Optic Nerve Disease
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
prepapillary vascular loops
95% are arterial
appear as loops that extend from the disc into the vitreous & then back to the disc
spontaneously move with the heartbeat in 50% of cases
sheathed in glial tissue in 30% of cases
bilateral 9-17% of the time
cilioretinal artery also present in 75% of cases
generally benign
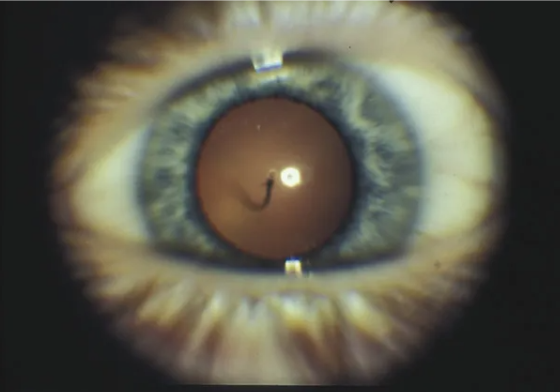
persistent hyaloid artery
single vessel traveling from disc to the posterior capsule of the lens
usually attaches inferonasal to the visual axis on the posterior capsule
present in 95% of premature infant eyes & 3% of full term infant eyes
usually bloodless
ocular associations:
persistent fetal vasculature
coloboma of the disc
optic nerve hypoplasia
posterior vitreous cysts
persistent Bergmeister’s papilla
develops around the posterior aspect of the fetal hyaloid artery
due to incomplete regression of sheath around hyaloid artery
appearance:
tuft of glial tissue
usually on nasal ONH
nerves w/ this have minimal physiological cupping
benign
congenital pit of the optic disc
appearance:
local depression that can be yellow-white, gray, black, or other color
0.25-0.4DD in size
>50% are temporal (but can be anywhere on disc or peripapillary)
nerve w/ this finding is often larger than fellow nerve
complications:
RD
posterior retinoschisis
no known systemic complications or hereditary pattern
optic nerve coloboma
congenital
etiology: incomplete closure of embryonic fissure during 2nd month of gestation
appearance:
enlargement of peripapillary area
partial/total excavation of the disc (inferior)
retinal vessels often are entering & exiting along the edges
unilateral or bilateral
variable VA (dependent on amount of neural tissue impacted)
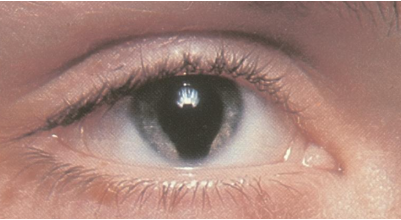
concomitant iris & retinal defects are possible
complications:
non-rhegmatogenous RD
systemic associations:
CV, GI, genitourinary, nasopharyngeal, musculoskeletal diseases
FAS
CHARGE syndrome
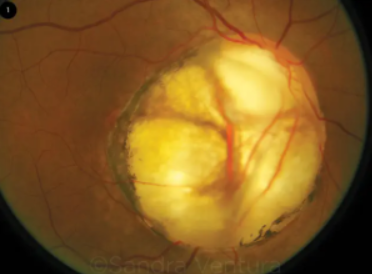
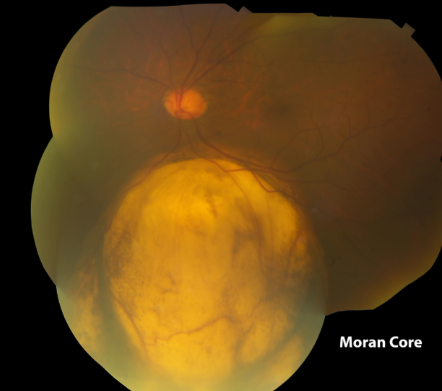
morning glory disc anomaly
congenital
rare
appearance
enlargement & excavation of ONH
central core of white tissue
peripapillary annulus of variably pigmented subretinal tissue
retinal vessels that enter & exit form the borders of the defect
vessels are usually straight & sheathed
complications:
non-rhegmatogenous RD (30%)
strabismus → amblyopia
amblyopia more common in unilateral cases
associations:
intracranial vascular abnormalities (ex: carotid artery stenosis)
megalopapilla
optic disc that is 2.1mm or larger in the horizontal & vertical dimensions
enlarged but otherwise normal looking disc
often mild peripapillary RPE disturbances
typically normal vision
associations:
optic disc coloboma
congenital optic pit
morning glory disc
high myopia
cleft palate
mandibulofacial dysostosis
optic nerve hypoplasia
highly variable presentation (normal - severely involved nerve)
etiology: failure of development of GCL
pharmacological insults prenatally
maternal infection
high hyperopia, strabismus, amblyopia
nystagmus
idiopathic
unilateral = bilateral
appearance:
small ONH
retinal vessels enter & exit centrally
double ring sign
highly variable VA
associations:
pituitary disfunction (anterior, posterior, or panhypopituitarism)
strabismus, amblyopia, anisometropia
fetal teratogens
endocrinology workup due to association w/ pituitary abnormalities
what is part of the general standard workup for any child w/ an optic nerve hypoplasia?
