Embryogenesis and Human Development: Key Concepts and Stages
1/16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is the process of fertilization?
Fertilization occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube when a secondary oocyte is met by sperm, which must penetrate the corona radiata and zona pellucida.
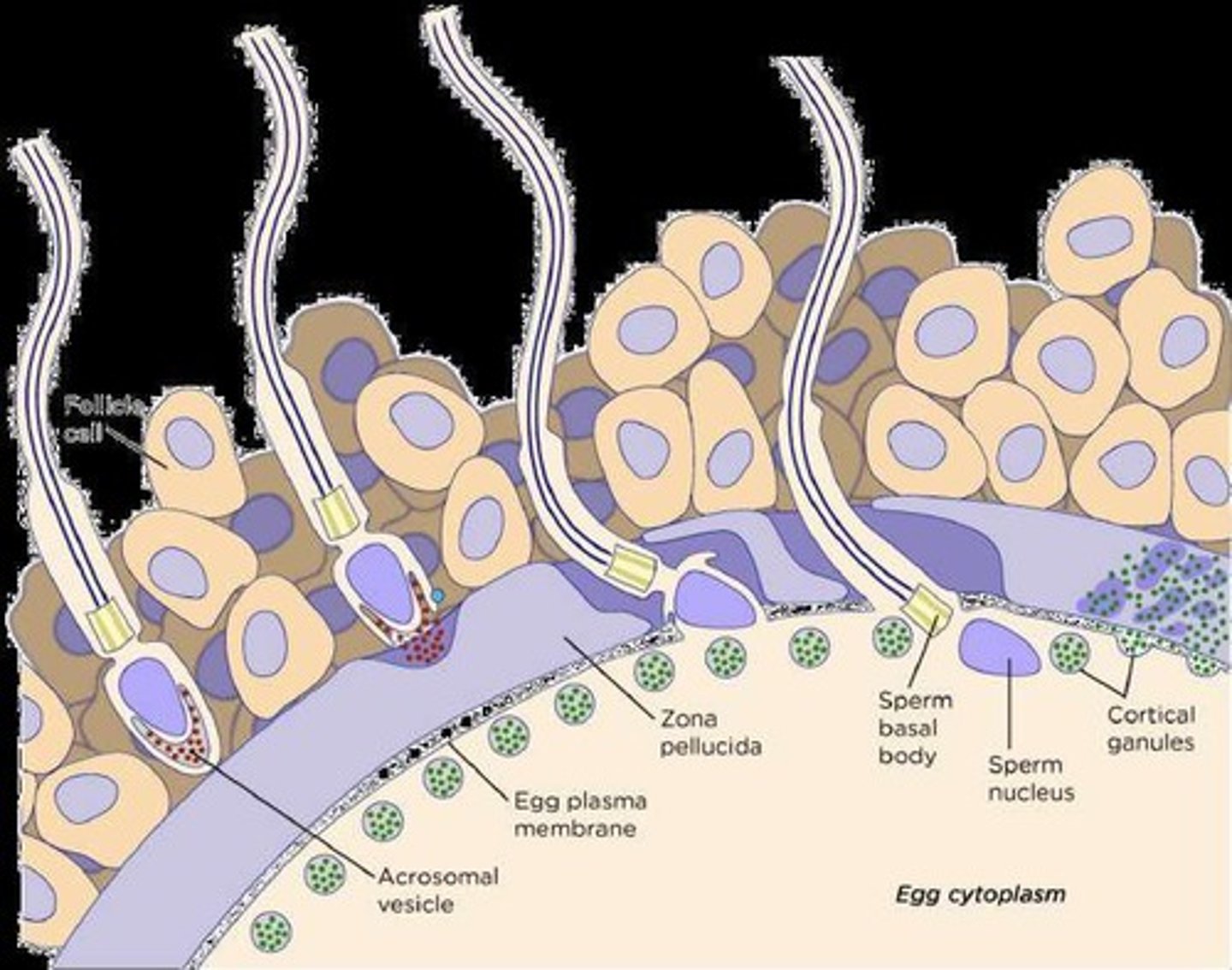
What happens during the cortical reaction after fertilization?
