Seminars in Clinical Physiology Bank
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
Based on Mr SOR Medical History what is the main cause of reduced capacity on exercise ?
A. Reduced coronary perfusion of myocardium
B. Reduced cardiac output
C. Impaired blood gas exchange
D. Impairment of baroreceptor reflex function
E. Combination of respiratory and cardiovascular problems
B. Reduced cardiac output
Based on the above mentioned heart rate (70bpm) which of the blood pressure parameters is out of normal range?
A. The systolic blood pressure
B. The diastolic blood pressure
C. The mean arterial pressure
D. The pulse pressure
E. All pressure parameters are in normal range
D. The pulse pressure
What ECG shows?
A. Normal cardiac electrical activity
B. Complete (3rd degree) Atrioventricular Block, CAVB
C. Incomplete Atrioventricular Block, AVB
D. Left Bundle Branch Block, (LBBB)
E. Atrial fibrillation
A. Normal cardiac electrical activity
Based on the ECG findings you can conclude that the heart ?
A. Is normal with vertical position
B. Has vertical position with right ventricular hypertrophy
C. Has vertical position with left ventricular hypertrophy
D. Has horizontal with right ventricular hypertrophy
E. Is horizontal with left ventricular hypertrophy
E. Is horizontal with left ventricular hypertrophy
How do you interpreted the above results?
A. Hypocalcemia
B. Hyperkaliemia
C. Metabolic alkalosis
D. Hypercholesterolemia
E. Normal values
D. Hypercholesterolemia
Temporal presentation and characteristics of 1st heart sound provide useful information for cardiac function mainly due to fact that 1st heart sound caused by:
A. Opening of atrioventricular valves
B. Fast ventricular filling
C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
D. Fast ejection of ventricles
E. Closing of ventricular valves
C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
At this stage of evaluation can you conclude if symptoms of shortness of breath, angina and syncope are caused by ?
A. Pulmonary valve stenosis
B. Mitral valve regurgitation
C. Aortic valve stenosis
D. Tricuspid valve regurgitation
E. Aortic valve regurgitation
F. B and C
G. A and E
F. B and C
What does wedge pressure (PCWP) represents ?
A. Pressure of left atrium
B. Pressure of left ventricle
C. Pressure of pulmonary artery
D. The pressure of pulmonic capillaries
E. The pulmonary blood gas exchange
A. Pressure of left atrium
Based on the pressure waveforms which of the following diagnosis must be excluded ?
A. Pulmonary valve stenosis
B. Mitral valve regurgitation
C. Tricuspid valve regurgitation
D. Aortic valve stenosis
E. A and C
E. A and C
What are the main causes of SOB on exertion ?
A. Hypercapnia due to reduced blood flow to skeletal muscles
B. Hypercapnia caused by the increased pressures of pulmonary veins
C. Metabolic acidosis due to reduced blood flow to skeletal muscles
D. Reduced lung due to cardiac hypertrophy
E. None of the above
C. Metabolic acidosis due to reduced blood flow to skeletal muscles
What are the main causes of angina on exercise ?
A. Reduced oxygen intake due to increased pulmonary vein pressures
B. Reduced removal of myocardial metabolites due to reduced coronary perfusion
C. Reduced removal of myocardial metabolites due to decrease time of coronary perfusion
D. B and C
E. All, A, B, C
D. B and C
What are the main cause of syncope on standing position ?
A. Inability to trigger vasoconstriction through baroreceptor activation due to high sympathetic nervous system function
B. Inability to increase cardiac output due to increased systemic resistance
C. Absent of baroreceptors activation due to low arterial pulse pressure
D. Reduced vein return due to high pulmonary vein pressures
E. B and C
B. Inability to increase cardiac output due to increased systemic resistance
Does patient symptoms will improve by ?
