Lymphoproliferative Neoplasms
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 255 - Intro to Oncology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What is the common ancestors of the lymphocytes
the common lymphoid progenitor: gives rise to all lymphocytes
what type of cells is CLL made of
Small lymphocytes: B and T lymphocytes
what type of cell is ALL made of
common myeloid progenitor cells
what type of cell is multiple myeloma made of
Plasma cells
what are lymphoprolifertive neoplasms (LPNs)
a heterogenous group of diseases characterized by the infiltration of lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other tissues by abnormal clonal proliferation of lymphoid cells
malignant lymphoid cells exhibit uncontrolled ______ and failure to undergo _____
proliferation, apoptosis
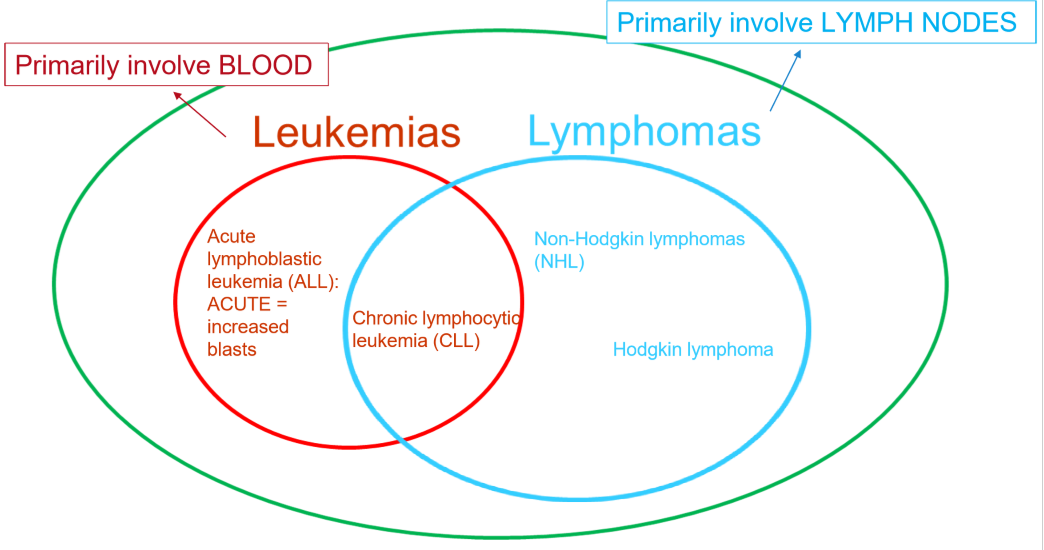
Lymphomas involve ____, and Leukemias involve ____
lymph nodes, blood
where do normal lymphocytes develop
in the bone marrow or thymus (primary lymphoid tissues)
what secondary lymphoid tissues to lymphocytes migrate to?
lymph nodes
spleen
tonsils
appendix
peyer’s patches
what do abnormaly lymph nodes look like
increased in number and size
hard/swollen
unusal location
infiltration of abnormal cells
alteration in architecture
what are the three main causes of lymphadenopathy
M.I.A
Malignancy
Infection
Autoimmune
Malignant causes of lymphadenopathy
lymphoma, metastasis
infection causes of lymphadenopathy
TB (bacterial)
Mono!!! (Viral)
histoplasmosis (fungal)
parasites
Autoimmune causes of lymphadenopathy
sarcdoidosis
Lupus
Sjogren’s
Kawasakis
what does a physical examination for abnormal lymph nodes look like
inspect for asymmetry, erythema and tenderness
palpate for location size, tenderness, etc
Fixed/Firm/Matter lymph nodes =
bad
tender lymph nodes =
reactive (most likely)
what clinical tests can be done for abnormal lymph nodes
imaging may be used to see all areas involved that aren’t palpable (appendix)
blood tests can help rule out infections or autoimmune
if we have a suspicion of lymphoma, what clinical test is done
LN biopsy
why are excisional biopsies preferred for potential lymphoma
better to see the architecture of the lymph ndoes
3 different types of biopsies
Fine Needle Aspiration
Core Biopsies
Excisional (best)
what type of biopsy should never be done to diagnose lymphoma
fine needle aspiration (FNA)
does not provide architecture of lymph nodes, lymphoma cells look a lot like normal lymphocytes when seen individually
what does an altered spleen look like>
too large, altered architecture, prescence of nodules
5 diagnosies that may cause splenomegaly
lymphoproliferative neoplasms
infections
inflammation
cirrhosis with portal hypertension
extramedually hematopoeisis
what type of imaging is used to see an abnormal spleen
ultrasound or CT
if the cause of an abnormal spleen is suspected to be LPN, what else should be done?