The cortical reaction involves the release of calcium ions, leading to depolarization, which prevents fertilization by additional sperm and increases the metabolic rate of the zygote.
What are the two types of twins and how do they differ?
Monozygotic twins are genetically identical twins formed from one zygote that splits, while dizygotic twins are fraternal twins formed from two separate eggs.
What is cleavage in embryonic development?
Cleavage is the rapid mitotic division of the zygote as it moves toward the uterus for implantation, marking the formation of an embryo.
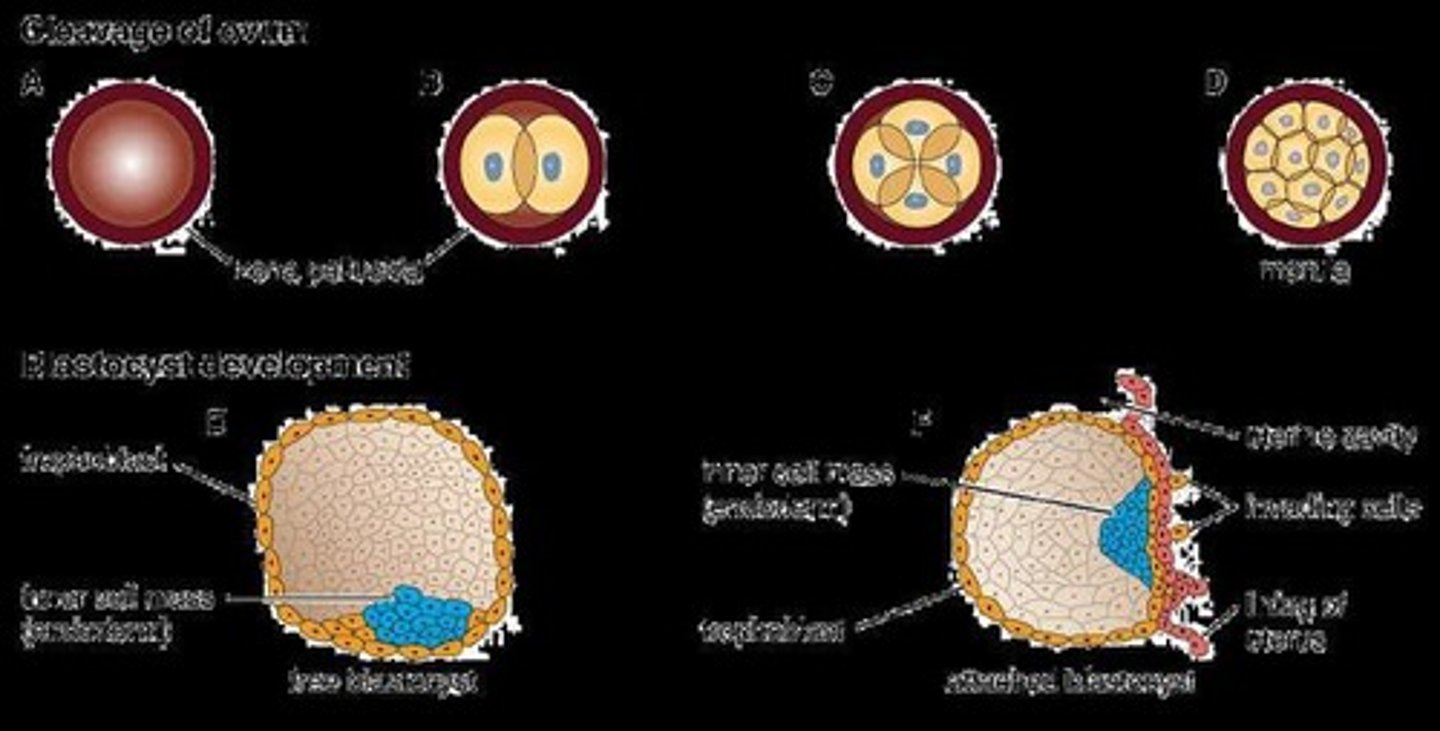
What is the blastula and how is it formed?
