MCAT Biochemistry - Biological Membranes
1/70
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
cell (plasma) membrane
semipermeable phospholipid bilayer; permits fat-soluble compounds to cross easily, while larger and water-soluble compounds must seek alternative entry
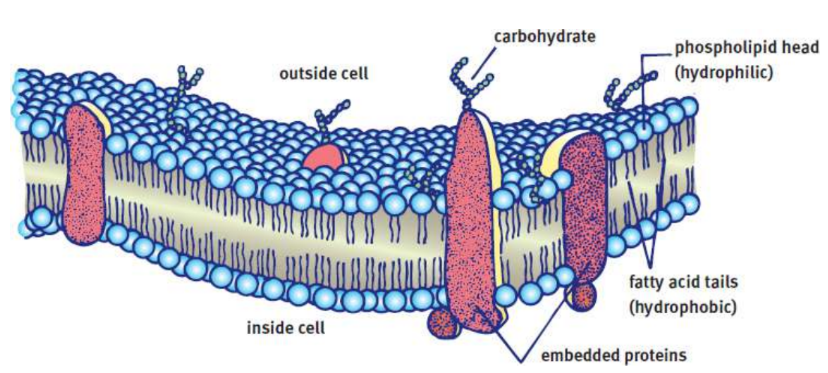
fluid mosaic model
the theory that underlies the structure and function of the cell membrane
glycoprotein coatt
Carbohydrates associated with membrane-bound proteins
cell wall
rigid structure outside the cell membrane; plants, bacteria, and fungi, contain high levels of carbohydrates
Phospholipid bilayer
hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head; two layers makes up membrane; move via simple diffusion
Lipid raft
collections of similar lipids with or without associated proteins that serve as attachment points for other biomolecules; toften serve roles in signaling
flippases
assist in the transition or “flip” between layers as the polar head group of the phospholipid must be forced through the nonpolar tail region in the interior of the membrane
Fatty acids
carboxylic acids that contain a hydrocarbon chain and terminal carboxyl group
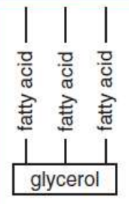
Triacylglycerols / triglycerides
storage lipids involved in human metabolic processes; contain three fatty acid chains esterified to a glycerol molecule; saturated or unsaturated
Unsaturated fatty acids
regarded as “healthier” fats, tend to have one or more double bonds and exist in liquid form at room temperature; impart fluidity to the membrane
chylomicrons
transport dietary lipids, such as fats and cholesterol, from the intestines to other locations in the body, within the water-based solution of the bloodstream
α-linolenic acid & linoleic acid
important essential fatty acids
Saturated fatty acids
main components of animal fats; tend to exist as solids at room temperature; found in processed foods and are considered less healthy; decrease the overall membrane fluidity
glycerophospholipid / phospholipid
replace a fatty acid chain of triacylglycerol with a phosphate group; used for membrane synthesis and can produce a hydrophilic surface layer on lipoproteins
micelles
small monolayer vesicles
liposomes
bilayered vesicles of phospholipids
low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)
a lipid transporter
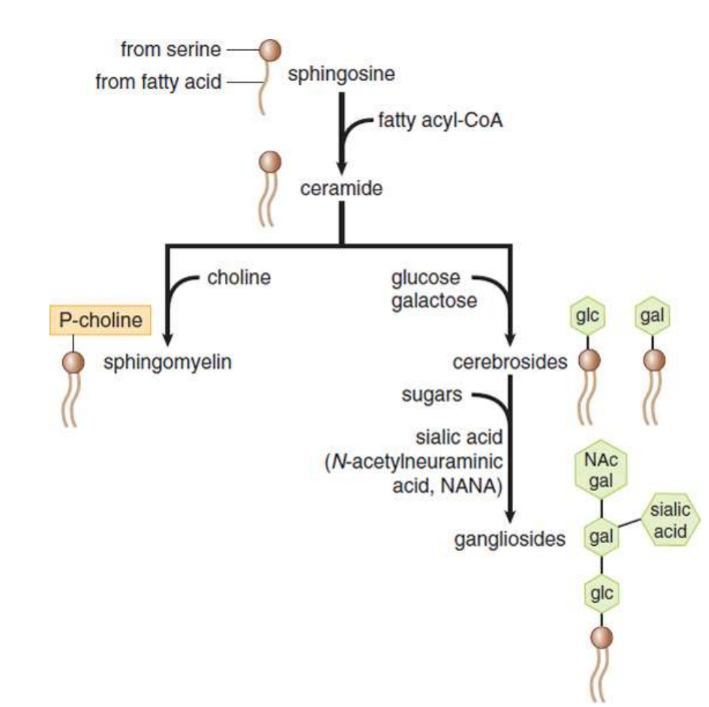
Sphingolipids
do not contain glycerol but contain a hydrophilic region and two fatty acid–derived hydrophobic tails
Cholesterol
regulates membrane fluidity; contains both a hydrophilic and hydrophobic region; prevents the formation of crystal structures in the membrane, increasing fluidity at lower temperatures; limiting movement of phospholipids, decreases fluidity and helps hold the membrane intact at high temperatures; 20% mass, 50% mole fraction of cell membrane
steroids
hormones derived from cholesterol
Waxes
