Final Exam (Additional Content) - Chordates & General Knowledge
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are four things that all chordates have at some point in their lives
notochord
hollow dorsal nerve cord
pharyngeal gill slits or pouches
postanal tail
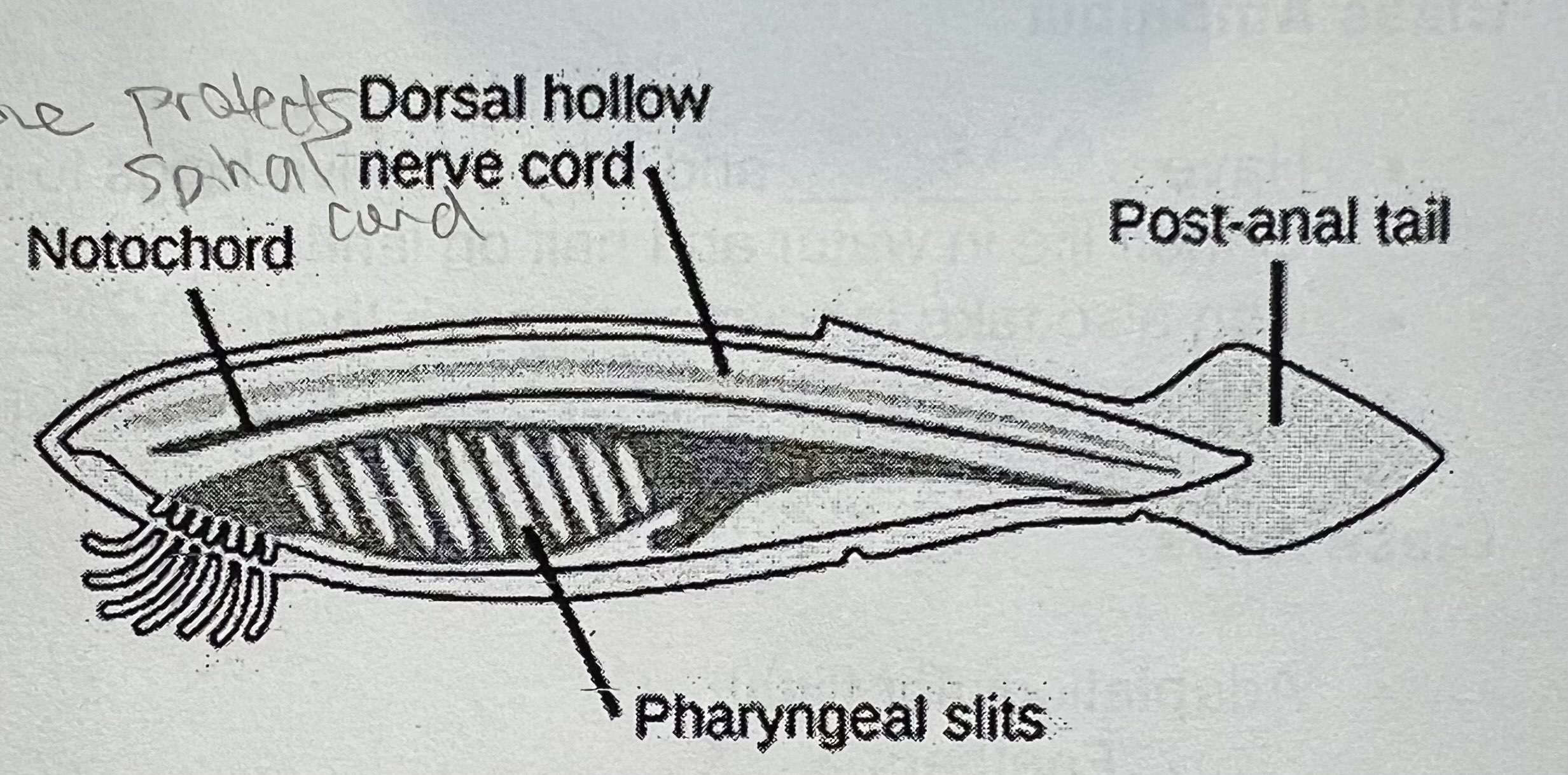
What happens to the notochord in animals with backbones.
