APBio Unit 4 Cellular Communication, Cell Cycle, Homeostasis
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Homeostasis
The body's ability to maintain relatively stable internal conditions even though the outside world is continuously changing.
Stimulus
causes change
Receptors
monitors changes then sends information to the control center
Set Point
the level that is to be maintained
Effector
causes a response to change conditions
Response
result of the stimulus
Negative Feedback
-depresses or stops the conditions to return toward set point
-Most conditions in the body
Positive Feedback
-enhances or continues the response away from set point
-Examples: childbirth, blood clotting
Ectotherm
internal temperature conforms to ambient temperature.
Endotherm
able to maintain body temperature at a different level than the environment
Standard Metabolic Rate
the metabolic rate of an ectotherm at rest at a specific temperature
Basal Metabolic Rate
minimum metabolic rate of an endotherm at rest.
Osmoconformers
their osmolarity equilibrates with that of seawater. results in energetic savings.
Osmoregulators
have tissue fluid that is different from the external environment. They must actively regulate the osmolarity of their extracellular fluids. Requires energy
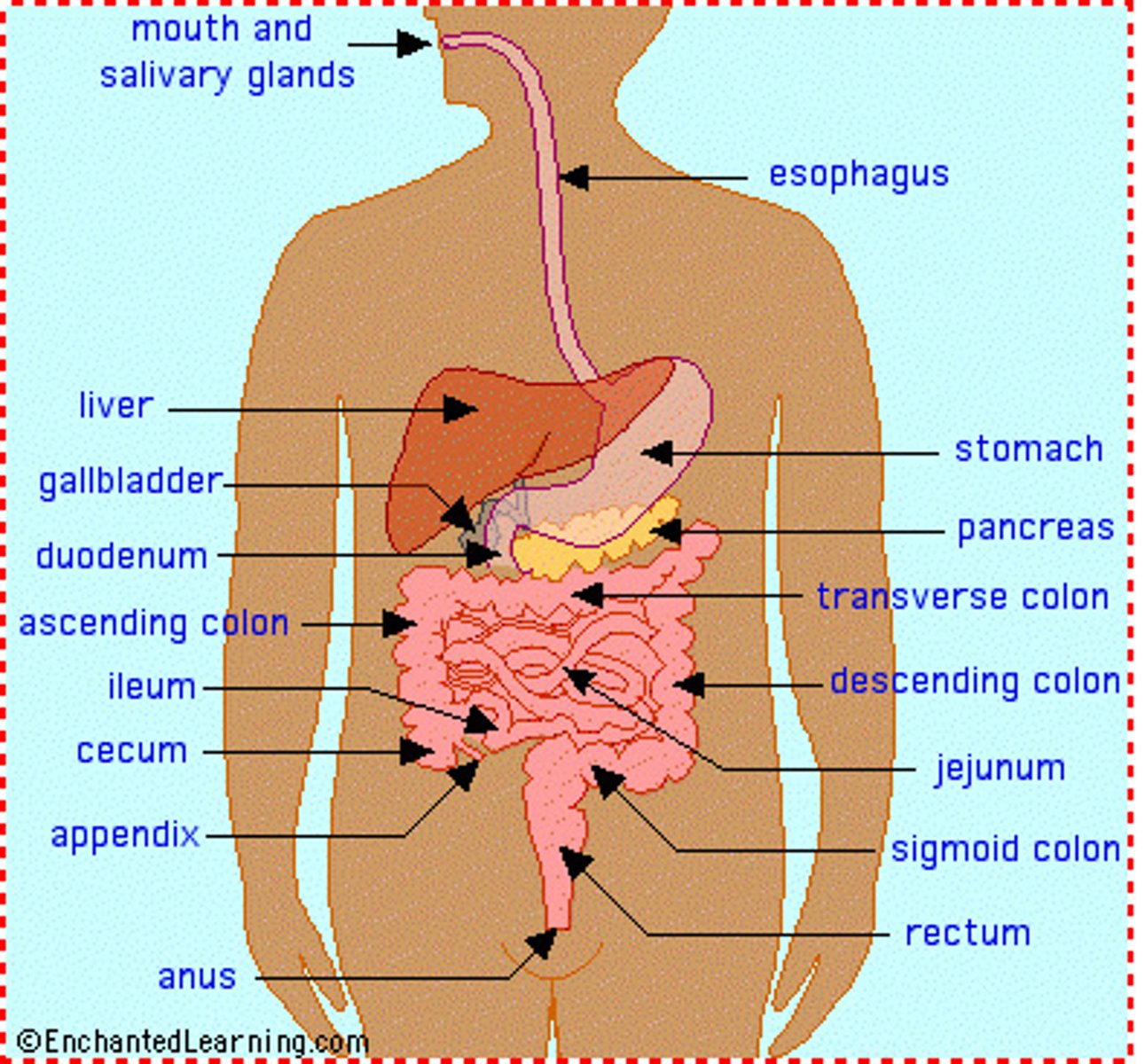
Digestive System
Composed of the alimentary canal and accessory structures. Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, and ileum), large intestine (colon), and anus, Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter the blood for distribution to body cells.
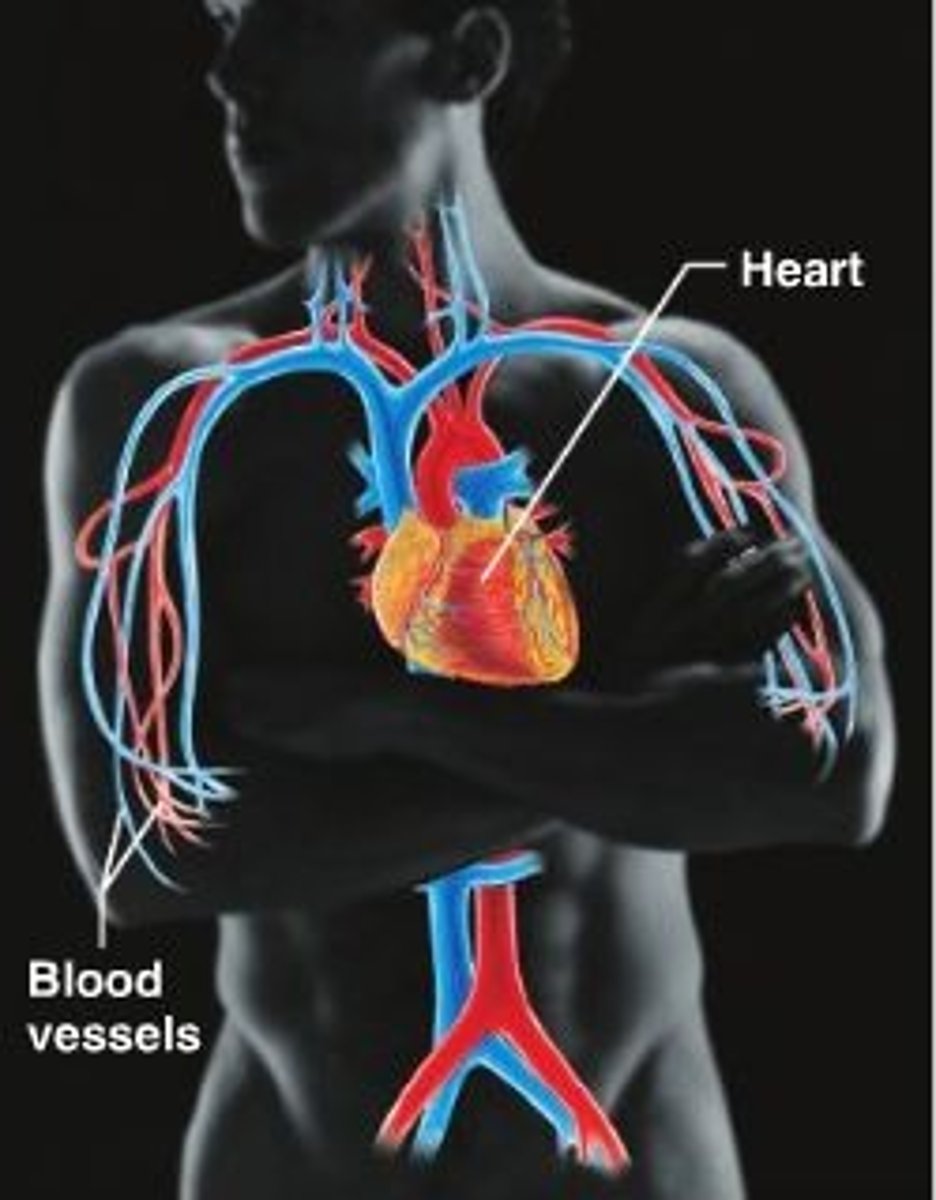
Circulatory System
(aka cardiovascular system) This system works as the transportation highway for the body. It consists of the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It transports substances such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, and nutrients in the body.
