Spine Patho
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP), Spondylosis, spondylolisthesis, spondylolysis, scoliosis, kyphosis, vertebral compression fracture, ankylosing spondylitis, tumors
What are the many causes are spinal stenosis?
Spinal stenosis
Nerve compression caused by narrowing of spinal cord or neural foramina that can occur along any area of the spine (cervical, thoracic, lumbar)
Central Stenosis
Compression of the spinal cord itself
Lateral stenosis
Compression of nerve root as it exits spinal canal - many accompany central
Exacerbation of pain when walking or relief of pain when leaning forward (neurogenic claudication), radiculopathy
Signs of spinal stenosis
Get good upper/lower extremity, R/o compressive neuropathy, Keep an eye out for cauda equinia
Must Haves for Spinal Stenosis exams

Cauda Equina
The bundle of spinal nerve roots at the end of the spinal cord (conus medullaris) in the lumbar region that include the sacral plexus that provides motor/sensory to the lower extremities and also bladder and bowel function
Severe low back pain, radiating pain down the leg, asymmetrical LE motor weakness and/or sensory loss (more than 1 nerve root), loss of reflexes in the LE (hypoactive), sensory loss seen around the anus, lower genitalia, perineum, buttocks, and posterior inner thigh (L3-L5), onset of bowel incontinence, bladder dysfunction (urinary retention or incontinence), recent onset of sexual dysfunction
Red Flags for Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES)
Large herniated lumbar disc, tumor, trauma, spinal epidural hematoma, infection
Possible etiology of CES
urinary retention (anal sphincter tone is only diminished 50-75%)
The most consistent sign in cauda equina syndrome (confirm with MRI)
Prompt surgery within 24-48 hours of presentations, PT (strength, ROM, bracing), Chronic pain medications, lifestyle modifications
Treatment plan for CES
extent of nerve damage, relation to length of time nerve was compressed, cause of compression
Prognosis of CES treatment depends
lumbar spine (L4/5, L5/S1, C4/5, C5/6 - but can happen anywhere)
The most common area to have HNP is in the
Annulus fibrosis (outer layer)
Disc herniation occurs when the __________ breaks open or cracks allowing the nucleus pulposus in escape
repetitive movements, bad posture, being overweight, heavy lifting, disc dehydration
Causes of HNP
X-ray (r/o other causes), MRI (🏆, CT if MRI C/I)
65 y/o male presents to the clinic for back pain that radiates down his legs. On physical exam you note weakness of the legs, patellar reflexes are +1 and pain is exacerbated by extension of the back. What diagnostics do you want?
Pain meds or therapies (u/s, massage, TENs), NSAIDs, PT, Rest, steroid injections (epidural steroid inject - last ditch effort)
65 y/o male presents to the clinic for back pain that radiates down his legs. On physical exam you note pain is exacerbated by extension of the back. MRI reveals a herniated disc at the L4/5 level. What is your conservative management?
Surgical treatment (discectomy - may include laminectomy/laminotomy, or foraminotomy) Note: does not repair/reverse nerve damage
65 y/o male presents to the clinic for back pain that radiates down his legs. On physical exam you note weakness of the legs, patellar reflexes are +1 and pain is exacerbated by extension of the back. What is your management plan?
Spondylosis (osteoarthritis, degenerative disc disease (DDD))
The result of degenerated discs and other cartilage and formation of osteophytes on the vertebrae usually caused by the normal wear-and-tear of aging (middle-age or elderly)
neck stiffness, pain, HA, pain in the shoulder/arm, inability to turn/bend the neck, grinding noise/sensation, improve with rest and are most severe in the morning, if bone spurs press against spinal nerves then weakness, abnormal reflexes, or arm pain
Signs and Symptoms of CERVICAL spondylosis
Lower back pain/stiffness, hip or leg pain, pain worsened with activity, improve with rest, most severe in the morning, if bone spurs press against spinal nerves then weakness, abnormal reflexes, or leg pain
Signs and Symptoms of LUMBAR SPONDYLOSIS
Xrays (if worried about nerves do MRI)
1st line imaging for spondylosis 🏆
rest, nsaids, PT, weight loss, ESI/facet steroid injection
Homies with spondylosis WITHOUT nerve compression → treatment plan
laminectomy/laminotomy, foraminotomy → Cervical fusion, lumbar fusion (for stabilization)
Homies with spondylosis WITH nerve compression → treatment plan
Spondylolysis
A fracture through the pars interarticularis (weakest portion) that can occur on 1 or both sides of the bone (usually L4 or L5)
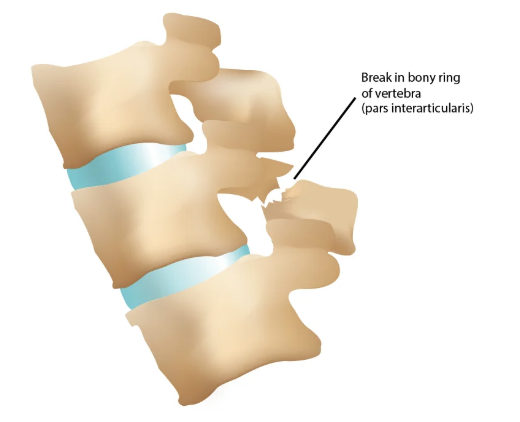
Spondylolisthesis
Where a bone in the spinal vertebra slips position (anterior or posterior usually lower back) that are graded based on the slippage - common with bilateral spondylolysis
Overuse (sports with hyperextension), Genetics, MVC,
Common causes of Spondylolysis
Congenital (dysplastic Spondylolisthesis), repetitive trauma (isthmic Spondylolisthesis), degenerative (old people), traumatic, bone abnormalities (pagets, TB, tumors)
Common causes of Spondylolisthesis
Standing X-rays with flexion/extension views (spondylolisthesis) or oblique (spondylolysis), MRI for nerve stuff
16 y/o male football player presents to the clinic for low back pain that radiates down to the back of the thighs and is exacerbated by activity. On physical exam you note increased lordosis. What diagnostics do you want?
