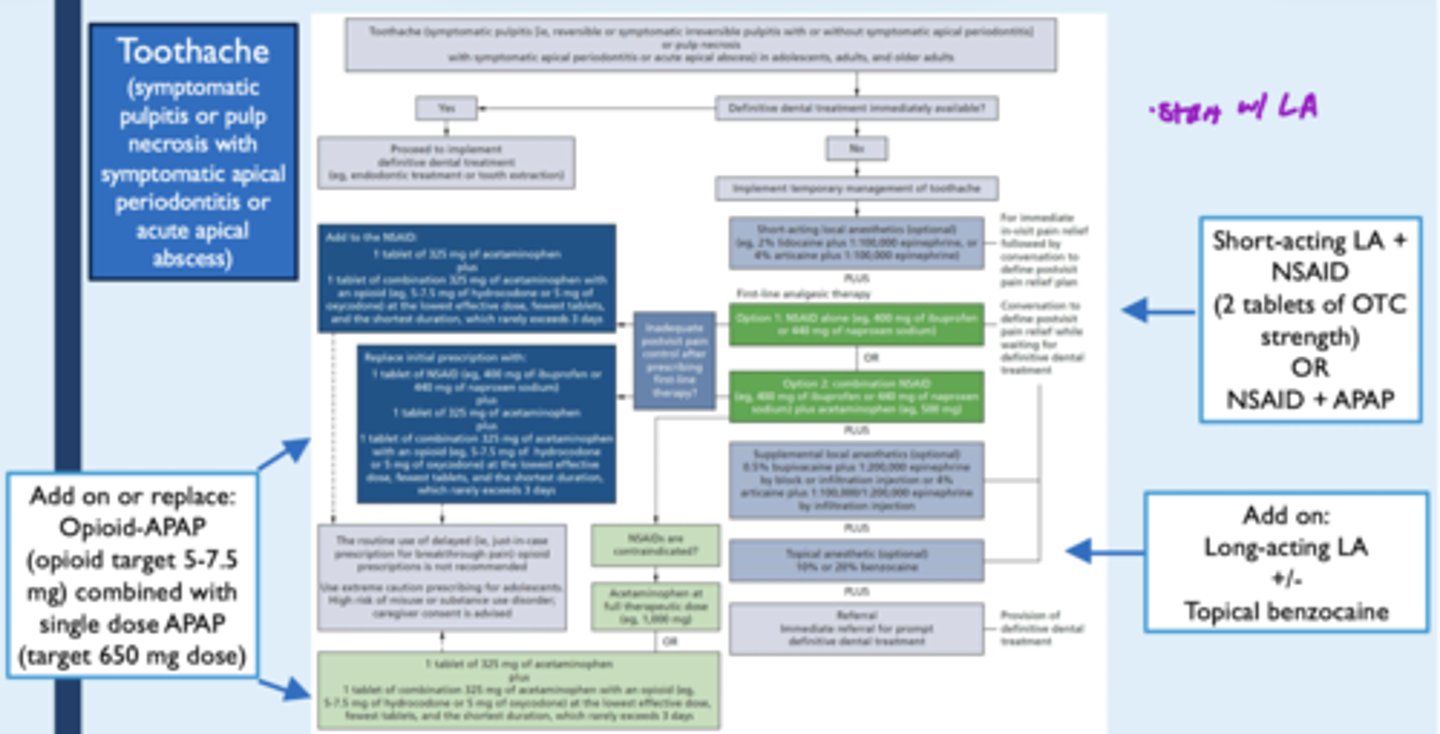
Pain reduction txt for toothache
What is the first-line for managing acute dental pain?
Nonopioid medications
--> current standards support use of combination NSAIDs and acetaminophen
- post-surgical pain is associated with inflammation, so control of acute pain = control of inflammation
When should opioid medications be used for managing acute dental pain?
opioids should be reserved for clinical situations when first-line therapy is insufficient to reduce pain or NSAIDs are contrainidcated
--> avoid routine use of "just-in-case" prescribing of opioids
--> use significant caution when prescribing opioids to adolescents and young adults
3 types of orofacial pain
- which is most common w/ ext?