formed early in embryonic development, as the embryo grows, the notochord is replaced by the vertebrae (backbone). (vertebrae forms around notochord)
By birth, the notochord is mostly gone, except for a bit left in the intervertebral discs (called the nucleus pulposus).
describe the notochord
flexible supporting rod that runs dorsal length
assists in support, shape and mobility (stiffens body)
is the backbone in vertebrae
describe the hollow dorsal nerve cord
runs independently above the notochord
front end develops into a brain
helps form our central nervous system
describe the pharyngeal gill slits or pouches
throat region of body
aid in respiration
aquatic: gills
terrestrials: lungs
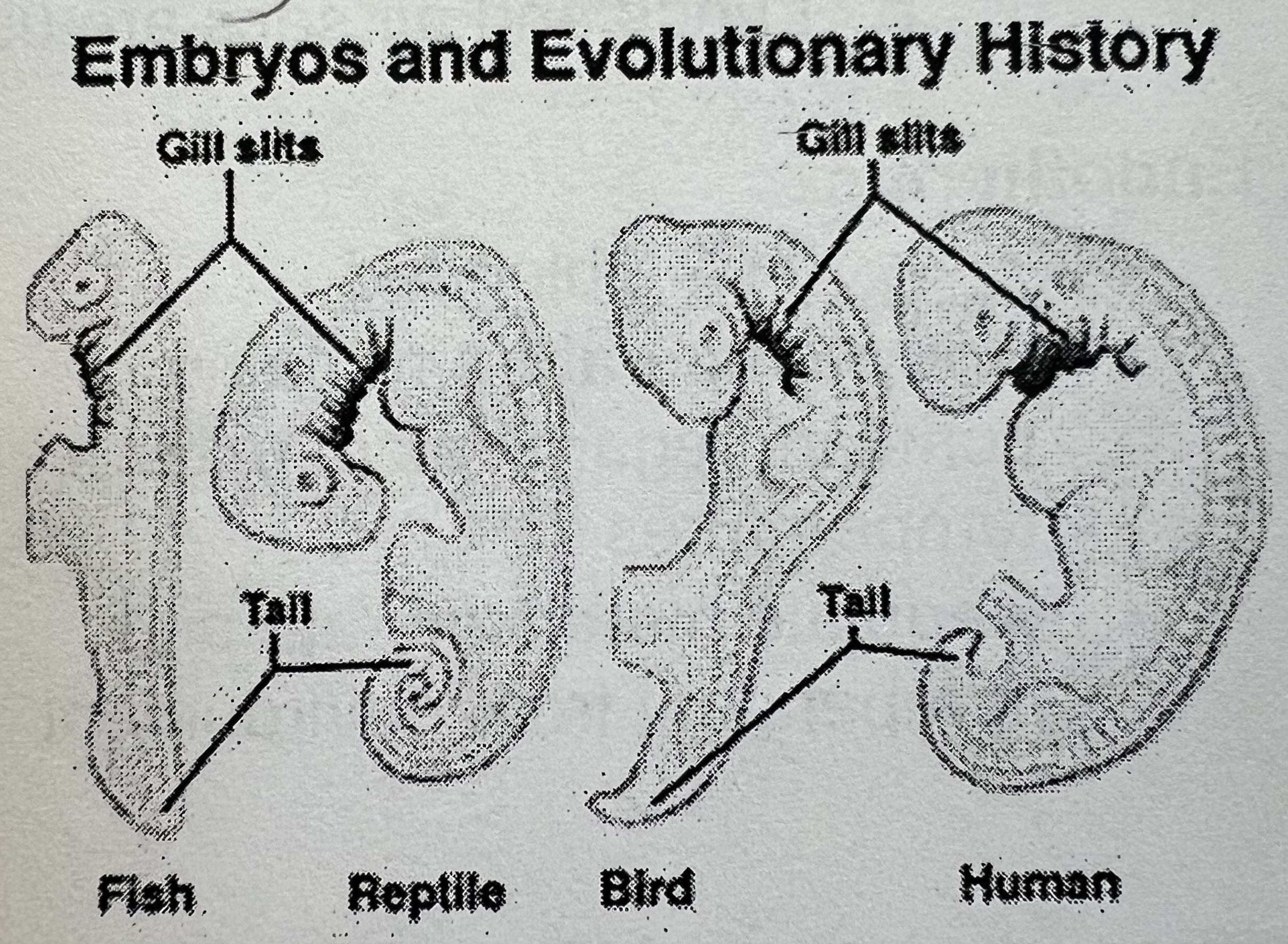
describe the postanal tail
extension of body running past anal opening
in some, only present in embryonic stages
body cavity status and symmetry
coelomates, bilateral
common characteristis in complex animals
big brain (cephalized)
bilateral symmetry
all 3 germ layers
coelomates
describe nervous system
advanced central nervous syetm
large brain
skull
Has unequivocal…
head, eyes and sensory organs
What complex systems do chordates have
heart and circulatory
where are chordates found
land, air, water
examples in class Amphibia
amphibians (frogs, toads, salamanders)
examples in class Sauropsida
reptiles
examples in class Aves
birds
examples in class Mammalia
mammals
examples in class Chondrichthyes
cartilaginous fish (sharks, rays) (skeleton of cartilage, no swim bladder, no operculum, teeth continuously replaced)
examples in class Osteichthyes
all bony fishes (operculum, teeth fixed to jaw bone, skeleton of bone, swim bladder) (e.g. trout, saslmon, goldfish)
describe class amphibia (4)
gills & primitive lungs
half life in water/on land
take in gasses through moist skin
lays eggs in water after sexual reproduction which develop into tadpoles
How did class Aves adapt for flight (5)
feathers
4 chambered heart
hollow bones for strength w/o weight
large sternum for wings to attach and put pressure
lungs & air sacs used to improve gas exchange at thin altitudes
Describe endotherms (4)
warm blooded
body temperature remains constant regardless of external temperature
regulates metabolic rate
independent from environment
Describe ectotherms (3)
cold blooded
body temps varies with environment
cannot regulate metabolic rate well
characteristics of mammels (11)
endotherms
air breathing
4 legged vertebrates
possess skin with hair and sweat glands
have teeth with a jawbone
fleshy lips
diaphragm
4 chambered heart
brain & spinal chords
bear live young
mammary glands
ecological roles of chordates (7)
all are part of food chain
amphibians contribute to wetland ecology by preying on insects and eats algae and dead plants
reptiles are predators of pests
birds control insect and vermin populations
birds act as pollinators