A. Beta adrenergic inhibitors which will decrease hear rate and thus improve left ventricular filling
B. Alpha adrenergic activators which induce peripheral vasoconstriction
C. Use of abdominal compression corset which will mobilize the congestive splanchnic blood
D. Use of Alpha adrenergic inhibitor which induce peripheral vasodilatation
E. None of the above
E. None of the above
ECG revealed bradycardia due to ?
A. 1st degree atrioventricular block
B. 2nd degree atrioventricular block
C. Complete (3rd degree) atrioventricular block
D. Left Bundle block
E. Sinus bradycardia
C. Complete (3rd degree) atrioventricular block
The location of pacemaker center is in ?
A. Atrioventricular node
B. Atrioventricular pathway
C. The bundle of His
D. The level of bundles
E. Ventricular myocardium
C. The bundle of His
Which is the lowest atrial pressure that could induce pulmonary edema ?
A. 15mmHg
B. 20mmHg
C. 25mmHg
D. 35mmHg
E. 60mmHg
C. 25mmHg
Thiazidic diuretics ?
A. Inhibit carbonic anhydrase
B. Function at level of distal convoluted tubule
C. Decrease potassium excretion
D. Act at the level of loop of Henle
B. Function at level of distal convoluted tubule
The antithrombotic action of warfarin :
A. Is often reduced in patients who takes antibiotics
B. Induce inhibition of Vit K connection with the apo-enzyme
C. Influence only the intrinsic pathway of thrombosis
D. Induce inhibition of thrombin function
E. Mimics the deficiency of thrombotic mechanism of haemophilia
B. Induce inhibition of Vit K connection with the apo-enzyme
Which are not clinical findings of severe aortic stenosis?
A. Diastolic murmur
B. Systolic murmur
C. Pulsus paradoxus
D. Pulsus alternans
E. Pulsus parvus et tardus
F. A, C and D
F. A, C and D
The 1st heart sound is caused by:
A. Opening of atrioventricular valves
B. Fast ventricular filling
C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
D. Fast ejection of ventricles
E. Closing of ventricular valves
C. Closing of atrioventricular valves
Pulse pressure is low when :
A. Contractility is increased
B. Preload is decreased
C. Afterload is decreased
D. Ventricular filling time is increased
B. Preload is decreased
Women have normally lower Hct levels compared to men because:
A. estrogens promote albumin production
B. testosterone stimulates erythropoiesis
C. women have a regular monthly blood loss due to menstruation
D. women have a lower ability to store iron
E. The red blood cell half life is shorter in women
B. testosterone stimulates erythropoiesis
Two of the students had pathologic findings in their CBC. This could exclude them from participating in the trip. Specifically Julie G., whose family has origins from Naples Italy, has the following findings:
RBC : 5.8 x 109 /ml
HB : 11.0 g/dl
MCV : 70 fl
MCH : 19 pg
Reticulocytes : 6%
Based on these findings, the diagnosis is:
A. hypochromic, normocytic anemia
B. hypochromic, macrocytic anemia
C. hypochromic, microcytic anemia
D. normochromic, microcytic anemia
E. normochromic, normocytic anemia
C. hypochromic, microcytic anemia
The anemia that Julie G. has is suggestive of:
A. β-thalassemia
B. iron deficiency
C. pernicious anemia
D. all the above
E. either only A or only B
A. β-thalassemia
The change of the RBC shape observed in sickle cell disease correlates with:
A. increased red blood cell production rate
B. decreased blood viscosity
C. Increased peripheral capillary refill time
D. reduced reticulocyte number
E. None of the above
E. None of the above
Sickling is more likely to present in hypertonic or hypoxemic conditions.
Considering this, which of the following is more possible to occur in people with sickle cell trait because of hypoxia?