Nociceptive
- tissue injury
- inflammation
- most common w extractions
Neuropathic
- primary lesion
- dysfunction of nervous system
Nociplastic
- hypersensitivity
- altered nociceptive with musculoskeletal involvement
Use of cold/heat therapy for dental pain
- directions?
- mechanism?
- For post0op (first 24-48 hrs), apply ice packs 15-20 mins on/10-15 mins off
- Switch to moist heat/pack afterward in the 2-3 days following to help w swelling and apply in 20 min cycles
- Rotation reduces skin irritation and helps expand blood vessels
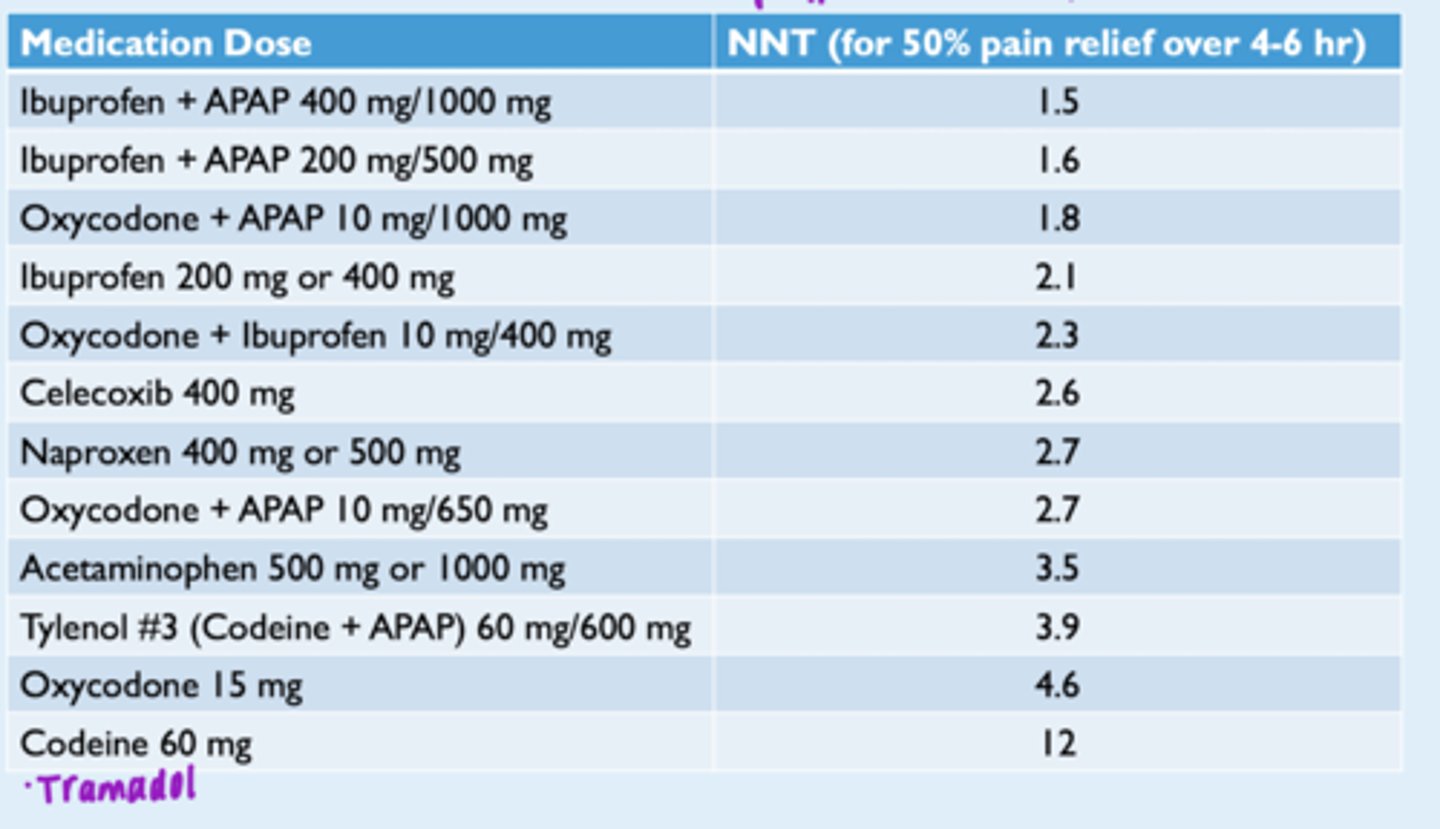
Number needed to treat/benefit (NNT/TB)
Ideally, want # to be close to 1
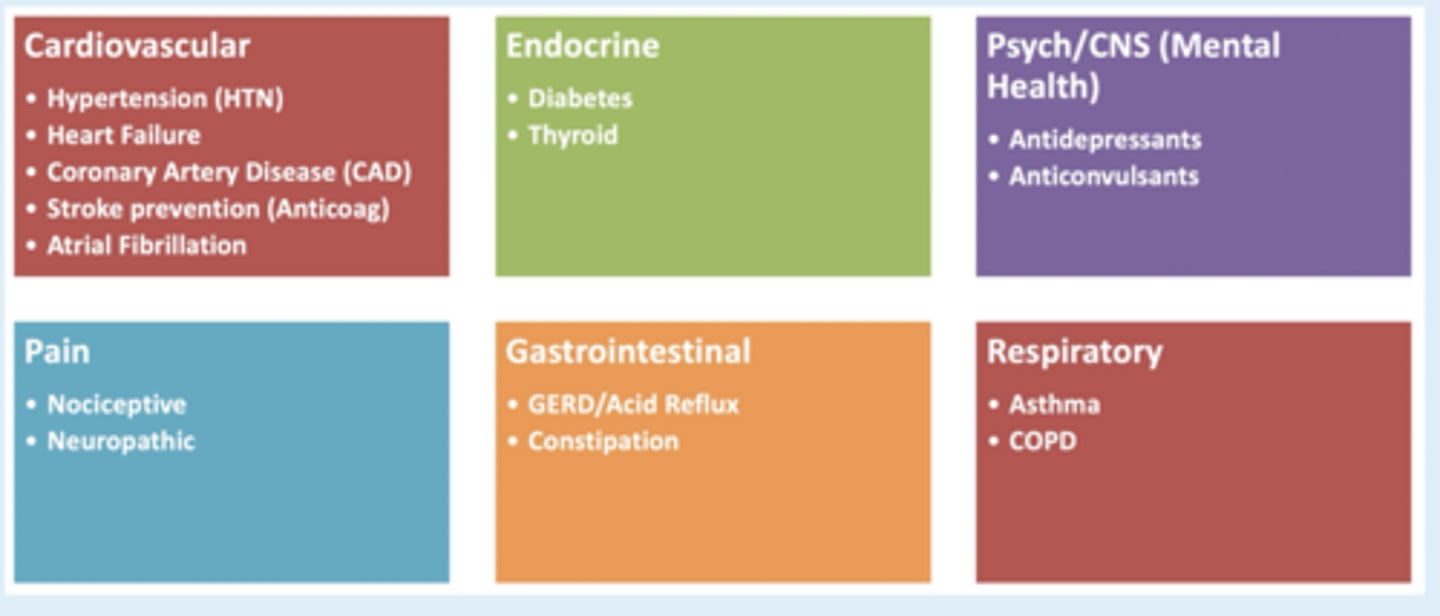
Co-morbidities considerations for prescribing meds for dental pain
NSAIDs - pt considerations -- conditions to be cautious of
CVD
- reduce hypotnesive effect of B-blockers if used >3 weeks
HTN
- interfere w efectiveness of anti-HTN meds and can decrease renal function in combo w diuretic
Heart failure
- avoid NSAID use --> promote Na+ and water retention = edema
Anticoagulation/Anti-platelet therapy
- increased bleeding risk
Diabetes
- can reduce effectiveness of diabetic txt, may induce hypoglycemia
Liver disorders
- cirrhosis - increases risk of hepatorenal bleeding
CKD (renal)
- acute nephrotoxicity, but is likely reversible
GI disorders
- GI ulcers, bleeding
Why use acetaminophen for txt of dental pain?
