DAANCE Module 5 questions and verified answers)frequently most tested questions | already passed!!
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
hypoxia
definition: deficiency of O2 in body tissues
consequences: cardiac dysrhythmias, cardiac arrest, neurologic damage, death
airway obstruction
posterior positioning of the tongue or foreign body
- causes: poor head positioning, deep anesthesia, sedation
- signs: choking, gagging, suprasternal notch retraction
- treatment: 100% O2, head tilt-chin lift, suction, airway adjuncts
foreign bodies
- causes: dentures, surgical packs, teeth
- treatment: removal, chest compressions, laryngoscopy
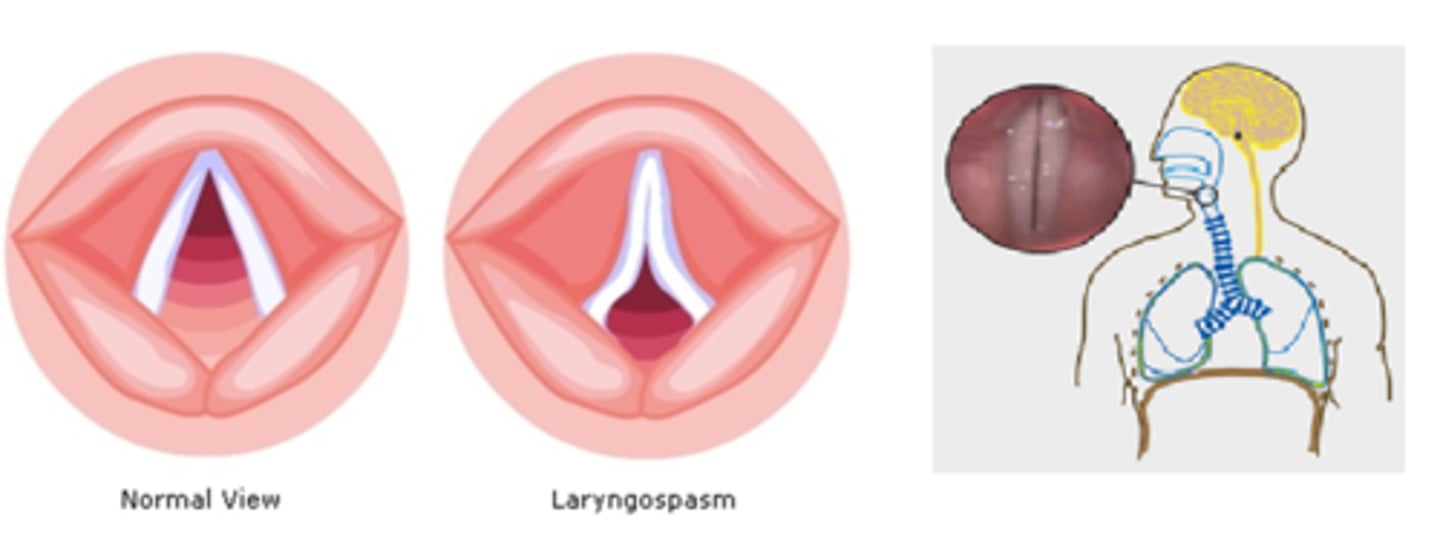
laryngospasm
definition: reflex protecting vocal cords, causing airway obstruction