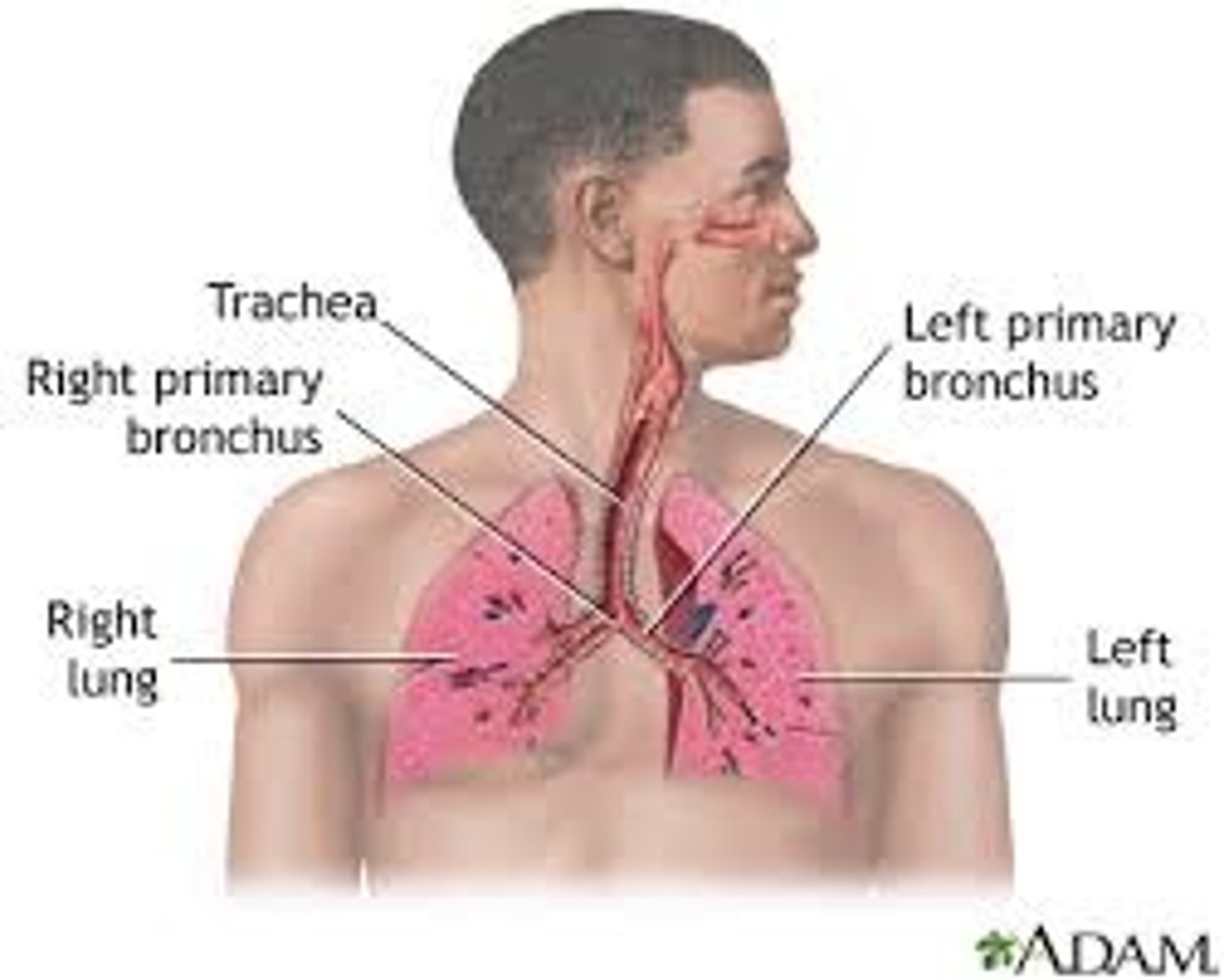
Respiratory System
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
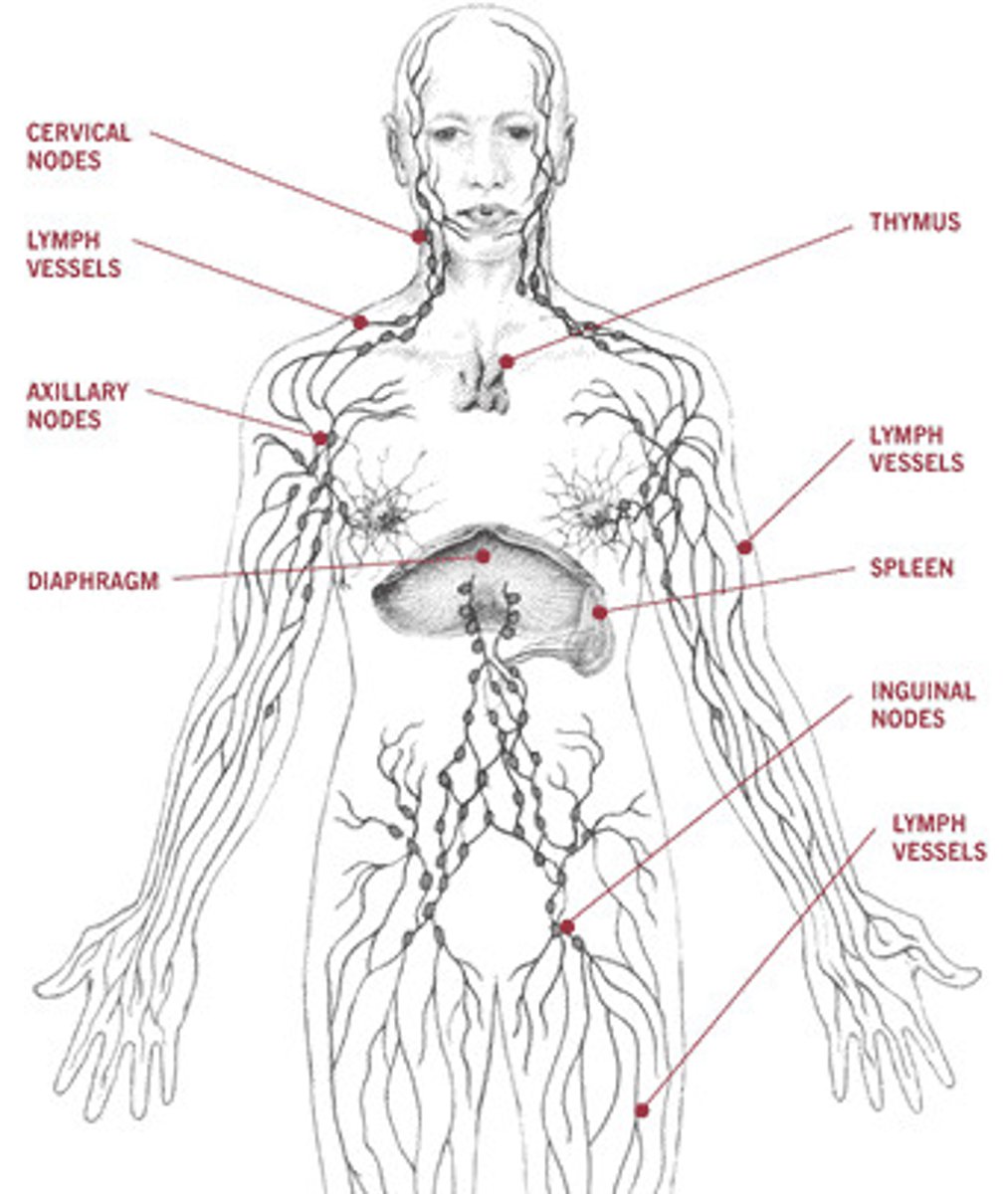
Lymphatic / immune System
Composed of red bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels; picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to the blood; Involved with immunity; Without the system, the body would swell as fluid becomes trapped in your tissues. Protects the body from foreign substances and pathogenic organisms by producing the immune response
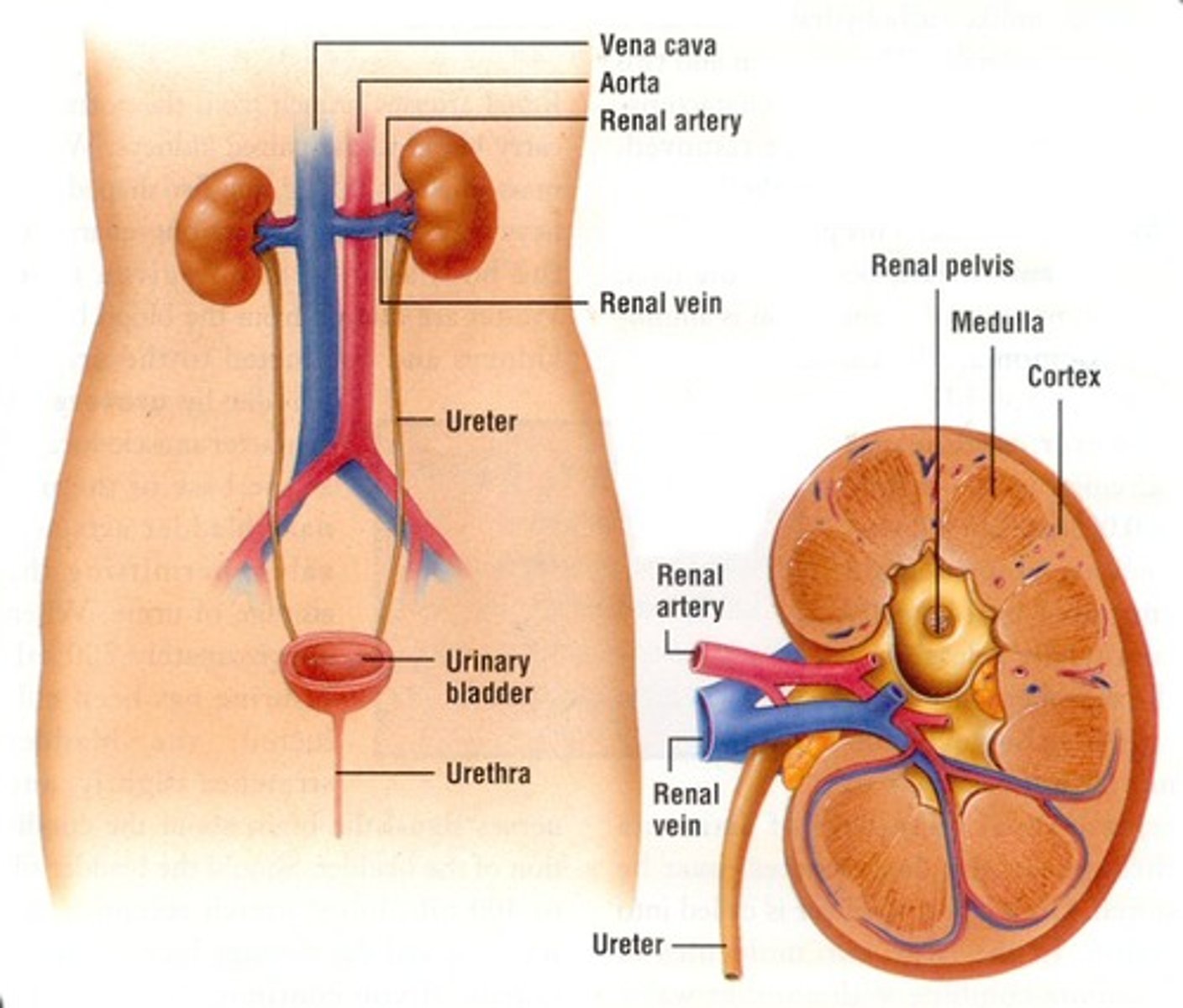
Excretory System
