Photosynthesis overview + Light reactions
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
How do diffrent organisms get glucose to preform cell respiration
humans - eating
plants - photosynthesis
Photosynthesis organims
Plants
Algae (protists)
Cyanbacteria
define autotrophs
Organisms that make thier own food
Photosynthesis energy transformation
Light energy is transfomred into chemical energy
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy —> Glucose + 6O2
where does the CO2 come from needed in photosynthesis
the atmosphere (enters through stomata)
Where does the H20 come from needed in photosyntheis
from the ground
what type of reaction is photosynthesis
Endergonic reaction
relation between cellular respiration and photosynthesis
inverse reaction equations
significance of chlorplasts
where photsynthesis happens
where are chloroplasts found
plant cell type called mesophyll cells
What is stroma in chloroplasts
gel-like substance
what are thylakoids in chloroplasts
one disk
what are granum in chlorplasts
stack of disks
Important pichure of photosynthesis
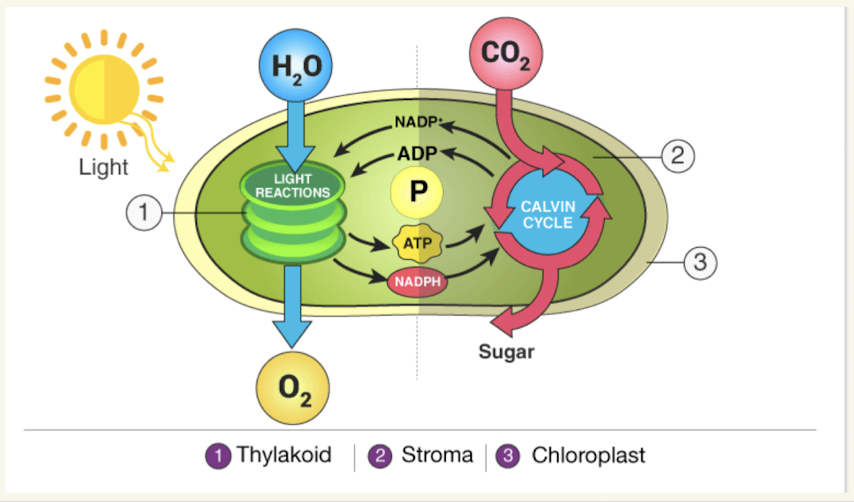
2 process in photsynthesis
Light reactions
dark reactions
general idea of light reaction
uses light energy to capture electrons and built up a little ATP
occurs in thylakoids
general idea of dark reactions
Uses ATP and electrons from light reactions to build glucose from CO2 (also called calvin cycle)
Occurs in Stroma
What does H20 get turned into during light reaction and where do the products go?
Oxygen - exists the cell
ATP - gets used in calvin cycle
NADPH - Gets used in Calvin Cycle
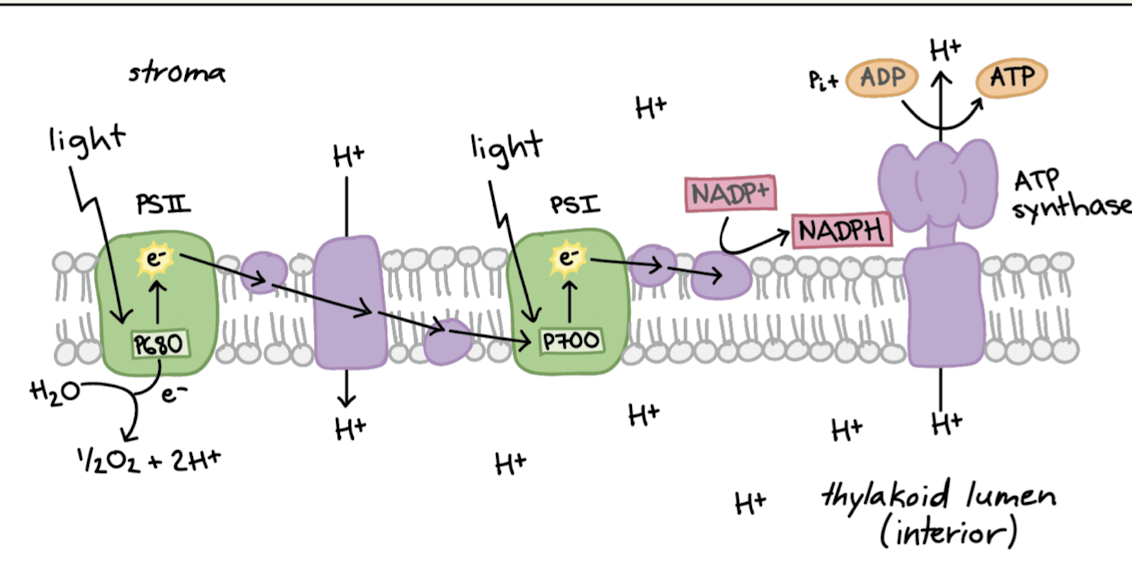
3 components of light reactions
Photosystem II
ETC
Photosystem I
what is a photosystem
A collection of light harvesting complexes containing chlorophyll and a reaction-center complex that contains a special pair of chlorophylls and a primary electron acceptor
Photosystem II steps
Sunlight energizes chlorophyll molecules which funnel energy to a special pair
Special pair receives too much energy that electron is taken by the primary acceptor (Pheophytin)
Electron is replaced in the speical pair by taking an electron from a water molecule
What is the primary acceptor in Photosytem II
Pheophytin
What happens when that speical pair takes an electron from the water molecules
produces oxygen and 2 hydrogens
ETC steps
Electrons are passed from pheophytin to the electron transport chain
The energy released when passing electrons between proteins is used to transport H+ and build up its concentration inside the thylakoids
H+ passivly diffuses through ATP synthase to make ATP
electron contuines to move through photosystem I
why cant the cell use the ATP used in the ETC
too unstable
Photosystem I steps
Electrons from the ETC are passed to a speical pair
These electrons replace the ones lost due to the primary acceptor (cholorphyll A0) during light energy transfer
These electrons are passed to ferrodixin
Ferrodoxin then hands the electrons over to NADP+ to create NADPH
NADPH carries electrons to calvin cycle
Primary electron acceptor of PS1
Chlorophyll A0
Wavelengths used in photosynthesis
400-450nm and 650-670nm
Important Pichure of light reactions