The blastula is a hollow ball of cells formed from the morula, containing a fluid-filled cavity called the blastocoel.
What is the role of trophoblasts during implantation?
Trophoblasts form chorionic villi that help establish the placenta and connect the embryo to the uterine wall.
What is gastrulation and what does it create?
Gastrulation is the process that creates three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm) through invagination of cells into the blastocoel.
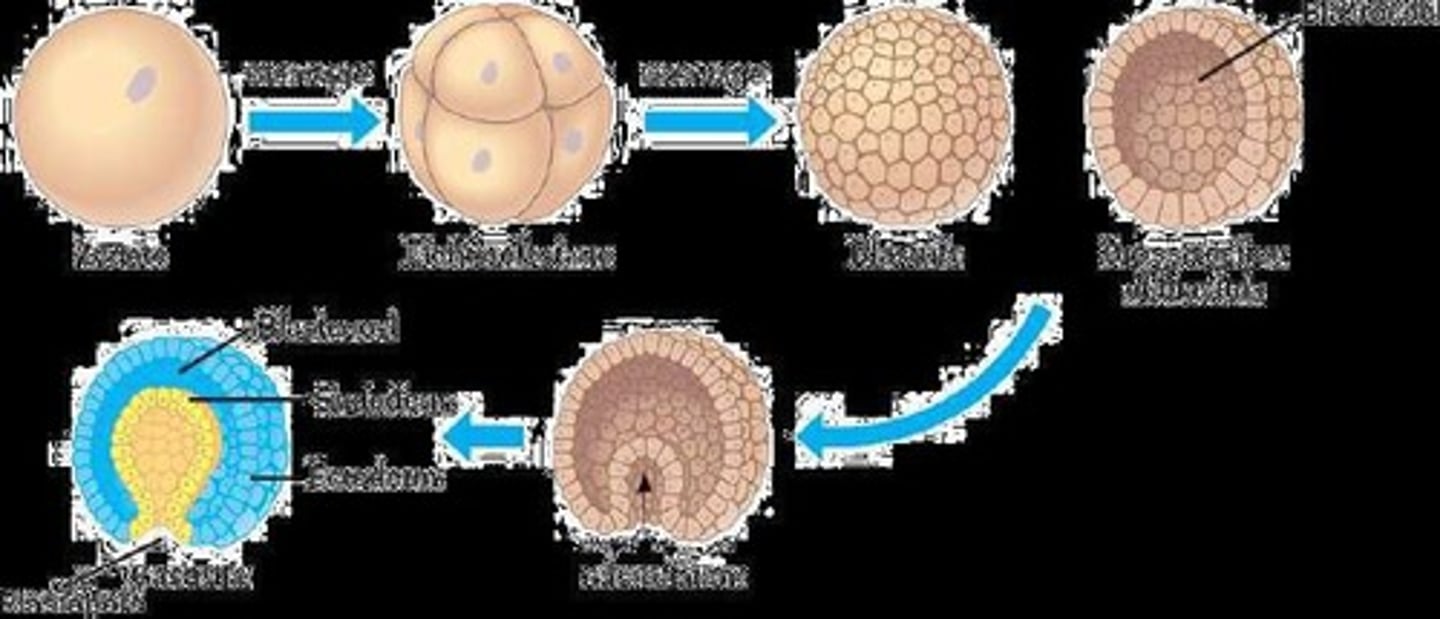
What are the three primary germ layers and their derivatives?
Ectoderm (skin, nervous system), mesoderm (muscles, bones, circulatory system), endoderm (GI tract, respiratory linings).
What is neurulation?
Neurulation is the development of the nervous system, initiated by the formation of the notochord from mesoderm cells, leading to the formation of the neural tube.
What are teratogens?
Teratogens are substances that interfere with embryonic development, potentially causing defects or death of the developing embryo.