Group of organs that purify the body by the elimination of waste matter
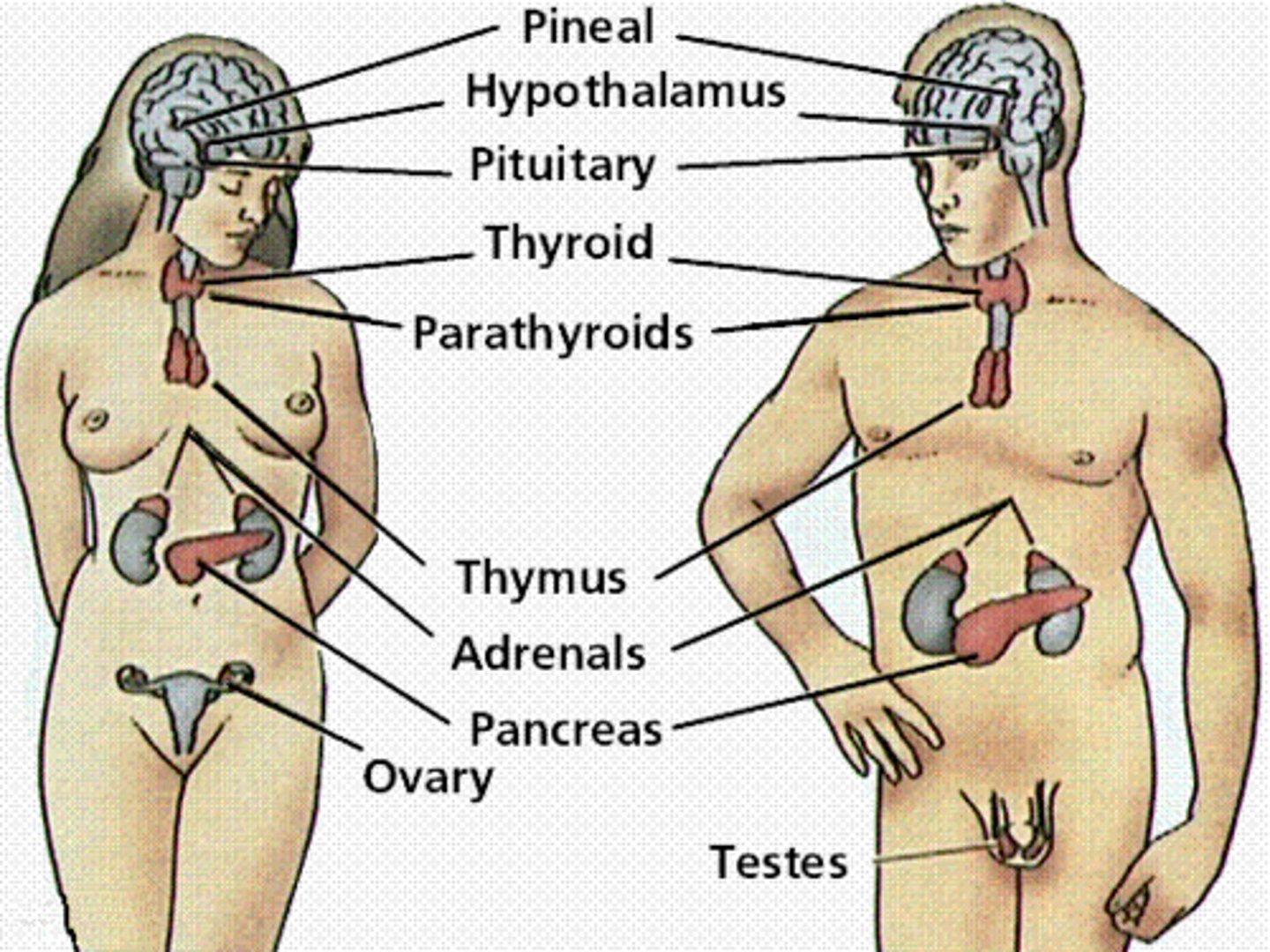
Endocrine System
The body's "slow" chemical communication system; The glands and parts of glands that produce endocrine secretions, help to integrate and control bodily metabolic activity, and include especially the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, islets of Langerhans, ovaries, and testes.
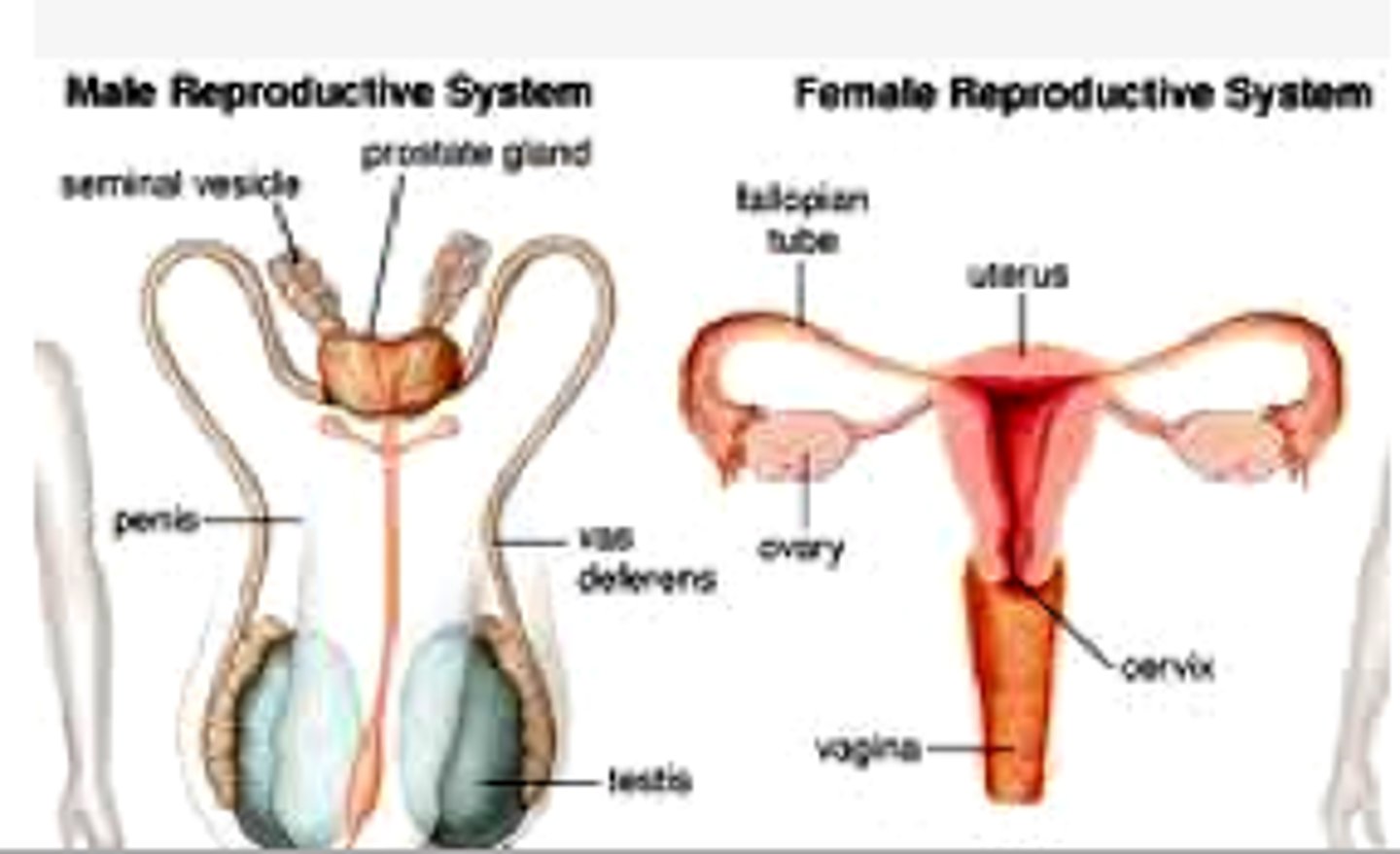
Reproductive System
organ system responsible for producing, storing, and delivering gametes
Nervous System
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems.

