Endocrine system
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
endocrine system
collection glands/organs
produce regulation hormone in bloodstream to control body functions
endocrine overlap/responsibilities
overlap w/ nervous and exocrine
metabolism, growth, sexual dev
regulatory molecules
hormone
neurohormone
pheromone
hormone
stimulate Gr
reg. chem secreted by endocrine gland into blood/organ exhibiting
neurohormone
hormone secreted by neuron to blood
dopamine
pheromone
carry Gr
communication messengers, outside body sensing
paracrine
near Gr
signal between cell
reg. molecule work w/o transmitted by blood
prostaglandins
4 chemical categories
polypeptide
amines
glycoprotein
steroids
adrenals
cortex
medulla
prostaglandins
diverse group
reg. of: reproductive, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, urinary, immune
polypeptides
short chain amino acid
insulin/ ADH
amines
derived from tyrosine/ tryptophan
epinephrine/ norepinephrine/ melatonin
glycoprotein
longer 100 AA w/ carb
FSH/ LH
steroids
lipid derived cholesterol
steroid sex, steroid corticosteroid
steroid sex
testosterone, estradiol, progesterone
testes, ovary, placenta.
steroid corticosteroid
adrenal cortex (cortisol, aldosterone)
reg. glucose/ salt
posterior pituitary gland
store/ release: antidiuretic, oxytocin hormone
anterior pituitary gland
produce hormone secretes
growth hormone GH
anterior pituitary gland
stimulate muscle/ bone growth
adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTH
reg. glucose homeostasis
anterior pituitary gland
thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH
anterior pituitary gland
stimulate production thyroxin
luteinizing hormone LH
anterior pituitary gland
ovulation/ testosterone production in testes
follicle-stimulating hormone
FSH
dev. ovarian follicle/ sperm
anterior pituitary gland
prolactin PRL
anterior pituitary gland
stimulate mammary gland (milk)
melanocyte-stimulating hormone MSH
anterior pituitary gland
synthesis/ dispersion of melanin pigment
thyroid gland
thyroxine
help set basal metabolic rate
stimulate rate cell respiration
parathyroid gland
4 small glands
produce parathyroid hormone
parathyroid hormone