mammals aerate soil
mammels are sensitive to environmental changes
scientific name of cat
Felis catus
Felis catus:
endotherm or ectotherm
nervous system
feeding
respiration
internal transport systems
excretion
movement
reproduction
development
2 special adaptations
Endotherm or ectotherm: Endotherm
Nervous system: Highly developed, complex brain and sensory organs
Feeding: Carnivorous predator; eats meat
Respiration: Lungs with diaphragm for breathing
Internal transport systems: Closed circulatory system with heart and blood vessels
Excretion: Kidneys filter waste; excreted as urine; also expels feces
Movement: Four-legged locomotion; agile and flexible muscles
Reproduction: Sexual; internal fertilization; dioecious (separate sexes)
Development: Viviparous; young develop inside mother; born relatively undeveloped, grow quickly
Two special adaptations: Retractable claws for hunting and climbing; excellent night vision for low-light hunting
For Porifera:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Filter feeders using choanocytes
Respiration: Diffusion through pores
Internal transport: Water flow system; no circulatory system
Excretion: Diffusion
Movement: Sessile (mostly immobile)
Examples: Bath sponge, glass sponge
Common name: Sponges
Coelom: None (acoelomate)
Germ layers: zero
Symmetry: Asymmetrical or radial
Nervous system: None
Reproductive system: Sexual (hermaphroditic) and asexual (budding)
For Cnidaria:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Carnivorous; stinging cells (nematocysts)
Respiration: Diffusion across body surface
Internal transport: Diffusion
Excretion: Diffusion
Movement: Pulsating bell or sessile (polyps)
Examples: Jellyfish, sea anemones, corals
Common name: Jellyfish and relatives
Coelom: None (acoelomate)
Germ layers: Two (diploblastic)
Symmetry: Radial
Nervous system: Nerve net
Reproductive system: Sexual and asexual; some hermaphroditic
For Platyhelmenthes:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Parasites or scavengers; mouth only
Respiration: Diffusion
Internal transport: Diffusion
Excretion: Flame cells (protonephridia)
Movement: Cilia and muscle contractions
Examples: Planarians, tapeworms
Common name: Flatworms
Coelom: None (acoelomate)
Germ layers: Three (triploblastic)
Symmetry: Bilateral
Nervous system: Simple brain and paired nerve cords
Reproductive system: Sexual and asexual; many hermaphroditic
For Nematoda:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Parasites or decomposers
Respiration: Diffusion
Internal transport: None (no circulatory system)
Excretion: Renette cells or excretory canals
Movement: Longitudinal muscles; whip-like motion
Examples: Ascaris, hookworms
Common name: Roundworms
Coelom: Pseudocoelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Bilateral
Nervous system: Simple nerve ring and cords