A bone marrow or LN biopsy should be performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess for lymphoproliferative disease.
are there more T cells or B cells bine marrow
more T cells
if LPN is suspected, are there more B cells or T cells in bone marrow
abnormal ratio of B cells to T cells
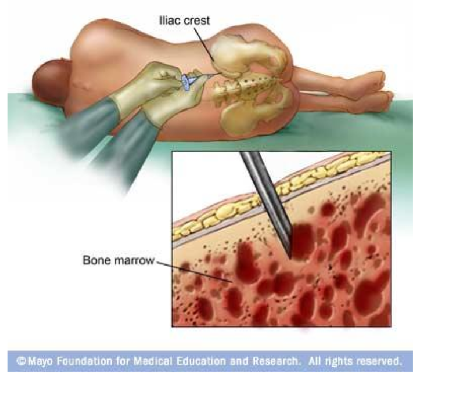
what is a bone marrow biopsy
A procedure to obtain a sample of bone marrow for examination, typically used to diagnose blood disorders or malignancies.
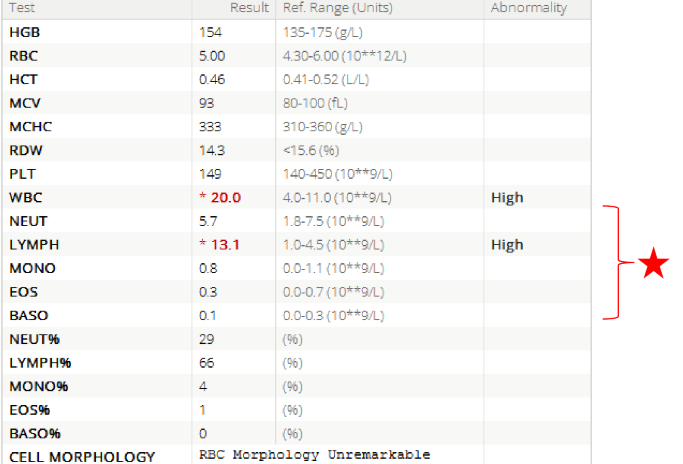
what is a CBCD
a complete blood count that includes the complete break down of types of white blood cells
what CBCD levels increase in LPNs
The levels of atypical lymphocytes, particularly B cell counts, typically increase in lymphoproliferative neoplasms.