A. bone pain
B. myocardial infarction
C. ischemic stroke
D. polyuria
E. Pulmonary edema
D. polyuria
An acute asthmatic crisis during exercise is caused by:
A. systemic hypoxia due to increased oxygen consumption
B. airway mucosal dehydration due to increased air flow
C. stimulation of chemoreceptors due to increased inhalation of allergens
D, direct bronchospasm due to increased oxygen pressure
E. airway shrinkage due to decreased circulating plasma volume
B. airway mucosal dehydration due to increased air flow
The barometric pressure at 3700 m (11500 feet) is equal to 480mmHg (64kPa).
The atmospheric PO2 is:
A. 480 mmHg (64 kPa)
B. 433 mmHg (58 kPa)
C. 380 mmHg( 51 kPa)
D. 100 mmHg (13 kPa)
E. 53 mmHg (7 kPa)
D. 100 mmHg (13 kPa)
In this atmospheric PO2 what will the PAO2 be if Kathy continued breathing with the same minute ventilation as on the level?
A. 100mmHg (13 kPa)
B. 90 mmHg (12 kPa)
C. 40 mmHg( 5.3 kPa)
D. 20 mmHg( 2.7 kPa)
E. it cannot be calculated without additional data
C. 40 mmHg( 5.3 kPa)
The direct increase of minute ventilation in high altitude compared to the altitude on sea level is due to:
A. the stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors by hypoxia
B. the stimulation of central chemoreceptors by hypoxia
C. the stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors by hypocapnia
D. the increase of the metabolism rate due to low environmental temperature
E. none of the above
A. the stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors by hypoxia
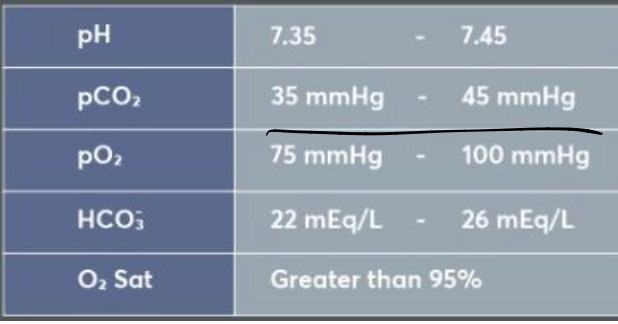
If at that moment Kathy underwent an arterial blood gas measurement, which of the below values would you expect?
A. P02 =110mmHg (14.7kPa), PCO2= 40mmHg (5.4kPa), ph=7.40
B. P02 =110mmHg (14.7kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa), ph=7.55
C. P02 =70mmHg (9.3kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa), ph=7.40
D. P02 =56mmHg (7.5kPa), PCO2=40mmHg (5.4kPa), ph=7.40
E. P02 =56mmHg (7.5kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa), ph=7.55
E. P02 =56mmHg (7.5kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa), ph=7.55
There have been 3 hours from their arrival at the research station and Kathy gets to know the facilities and the personnel. It’s noon and some of the team members, including Kathy, do not feel well. She has headache, nausea, and vomiting. She understands that she has possibly developed acute mountain sickness. All the team members have been taking a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (acetazolamide) starting some days before the trip. Kathy realizes that she forgot to take the medication. The enzyme carbonic anhydrase is implicated in:
A. the pancreatic exocrine function
B. the renal tubular reabsorption of the infiltrated HCO3
C. the CO2 transfer by red blood cells
D. all the above
E. none of the above
D. all the above
Given that the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase minimizes the symptoms of acute mountain sickness, we can conclude that these symptoms are caused by:
A. the metabolic alkalosis due to bicarbonate retention by the kidneys
B. the respiratory alkalosis due to hypocapnia
C. the metabolic acidosis due to increased bicarbonate secretion by the kidneys
D. dehydration due to increased ventilation
E. hypoxia
B. the respiratory alkalosis due to hypocapnia
Kathy stayed in bed until the next morning, when she felt better since the headache and the nausea subsided. After she walked out of bed and started moving she noticed that her shortness of breath was improved compared to the previous day –it persisted only when she was climbing stairs. After she underwent some measurements, she found that her minute ventilation was 12 l/min and her hematocrit increased from 41% (before her departure) to 45%. These changes observed in Kathy – that had obviously taken place overnight –, i.e. remission of her symptoms, improvement of the shortness of breath, increase in the minute ventilation, are the result of:
A. central chemoreceptor sensitization due to local diffusion of bicarbonate
B. central chemoreceptor sensitization due to CO2 retention
C. restoration of acid-base balance via renal compensation
D. increased stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors by persistent hypoxia
E. Increased stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors by an imbalance in ventilation/perfusion
A. central chemoreceptor sensitization due to local diffusion of bicarbonate
The hematocrit increase is due to:
A. the hypocapnia causing peripheral vasodilation
B. the renal hypoxia resulting in increased erythropoietin
C. the increased ventilation leading to increased water loss through the respiratory system
D. the reduced atmospheric pressure leading to peripheral venous
E. None of the above
C. the increased ventilation leading to increased water loss through the respiratory system
Kathy underwent another arterial blood gas measurement. Which of the following results would you expect?