Reproductive system: Sexual; usually separate sexes (dioecious)
For Mollusks:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Radula (scraping), filter feeding, or predation
Respiration: Gills or lungs
Internal transport: Mostly open circulatory (closed in cephalopods)
Excretion: Nephridia
Movement: Muscular foot or tentacles
Examples: Snails, clams, squids
Common name: Mollusks
Coelom: Coelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Bilateral (some secondarily asymmetrical)
Nervous system: Varies; advanced in cephalopods
Reproductive system: Mostly sexual; dioecious or hermaphroditic
For Annelids:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Detritivores, predators, filter feeders
Respiration: Diffusion through skin or gills
Internal transport: Closed circulatory system
Excretion: Nephridia
Movement: Segmented muscles with setae
Examples: Earthworms, leeches
Common name: Segmented worms
Coelom: Coelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Bilateral
Nervous system: Brain and ventral nerve cord
Reproductive system: Sexual; hermaphroditic or separate sexes
For Arthropods:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Diverse; herbivores, carnivores, parasites
Respiration: Gills, tracheae, or book lungs
Internal transport: Open circulatory system
Excretion: Malpighian tubules or green glands
Movement: Jointed appendages
Examples: Insects, spiders, crabs
Common name: Arthropods
Coelom: Coelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Bilateral
Nervous system: Brain and ventral nerve cord
Reproductive system: Sexual; mostly dioecious
For Echinoderms:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Filter feeding, scavengers, predators
Respiration: Tube feet and skin gills
Internal transport: Water vascular system
Excretion: Diffusion
Movement: Tube feet with hydraulic pressure
Examples: Starfish, sea urchins
Common name: Echinoderms
Coelom: Coelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Radial (adult), bilateral (larvae)
Nervous system: Nerve ring and radial nerves; no brain
Reproductive system: Sexual; separate sexes
For Chordata:
Feeding
Respiration
Internal transport
Excretion
Movement
Examples
Common name
Coelom
Germ layers
Symmetry
Nervous system
Reproductive system
Feeding: Varied (filter feeders, herbivores, carnivores)
Respiration: Gills or lungs
Internal transport: Closed circulatory system with heart
Excretion: Kidneys or nephridia
Movement: Muscles attached to endoskeleton or notochord
Examples: Fish, birds, mammals
Common name: Chordates
Coelom: Coelomate
Germ layers: Triploblastic
Symmetry: Bilateral
Nervous system: Brain and dorsal nerve cord
Reproductive system: Sexual; dioecious or hermaphroditic
All 11 systems in humans
cardiovascular
nervous
digestive
respiratory
skeletal
muscular
urinary
reproductive
integumentary (skin)
endocrine
lumphatic/immune