signs: crowing sounds, labored breathing, suprasternal retraction (skin in middle of neck sucks in)
treatment: 100% O2, proper head position, suction, succinylcholine
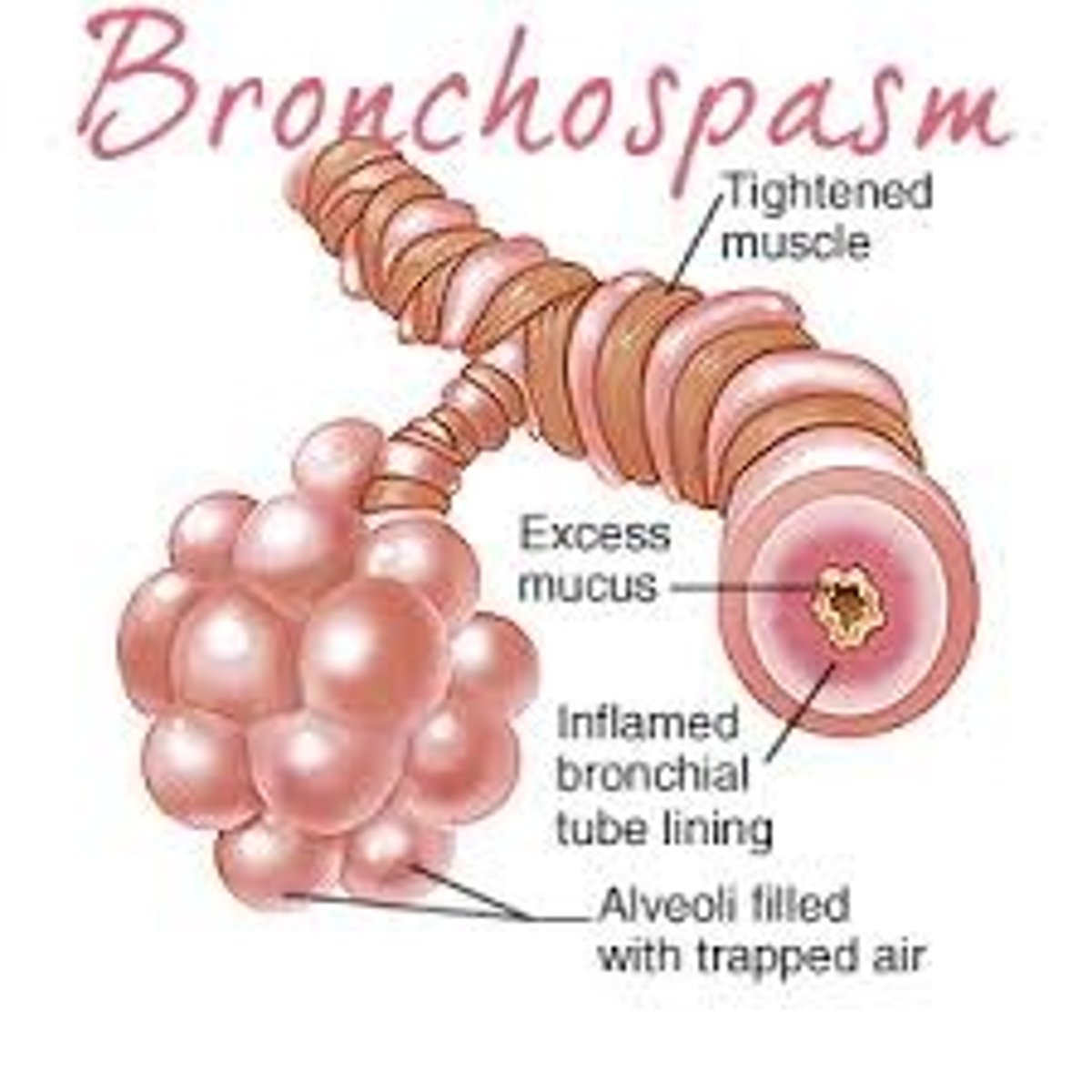
bronchospasm
definition: contraction of bronchi smooth muscles, restricting airflow
signs: wheezing, labored breathing
treatment: 100% O2, albuterol, Ipratropium, epinephrine, intubation
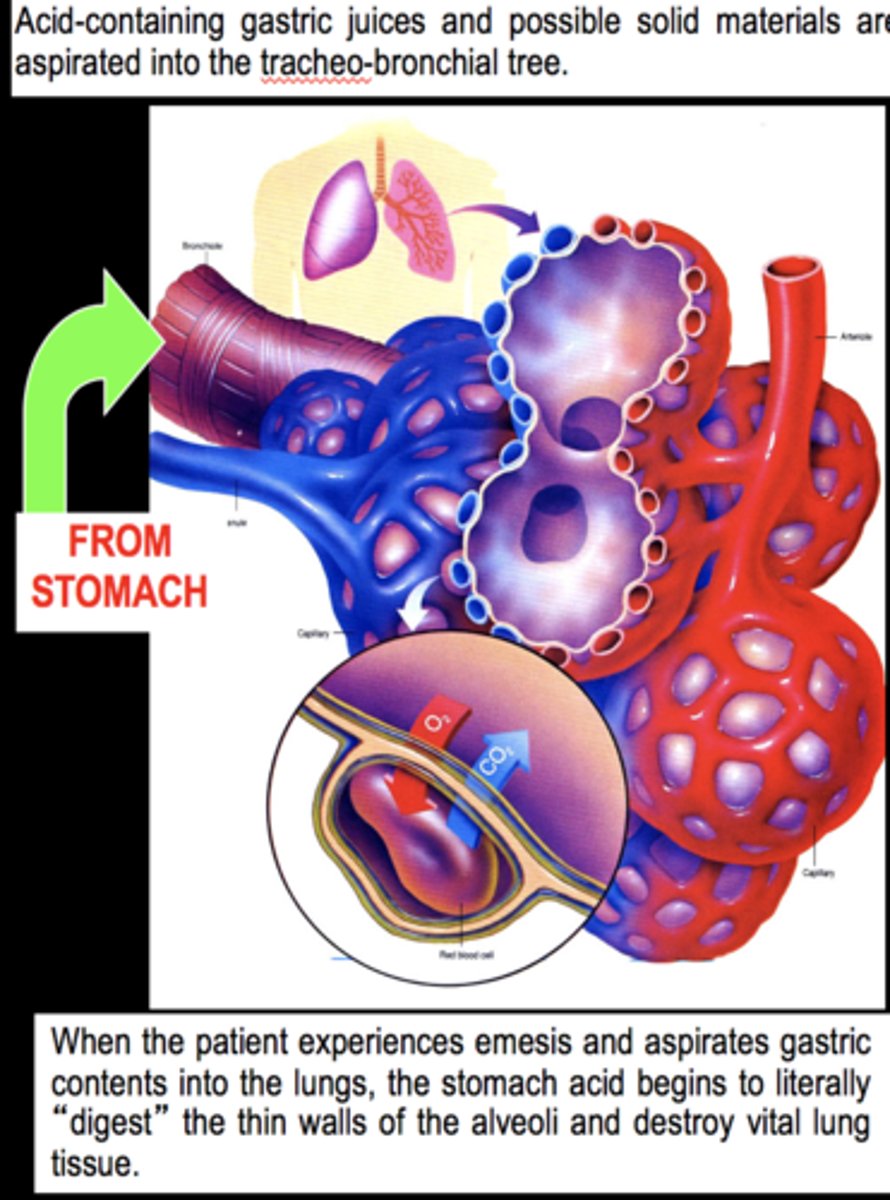
emesis with aspiration
definition: entry of stomach contents into lungs
signs: pneumonitis (lung tissue inflammation), rales (small clicking, bubbling, rattling sounds in lungs), tachycardia, dyspnea (difficulty breathing)
prevention: NPO guidelines, protective reflexes
hyperventilaiton