Integumentary system
Consists of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, and nail, largest organ of the human body.
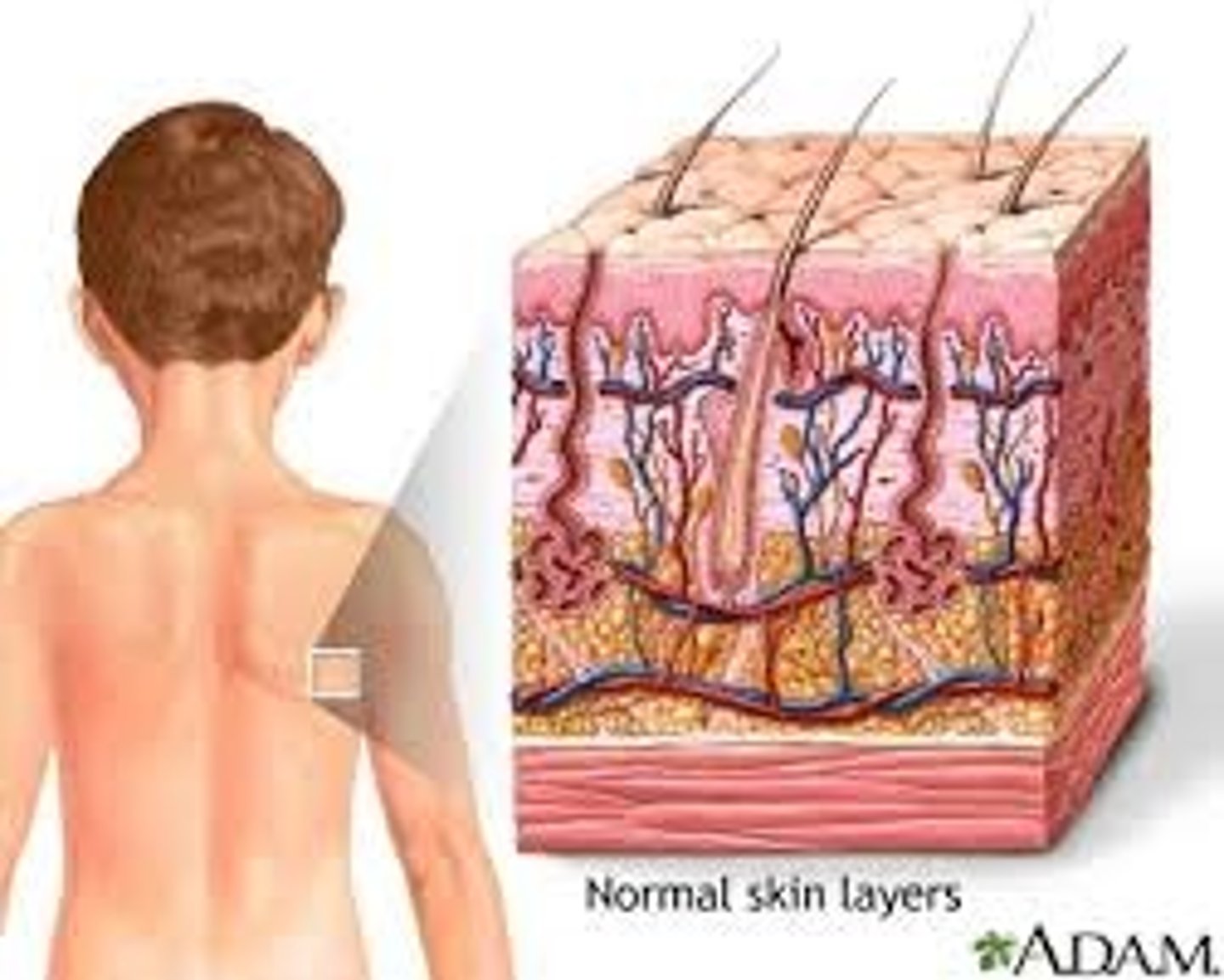
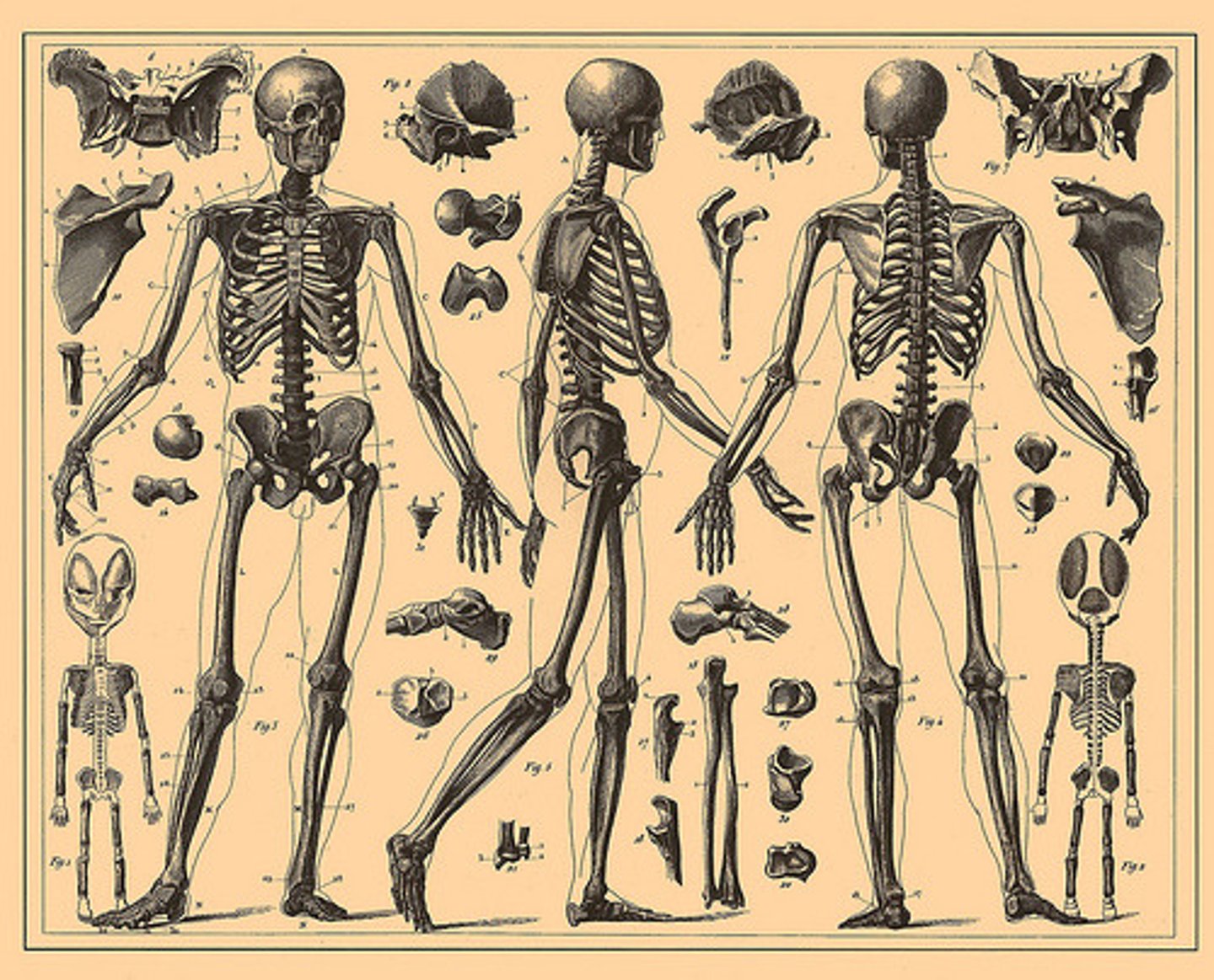
Skeletal System
Creates framework of the body, protects internal organs, produces blood cells, acts as levers for muscles. Ex: bones and cartilage, provide for organ attachment.
