Theme 2 Quick notes
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Economic influence definition
When a business is impacted in any way by economic factors
Effect on businesses of changes in inflation:
Cost of supplies and materials goes up
Businesses may need to increase prices
Businesses may lower profit margins
Effect on businesses of changes in exchange rates:
Appreciation means the pound is stronger and can buy more of other currencies - depreciation is the opposite.
When the pound is stronger (appreciation) businesses will find it harder to export UK made goods abroad as they will appear more expensive to other countries.
When the pound is strong UK businesses that import materials from abroad will have cheaper costs
SPICED - Strong Pound Imports Cheaper Exports Dearer
Effect on businesses of changes in interest rates:
If interest rates rise then the cost of borrowing will rise and this will mean that the cost of supplies for a business may increase
A fall in interest rates means that the cost of lending falls which may lead to an increase in profits (costs less to borrow so less to pay back)
Effect on businesses of changes in taxation and government spending:
Lower taxes can result in more demand in the economy and lead to higher output and employment
If taxes are high then UK businesses will have higher costs
This makes them less competitive in a global marketplace
It may also mean unemployment rates may rise as businesses have to lay off extra staff due to the reduction in demand
Less government spending will affect businesses that supply goods and services to public organisations (e.g. the NHS, farmers or care home providers)
Effect on businesses of changes in the business cycle:
Boom - Increased demand as increased work, lower unemployment and higher wages.
Recession - Falling demand as consumers are saving as interest rates go up. Businesses will typically make redundancies to lower costs as demand falls.
Slump - Lowest spending, little investment in businesses and higher wages levels of unemployment.
Recovery - Demand increases again as unemployment falls.
The effect of economic uncertainty on the business environment:
Risk of unemployment so consumers delay purchase of goods
Demand falls
Manufacturers are reluctant to expand and grow which reduces supply of goods and services.
The effect of consumer protection on businesses:
Businesses must not give false or misleading information about products.
Unhappy customers can get a refund or replacement.
Consider cost, reputation and profitability.
The effect of employee protection on businesses:
Consider cost, reputation and profitability.
Gives sick pay/maternity leave
Minimum wage
The effect of environmental protection on businesses:
Consider cost, reputation and profitability.
Controls pollution in terms of business waste that is disposed of in the air, on land and in the sea.
The effect of competition policy on businesses:
Consider cost, reputation and profitability.
The competition and markets authority stops things like businesses agreeing to set prices really high for all products of one type.
The CMA also investigates mergers that restrict competition - gives consumers the right to choose.
The effect of health and safety on businesses:
Consider cost, reputation and profitability.
Businesses must provide health and safety training
Businesses must make work environment safe and prevent accidents
Factors affecting competitiveness in a market:
Growth rate of market
Level of regulation (legislation)
Type of business ownership
The products/services produced
The nature of product range
Seasonality
Pricing and pricing strategies
Marketing methods used.
The impact of competition of businesses
Fall in prices
Increased costs of promotion
Improved efficiency
Increased innovation
Wider product ranges
Productivity definition
The output per input (person or machine) per hour
Production definition
The total amount of output that is produced in a time period
The methods of production:
Job
Batch
Flow
Cell
Job production definition
When one single product is made at a time (e.g. a cake) for a specific client. Products are high quality and the production process can be slow and labour intensive.
Advantages of job production:
Products are unique and personal to the customer - can charge premium price
Disadvantages of job production:
Skilled labour and craftsmen are expensive
Hard to speed up if demand increases
A wide range of tools may be required
Batch production definition
When standardised components can be made in relatively large quantities, but the system can be modified or adjusted to the specification, like changing the size, colour or features. (e.g. In a bakery, making similar cupcakes that may have different icing, but are still the same).
Advantages of batch production:
Can be changed to meet customer needs or fluctuations in demand.
Standard productions of items means machinery can be used.
Lower skilled workforce than job production → lower wages can be paid
Disadvantages of batch production:
Smaller batch’s carry average unit costs (EOS)
Workers may be less motivated with repetitive work
Flow production definition
Production that uses production lines with continuous movements of items through the process in assembly lines (e.g. toothpaste).
Advantages of flow production:
Products are made in large quantities so business can bulk buy raw materials and save money (EOS)
Disadvantages of flow production:
High costs for factory + machinery
Low motivation of staff as repetitive
Break downs and lost production can be costly
Very inflexible
Cell production definition
Dividing up a production line into separate self contained areas that are each responsible for a section of work (e.g. a car assembly line where one group makes the engine, one makes the interior etc.)