- Believed to be weak inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in CNS , work peripherally to block pain impulse
- provides synergistic effect when combined w ibuprofen
Acetaminophen (APAP)
- dosing?
- maximum daily dose?
- pt considerations?
General dosing:
- 325mg-650mg every 4-6 hrs
- 500mg-1000mg every 6-8 hrs
Maximum daly dose: 3000mg or 3g
- safer in pregnancy
- Pt considerations: liver disorders (concern for hepatotoxicity and dependent on alcohol intake)
Opioid - pain relieving effects
- Act in the brainstem and peripheral receptors
-- Mu receptor: analgesia, respiatory depression, euphoria, GI motility, miosis
-- Delta receptor: physical dependence
-- Kappa receptor: analgesia, dysphoria, miosis
T/F: Opioids are anti-inflammatory
FALSE
-- so not drugs of choice for nociceptive orofacial pain
-- best prescribed as combo product w clear instructions for optimal effect
Opioids - pt considerations
GI disorders
- nausea, vomiting, decreased GI motility
Depression/anxiety
- increase additive CNS depression (esp Tramadol)
Asthma/COPD
- potential to cause respiratory depression
T/F: Tramadol is a good opioid option for managing acute postop dental pain
- False - has limited therapeutic advantage as monotherapy
- efficacy is similar to codeine, less than opioid combination (Codeine + APAP)
Tramadol has a higher risk for what condition?
*exam q*
Serotonin syndrome "Triad of Trouble" = Tramadol, trazodone, and SSRI or SNRI
Different doses of tramdol and effects
- 100 mg
- 200 mg
- 300 mg
- 100 mg: analgesia
- 200 mg: opiate-like euphoria/hallucinations
- 300 mg: seizures
T/F: It is safe to prescribe opioids and benzodiazepines together