definition: excessive breathing, imbalance of oxygen and CO2
causes: anxiety, fear, pain, medication overdose
treatment: maintain airway, calm patient, avoid giving oxygen
respiratory depression and apnea
definition: cessation of breathing due to drugs or other causes
causes: narcotics, sedatives, muscle relaxants
treatment: drug reversal agents, mechanical ventilation
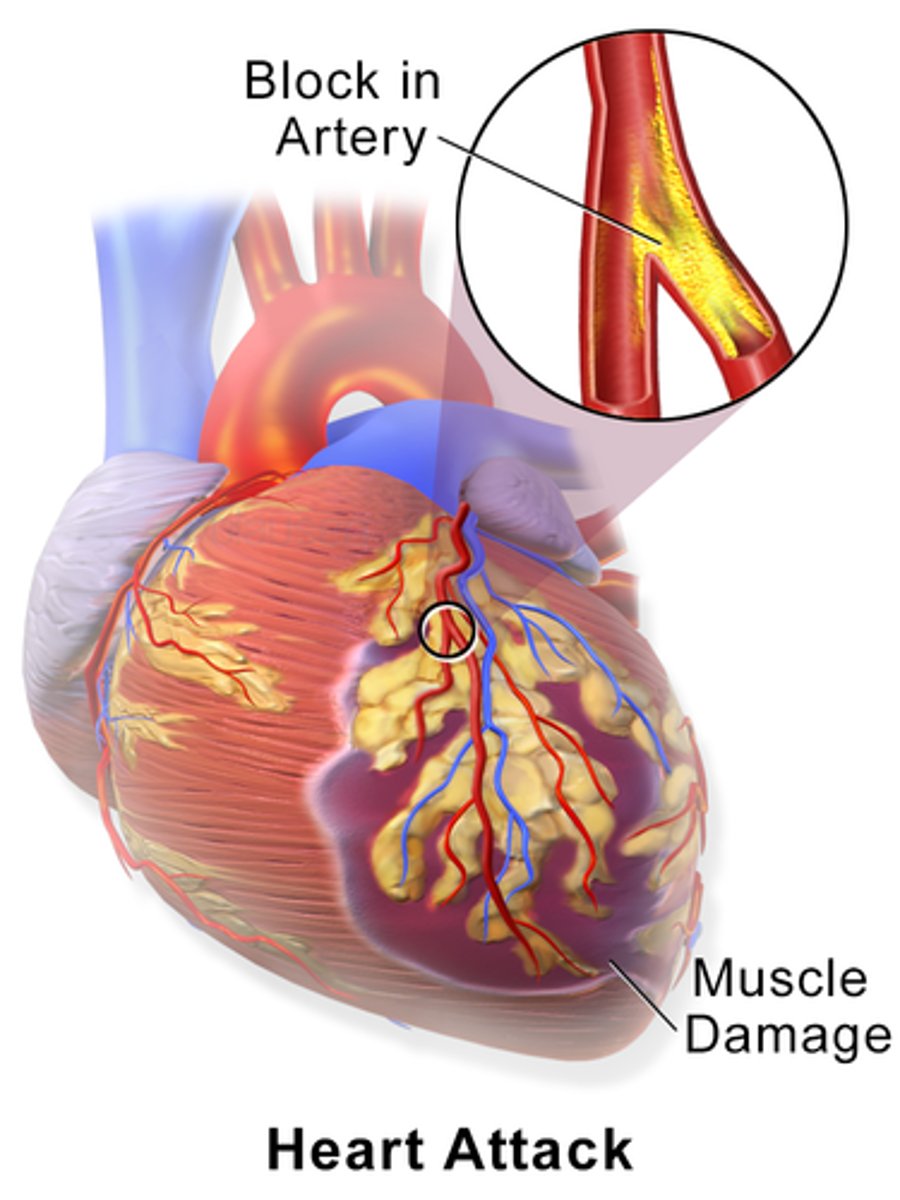
acute coronary syndrome
syndrome consisting of angina and MI
angina
chest pain due to diminished blood flow in coronary arteries
myocardial infarction
death of myocardial tissue due to total occlusion of coronary arteries
MONA acronym
memory tool for interventions in acute coronary syndrome
administer in the order of oxygen, nitroglycerin, aspirin, morphine sulfate
