Biochem Exam 2
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
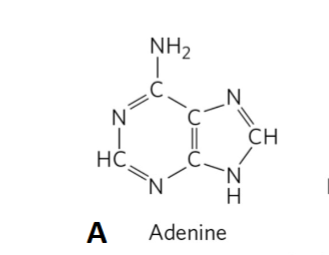
Adenine
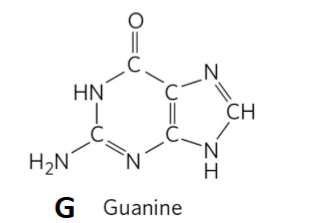
Guanine
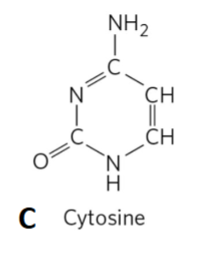
Cytosine
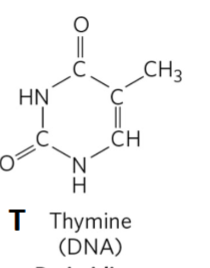
Thymine
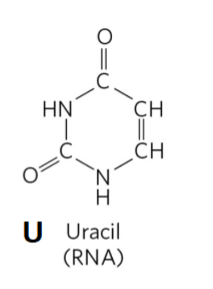
Uracil
DNA strand orientation
antiparallel, asymmetric with a minor and major groove
Major groove
presents opportunities for sequence specific interactions to occur from the outside without unwinding
Alternate DNA geometries
sugar pucker, syn/anti position of nucleobase
Hoogsteen base pairs
allows ¾ strands to be present in helix, found in damaged DNA and DNA bound by drugs
RNA folding
can form base pairs with itself to form secondary structures
Melting dsDNA
seperating 2 strands
Melting temperature
temperature at which half of dsDNA is denatured and is a useful measure of dsDNA stability
Linking number
sum of writhe and twist
Changing twist →
supercoiling
Topoisomerases
change linking number of DNA by cutting, rearranging, or resealing structure
Topoisomerases effect on DNA
help DNA compaction and dealing with disruptive structures
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around histone proteins
Inacessible DNA
packing DNA into chromatin
Histone acetylation
DNA more acessible
Histone methylation
DNA less acessible
Chemical mechanism of DNA synthesis
base activation of 3’ OH for nucleophilic attack on 5’ P of dNTP
Synthesis direction
5’ to 3’
Polymerases
use metals to facilitate 3’ OH attack and stabilize negatively charged phosphates
DNA Polymerase requirement
short stretch of existing dsDNA
Primer
short piece of DNA annealed to template, facilitates addition of complimentary base pairs to growing strand
Polymerase error rate
1 in 10,000 to 1 mil base pairs
Tautomeric forms and wobble pairs →
lead to addition of non-complimentary nucleotide
Mistakes effect on DNA strand
growing strand gets passed into 5’ to 3’ exonuclease
Fixing mistakes
errogenous base gets removed and DNA polymerase gets second chance to add correct base
DNA repilication start site
starts at origin sequence and replication forks advance in opposite directions
Helper enzymes
help unwinding and synthesis of DNA at replication fork
Leading strand
undergoes continous sequences
Lagging strand
made of serious discontinuous okazi fragments that are sealed by DNA ligase
Telomerase
prevents shortening at end of lagging strand
DNA polymerase direction
3’ to 5’
Mismatch repair pathway
corrects against misincorporation, distinguishes parental strand from daughter based on DNA methylation
Alkylation
addition of methyl or ethyl that disrupts H bond that forms base pair
Deamination
removal of amine, replaced by carbonyl
Depurination
removal of entire purine base
UV induced modifactions
dimerization
Direct repair
sacrifices a protien to undo a DNA alkylation event
Base excision repair
damaged bases are removed to generate abasic sites which are then repaired
Nucleotide excision repair
used to remove larger stretches of damaged DNA like dimers
Homologous recombination
repairs double strand breaks, occur between highly similar sequences
Testing homology
generating single stranded 3’ overhangs and sampling for base pairing interactions
Polymerase function in homologus recombination
extends 3’ overhangs using the target as a template
Holliday junctions
4 way DNA structures that can be resolved in different ways to produce different gene products
Homologous recombination affect on diversity
increases chromosome diversity by exchanging portions of mom and dad chromosomes
Sequence specific recombinasaes
mediate recombination at defined sites
Recombination can result in →
insertion/excision or inversion
Tyrosine recombinases