False!
- Avoid prescribing opioids and benzodiazepines concurrently whenever possible
Key risk mitigation strategies
1. Assess pt history
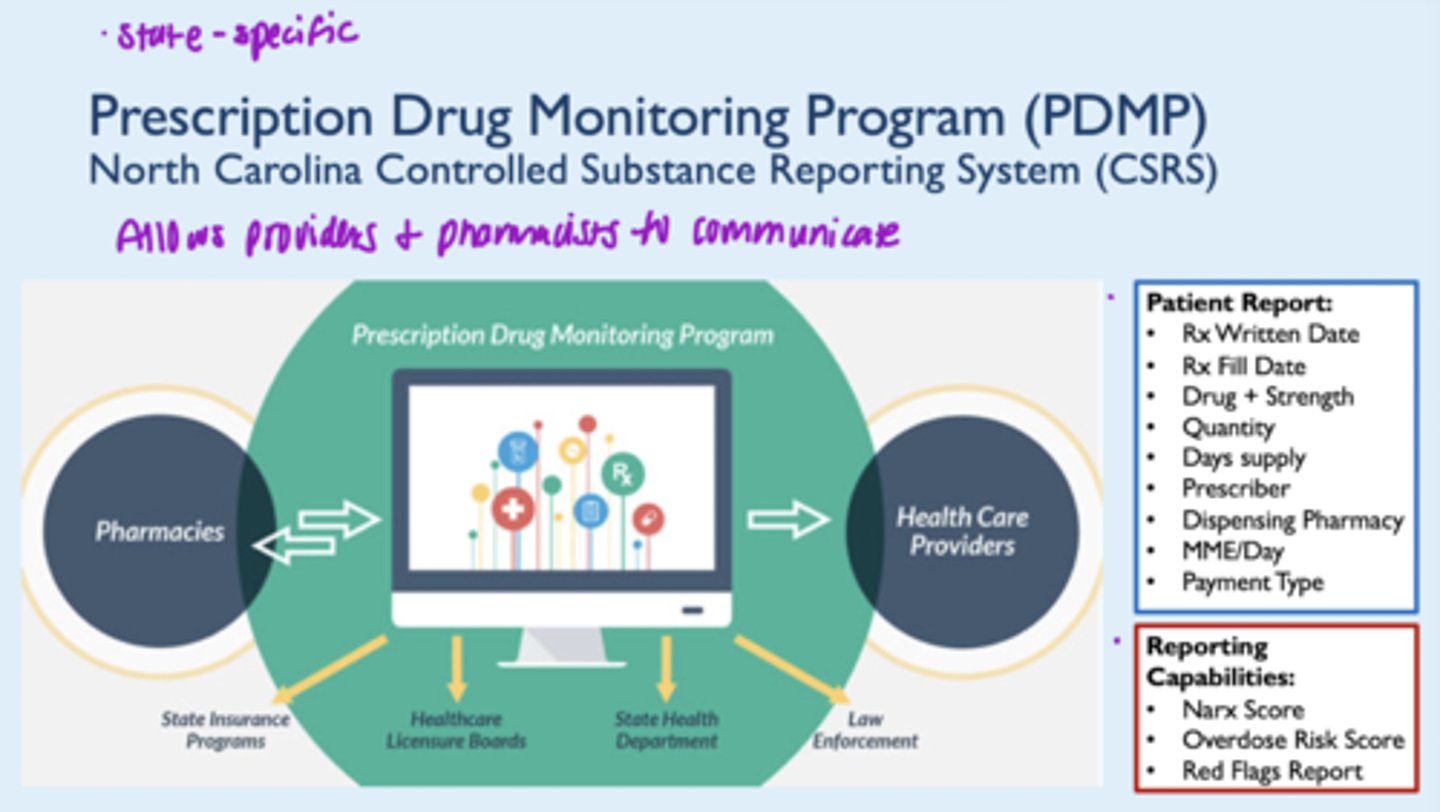
2. Use of prescription drug monitoring program (PDMP)
3. Optimal pt communication and set expectations
4. Appropriate storage and disposal
5. Consideration for naloxone co-prescribing when appropriate
Discussing expectations with pts when prescribing meds for postoperative pain

Options for disposal of unused meds (opioids)

What is nalaxone?
= Opioid antagonist for reversal of opioid overdose; quickly binds opioid receptors and reverses and blocks the effects of opioids
- injectable and nasal formulations (nasal available rx and OTC)
- safe to use on pets and children

What is Nalmafene?
= Rx only, FDA approved nasal opioid-overdose reversal agent
- opioid inverse agonist
- Benefit: longer half life compared to naloxone (T1/2= 11.4 hr)

Naloxone - rules in NC
- Any pharmacist in NC may dispense opioid antagonists, indicated for txt of opioid overdose
--> all 50 states have some form on naloxone access law, allowing pts to receive naloxone w/o a prescription

What is the Dental Impaction Pain Model (DIPM)?
Follows that postsurgical dental pain generally has a predictable trajectory over the course of one to 3 days
- postsurgical dental pain may be moderate to severe but typically resolves w/in 1-2 days aftee ext
T/F: Well-designed studies have shown that presurgical NSAID use significantly delay onset of post-op dental pain
True
- reach therapeutic blood levels of the NSAID before the surgical trauma generates various prostaglandins