A. PO2=64 mmHg (8.5kPa), PCO2= 25mmHg (3.3 kPa), ph=7.40
B. PO2= 64 mmHg (8.5kPa), PCO2=30mmHg (4.0kPa), ph=7.55
C. PO2= 64 mmHg (8.5kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa) ph=7.40
D. PO2=56 mmHg (7.5kPa), PCO2=35mmHg (4.7kPa) ph=7.40
E. PO2=56 mmHg (7.5kPa), PCO2=25mmHg(3.3kPa) ph=7.55
B. PO2= 64 mmHg (8.5kPa), PCO2=30mmHg (4.0kPa), ph=7.55
The morphology of the QRS complexes in leads V1 – V6 indicates:
A. Hypertrophy of the left ventricle
B. Hypertrophy of the left atrium
C. Hypertrophy of the right ventricle
D. Right bundle brunch block
E. Bilateral ventricular hypertrophy
C. Hypertrophy of the right ventricle
Considering the effects of altitude on the cardiovascular system, you could assume that the changes in heart function were caused by:
A. increase of the left heart afterload due to polycythemia
B. increase of the right heart afterload due to hypoxemic vasoconstriction
C. increase of the left heart afterload due to hypocapnia induced vasoconstriction
D. secondary ventricular dilation due to hyperventilation
E. secondary ventricular dilation due to hypoxia
B. increase of the right heart afterload due to hypoxemic vasoconstriction
In an untrained person fully adapted in high altitude conditions, you would expect his exercise ability to be:
A. increased only in high altitude
B. increased in all altitude levels, but more in high altitude
C. increased in all altitude levels, but more in low altitude
D. increased regardless of altitude
E. Increased in high altitude and decreased in low altitude
C. increased in all altitude levels, but more in low altitude
After how long of regular, unprotected intercourse without conception should a couple consider
evaluation for possible infertility?
A.1 month
B.5 years
C.3 years
D.1 year
E.6 months
D.1 year
Katerina and her partner have been trying to conceive for two years without success. What is the
most appropriate next step in managing this couple?
A.Advise timed intercourse for an additional 6 months
B.Recommend comprehensive fertility evaluation for both partners
C.Begin hormonal therapy for the female partner immediately
D.Begin antioxidant supplementation for both partners
B.Recommend comprehensive fertility evaluation for both partners
Which tests are of relevance to assess for a potential endocrine cause of infertility?
A.FSH
B.E2
C.AMH
D.AFC
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
At which phase of the menstrual cycle should FSH levels be evaluated?
A. Early Follicular Phase
B.Late Follicular Phase Ovulation
C.Early Luteal Phase
D.Late Luteal Phase
A. Early Follicular Phase
At which phase of the menstrual cycle should Progesterone levels be evaluated?