catalyze sequential single strand cleavages and proceed through a holliday junction
Serine recombinases
catalyze simultaneous double stranded breaks, rotate DNA fragments and ligate them together
Transposases
mobile DNA elements that copy/paste or cut/paste themselves from one location in the genome to another
Transposase activation
lead to mosaic genotypes where different cells harbor different alleles
2 classes of transposase
retrotransposons, DNA transposons
Retrotransposons
copy/paste, RNA intermediate
DNA transposons
cut/paste, no intermediate
Transposons
can generate phenotypic variations if insertions/excisions modulate gene expression
RNA polymerase
catalyzes RNA synthesis using DNA template, doesn’t require a primer, seperate helicase, or exonuclease
RNA polymerase product
single strand RNA copy of coding strand, using template strand
Promoters
position RNA polymerase to initiate at a defined location
2 Prokaryote mechanisms for termination
Rho dependent or independent
Rho-dependent
relies on helicase
Rho- independent
relies on hairpin structure
Lac operon
expresses lac genes when LacI repressor and lactose are present
Lac operon mechanism
glucose inhibits production of cAMP, cAMP increases as glucose decreases, cAMP binds to CAP, CAP binds to promoter and stimulates RNAP to activate transcription
Activator and repressor interactions
make sequence specific interactions with DNA
Sequences read through →
side chains that h-bond with DNA bases
DNA binding activity
DNA not melted, activity seperate from regulatory activity
Epigenetics
changes in gene expression not caused by changes in DNA sequence
Chromatin
organized into accessible (euchromatin) and inacessible (heterchromatin) regions
Euchromatin
characterized by histone acetylation
Heterochromatin
characterized by histone methylation
DNA methylation
heritable type of epigenetic regulation
5 methylcytosine
silences gene expression
Pre-mRNA
composed of introns and exons
Spliceosome
removes introns to produce mature mRNA
Alternative splicing
produces different combinations of exons and different protein isoforms
Modifications of pre-mRNA
5’ cap and 3’ poly A tail
Self splicing introns
segments of RNA that can splice themselves out of RNA polymer without assistance of proteins
Group 2 introns
removed by mechanism similar to spliceosome
Micro RNA
small 22 nt RNA sequences that down regulate gene expression, encoded in genome
Micro RNA processing
processed in multiple steps and assemble with proteins to form RNA silencing complex
Precise pairing
cleavage of target RNA, reversible
Imprecise pairing
represses gene expression without cleavage, reversible
Making proteins
ordering of nucleotides specifies order of amino acids
Genetic code
mapping between 3 nt codons in mRNA and 20 amino acids
tRNAs
biochemcial adapters that are charged to link codons to specific amino acids
Open reading frame
continous sequence of codons flanked by start and stop codon specifying gene’s protein sequence
Ribosome
ribonucleoprotein machine that organizes polypeptide sequences using mRNA/tRNA interactions
3 interaction sites for mRNA/tRNA
A, P, E
Start codon
initiates translation that is recognized in different ways by prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Ribosome mechanism
N terminal amine of A site attacking ester linkage of C terminal polypeptide to P site, transferring polypeptide to tRNA in A site
Translocation of tRNA
A to P to E to gone
Termination
release factor recognizes stop codon
Translational control
provides a means of regulating gene expression
Prokaryotic translation
translation and transcription are coupled
Eukaryotic translation
assembly of initiation complex through 5’ cap and 3’ poly A tail creates range of regulatory possibilities