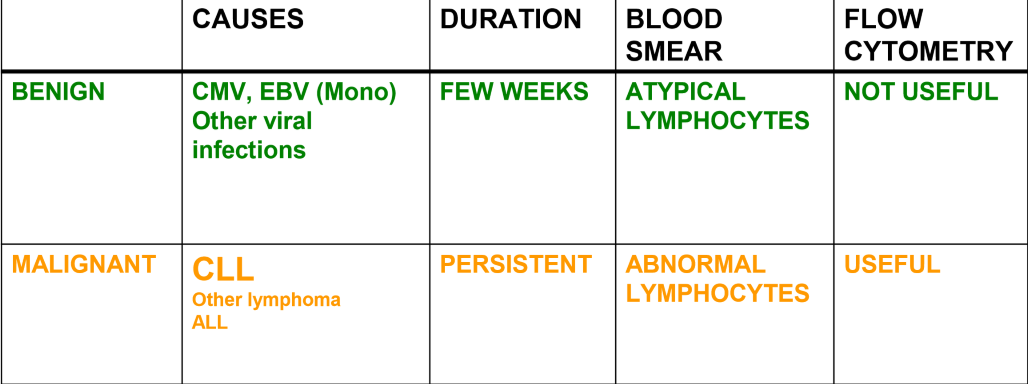
what are the only two pathologies that increase lymphocyte count
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Mononucleolis Virus
why is flow cytometry used to identify different types of lymphocytes
under a microscope, B and T cells look nearly identical, however they have different surface antigens that can be used to detect the type of lymphocyte
what type of cell surface markers are consister with B cells
CD19 and CD 20 (high numbers)
what type of cell surface markers are consistent with T cells
CD3, CD4, CD8 (low numbers)
what leukemia is the most frequent cause of persistent blood lymphocytosis
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
what 3 tests are used to confirm CLL diagnosis
Blood smear with MATURE lymphocytes
Flow cytometry profile
bone marrow biopsy or aspiration
3 constituinal (B) symptoms
weight loss of 15-20 pounds
fever of over 100
sustained DRENCHING night sweats
What lab tests should be done for lymphoma
CBCD
electrolytes
creatinine (kidney)
Uric acid
what is biopsied for lymphoma diagnosis
Lymph node or involved organs
what viral studies are used for lymphoma
Test for HIV and HEP B/C which increase risk of lymphomas
What genetic tests can be done for lymphoma
Karyotype
FISH
oncogene testing
three types of LPN/Lymphoma
B cell Non-Hodgkins
T cell Non-Hodgkins
Hodgkins
two types of of Non-Hodgkins
Indolent
agressive
what is the most aggressive lymphoma
Burkitt’s
HIV subtype: true next day emergency
second most agressive lymphoma
DLBCL
diffuse large B cell lympgoma
most indolent aggressive lymphoma
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
watch and see treatment
do lymphomas have good or bad prognosis
typically decent prognosis: lots of stage 4 ones are manageable
what staging system is used for lyphomas, how is it different than solid tumors
The Ann Arbor staging system is used for lymphomas
solid tumors use TMN, but lymphoma has no primary tumor, so you can’t use it
Ann Arbor Stage 1
one site
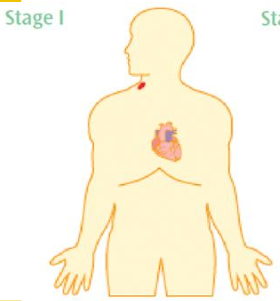
Ann Arbor Stage 2
multiple sides on one side of the diaphragm
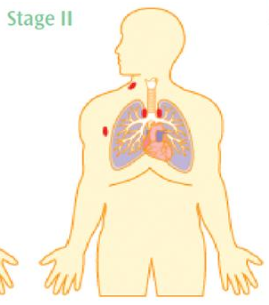
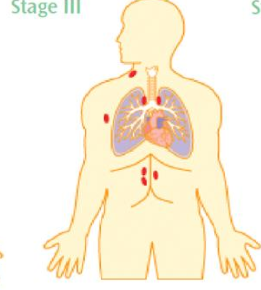
Ann Arbor Stage 3
multiple sites on both sides of the diaphragm
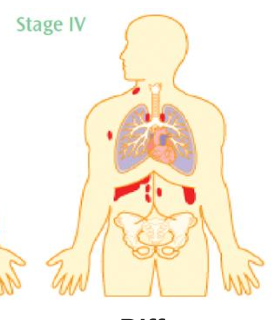
Ann Arbor Stage 4
Diffuse involvement of extra-lymphatic organs
what is the most common treatment modality for lymphoma
chemotherapy or immunotherapy
is radiation therapy used often for lymphoma
it is fairly rare to treat lymphoma with radiation
what can corticosteroids (prednisone) used for in lymphoma treatment
reduce tumors and relieve symptoms
but must be used after biopsy to ensure proper diagnosis
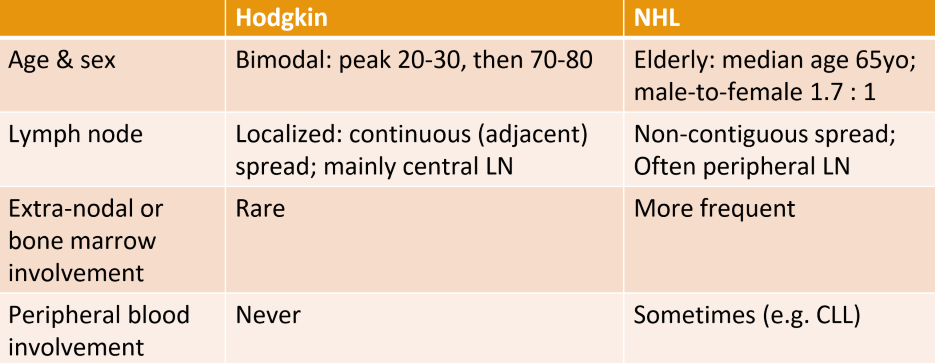