A.Early Follicular Phase
B.Late Follicular Phase
C.Early Luteal Phase
D.Mid Luteal Phase
E.Late Luteal Phase
D.Mid Luteal Phase
What is the role of the corpus luteum in the physiology of the menstrual cycle?
A. It inhibits further ovulation
B. It stimulates endometrial angiogenesis
C. It promotes the development of endometrial glands
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
D. All of the above
How does a short luteal phase (less than 7 days) impact the normal implantation process?
A. Insufficient time for endometrial preparation
B. Inadequate progesterone secretion to support implantation
C. Lack of sufficient glycogen in the endometrium for blastocyst development
D. Early regression of the corpus luteum leading to reduced estrogen levels
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
When is it preferable to perform the ultrasound examination for detecting endometrial polyps?
A.Early proliferative
B.Late
C.Early Luteal
D.Late Luteal
E.All of the above
A.Early proliferative
Your patient presents with an endometrial polyp in the pelvic ultrasound
What is the most common clinical implication of an endometrial polyp in relation to fertility?
A. It may cause endometrial adhesions
B. It can obstruct the fallopian tubes, preventing fertilization
C. It can impact embryo implantation, leading to infertility or recurrent miscarriage
D.All of the above
C. It can impact embryo implantation, leading to infertility or recurrent miscarriage
Why does the gynecologist insist on seeing the couple together?
A. To subject the partner to testicular biopsy
B.Only to discuss with the partner his medical history
C. To discuss with the partner his medical history highlighting the need of performing a semen analysis
D. To perform a testicular ultrasound to the partner
C. To discuss with the partner his medical history highlighting the need of performing a semen analysis
How Chlamydia infection may be associated with female infertility?
A.Inflammation and scarring of fallopian tubes
B.Pelvic inflammatory disease
C.Lacerations and adhesions
D.All of the above
D.All of the above
Surgical management of endometrioma:
A. May reduce ovarian reserve
B.May Impair endometrial receptivity
C.May increase estrogen levels
D.All of the above
A. May reduce ovarian reserve
At which phase of the menstrual cycle should AMH levels be evaluated?
A.Early Follicular Phase
B.Late Follicular Phase
C.Early Luteal Phase
D.Late Luteal Phase
E.None of the above
E.None of the above
About cryopreservation of oocytes for social reasons?
A. Cryopreserving oocytes before the age of 35 is associated with optimal outcomes
B. Cryopreserving oocytes ascertains a success of 95%
C. Survival rate after thawing is less than 60%
D. None of the above is correct
A. Cryopreserving oocytes before the age of 35 is associated with optimal outcomes
Which urine marker would you choose to confirm pregnancy?
A. Detection of estrogens in urine
B. Detection of prolactin in urine
C. Detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine
D. Detection of progesterone in urine
E. There is no urine marker until at least 28 days post-fertilization
C. Detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in urine
Which is the most abundant antibody class in the blood?
1.IgA
2.IgD
3.IgE
4.IgG
5.IgM
4.IgG
Which antibody class is present in most secretions?
1.IgA
2.IgD
3.IgE
4.IgG
5.IgM
1.IgA
Which antibody class mediates allergic reactions to insect stings
1.IgA
2.IgD
3.IgE
4.IgG
5.IgM
3.IgE
Which antibody class acts as the B cell antigen receptor?
a. IgA
b. IgD
c. IgE
d. IgG
e. IgM
e. IgM
During an allergic reaction, antibodies are produced by:
1.Β-lymphocytes
2.Τ-lymphocytes
3.Eosinophils
4.Basophils
5.Neutrophils
1.Β-lymphocytes
The mediators of an allergic reaction are released when the antibody is bound on and activates:
1.Enterochromaffin cells
2. Mast cells
3.Endothelial cells
4.Adrenocortical cells
5.None of the above
2. Mast cells
Which mediator(s) are released during anaphylaxis?
1.Histamine
2.Leukotrienes
3.Prostagladins
4.All of the above
5.A + B
4.All of the above
Which is the most frequent trigger of anaphylaxis?