class of lipids that are extremely hydrophobic and are rarely found in the cell membranes of animals, but are sometimes found in the cell membranes of plants; long-chain fatty acid and a long-chain alcohol, which contribute to the high melting point; stability and rigidity within the nonpolar tail region; serve an extracellular function in protection or waterproofing
Transmembrane proteins
pass completely through the lipid bilayer; Transporters, channels, and receptors
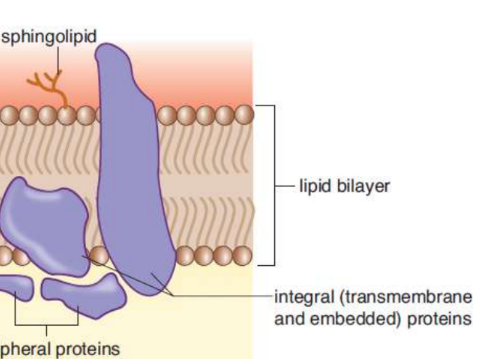
Embedded proteins
are associated with only the interior (cytoplasmic) or exterior (extracellular) surface of the cell membrane
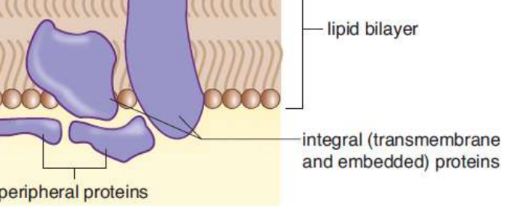
integral proteins
association with the interior of the plasma membrane, which is usually assisted by one or more membrane-associated domains that are partially hydrophobic; transmembrane and embedded
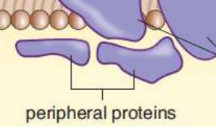
Membrane-associated (peripheral) proteins
bound through electrostatic interactions with the lipid bilayer, especially at lipid rafts, or to other transmembrane or embedded proteins
ex. G proteins found in G protein-coupled receptors
ABO antigens
red blood cells; sphingolipids that differ only in their carbohydrate sequence; allows for identification and targetting
biofilm
carbohydrates are generally hydrophilic, interactions between glycoproteins and water can form a coat around the cell
membrane receptors,
transporters for facilitated diffusion and active transport can be activated or deactivated; tend to be transmembrane proteins
ex. ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors
cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
proteins that allow cells to recognize each other and contribute to proper cell differentiation and development
intercellular junctions
provide direct pathways of communication between neighboring cells or between cells and the extracellular matrix; generally comprised of cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
Gap junctions / connexons
direct cell–cell communication and are often found in small bunches together; formed by the alignment and interaction of pores composed of six molecules of connexin
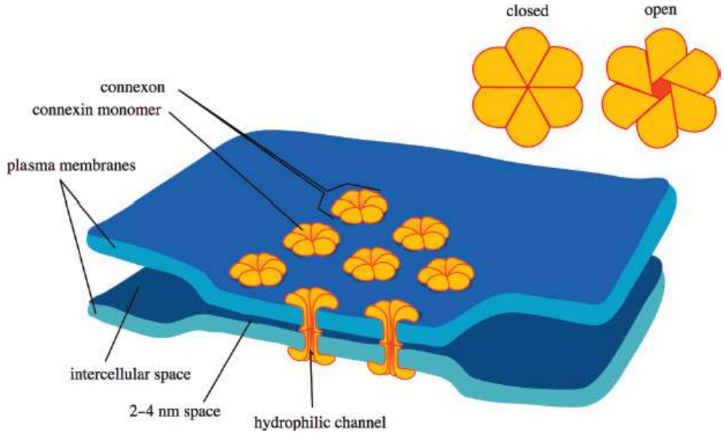
connexin
molecules that create pores in the cell membrane
Tight junctions
prevent solutes from leaking into the space between cells via a paracellular route; found in epithelial cells and function as a physical link between the cells as they form a single layer of tissue; limit permeability enough to create a transepithelial voltage difference based on differing concentrations of ions on either side of the epithelium; form a continuous band around the cell
Desmosomes
bind adjacent cells by anchoring to their cytoskeletons; formed by interactions between transmembrane proteins associated with intermediate filaments inside adjacent cells; primarily found at the interface between two layers of epithelial tissue
Hemidesmosomes
similar function to desmosomes, but their main function is to attach epithelial cells to underlying structures, especially the basement membrane
passive transport
Spontaneous transport processes that do not require energy (negative ΔG); affected by temperature positively
active transport.