Referral to ortho spine, activity modification, PT (🔑), bracing to allow fracture to heal, ESI
16 y/o male football player presents to the clinic for low back pain that radiates down to the back of the thighs and is exacerbated by activity. On physical exam you note increased lordosis. X-rays reveal spondylolisthesis. What is your treatment plan?
Spinal stabilization via posterior fusion
16 y/o male football player presents to the clinic for low back pain that radiates down to the back of the thighs and is exacerbated by activity. On physical exam you note increased lordosis. X-rays reveal spondylolisthesis. Your conservative treatment FAILED and now he has weakness, decreased sensation and reflexes what do you want to do now?
Kyphosis (hunchback)
An increased CONVEX curvature (over 45 degrees) of the thoracic spine usually seen in the elderly population with compression fractures or idiopathic (Scheurmann’s disease/juvenile)
Standing lateral x-rays
Imaging for Kyphosis
Repeat X-rays q3-4 months, PT, if over 60 degrees or with persistent pain (Milwaukee brace), Brace them kids, Surgery (if refractoy)
Treatment for Kyphosis
thoracic spine
Most common area for vertebral fractures
Compression fracture
A fracture commonly associated with osteoporosis and NO neuro compromise (stable)
Burst fracture
A fracture usually associated with trauma (MVC, fall from height) and possible neuro compromise (unstable)
Pathologic fractures
Fractures that occur secondary with secondary other diseases
Anterior (looks like a wedge)
Compression fractures usually happen on the ________ aspect of the vertebrae
sudden midline back movement, worse with movement, kyphosis
Symptoms of compression fractures
Xray, MRI (water content with bony edema → shows acute), CT
Imaging for compression fractures
Education on nutrition/exercise, Vitamin D/Ca, Osteoporosis treatments, pain meds, Surgery (IF 50%+ of vertebral height (Kyphoplasty))
Treatment plan for compression fractures
anterior AND posterior aspect (high risk of spinal cord compromise)
With a burst fracture, where does the vertebra lose height?
Significant comminution, severe loss of vertebral body height, excessive angulation at the injury site, significant nerve compression
Treatment of Burst fractures is usually surgical, what are some indications
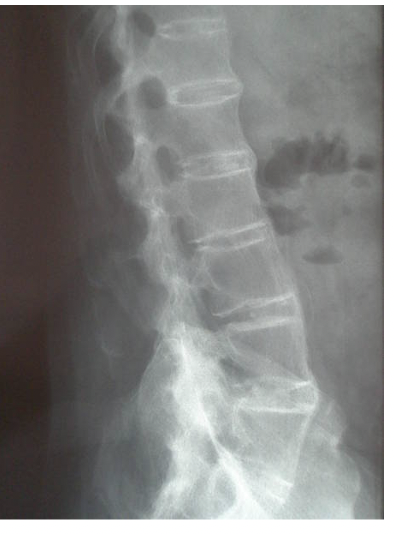
Ankylosing Spondylitis (seronegative spondyloarthropathy)
An inflammatory disease that over time causes the “fusion of the vertebrae” which can lead to a hunched forward position that begins in the 30-40s (men > women)
Affects the SI joints symmetrically and the spine in a progressively ascending patterns
Describe the pattern of Ankylosing Spondylitis
limited ROM of back, shoulders, hips; kyphosis, synovitis of knee, plantar fasciitis, achilles tendinitis, Schober’s test (tests spine mobility - lumbar flexion)
Physical exam findings on Ankylosing Spondylitis
Uveitis, cardiac abnormalities (1st degree AV block, widened QRS), interstitial lung disease
Extra-Articular Manifestations of Ankylosing Spondylitis
Elevated CRP and ESR, HLA-B27 positive
Labs for Ankylosing Spondylitis
BAMBOO appearance 🎍, sacroiliitis may be an early finding, fractures are common due to fusion
Imaging findings of Ankylosing Spondylitis
PT, NSAIDs, Surgery for any fractures or stabilization
Treatment for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Winking owl sign
Since the spine is a common metastasis point, what is an early sign on the AP view