What is the difference between specification and determination in cell development?
Specification is when a cell is reversibly designated to a type, while determination is when a cell is irreversibly committed to a specific fate.
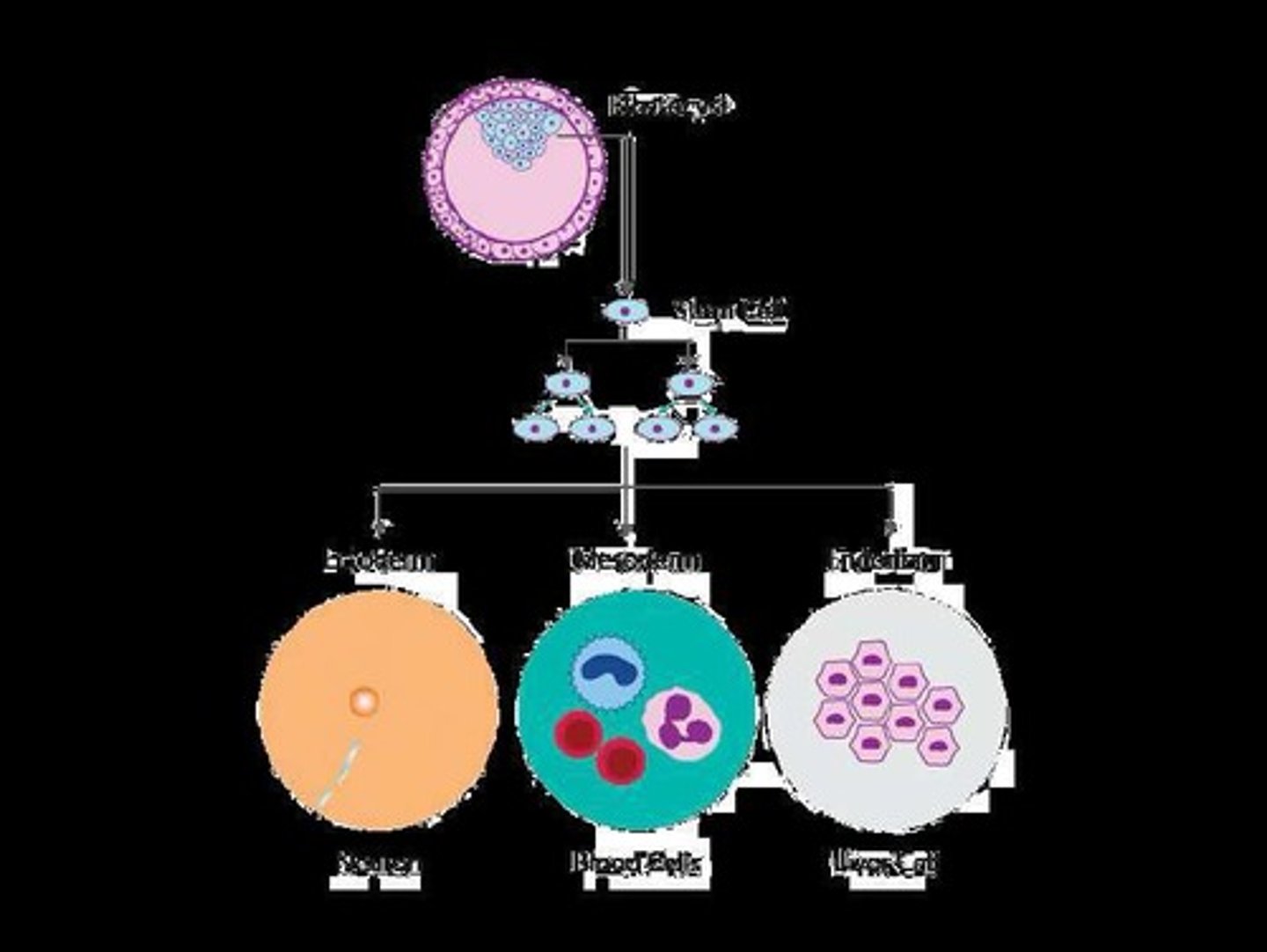
What are stem cells and how are they classified?