survival, stimulate osteoclast, dissolve calcium phosphate crystal, release Ca in blood
adrenal cortex
corticosteroids hormone
cortisol
cortisol
adrenal cortex
maintain glucose homeostasis, modulate aspect immune response
adrenal medulla
recieve neural input from axons of sympathetic division of autonomic NS
secrete epinephrine/ norepinephrine
islets of langerhans
B cell: secrete insulin, lower blood glucose
a cell: secrete glucagon, raise blood glucose
antagonistic
pancreas
secrete bicarbonate ions and variety digestive enzyme to small intestine
islet of langerhan
ovaries, testes
produce androgen
secondary sex characteristic
pineal gland
3rd eye, seat of soul
melatonin
negative feedback
maintain relatively constant level of target cell hormone
positive feedback
cannot maintain constancy internal env.
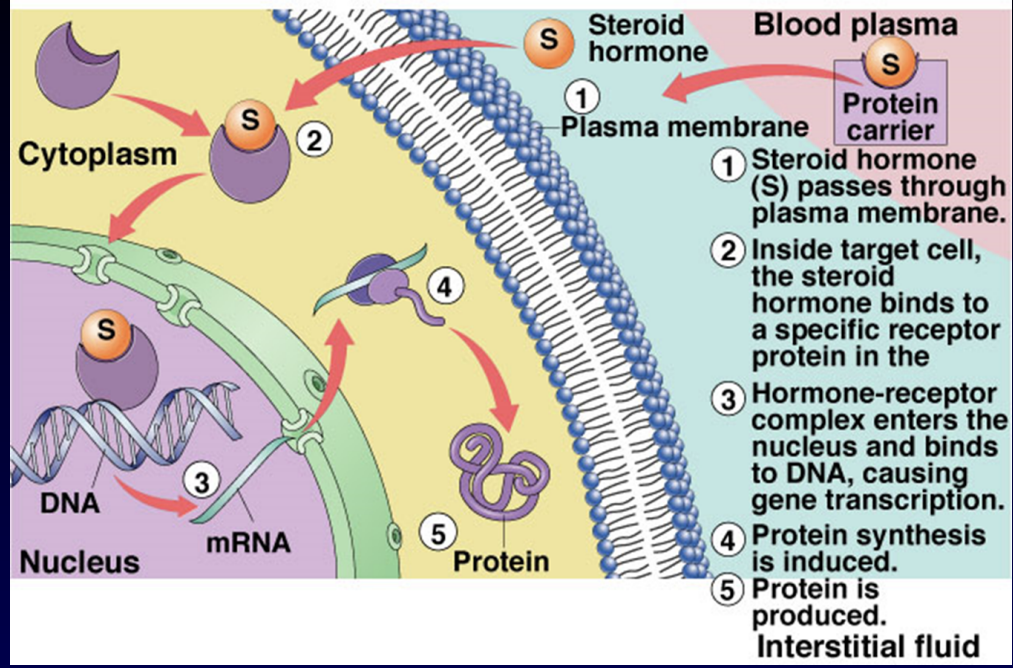
lipophilic
hormone enters cells
fat-soluble, pass through membrane easily
bind to intracellular receptor protein, form hormone-receptor complex, move to DNA turn genes on/off, affects function of target cell
lipophobic
do not enter cell
water-soluble, cannot pass through membrane
bind to receptor outside of membrane, activate signal pathway inside cell
major endocrine glands
pituitary gland, hang from hypothalamus
master gland
posterior pituitary gland hormones
ADH: help retain water
Oxytocin: causes uterine contraction, milk ejection
produced by hypothalamus and released by posterior pituitary
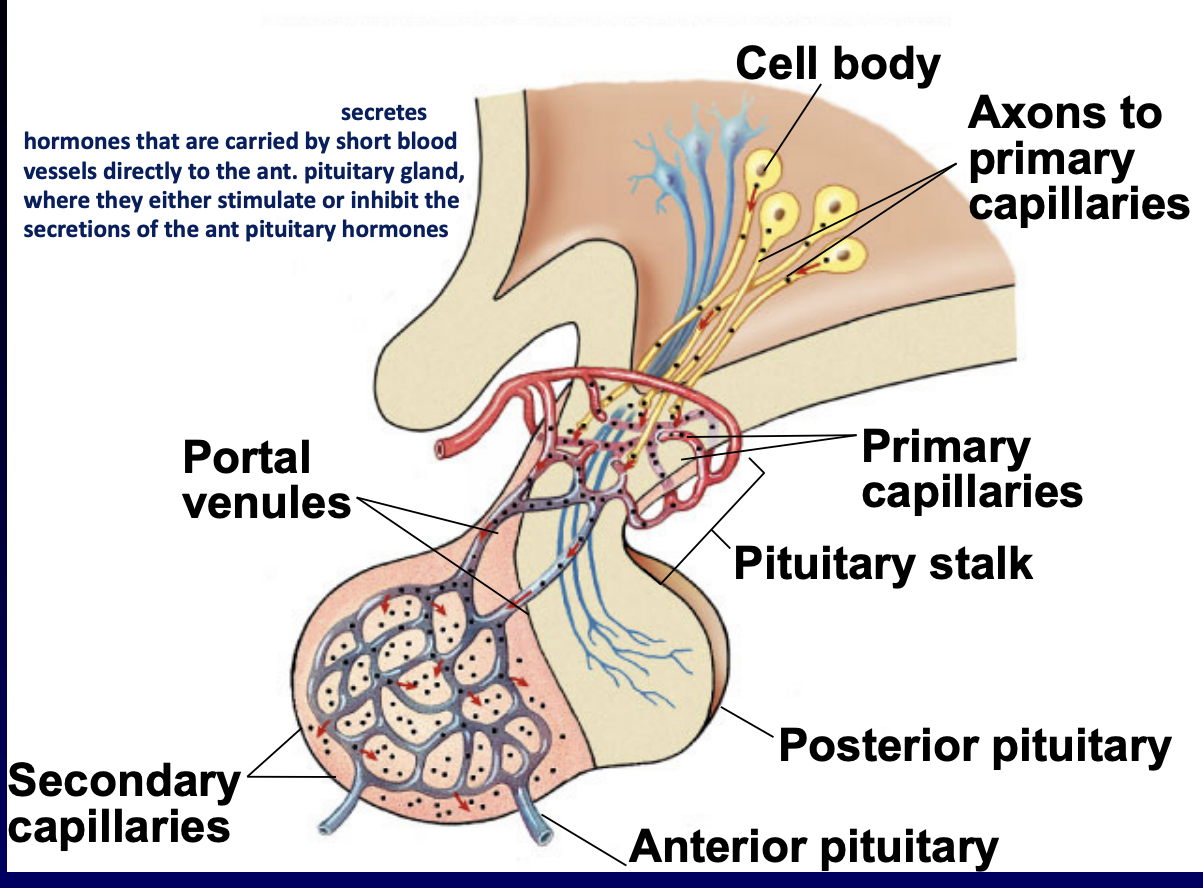
anterior pituitary
hormone made/ secreted in response to hormone from hypothalamus
hypothalamus uses special blood vessel system
thyrotropin, corticotropin, gonadotrophin releasing hormone (TRH, CRH, GnRH)
blood vessel system
hypophyseal portal system
communicate anterior pituitary
regulation thyroxine secretion
thyroxine T4
The hypothalamus releases T4, tells the anterior pituitary to release TSH, and tells the thyroid to release T4, T4 high—shut off and release negative feedback
blood Ca level regulation
calcium level in blood tight controlled
blood Ca low: parathyroid gland release to bone breakdown, increase Ca absorption
blood Ca high: thyroid release calcitonin, bone formation, increases excretion