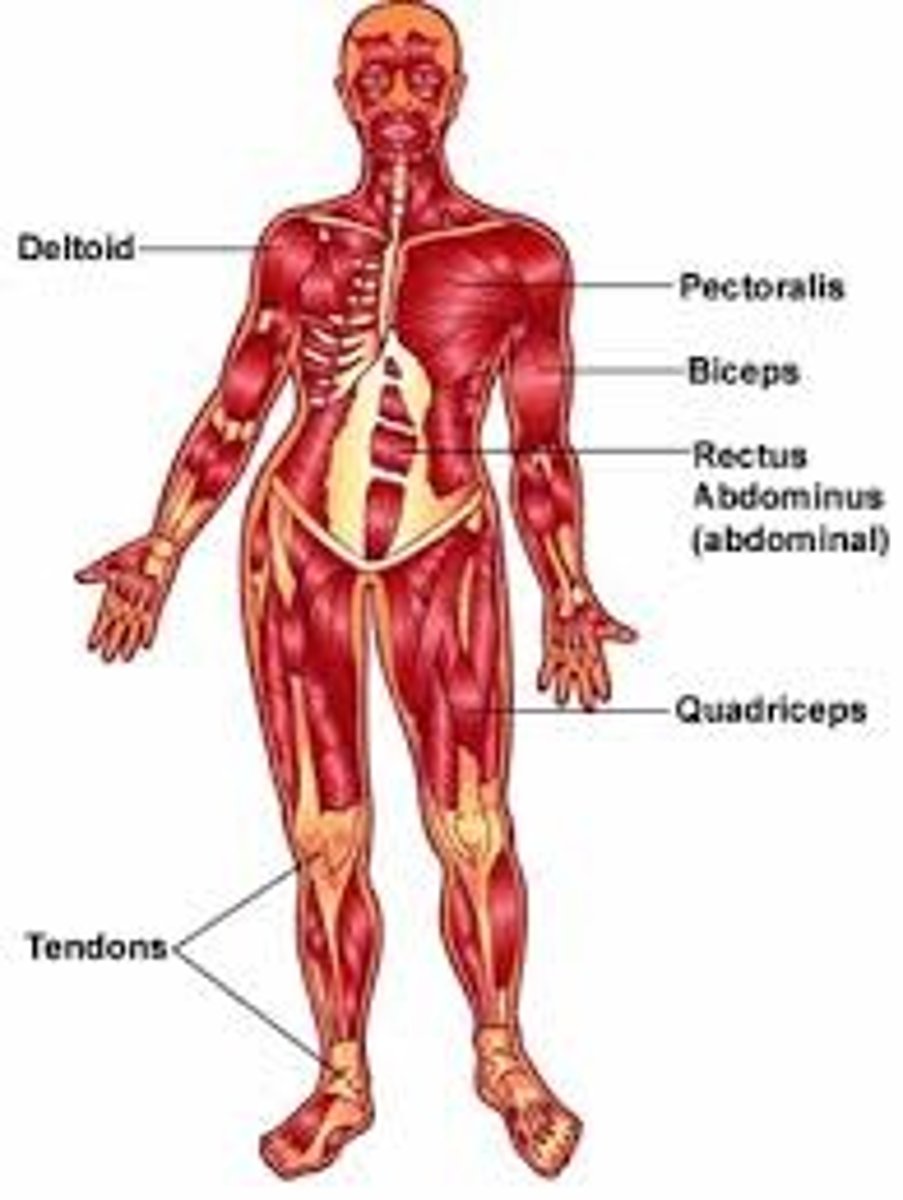
Muscular System
Consists of skeletal muscles, tendons that connect muscles to bones, and ligaments that attach bones together to form joint, enables movement of the body and internal organs
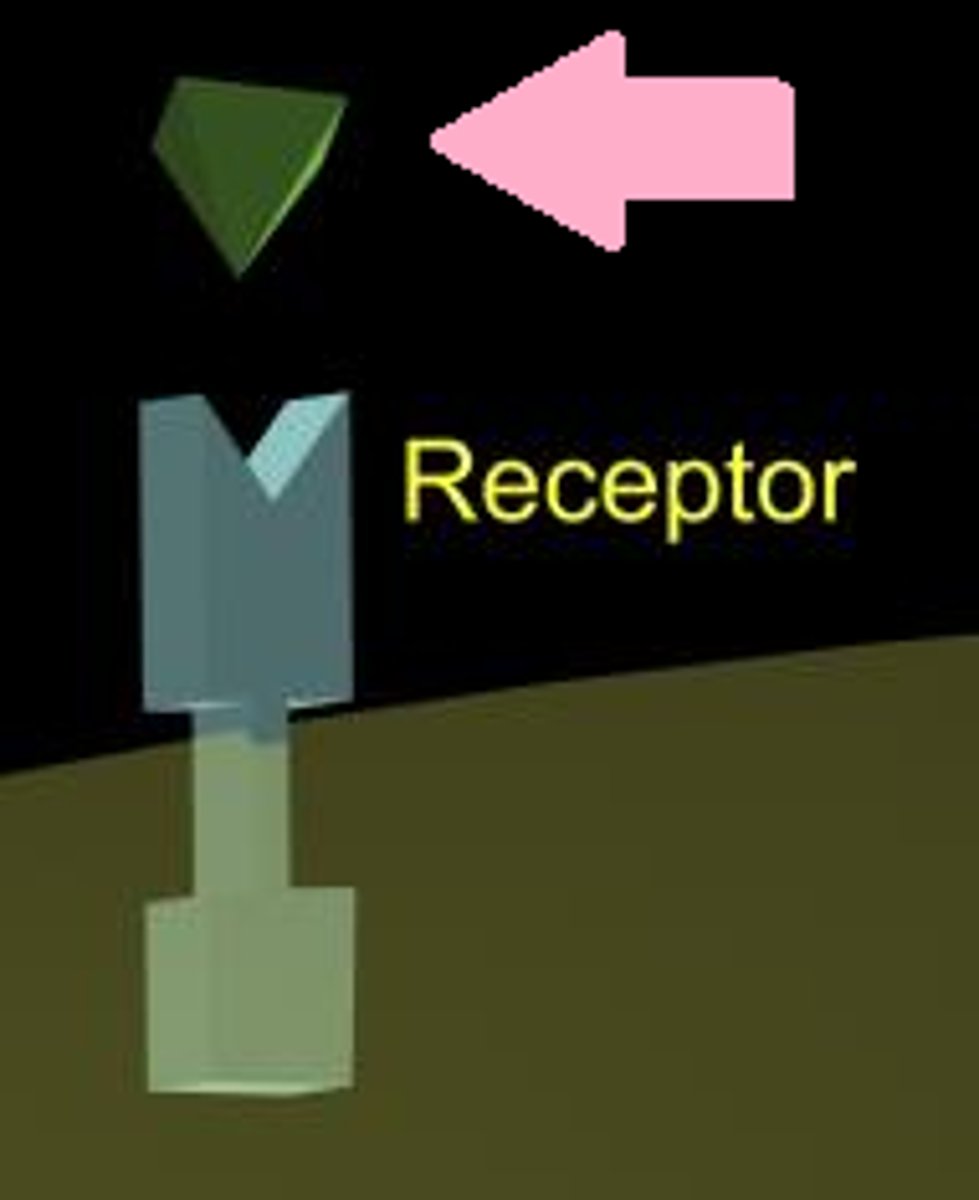
ligand
A molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule.