difference between Non-Hodgkins and Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is characterized by the absence of Reed-Sternberg cells, while Hodgkin's lymphoma includes these cells and typically has a better prognosis.
which lymphoma is more common, NHL or HL
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) is more common than Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL), making up the majority of lymphoma cases.
age range of Hodkin’s lymphoma
bimodal: peak 20-30, then 70-80
NHL more common above 65 (and more common in men)
is there more LN spread in HL or NHL
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma generally demonstrates more extensive lymphatic spread compared to Hodgkin's lymphoma, which usually spreads in a more predictable manner.
what intent is treatment of HL
alway curative
why is radiation not used in treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma
increases CV disease
secondary malignancies
thyroid dysfunction
what is the Chemotherapy standard for HL
ABVD regimen, which includes Adriamycin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine.
what are the two cell origins of NHL
B-cell
T-cell
Agressive NHL example
Diffuse Large B-Cell lymphoma (DLBCL)
TLS syndrome possible
fatal in months
Indolent NHL example
Follicular lymphoma
no TLS
watch and wait treatment
what is tumor lysis syndrome
rapid death (lysis) of tumor cells, resulting in intracellular contents dumped into blood stream
effects of TLS (PUCCK)`
PUCCK
increased PO4
increased Urate
decrease Ca (as it binds to PO4)
increased creatinine
increased potassium
how does renal damage occur due to TLS
when calcium binds to PO4, it enters the kidnets where it causes calcium crystals to form = damage
prophylactic treatment of TLS
allopurinol
prevents metabolism of uric acid
Treatment of TLS
Rasburicase
metabolises uric acid to allantoin, a more soluble compound to be excreted by kidneys
when is radiation therapy used for aggressive NHL
if disease is bulky
when do you treat aggressive NHL, when do you treat indolent?
aggressive: treat immediatly with CHOP
indolent: treat when symptomatic
what type of NHL is CLL
indolent NHL
Staging of CLL (LLSAT)
LLSAT
Stage 0: lymphocytosis
Stage 1: lymphadenopathy
Stage 2: splenomegaly
Stage 3: anemia
Stage 4: thrombocytopenia
Does not use Ann Arbor!
is CLL curable?
no
what anti-CD20 IgG is used to treat CLL (when patient is symptomatic)
Rituximab is used to treat symptomatic CLL patients.
Side effects of Rituximab
may include infusion reactions, fever, chills, hypotension, and increased risk of infections.
normal for all antibodies
treat with acetominophen and corticosteroids
Leukemia = ____ malignancy
peripheral blood
Lyphoma = ____ malignancy
solid lymph node
do NOT do an _____ to diagnose a lymphoma
Fine needle aspiration
Lymphadenopathy Differential
M.I.A
malignancy
infection
autoimmune