bradycardia treatment
terminate, 100% O2, IV atropine transport
SVT treatment
supine position, adenosine, saline flush, repeat if needed
premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) treatment
identify cause, correct, lidocaine

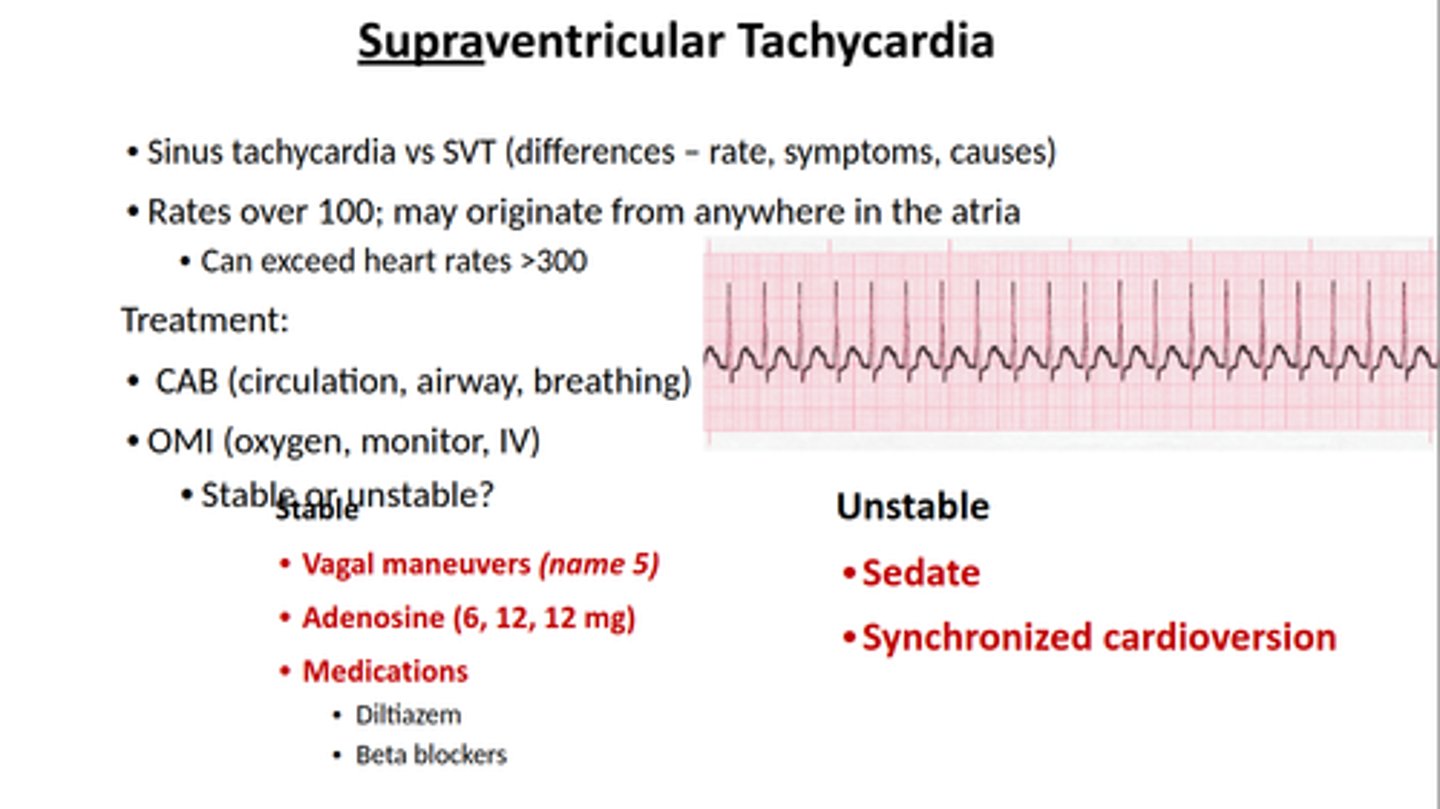
ventriciular tachycardia treatment
rapid, wide waveform with no discernable p waves
- 100% O2, amiodarone, cardioversion (treatment to restore normal heartbeat) if unstable
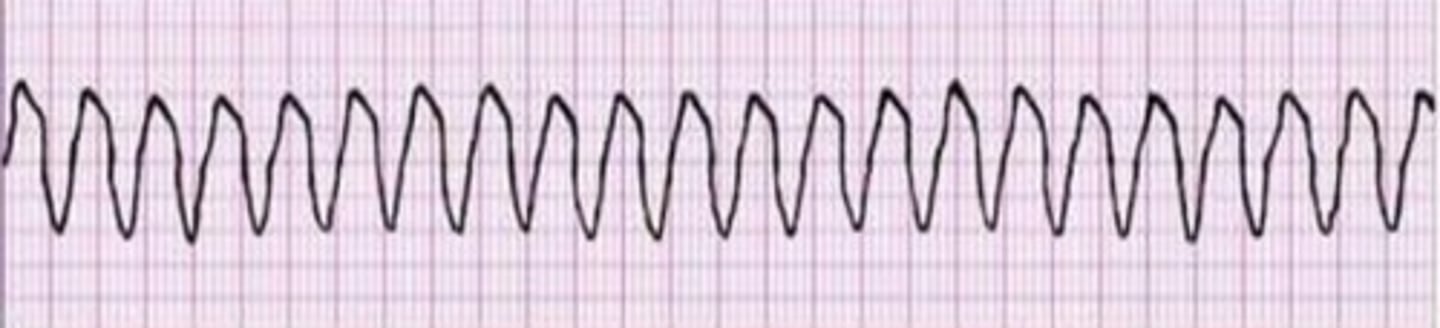
ventricular fibrillation treatment
CPR, AED, epinephrine, amiodarone
amiodarone
Antiarrhythmic
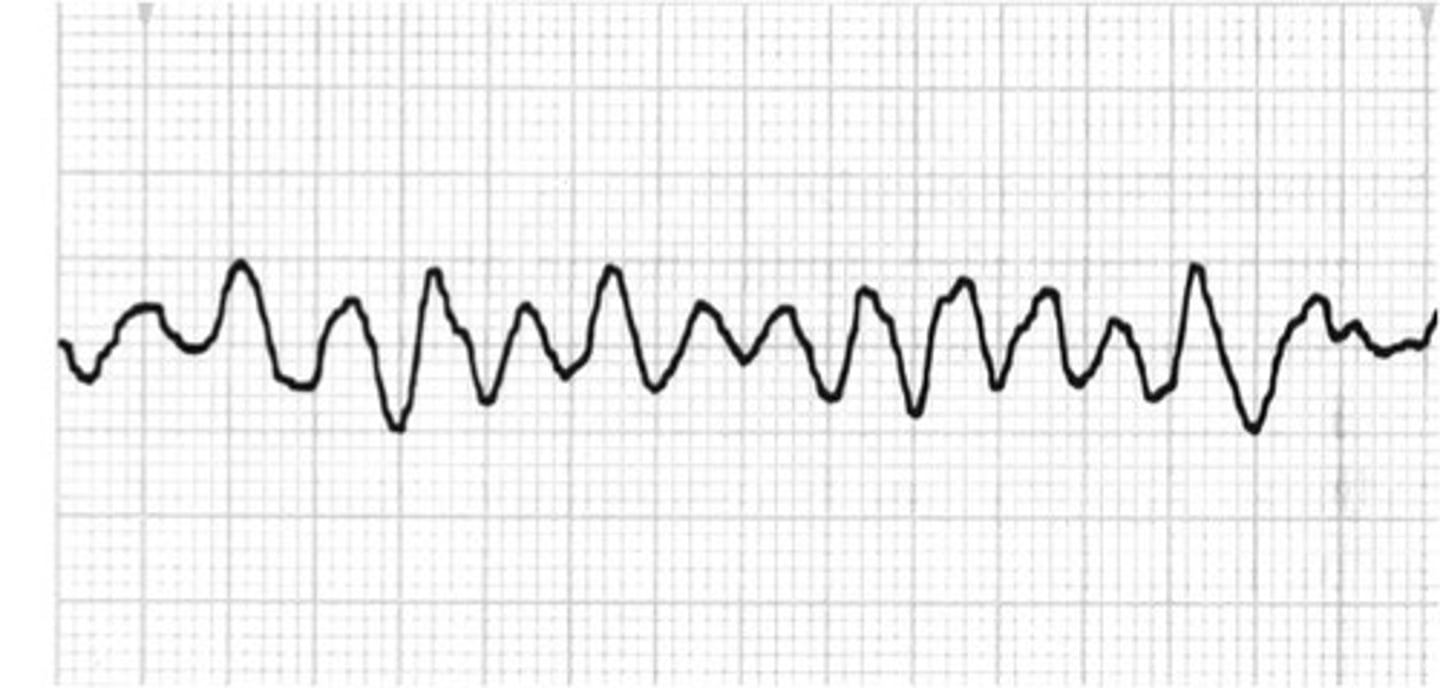
asystole/PEA treatment
administer CPR, epinephrine, consider vasopressin
vasopressin