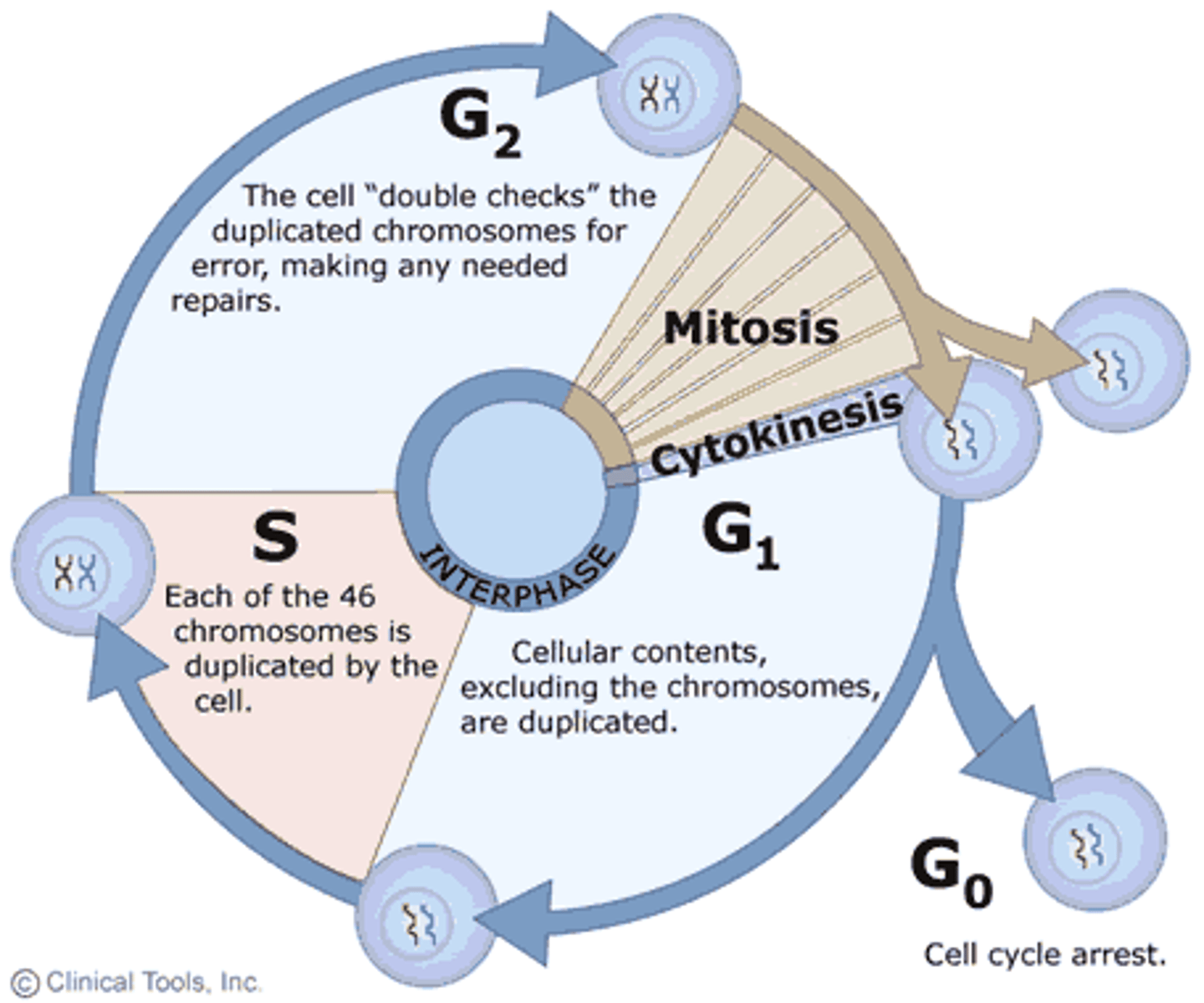
Cell Cycle
The regular sequence of growth and division that cells undergo
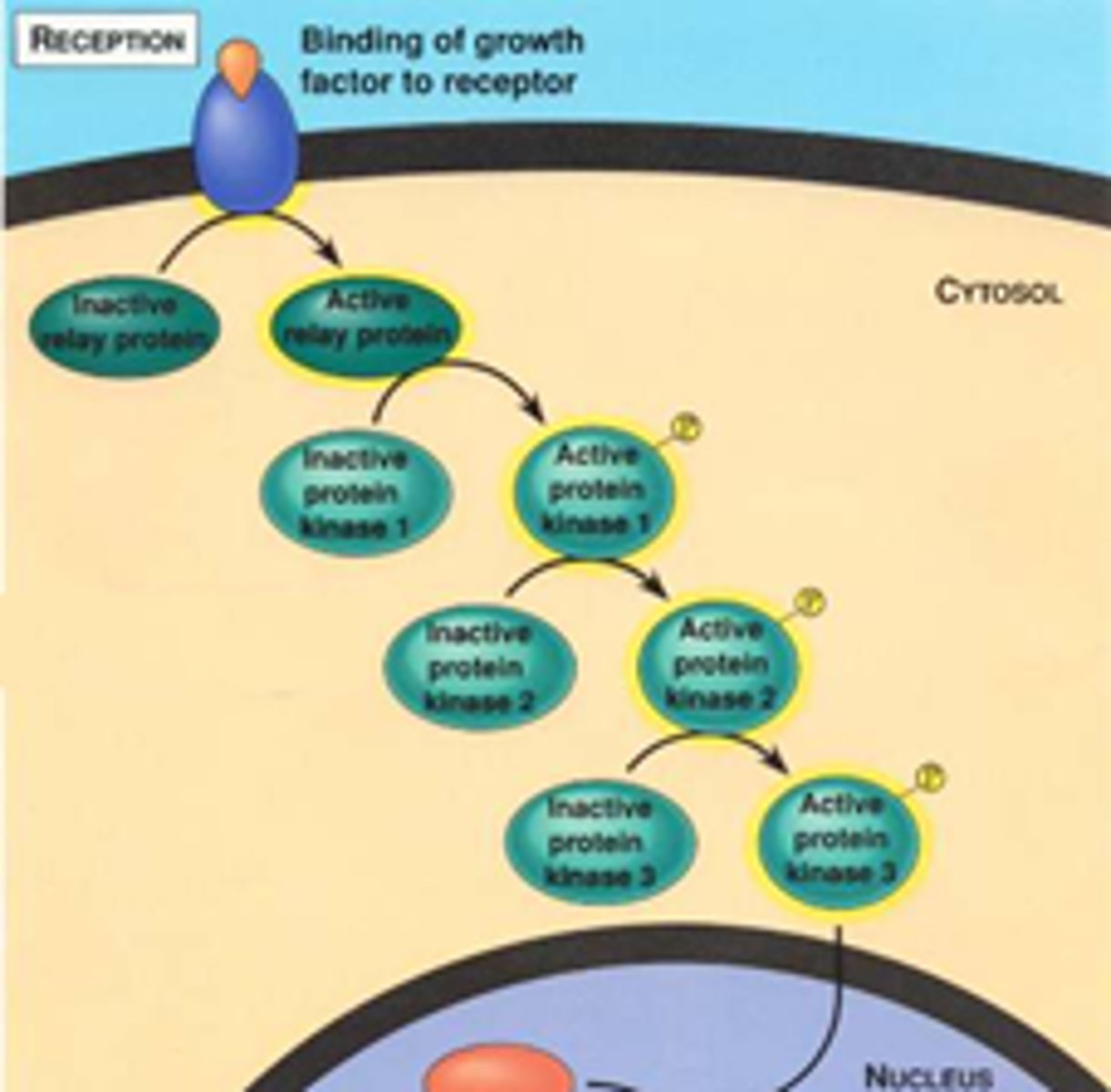
signal transduction pathway
The process by which a signal on a cell's surface is converted into a specific cellular response.
