Protocols and Models in Communications Fundamentals
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Network Size
Networks can vary in size and complexity.
Communication Agreement
Devices must agree on communication methods.
Communication Elements
Includes source, destination, and channel.
Protocols
Rules governing how communications occur.
Sender
Identified source of the communication.
Receiver
Identified destination of the communication.
Channel
Media providing the path for communication.
Message Encoding
Converts messages into bits for transmission.
Message Formatting
Structures messages for proper interpretation.
Message Size
Defines the maximum size of messages.
Message Timing
Regulates the timing of message delivery.
Flow Control
Manages data transmission rates and limits.
Response Timeout
Duration a device waits for a reply.
Access Method
Determines when messages can be sent.
Collisions
Occurs when multiple devices send traffic simultaneously.
Delivery Options
Methods for delivering messages across networks.
Network Protocols
Common rules for communication in networks.
Protocol Functions
Each protocol has a specific function.
Protocol Format
Defines how protocols are structured.
Protocol Implementation
Protocols can be implemented in software or hardware.
Protocol Interaction
Networks require multiple protocols to function.
Common Language
Protocols require a shared language for communication.
Protocol
Set of rules for data communication.
Protocol Suite
Group of inter-related protocols for communication.
Network Protocol Suite
Protocols specifically designed for network communication.
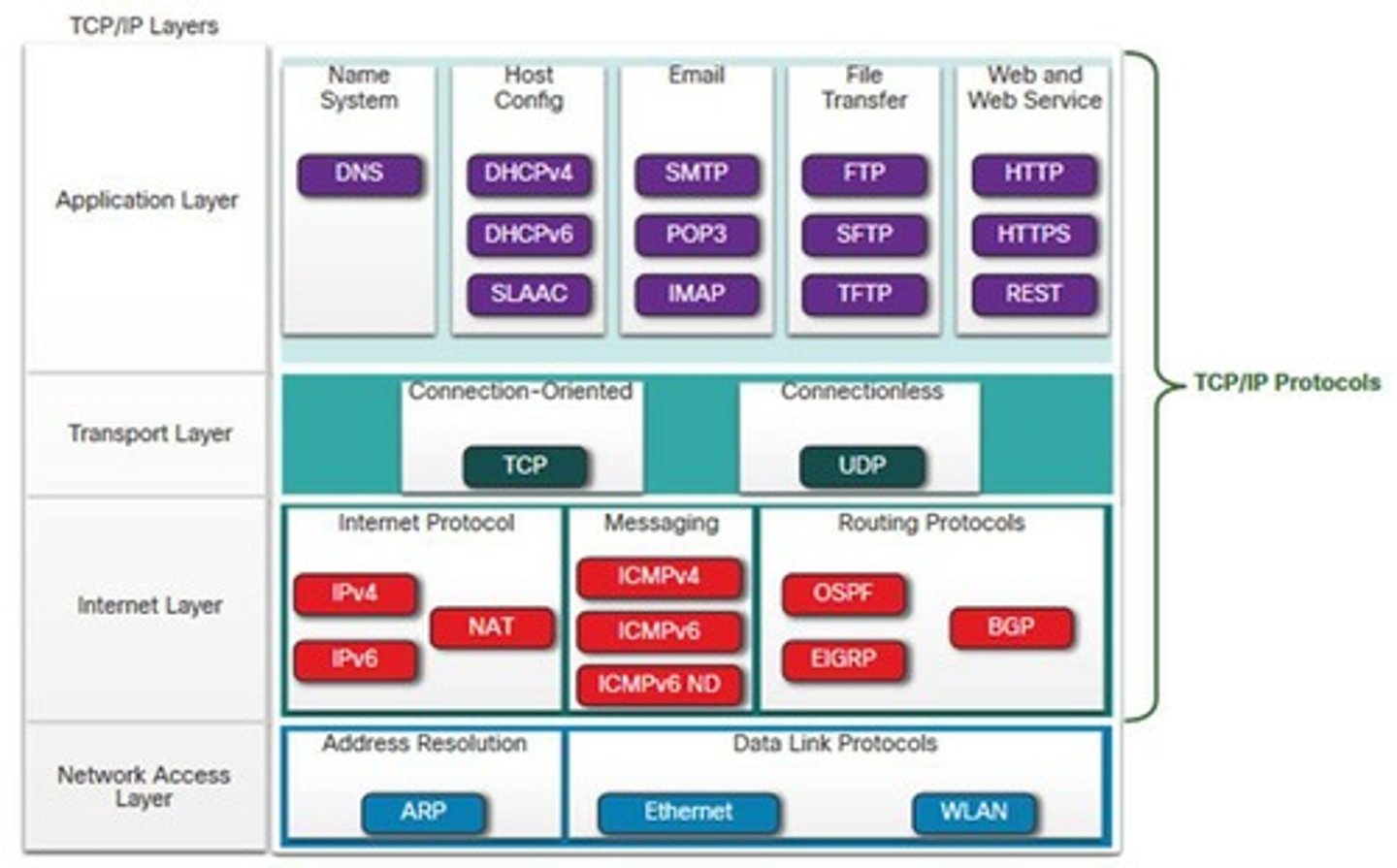
TCP/IP
Open standard protocol suite for internet communication.
Application Layer
Layer where user applications interact with the network.
Transport Layer
Layer responsible for end-to-end communication.
Internet Layer
Layer that routes packets across networks.
LAN Protocols
Protocols for local area network communication.
Ethernet
Common LAN protocol using wired connections.
WLAN
Wireless LAN protocol for wireless communication.
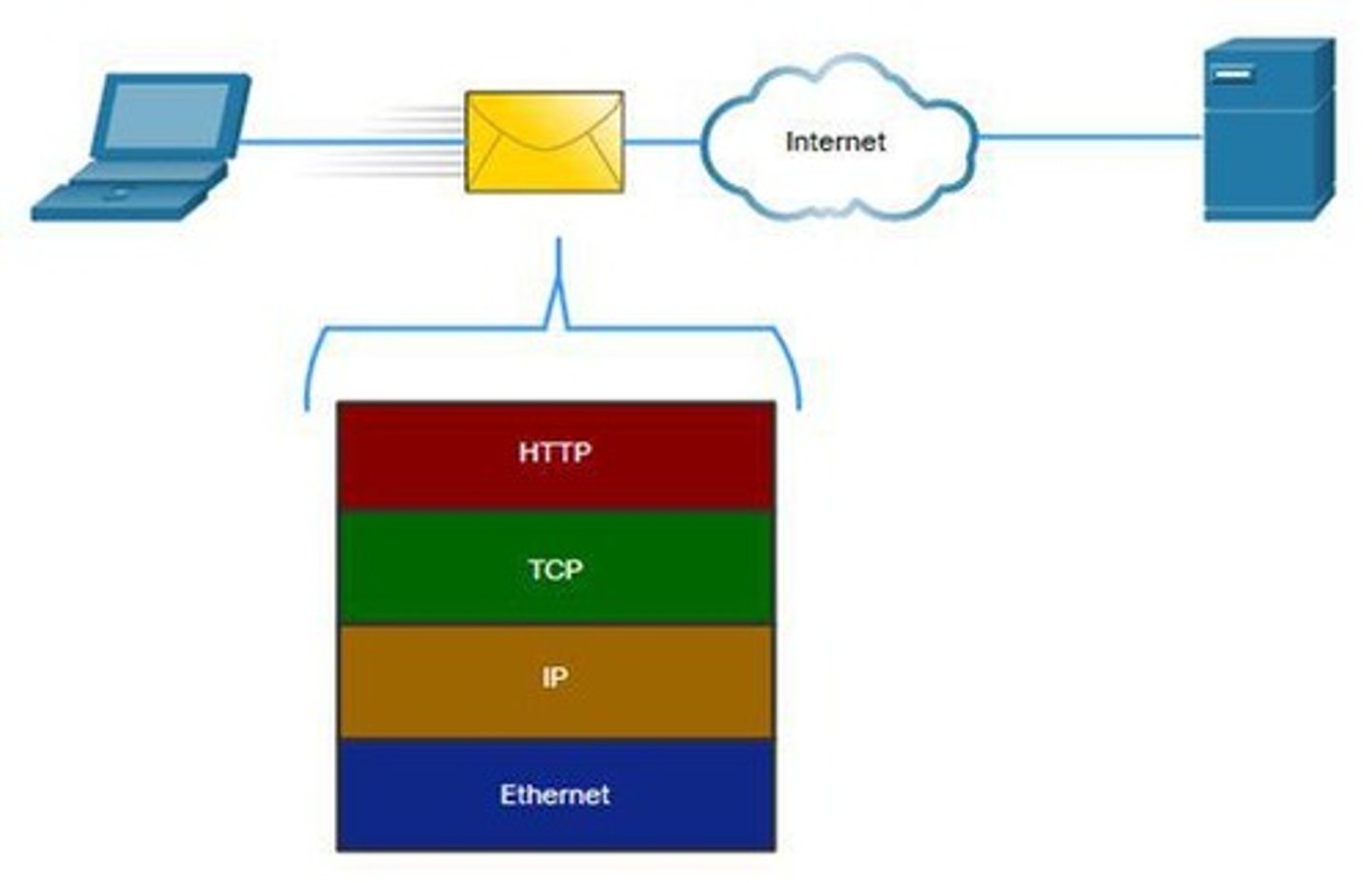
Encapsulation
Wrapping data with protocol information for transmission.
De-encapsulation
Removing protocol information from received data.
Standards Organizations
Groups promoting open standards for interoperability.
Open Standards
Standards that promote interoperability and competition.
Vendor-neutral
Not favoring any specific vendor or product.
Non-profit Organizations