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells with the potential to become various cell types, classified by potency: totipotent, pluripotent, and multipotent.
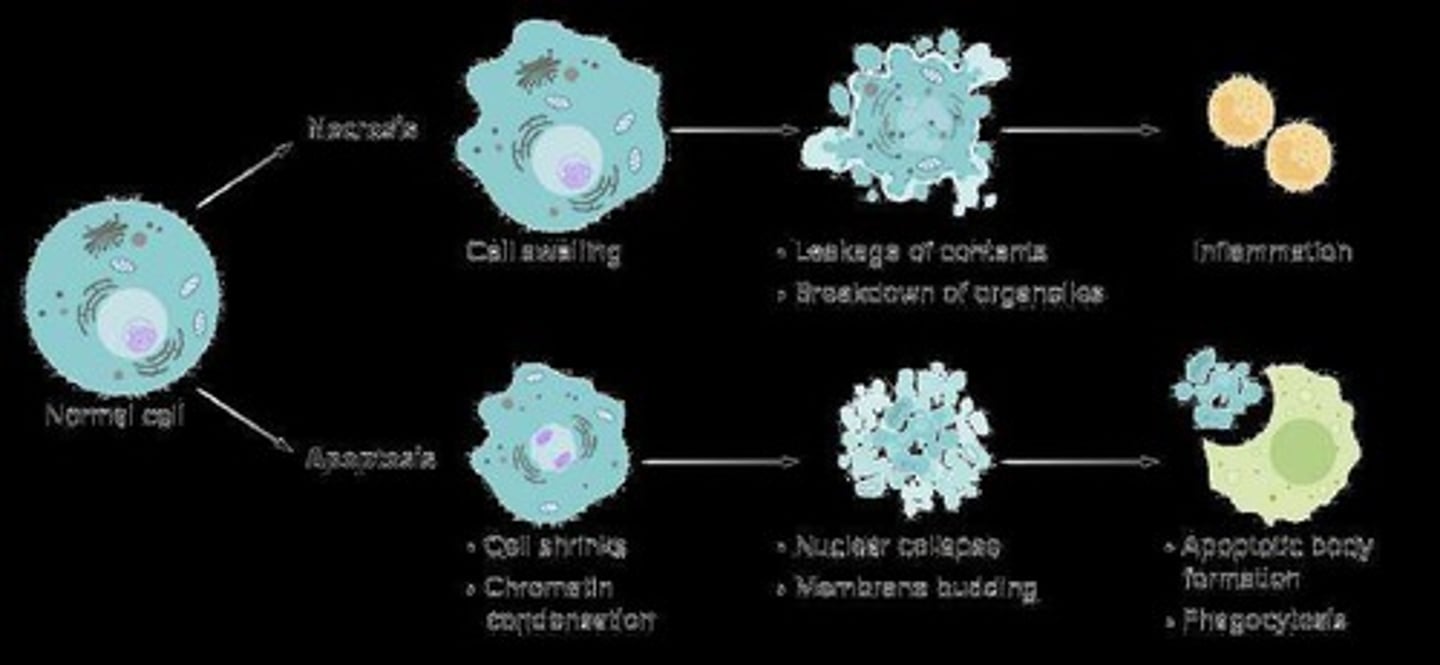
What is apoptosis?
Apoptosis is programmed cell death, while necrosis is uncontrolled cell death due to injury.
