The Atmosphere & Greenhouse gasses and Energy Balance
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
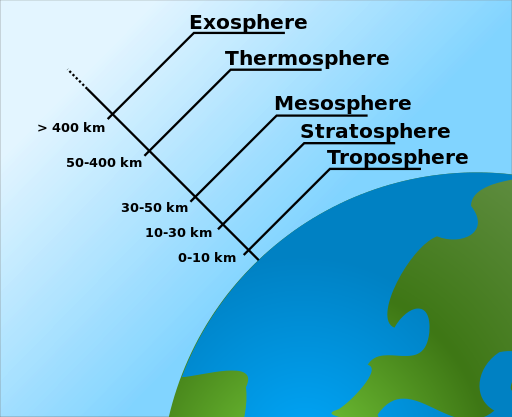
Order of the layers

Stratopause
the level of the atmosphere which is the boundary between two layers: the stratosphere and the mesosphere
tropopause
the upper limit of the troposphere
thermopause
The thermopause is the atmospheric boundary of Earth's energy system, located at the top of the thermosphere.
atmosphere
The atmosphere surrounds the Earth and holds the air we breathe; it protects us from outer space; and holds moisture (clouds), gases, and tiny particles. In short, the atmosphere is the protective bubble in which we live
Ozone layer
The ozone layer sits in the stratosphere between 15 km and 30 km above the earth and shields us and other living things from the sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation
aurora borealis
a natural electrical phenomenon characterized by the appearance of streamers of reddish or greenish light in the sky, especially near the northern or southern magnetic pole. The effect is caused by the interaction of charged particles from the sun with atoms in the upper atmosphere. In northern and southern regions it is respectively called aurora borealis
Altitude
height relative to sea level (eg 5280)
pressure
continuous physical force exerted on or against an object by something in contact with it.
temperature
the measure of heat
Popular greenhouse gasses
Methane, carbon dioxide, ozone, CFCs, greenhouse gases, nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides
Concentration, intensity
The amount of that substance in a space
intensity
the quantity of energy which the wave conveys per unit time across the surface of the unit area
duration
amount of time something takes
albedo energy budget/balance
describes the balance between the radiant energy that reaches Earth from the sun and the energy that flows from Earth back out to space
photon
a tiny particle or bundle of electromagnetic radiation
infrared
that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that extends from the long wavelength, or red, end of the visible-light range to the microwave range
heat
the quality of being hot; high temperature; form of energy
Reflect
throw back heat/energy
absorb
take in or soak
Urban Heat Islands
Heat islands are urbanized areas that experience higher temperatures than outlying areas
transpiration
occurs when plants take up liquid water from the soil and release water vapor into the air from their leaves
Albedo
Albedo is the fraction of light that a surface reflects