septo-optic dysplasia
developmental disorder characterized by ONH hypoplasia, midline brain defects, & pituitary gland abnormalities
pts can have developmental delays, hormone deficiencies, seizures, & other neurological issues
prepapillary vascular loops
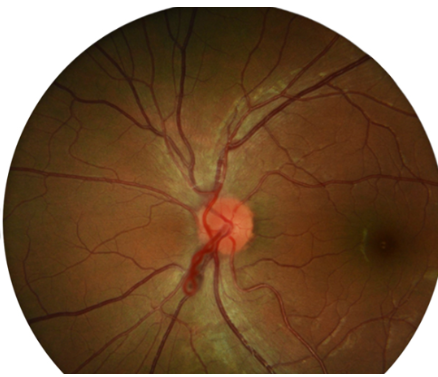
prepapillary vascular loops
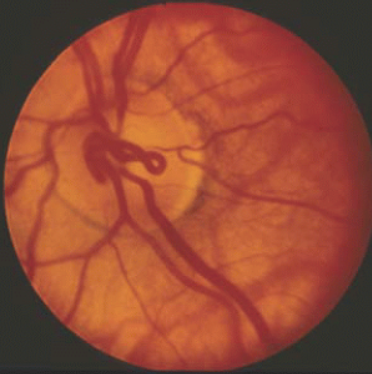
persistent hyaloid artery
persistent Bergmeister’s papilla
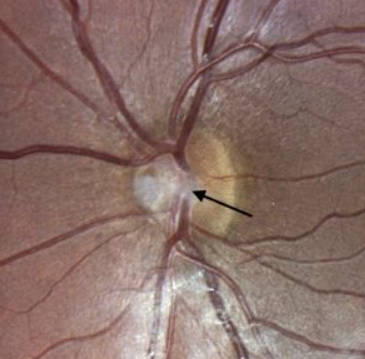
persistent Bergmeister’s papilla
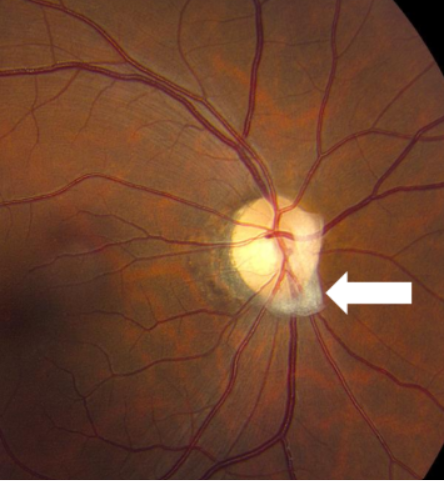
persistent Bergmeister’s papilla
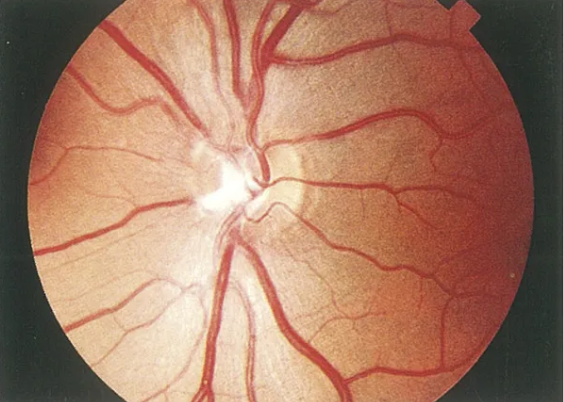
congenital pit of the optic disc
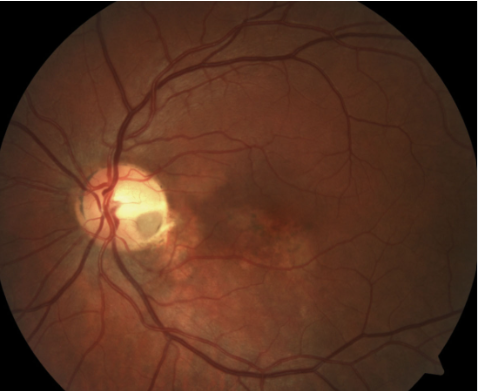
optic nerve coloboma