1.Drugs
2.Exercise
3.Food
4.Idiopathic
5.Insect stings and bites
3.Food
What is the effect of these mediators?
1.Pulmonary edema
2.Peripheral edema
3.Decrease peripheral vascular resistance
4.All of the above
5.None of the above
4.All of the above
Which is the effect of these mediators on the respiratory system?
1. Reduced work of breathing
2. Increased airway resistance
3. Reduced alveolar surface available for gas exchange
4. Reduced airway resistance
5. 2 & 3
2. Increased airway resistance
Adrenaline if beneficial because it causes
1.Bronchodilation
2.Peripheral vasoconstriction
3.Enhanced cardiac contractility
4.All of the above
5.1 and 3
4.All of the above
What the area of the lung where no adequate gas exchange occurs is called?
1.Alveolar dead space
2.Anatomic dead space
3.Functional dead space
4.Residual volume
5.None of the above
3.Functional dead space
The fact that Sean breaths normally shows that brain connections to the spinal nerves are intact downwards at least to the:
A. nerve C2
B. nerve C5
C. nerve C6
D. nerve C7
E. nerve C8
B. nerve C5
If neural function remains intact till this segment, the highest level where spinal lesion could have occurred is:
A. between vertebrae C4 and C5
B. between vertebrae C5 and C6
C. between the vertebrae C6 and C7
D. between the vertebrae C7 and C8
E. none of the above
A. between vertebrae C4 and C5
Given the level of the spinal injury, you would predict that, in comparison to a healthy person in supine position, there would be:
A. high arterial pressure and low cardiac rhythm
B. high arterial pressure and high cardiac rhythm
C. low arterial pressure and low cardiac rhythm
D. low arterial pressure and high cardiac rhythm
E. no difference from normal
C. low arterial pressure and low cardiac rhythm
This distribution of sensory impairment shows that the lowest intact spinal nerve is:
A. C5
B. C6
C. C7
D. C8
E. T1
B. C6
Which eye function would be impaired from a spinal injury at this level ?
A. Closure of eyelids in response to irritating the cornea
B. Tears secretion
C. Level of rest of the upper eye lid
D. A and B
E. A, B, and C
C. Level of rest of the upper eye lid
Which circulatory reflexes would be impaired from a spinal injury at this level ?
A. bradycardia in response to the activation of the baroreceptors (baroreceptor reflex) of the left ventricle
B. Bradycardia in response to the arterial baroreceptors of the carotid
C. Bradycardia in response to the activation of the baroreceptors of the aortic arc
D. All the above
E. None of the above
E. None of the above
Which respiratory function would be normal in the case of a spinal injury at this level ?
A. Clearance of the bronchial mucus
B. Secretion of bronchial mucus
C. forced expiratory vital capacity
D. A and B
E. A, B, and C
B. Secretion of bronchial mucus
Which function of the upper digestive tract would be normal in the case of a spinal injury at this level ?
A. saliva secretion
B. swallowing
C. gastrin secretion in the duodenum
D. gastric receptive relaxation
E. all the above
E. all the above
Which function of the lower digestive tract would be affected in a spinal injury at this level ?
A. gastrocolic reflex in response to the food entry to the stomach
B. opening of the ileocecal sphincter in response to the ileal filling
C. jejunal peristalsis during food digestion
D. defecation
E. A and D
D. defecation
Which endocrine functions would be affected in a spinal injury at this level ?
A. aldosterone secretion in response to potassium decrease in the plasma
B. vasopressin secretion in response to increased osmolarity of plasma volume
C. adrenalin secretion in response to decrease of plasma volume
D. insulin secretion in response to decrease of plasma glucose
E. none of the above
C. adrenalin secretion in response to decrease of plasma volume
Which motor functions would be normal in the case of a spinal injury at this level ?