Advantages of cell production:
Wastage through movement of materials is reduced
Time waiting for stock to arrive is reduced
Bottlenecks in production process are reduced (where everything builds up waiting to go to the next stage)
Increased worker commitment and motivation
Disadvantages of cell production:
Any breakdown of machinery will stop production
Needs more staff to supervise than a continuous flow
Expanding can be hard as space may be limited
Factors affecting productivity:
Quality of inputs (workers, machines)
Having the right no. staff at peak times - stretched staff are demotivated by being overloaded
No. machines/staff - machines can work 24/7, staff can’t and become demotivated
The link between productivity and competitiveness:
To make a business more competitive, the business can produce more with the same levels of resources by:
Training staff
Introducing financial incentives
Maintaining machines
Improving working practices
This means that costs will be lowered so prices can be lowered, meaning:
You can undercut competitors’ prices
You can gain market share
You can improve your brand recognition
Profit is increased
You can invest in ways to improve productivity - this ends up reducing costs, making a cycle
Efficiency definition
Try to produce goods at the minimum unit or average cost
Factors influencing efficiency:
Standardisation of the production process
Relocation or downsizing
Investment in capital equipment
Organisational restructuring
Outsourcing
Adoption of lean production techniques
Distinction between labour and capital intensive production
Labour intensive means making products using mostly human effort, capital intensive means making products using mostly machines and equipment
Capacity utilisation calculation
Capacity utilisation = (Current output/Maximum possible output) *100
Implications of over-utilisation:
Can damage reputation of business
Can put too much strain on resources
Staff may do too much overtime and have accidents when tired
No time to maintain machinery or train staff
Quality suffers as mistakes are made
Implications of under-utilisation:
Higher fixed costs per unit
Unmotivated staff
Impact on brand image (e.g. empty restaurant)
Business may need to rationalise:
Can mean redundancies
Sale of assets
Hiring temporary staff instead of full time permanent
Reduction in overtime hours
Partial shutdown
Increases flexibility of business:
Able to accept a non-standard order
Have time to maintain machinery or update tech
Have time to train staff
How to improve capacity utilisation:
Increase demand through a price cut sale or promotion
Make staff redundant
Sell assets such as machinery and lease is back when needed
Lease capacity out to other businesses
Move to smaller premises and rationalise
Increase sales (cut prices) or increase usage (off peak travel)
The stock control diagram:
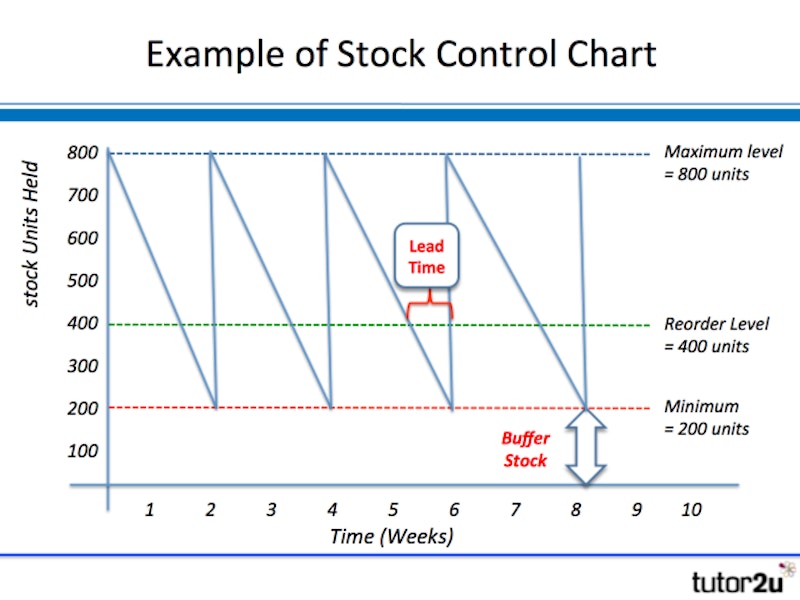
Buffer stock definition
Stock that is held in case there is an unforeseen rise in demand or a problem with supply
Implications of poor stock control:
Loss of customer goodwill
Loss of sales revenue
Damage to reputation
Disruption to production
Just in time (JIT) management of stock definition
When a business does not keep stock and instead orders parts from the supplier on the same day the product is ordered. It is a form of lean manufacturing.
Impacts of waste minimisation
Improves efficiency
Reduces unit costs of production
Improves the public image of the business - more eco friendly
Can have large legal fines for non-compliance.
Competitive advantage of lean production:
Improved customer service through delivering exactly what is wanted when it is wanted
Improved productivity
Quality improvements through reduction in defects
Shorter lead times
Reduced waste
Safer work environment as production is more organised.
Quality definition
How well a product or service does what it was designed to do
Quality control definition
The traditional way of managing quality. It is concerned with checking and reviewing work that has already been done. Done at the end.
Quality assurance definition
About how a business can design the way a product or service is produced or delivered to minimise the chances that the output will be sub-standard. Done at the design/development stage.
Quality circle definition
A group of employees who meet on a regular bases to talk about quality problems that are relevant to the part of the process that they work on.
Total quality management (TQM) definition
A management approach that puts quality at the heart of everything in the business. Includes “putting the customer first” in customer service.
Continuous improvement (Kaizen):
A policy of constantly introducing small changes in a business to improve quality and/or efficiency.
Assumes that employees are the best people to identify room for improvement
Ideas come from workers themselves so are easier to implement
Competitive advantage from quality management:
Competitive advantage through quality.
Consumers willing to pay more
Customers may repeat purchase products which have the best of most consistent quality.