Organizations that do not operate for profit.
Interoperability
Ability of systems to work together seamlessly.
Innovation
Introduction of new ideas or methods in technology.
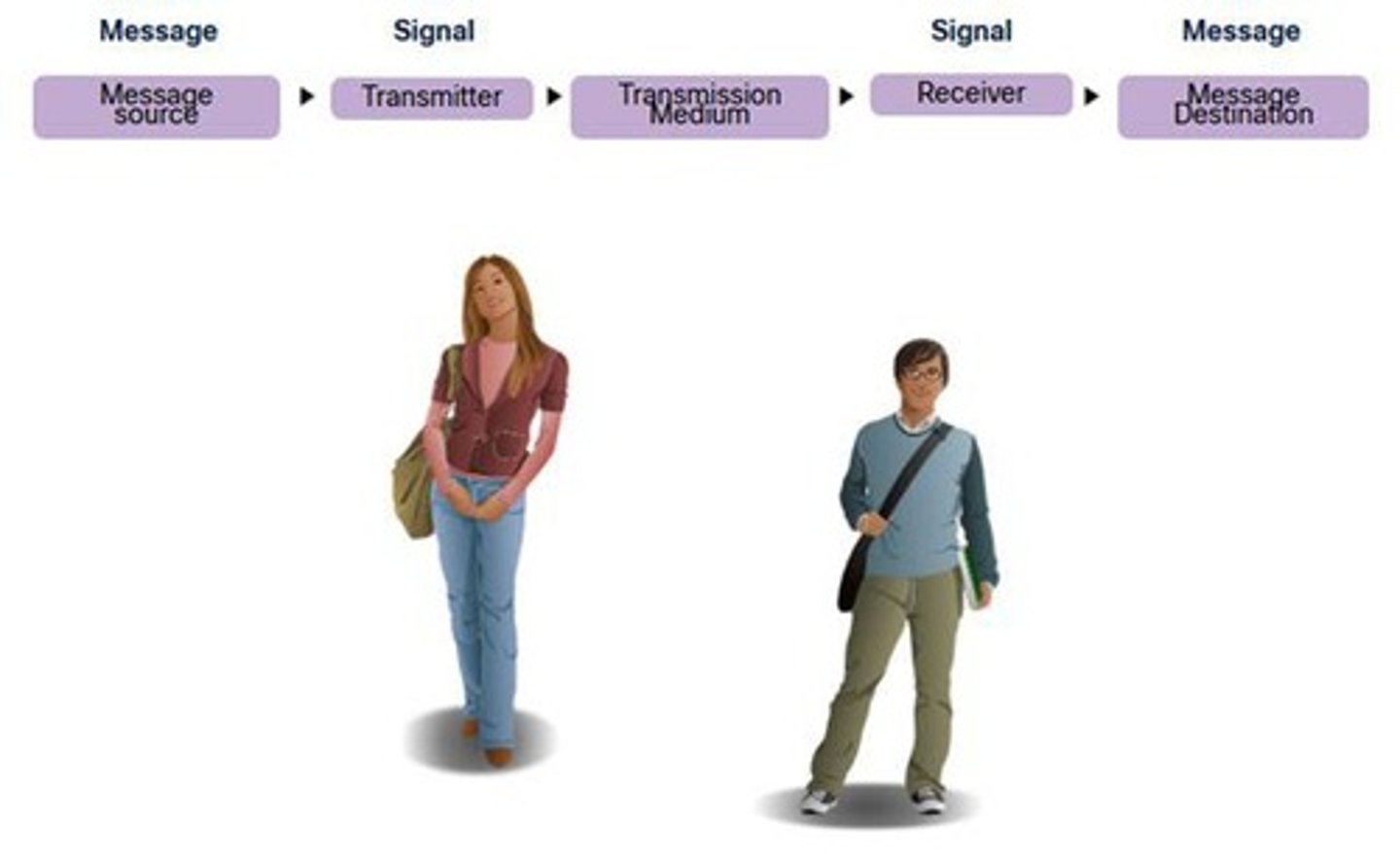
Communication Process
Steps involved in data exchange between devices.
Internet Society (ISOC)
Promotes open development and evolution of internet.
Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
Manages and develops internet standards.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Develops and maintains internet and TCP/IP technologies.
Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
Focuses on long-term research for internet protocols.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
Coordinates IP address allocation and domain name management.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
Manages IP address allocation and protocol identifiers.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
Creates standards in power, healthcare, and telecommunications.
Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA)
Develops standards for electrical wiring and connectors.
Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
Creates communication standards for radio and VoIP devices.
International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
Defines standards for video compression and broadband communications.
Open System Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model
A layered model for explaining network operations.
TCP/IP Reference Model
A model describing internet protocol suite operations.
Layered Model Benefits
Simplifies complex network concepts and operations.
Protocol Design Assistance
Layered models help define protocol interfaces.
Vendor Competition Facilitation
Layered models allow interoperability among different vendors.
Technology Independence
Changes in one layer don't affect others.
Common Networking Language
Layered models provide terminology for networking functions.
Data Encapsulation
Process of segmenting messages into smaller units.
Segmenting Messages
Breaking messages into smaller, manageable parts.
Broadband Communications Standards
Standards for DSL and other high-speed internet technologies.
Video Compression Standards
Protocols for reducing video file sizes.
Multiplexing
Interleaving multiple data streams together.
Data Encapsulation
Adding protocol information to data.
Segmenting Messages
Dividing messages for speed and efficiency.
Sequencing Messages
Numbering segments for proper reassembly.
