Cell Junctions Review
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What structures make up muscle cells?
Myofibrils
What filaments make up myofibrils?
Actin and Myosin
How does moving an arm or leg occur via muscle cells?
They contract and expand together
How do bone cells form bones?
They secrete calcium and other materials that harden
What are cell junctions?
Structures that connect cells to each other
In what tissue are cell junctions most commonly found?
Epithelial
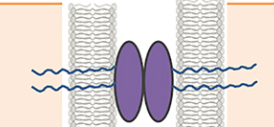
What kind of junction is depicted?
Tight Junction

What kind of junction is depicted?
Desmosome

What kind of junction is depicted?
Gap Junction
What sorts of molecules can pass through a tight junction?
Nothing
Where can we find tight junctions?
Bladder, Intestines, and Kidney’s
Where do desmosomes attach at?
The cytoskeleton
What sorts of molecules can pass through a desmosome?
Water and Ions
Where can we find desmosomes?
Skin and Intestines
What do gap junctions allow to occur?
The passing of water and ions between cells
Where can we find gap junctions?
Cardiac Muscles and Neurons
What are the four tissue types found in animals?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nerve
What is the function of epithelial tissue?
Covers and lines body surface, provides protection
What is the function of connective tissue?
Provides structural support and connects other tissues
What is the function of muscle tissue?
Contracts to enable movement
What is the function of nervous tissue?
Transmits electrical impulses
Which of the following organelles often occupies the majority of the volume of a plant cell?
Central Vacuole
Specialized epithelial cells that protect underlying tissues and organs
Keratinocytes
Specialized epithelial cells that produce the pigments of skin
Melanocytes
What does extracellular meaning?
Outside the cell
What are the three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton?
Microtubules, Microfilaments, and Intermediate filaments
What is dynamic instability?
The cycles of polymerization and depolymerization in microtubules
Why does microtubule catastrophe take place?
The plus end of a microtubule is structurally unstable
What is the process of microtubule catastrophe?
The dramatic shrinkage of microtubule
What is epidermolysis bullosa?
A genetic defect that disrupts the intermediate filament network
What cell-surface proteins attach cells to each other and to the extracellular matrix?
Integrins
Where are microtubules found?
The interior of the cell
What do microtubules do?
They maintain cell shape and provide transport
Where are microfilaments found?
Around the inner edge of a cell
What do microfilaments do?
Resist tension, provides cell shape and movement
Where are intermediate filaments found?
Throughout the cell
What do intermediate filaments do?
Holds organelles in place, provides structural support to the cell

A double helix of actin monomers is…
A microfilament
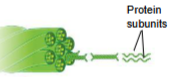
A strong fiber composed of intermediate filament protein subunits is…
An intermediate filament
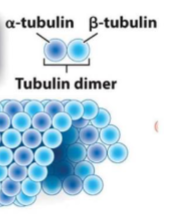
A hollow tube formed from tubulin dimers is…
A microtubule
What are motor proteins used for?
Moving cells, changing cell shape, and moving substances inside and outside of cells
In which direction does Kinesin move granules out towards?
The plus end
When does kinesin move the granules?
During dispersal
In which direction does Dynein move granules out towards?
The minus end
When does dynein move the granules?
During Aggregation
What subunits make up microtubules?
Tubulin dimers
What subunits make up microfilaments?
Actin monomers
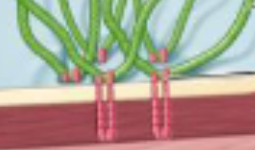
Which cell junction type is depicted?
Hemidesmosome

Which cell junction type is depicted?
Adherends
What is another name for microfilaments?
Actin
What are myofibrils?
Rod-like organelles found in muscle cells that are responsible for muscle contraction
What is the function of hemidesmosome junctions?
They anchor epithelial cels to the basal lamina