A. extension of the wrist
B. flexion of the wrist
C. extension of the elbow
D. flexion of the fingers
E. all the above
A. extension of the wrist
Urination controlled by spinal reflex pathways will differ from that in healthy individuals as follows:
A. Bladder empties automatically when filling reaches a critical volume
B. Emptying is activated by stimulation of skin mechanoreceptors
C. Bladder is not emptying even when full, without stimulation of skin mechanoreceptors
D. A and B
E. B and C
D. A and B
Efficient strategies to decrease the risk of infection of the urinary system are:
A. systematic per os antibiotics
B. systematic administration of alkaline agents
C. systematic administration of large quantities of liquids
D. protein restriction diet
E. none of the above
C. systematic administration of large quantities of liquids
The reason why Sean feels his face hot when his bladder is distended is:
A. spinal reflex of activation of sympathetic vasocontricting nerves above the lesion
B. spinal reflex of inhibition of sympathetic vasocontricting nerves above the lesion
C. The spinal reflex of activation of sympathetic vasocontricting nerves under the lesion
D. spinal reflex of inhibition of sympathetic vasocontricting nerves under the lesion
E. spinal reflex of inhibition of sweating above the lesion
C. The spinal reflex of activation of sympathetic vasocontricting nerves under the lesion
spasticity in the limbs, under the level of a spinal injury is due to:
A. degeneration of damaged motor neurons
B. rebirth of damaged motor neurons
C. degeneration of denervated muscles
D. development of automatic activity in spinal motor neurons
E. loss of descending inhibitory activity on the spinal motor neurons
E. loss of descending inhibitory activity on the spinal motor neurons
these symptoms occurring when changing body positions are due to:
A. decrease of blood pressure due to redistribution of regional perfusion
B. decrease of blood pressure due to increase of blood pooling
C. decrease of brain irrigation due to self-regulation
D. increase of blood pressure due to sympathetic reflexes’ dysfunction
E. increase of brain irrigation due to self-regulation
B. decrease of blood pressure due to increase of blood pooling
This problem could be contained by:
A. increasing the levels of plasma vasopressin (ADH) with water restriction
B. increasing the levels of plasma angiotensin with salt restriction
C. mechanical compression of veins
D. increasing levels of plasma adrenalin with regular intake of glucoze
E. the A, B and C
C. mechanical compression of veins
Think about the consequences of Sean’s injury on his motor activities. Designing necessary domestic installations, you must think that:
A. it will be impossible for him to type without control of the mouth
B. it will be necessary to use his shoulders or mouth to turn on the lights
C. wrist support will be necessary to wash his teeth
D. he will be incapable to help with his dressing
E. all the above
C. wrist support will be necessary to wash his teeth
Advising Sean is important to remember that his ability to have children is limited from the fact that:
A. Number of spermatozoa is reduced due to vasodilatation in the scrotum
B. Sperm volume is decreased due to denervation of the prostate
C. Ejaculation is limited due to sperm reflux to the bladder
D. Erection is impaired due to loss of corticospinal disconnection
E. all the above ?
E. all the above ?
if an injury like Sean’s happened in a young woman, what would be the consequences on her sexuality and her capacity to become a mother ?
issues in women: sensation of perineal area, orgasm, amenorrhea (1-9 months), fertility, labor (epidural anesthesia, prevention of autonomic hyperreflexia), contraception (vein thrombosis)
Which other long term physiological problems you think they must be taken in consideration in planning his way of living and a proper rehabilitation program?
immobility, spasticity, muscle atrophy, ankylosis, ectopic ossifications, osteoporosis – pathological fractures, pressure ulcers, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism
Which eye function would be impaired from a spinal injury in segment C7?
A.Closure of eyelids in response to irritating the cornea
B.Tears secretion
C.Level of rest of the upper eye lid
D.A and B
E.A, B, and C
C.Level of rest of the upper eye lid
Which circulatory reflexes would be impaired from a spinal injury in segment C6?