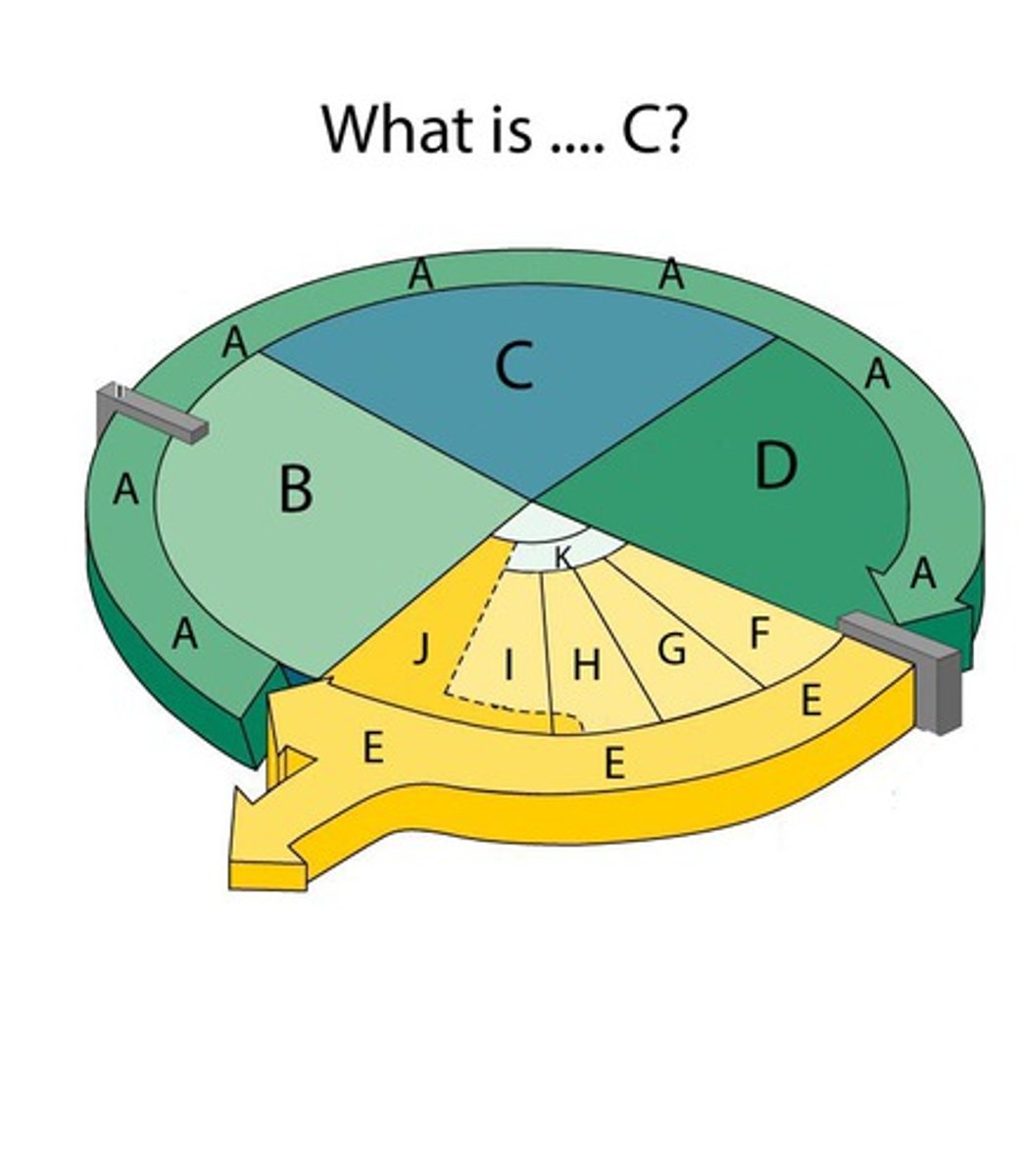
Interphase
Cell grows, performs its normal functions, and prepares for division; consists of G1, S, and G2 phases
local regulators
These regulators influence cells in the vicinity of them.
G1 Phase
stage of interphase in which cell grows and performs its normal functions
hormones
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another
G2 Phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs.
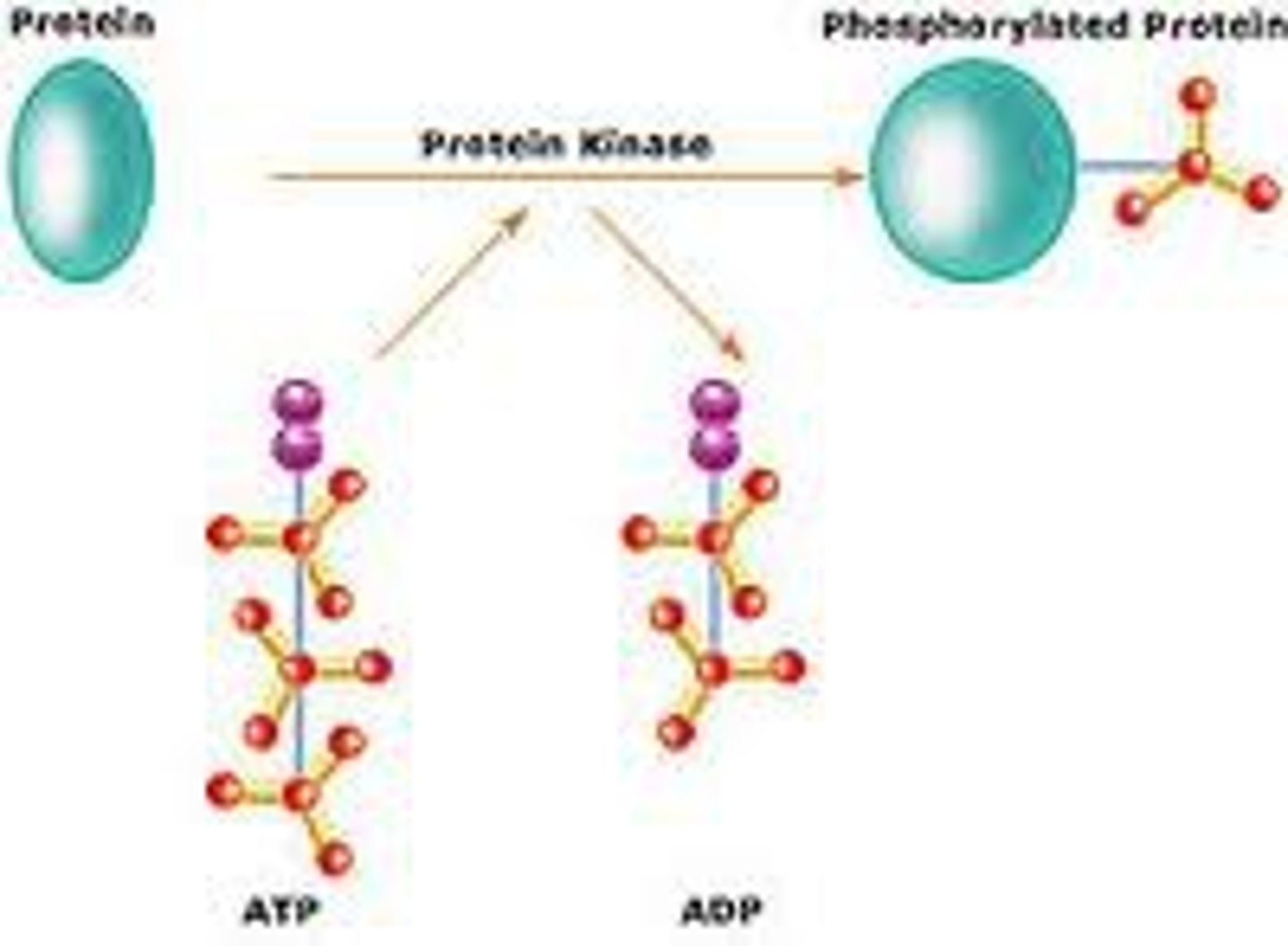
protein kinases
The enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to protein.
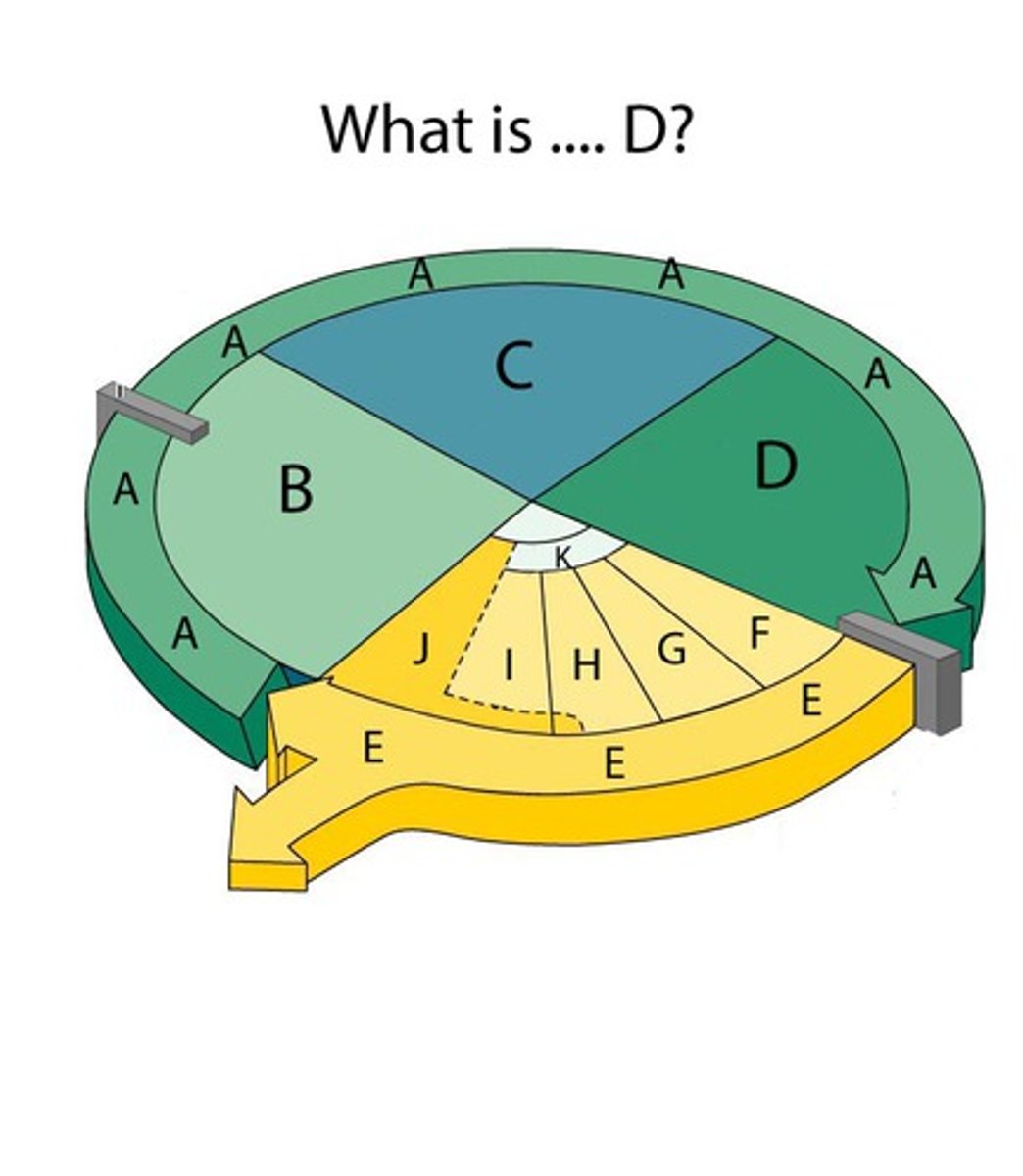
S Phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
second messengers
Small, non-protein water soluble molecules or ions that send messages throughout the cells by diffusion.