optic nerve coloboma
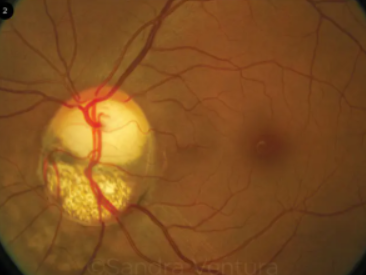
optic nerve coloboma
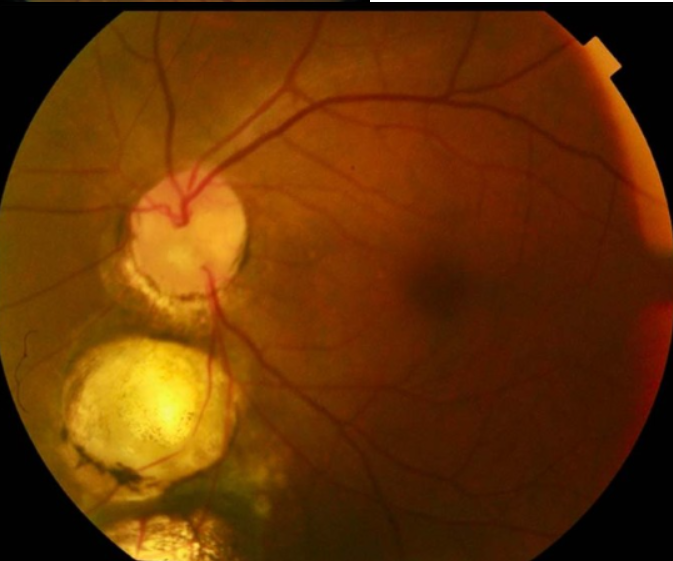
optic nerve coloboma
iris coloboma
morning glory disc anomaly
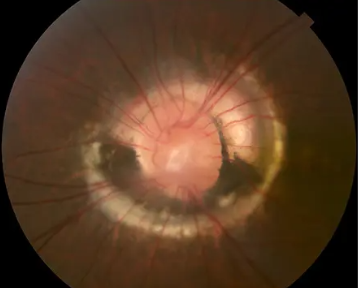
morning glory disc anomaly
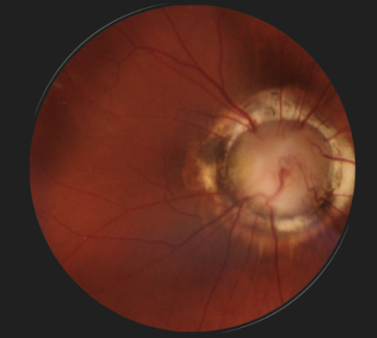
optic nerve hypoplasia
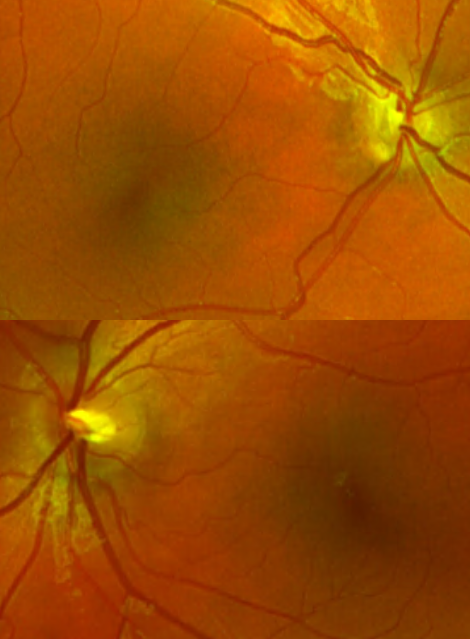
optic nerve hypoplasia
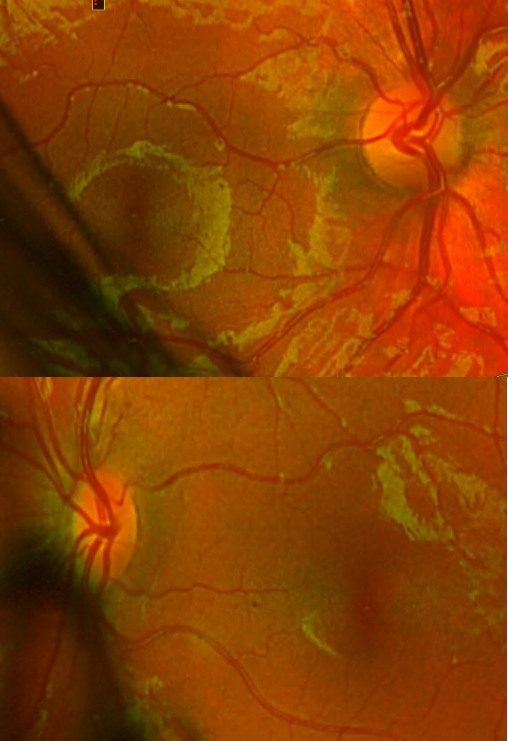
optic nerve hypoplasia
junction of sclera & lamina cribosa & corresponds w/ size of normal optic disc
what is the outer ring in the “double ring sign” in optic nerve hypoplasia?
border or central ONH tissue w/ retina & RPE
what is the inner ring in the “double ring sign” in optic nerve hypoplasia?