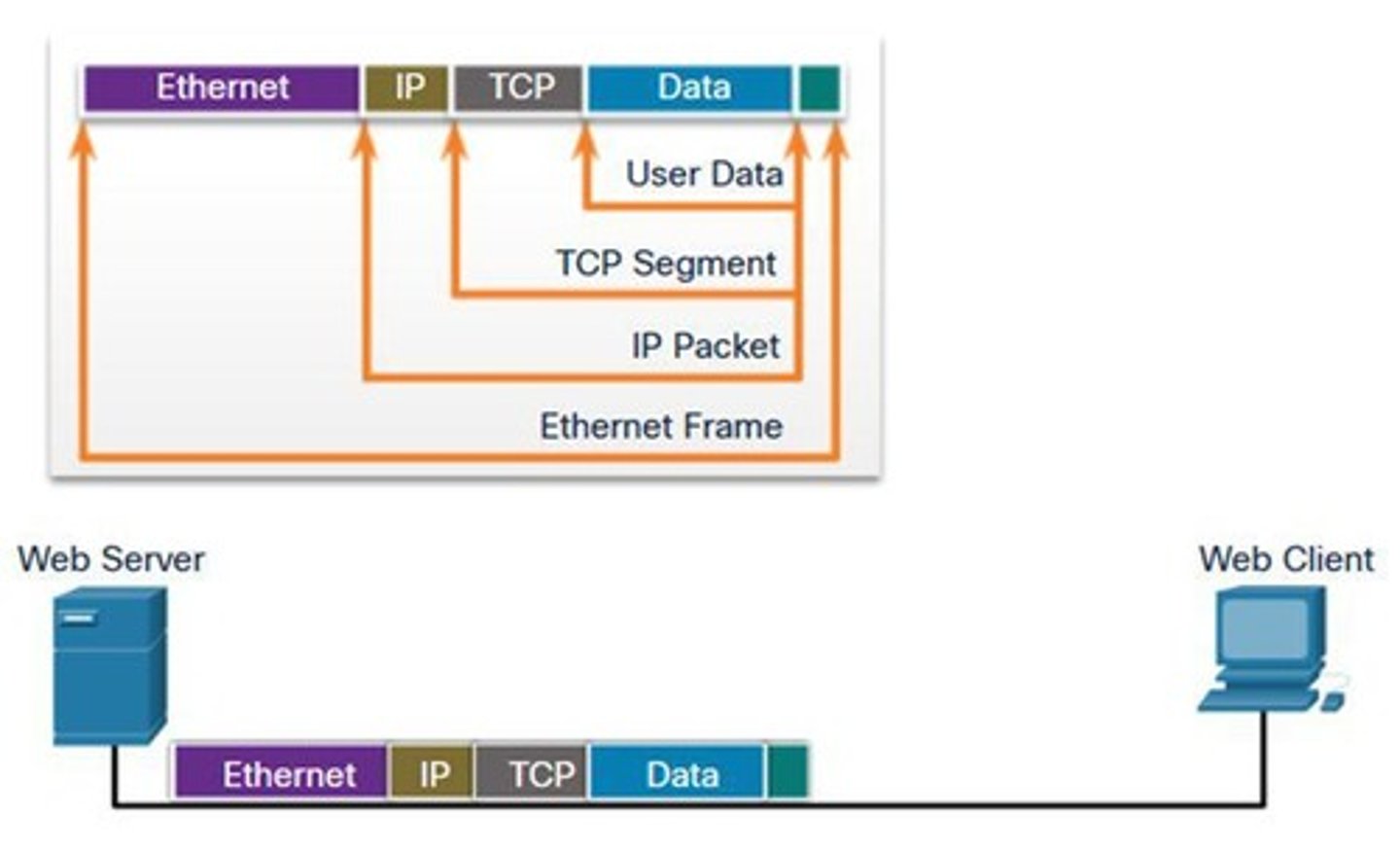
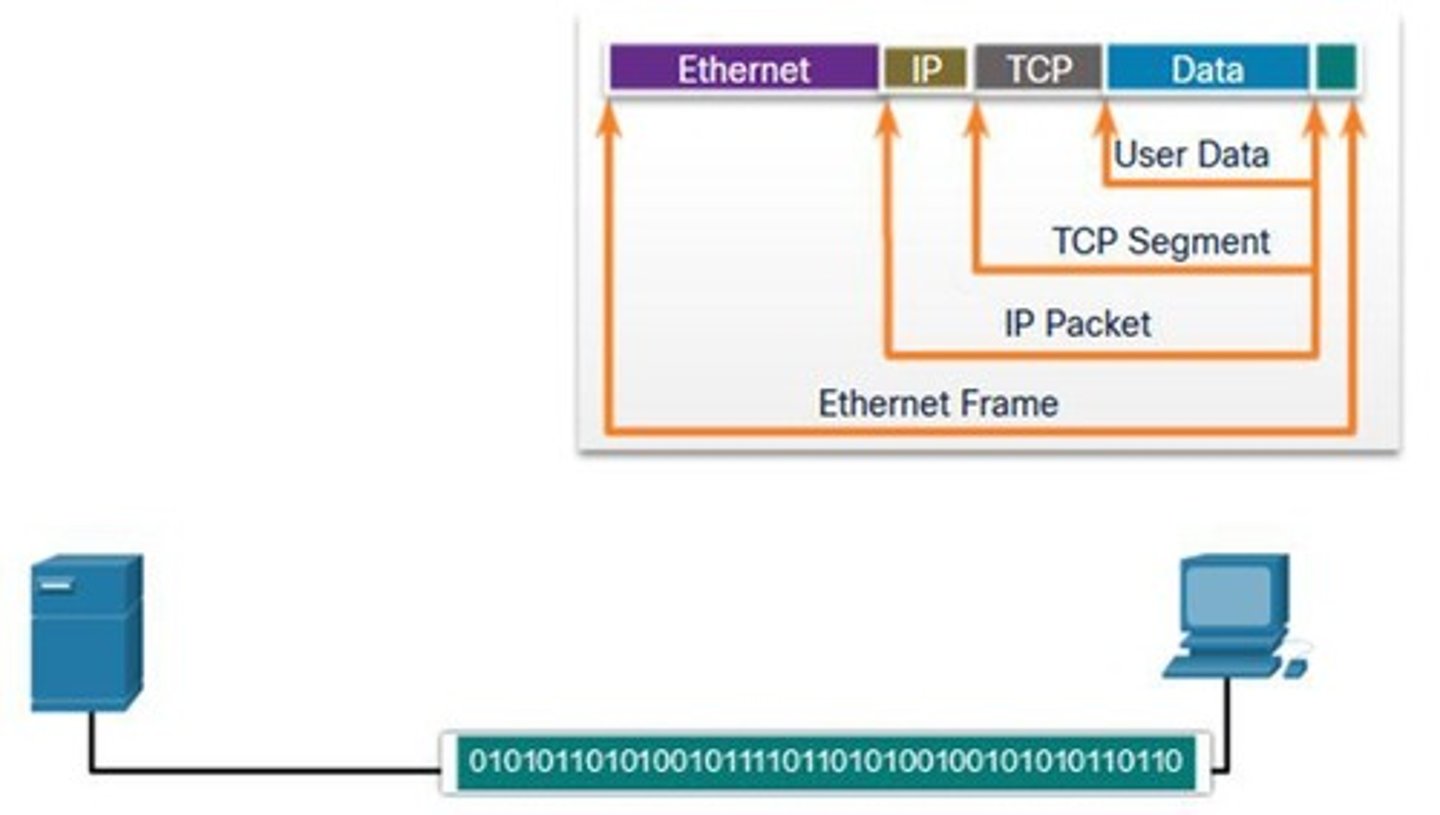
Protocol Data Unit (PDU)
Data unit with different names at each layer.
Data Stream
Initial form of data before segmentation.
Segment
Data unit after message segmentation.
Packet
Data unit encapsulated for network transmission.
Frame
Data unit for data link layer transmission.
Bit Stream
Raw binary representation of data.
De-encapsulation
Process of removing protocol information from data.
Network Layer
Responsible for IP packet delivery.