A.bradycardia in response to the activation of the baroreceptors (baroreceptor reflex) of the left ventricle
B.Bradycardia in response to the arterial baroreceptors of the carotid
C.Bradycardia in response to the activation of the baroreceptors of the aortic arc
D.All the above
E.None of the above
E.None of the above
Which one of the patient’s symptoms suggests a kidney or cardiac problem?
A. Exercise fatigue
B. Peripheral edema
C. Swollen face
D. Chest pain
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
Lab tests show:
A. All values are normal
B. Anemia
C. Anemia and hyponatremia
D. Anemia, hyponatremia and hypercholesterolemia
E. Hypokalemia and hypercholesterolemia
B. Anemia
Given the above data, which of the following hormones would you test?
A. Thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and growth hormone (GH)
B. Thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
C. TSH and GH
D. GH and GH-Releasing Hormone (GHRH)
E. GH and cortisol
B. Thyroid hormones and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Which findings support the diagnosis of hypothyroidism?
A. Low thyroid hormone
B. High TSH.
C. Delayed Achilles tendon reflexes
D. Sluggishness and low intellectual performance
E. All of the above
E. All of the above
TSH is increased in hypothyroidism because of:
A. Lack of negative feedback on the hypothalamus
B. Lack of negative feedback on the adenohypophysis
C. Iodine deficiency
D. Lack of physical activity
E. None of the above
B. Lack of negative feedback on the adenohypophysis
You examine a 62-year-old patient with a medical history of COPD. Air blood gas analysis reveals a pO2 of 54 mmHg, pCO2 59 mmHg, pH 7.32, HCO3 31, while breathing ambient air. What is the acid base disorder?
A.Acute Respiratory Acidosis
B.Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
C.Acute Metabolic Acidosis
D.Acute Respiratory and Metabolic Acodisis
B.Chronic Respiratory Acidosis
A 60-year-old patient with a smoking history of 40 pack.years complains of dyspnea and cough starting 6 months ago. A post-bronchodilator spirometry is performed showing an FEV1 1.8 L (65% predicted) and FVC 3.5 L (110% predicted). Based on these results:
A.The diagnosis of COPD is confirmed.
B.Spirometry reveals a restrictive pattern.
C.An obstructive pattern cannot be confirmed without body plethysmography.
D.Order a gas transfer test to confirm COPD diagnosis.
A.The diagnosis of COPD is confirmed.
Hyperinflation in COPD patients is caused by:
A.Increased airway resistance
B.Reduced elastic recoil of the lung
C.Increased activity of the diaphragm.
D.A+B
D.A+B
What is correct regarding edema
A. Edema is an increase of the interstitial fluid volume
B. It is manifested as palpable swelling of subcutaneous tissues
C. It does not become apparent until the interstitial volume has increased by at least 2.5-3 liters
D. It involves an alteration in the capillary hydrostatic and/or oncotic pressures as well as retention of dietary sodium and water by the kidneys
E. All the above are correct
E. All the above are correct
Edema formation caused by decreased capillary oncotic pressure is related with
A. Conditions causing protein loss from the kidney (nephrotic syndrome) or the intestine (protein-
losing enteropathy) and malnutrition.
B. The decrease in oncotic pressure leads to a decrease in reabsorption of fluid from the interstitium to the intravascular compartment, hence a net increase in filtration and formation of edema.
C. The decrease in oncotic pressure leads to a increase in reabsorption of fluid from the interstitium to the intravascular compartment, hence a net decrease in filtration and formation of edema.
D. A and B are correct
E. A and C are correct
D. A and B are correct
What is wrong regarding acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
A.The most common cause of acute glomerulonephritis among children
B.Mostly caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococci
C.Primarily affects children aged between 3-12 years
D.The renal disorder runs concurrently with the infection
E.Generally, it is a self-limiting condition and has a good long- term prognosis
D.The renal disorder runs concurrently with the infection