Gross profit calculation
Gross profit = Sales revenue - Cost of sales
Profit definition
The financial gain of a business through trading and can be found by deducting expenditure from income
Types of profit:
Gross profit
Operating profit
Net profit (profit for the year)
Operating profit calculation
Operating profit = Gross profit - Expenses
Net profit calculation
Net profit = Operating profit - Interest
Gross profit margin calculation
Gross profit margin = (Gross profit/Sales revenue) * 100
Operating profit margin calculation
Operating profit margin = (Operating profit/Sales revenue) * 100
Net profit margin calculation
Net profit margin = (Net profit/Sales revenue) * 100
Ways to improve profitability (by either increasing revenue or reducing costs):
Having a sale (reducing prices but increasing no. sales)
Advertising more
Promoting the products more
Restructuring, delayering and redundancies
Automating production
Distinction between profit and cash:
Profit:
Recorded straight away
A business can trade for years without profit
Cash:
Cash is not recorded until it is paid out or received which could be in a different trading year
A profitable business may go bust if it runs out of cash to pay a supplier or wages of staff
If owners introduce cash via savings or a loan this will not affect the profit figure.
Liquidity definition
The ability of a business to turn its assets into cash to pay its current liabilities
Ways of measuring liquidity:
Current ratio
Acid test ratio
Current ratio calculation
Current ratio = Current assets:Current liabilities (in its simplest form)
Acid test ratio calculation
Acid test ratio = (Current assets - Inventory):Current liabilities
The purpose of the acid test ratio
It compares a company’s assets and liabilities to see if it can meet its short-term debts. It removes inventory which can be difficult for it to liquidate quickly.
Ways to improve liquidity:
Reduce the amount of stocks the business holds, so the finished goods need to be dispatched faster to customers.
Reduce the credit period offered to customers, for example insist that customers pay in 30 days not 90
Pay suppliers later
Increase borrowing long term and clear short term debts
Working capital definition
The day-to-day finance needed to trade in a business
Working capital calculation
Working capital = Current assets - current liabilities
The working capital cycle:
Cash
Cash paid by debtors for goods or services bought (current assets)
Sales
Stock purchased from suppliers on credit (current liabilities)
Repeat
The importance of cash:
Cash and the working capital of the business is the finance available for the business to meet its short term debts.
Working capital is the finance required to pay day-to-day expenses to keep the business running
Business failure definition
When a business ceases to trade or when a business does not trade in a profitable way or when a business makes a terrible decision
Liquidation definition
The process of closing an Ltd or PLC. There will be a sale of assets and the company (as it stands) is dissolved
Administration definition
When a business that is failing is bought by another business
Financial causes of business failure:
Cashflow problems (e.g. allowing too much trade credit) - Internal
Economic conditions (e.g. inflation) - External
Non-financial causes of business failure:
Competition - External
Legislation (e.g. minimum wage increases) - External
Market conditions (e.g. consumer trends) - External
Poor planning - Internal
Poor marketing - Internal
Lack of skills - Internal
Sales forecast definition
An estimate of the volume or value of future sales using market research or past sales data.
The purpose of sales forecasts:
To avoid cashflow problems
To free up management time
To manage production capacity
To employ more workers
To help start a promotional activity
Factors affecting sales forecasts
Consumer trends
Economic variables (e.g. interest rates, inflation rate, unemployment rate etc.)
Actions of competitors
Difficulties of sales forecasting:
Dynamic markets
Not useful for businesses that operate over a time period longer than a year (e.g. ship building)
No guarantees that it will be correct as it is an estimate
Sales revenue definition
Cash that buyers pay you for goods
Profit definition
When total revenue is more than costs
Sales volume calculation
SV = Sales revenue/Selling price
Fixed costs definition
Costs that do not vary with the level of output (e.g. rent)
Variable costs definition
Costs that do vary with level of output
Total variable costs calculation
Total variable costs = Average variable cost * Quantity sold
Total costs calculation
Total costs = Variable costs + Fixed costs
Contribution calculation
Contribution = Selling price - Variable costs per item
Contribution definition
The amount that each unit produced ‘contributes’ towards the fixed costs of the business (or the profit made per item)
Break even definition
The point at which revenue equals cost, so the business is making neither a profit or a loss
Break even point calculation
Break even point (expressed as an amount of units) = Fixed costs / Contribution per unit
Margin of safety definition
The difference between the break-even point and the current sales
Margin of safety calculation
Margin of safety = Actual sales - Breakeven level of safety
Limitations of break even:
Break-even does not take into account any sales discounts if customers buy in bulk
Break-even assumes everything that is made is sold, and this is not always the case
The break-even calculations are only as accurate as the data they are based on
Budget definition
An estimate of income or expenditure for a set period of time (usually a month or a year of trading)
The purposes of budgets:
Planning
Forecasting
Communication
Motivation
Types of budget:
Historical budget
Zero based budget
Historical budget definition
A budget set for the business using current financial figures and based on historical performance of the business
Zero-based budget definition
A budget set for a business by using figures based on potential performance. It takes away all historical assumptions and starts with a clean slate.
Variance definition
The difference between estimated budget vs the budget that actually happens