Anatomical Locations and Positions
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Medical Terminology for Healthcare Professionals 10/e
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Anatomical position assumes what?
the body is erect
the head is facing forward
arms are by the sides with palms to the front
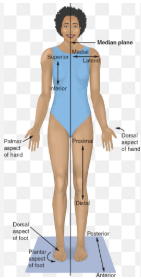
Left and right refer to who’s point of view?
the patient
What are planes?
imaginary lines that divide the body into different sections
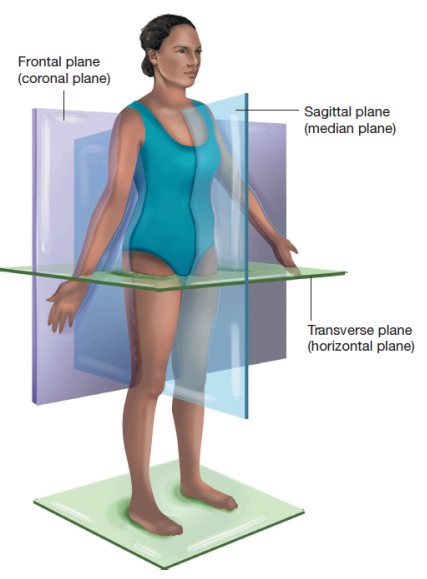
Sagittal plane
vertically divides body into right and left sides
Midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
Transverse/horizontal plane
divides the body into superior and inferior portions
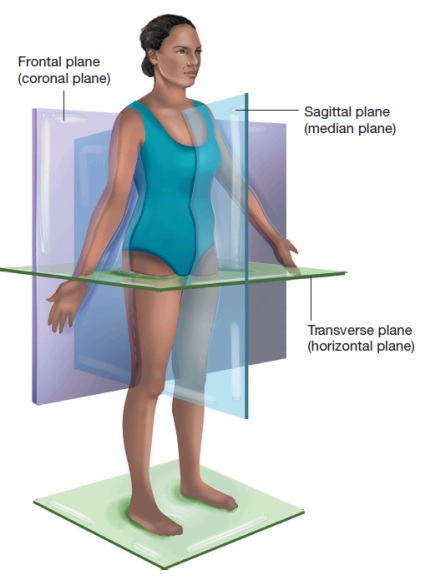
Coronal/frontal plane
divides the body into front and back portions
What are directional and positional terms?
describe the location of organs or body parts in relationship to one another
Anterior/ventral
towards the front
Anterior combining form
anter/o
Posterior/dorsal
towards the back
Posterior combining form
poster/o
Superior/cranial
towards the head
Inferior/caudal
towards the tail
Inferior combining form
infer/o
Caudal combining form
caud/o
Proximal
closer to the point of origin; generally the trunk
Proximal combining form
proxim/o
Distal
Farther away from the point of origin; generally the trunk
Distal combining form
dist/o
Medial
closer to the midline of the body or body part
Medial combining form
medi/o
Lateral
farther away from the midline of the body or a body part
Lateral combining form
later/o
Superficial
closer to the surface
Deep
farther below the surface
What are body cavities?
a hollow space containing body organs
What are the two primary body cavities?
the ventral/inferior and dorsal/posterior cavity
What is the ventral cavity?
the hollow part of the torso, extends from the neck to the pelvis
What are the three subdivisions of the ventral cavity?
thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavity
Where is the thoracic cavity and what does it contain?
in the chest area, contains the heart, lungs, esophagus, trachea, and thymus
What are the cavities within the thoracic cavity?
pericardial and pleural cavity
Where is the abdominal cavity, and what does it contain?
below the diaphragm and contains most digestive organs
How is the pelvic cavity formed and what does it contain?
formed by the bones of the pelvic area and contains the reproduction and elimination organs
What does the dorsal cavity contain?
contains the structures of the nervous system
What are the subdivisions of the dorsal cavity?
cranial and spinal cavity
What is the abdominopelvic cavity?
a combination of the abdominal and pelvic cavity
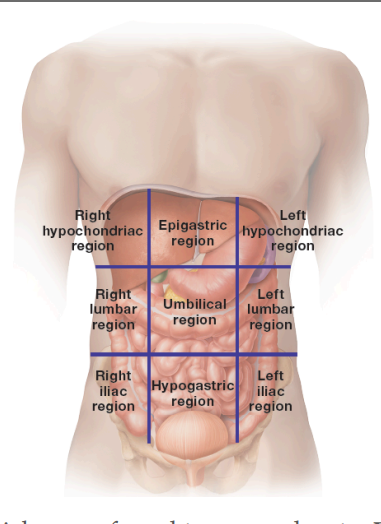
What are the nine regions of the abdominal pelvic cavity?
right/left hypochondriac: the upper right/left region at the level of the ninth rib cartilage
epigastric: region over the stomach
right/left lumbar: right/left middle lateral region
umbilical: in the center/the navel
right/left iliac (inguinal): right/left lower lateral region
hypogastric: lower middle region below navel
What are the quadrants of the abdomen
right upper quadrant (RUQ)
left upper quadrant (LUQ)
right lower quadrant (RLQ)
left lower quadrant (LLQ)
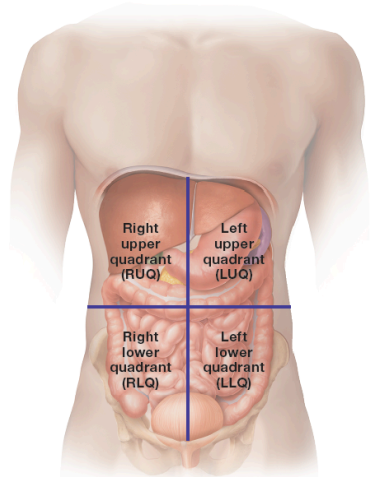
What does the RUQ contain
contains the right lobe of the liver, gallbladder, part of the pancreas, and part of the small and large intestines
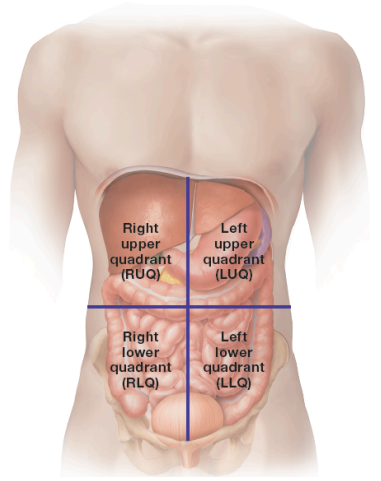
What does the LUQ contain
contains the left lobe of the liver, stomach, spleen, part of the pancreas, and part of the small and large intestines
What does the RLQ contain
contains part of the small and large intestines, appendix, right ovary, right fallopian tube, right ureter
What does the LLQ contain
contains part of the small and large intestines, left ovary, left fallopian tube, left ureter
What is the trunk of the body?
the torso; central part of the human body