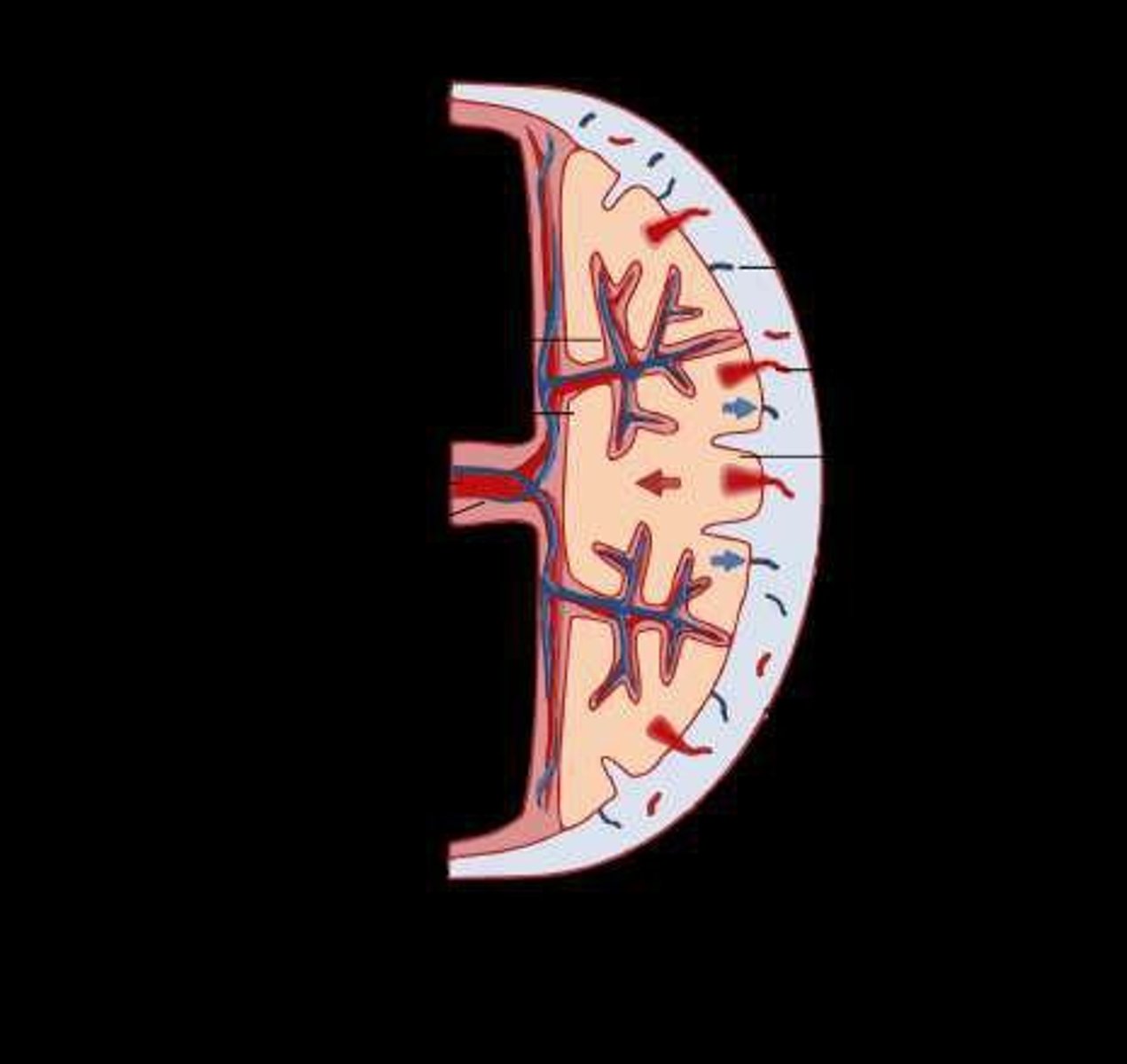
What is fetal circulation and how does it differ from adult circulation?
Fetal circulation involves the placenta for nutrient and gas exchange, with structures like the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus bypassing the lungs.
What is the role of the placenta during pregnancy?
The placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients, gases, and waste between the mother and fetus, and acts as an immune barrier and endocrine organ.