hypertension treatment
terminate procedure, check monitor, manage cause, record vital signs, consider EMS
hypotension treatment
trendelenburg position, support airway, 100% O2, monitor, IV, fluid bolus
infiltration
- leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues, edema
- stop infusion, restart at another site
hematoma
- blood leakage into surrounding tissue results in firm, tender swelling
- firm pressure, later moist heat
phlebitis
- inflammation of a vein resulting in warm/cold feeling, edema, redness
- elevation, moist heat, NSAIDs
intra-arterial injection
prevention: angiocatheters, palpation, check blood flash
treatment: activate EMS, secure catheter, lidocaine injection, ice pack
hypoglycemia
blood glucose levels fall below normal, leading to various symptoms like nausea, hunger, tachycardia, irritability, lack of energy, restlessness, loss of consciousness, seizures, coma, hypothermia
treatment for mild hypoglycemia
- oral glucose or juice
- sugar rich foods
- confirm blood sugar with glucometer
treatment for severe hypoglycemia
1. activate EMS
2. establish IV access
3. measure blood sugar with glucometer
4. administer 1 amp of IV glucose (50 mL of 50% glucose solution)
5. IV influsion of destrose (5-20% in water)
6. if no IV access, then 1 mg glucagon IM
acute adrenal insufficiency
rare, life threatening condition due to inadequate production of cortisol by adrenal gland
caused by inadequate cortisol production or suppression by exogenous steroids