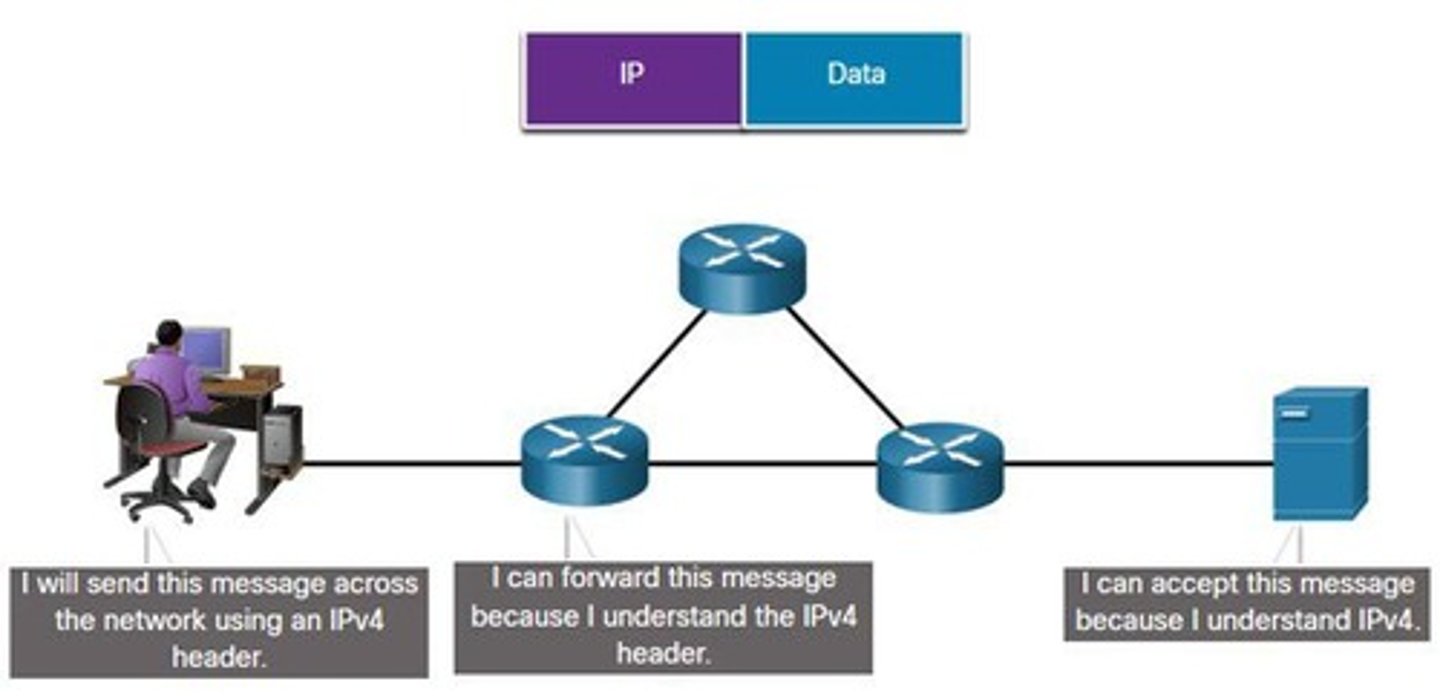
Data Link Layer
Delivers frames between network interface cards.
Source IP Address
IP address of the sending device.
Destination IP Address
IP address of the receiving device.
Network Portion
Indicates the network group of an IP address.
Host Portion
Identifies a specific device within a network.
Same Network Devices
Same network portion in IP addresses.
MAC Address
Unique identifier for network interface cards.
Data Link Frame
Encapsulated data for transmission over Ethernet.
Addressing
Method to deliver data from source to destination.
IP Packet
Encapsulated data unit used in network layer.
MAC Address
Physically embedded address in Ethernet NIC.
Local Addressing
Addressing method used within a local network.
Data Link Layer
Layer responsible for node-to-node data transfer.
Source Address
Address of the sender in a data frame.
Destination Address
Address of the intended recipient in a data frame.
Default Gateway
Router IP for accessing remote networks.
Router
Device that forwards data between networks.
Frame
Data packet at the Data Link Layer.
Segment
Part of data transfer between two nodes.
Ethernet NIC
Network Interface Card for Ethernet connections.
Remote Network
Network located outside the local network.
Layer 3
Network layer responsible for routing data.
Layer 2
Data link layer managing local addressing.
PC1
Example source device in the notes.
Web Server
Example destination device in the notes.
Router 1
First router in the data transmission path.