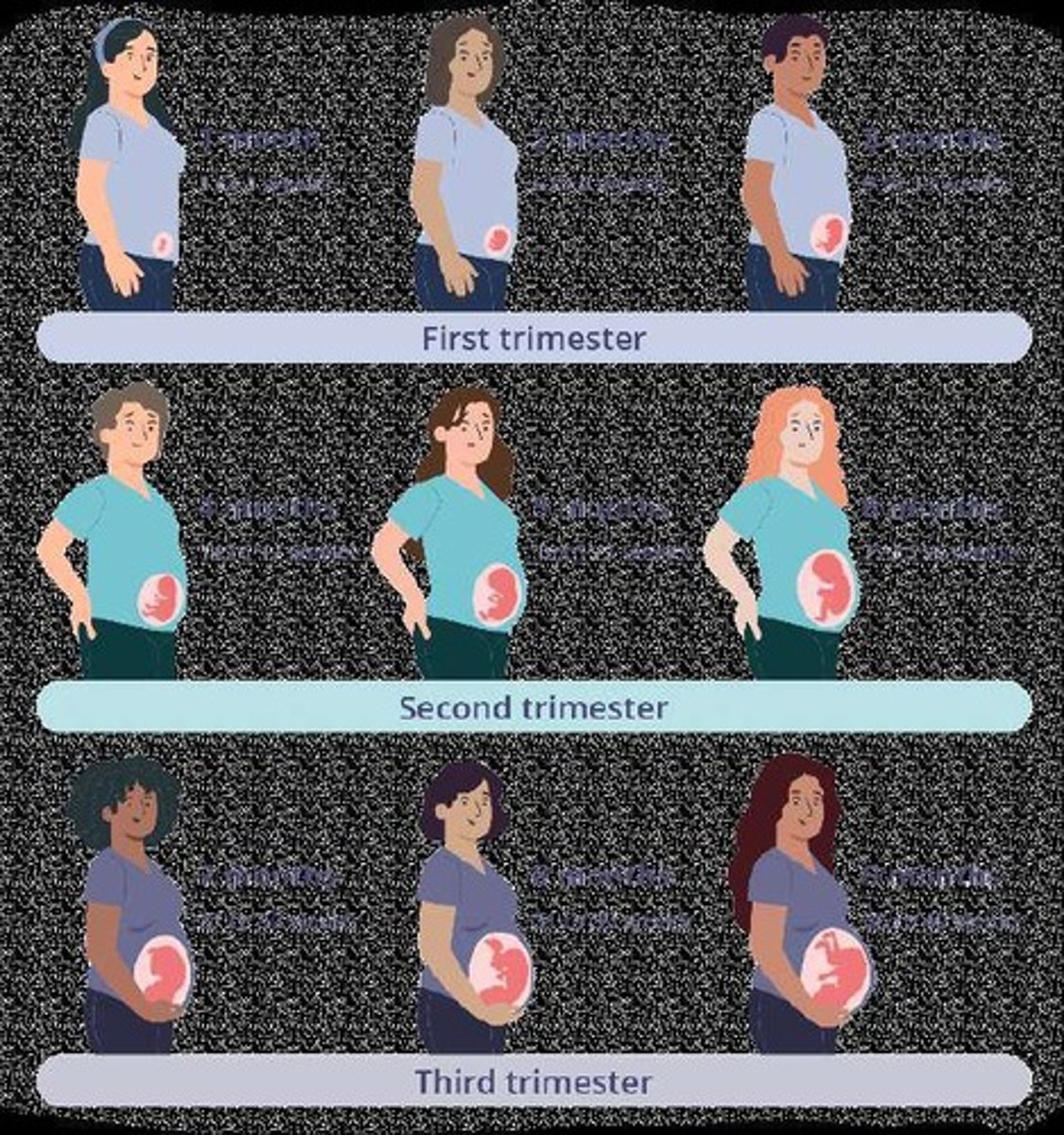
What are the three trimesters of human gestation?
The first trimester involves organogenesis, the second trimester involves growth and movement, and the third trimester involves rapid growth and brain development.
What triggers the birth process?
The birth process is triggered by uterine contractions, coordinated by prostaglandins and oxytocin, leading to the expulsion of the fetus and placenta.