nonspontaneous transport that requires energy (positive ΔG); temperature effect depends on enthalpy
simple diffusion
substrates move down their concentration gradient directly across the membrane; only particles that are freely permeable to the membrane
Osmosis
specific kind of simple diffusion that concerns water; water will move from a region of lower solute concentration to one of higher solute concentration
hypotonic solution
concentration of solutes inside the cell is higher than the surrounding solution; cause a cell to swell as water rushes in, sometimes to the point of bursting (lysing)
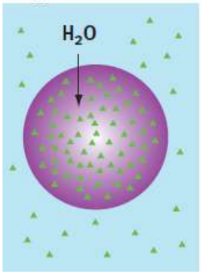
hypertonic solution
solution that is more concentrated than the cell; water will move out of the cell

isotonic solution
solutions inside and outside are equimolar; equal movement in and out
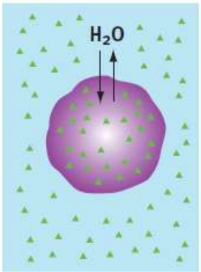
Osmotic pressure
driving force behind osmosis; water level will only rise to the point at which it exerts a sufficient pressure to counterbalance the tendency of water to flow across the membrane
∏ = iMRT
where M is the molarity of the solution, R is the ideal gas constant, T is the absolute temperature (in kelvins), i is the van’t Hoff factor
colligative property
a physical property of solutions that is dependent on the concentration of dissolved particles but not on the chemical identity of those dissolved particles
van’t Hoff factor
the number of particles obtained from the molecule when in solution
ex. glucose = 1, NaCl = 2
Facilitated diffusion
simple diffusion for molecules that are impermeable to the membrane (large, polar, or charged); requires integral membrane proteins to serve as transporters or channels for these substrates
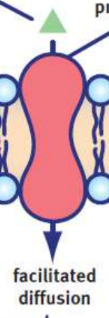
Carrier proteins
only open to one side of the cell membrane at any given point
occluded state
carrier is not open to either side of the phospholipid bilayer
channel proteins
open or closed conformation, open are exposed to both sides of the cell membrane and act like a tunnel for the particles to diffuse through, thereby permitting much more rapid transport kinetics
Active transport
net movement of a solute against its concentration gradient
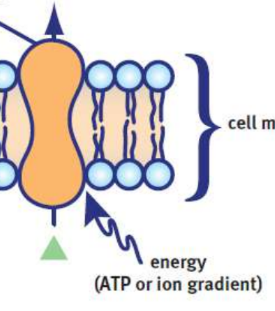
Primary active transport
uses ATP or another energy molecule to directly power the transport of molecules across a membrane involving the use of a transmembrane ATPase
Secondary active (coupled) transport
no direct coupling to ATP hydrolysis; harnesses the energy released by one particle going down its electrochemical gradient to drive a different particle up its gradient
symport
both particles flow the same direction across the membrane
antiport
particles flow in opposite directions
Endocytosis
when the cell membrane invaginates and engulfs material to bring it into the cell; encased in a vesicle
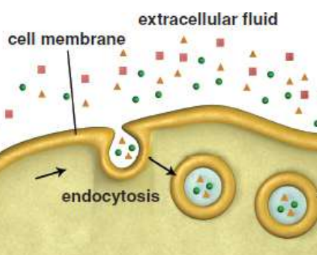
Pinocytosis
endocytosis of fluids and dissolved particles
phagocytosis
ingestion of large solids such as bacteria
vesicle-coating proteins
Invagination will then be initiated and carried out
ex. clathrin
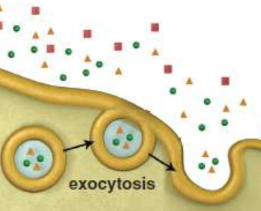
Exocytosis
when secretory vesicles fuse with the membrane, releasing material from inside the cell to the extracellular environment
membrane potential, Vm
difference in electrical potential across cell membranes
resting potential
between −40 and −80 mV
leak channels
ions may passively diffuse through the cell membrane over time, changing membrane potential
sodium–potassium pump (Na+/K+ ATPase)
regulates the concentration of intracellular and extracellular sodium and potassium ions; maintain a low concentration of sodium ions and high concentration of potassium ions intracellularly by pumping three sodium ions out for every two potassium ions pumped in
Nernst equation
used to determine the membrane potential from the intra- and extracellular concentrations of the various ions
where R is the ideal gas constant, T is the temperature in kelvins, z is the charge of the ion, and F is the Faraday constant (96, 485 C/mol e− )
simplification assumes body temperature
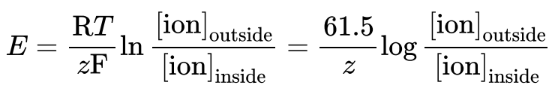
Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz voltage equation
flows from the Nernst equation, taking into account the relative contribution of each major ion to the membrane potential

Mitochondria
the “powerhouse” of the cell because of their ability to produce ATP by oxidative respiration
outer mitochondrial membrane
highly permeable due to many large pores that allow the passage of ions and small proteins; completely surrounds the inner mitochondrial membrane
intermembrane space
space between inner and outer mitochondrial membranes
inner mitochondrial membrane
involved in the electron transport chain and ATP synthesis; very high level of cardiolipin and does not contain cholesterol
cristae
inner mitochondrial membrane infoldings; numerous; increase the available surface area for the integral proteins associated with the membrane
mitochondrial matrix
where the citric acid cycle produces high-energy electron carriers used in the electron transport chain; inside inner mitochondrial membrane