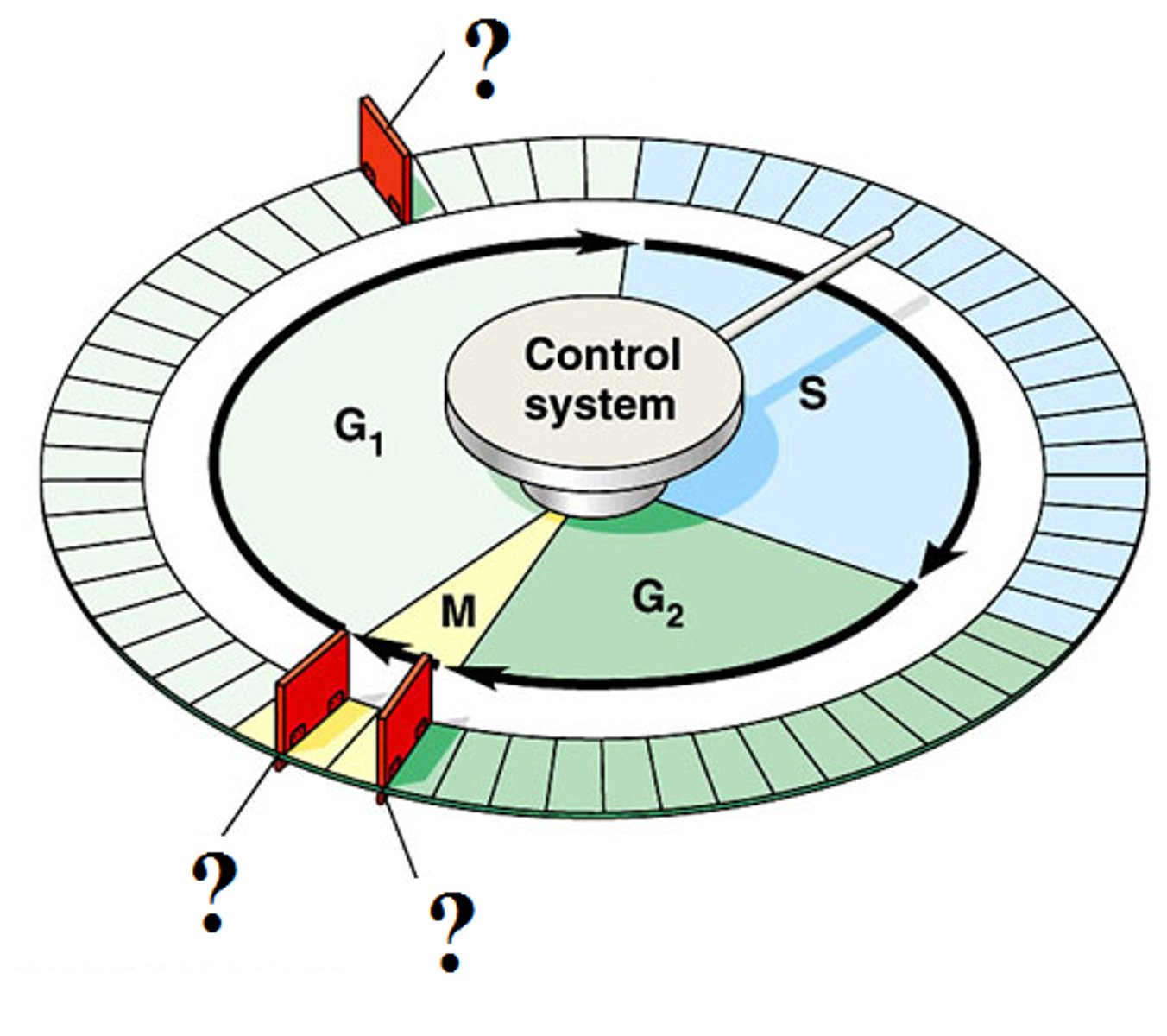
Checkpoint
A critical control point in the cell cycle where stop and go-ahead signals can regulate the cycle.
Mitosis
A nuclear division resulting in the production of two somatic cells having the same genetic complement as the original cell.
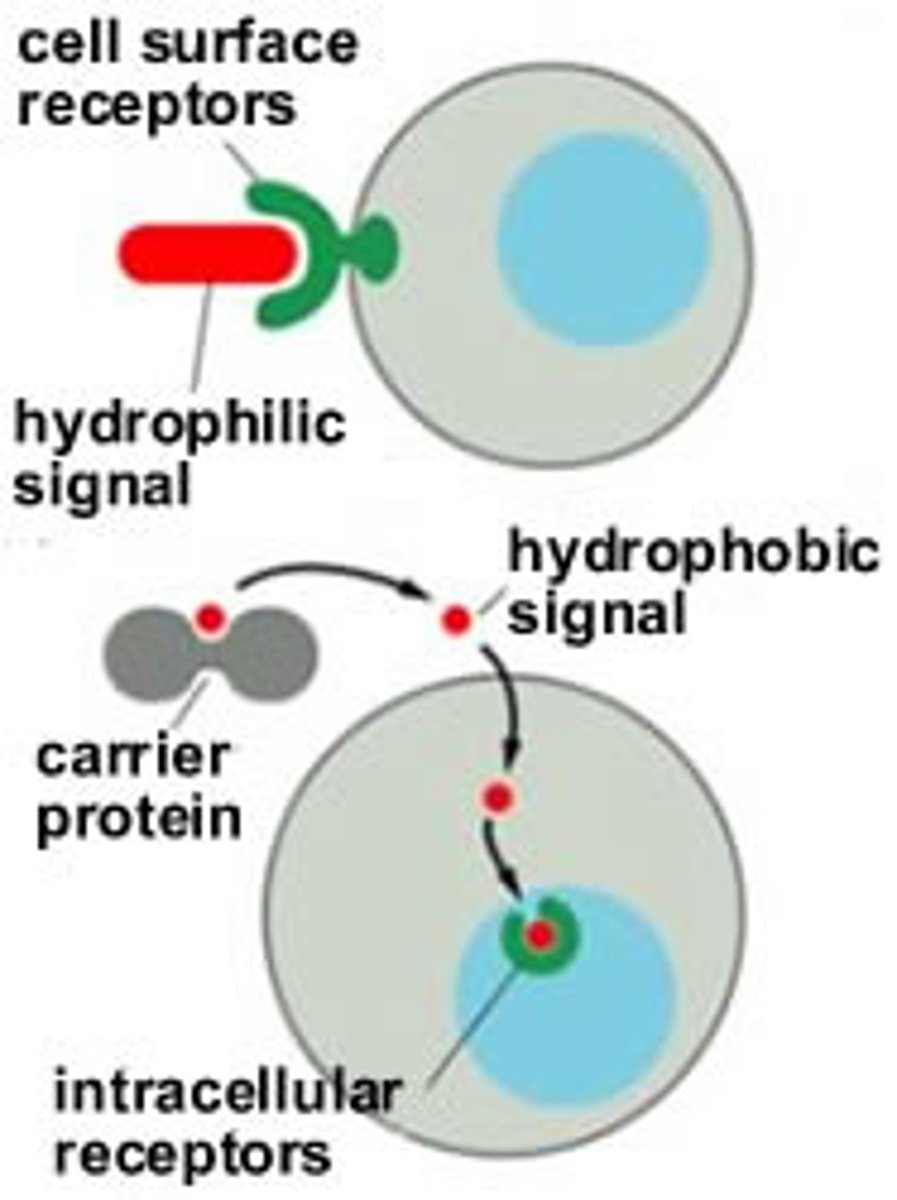
hydrophobic ligands
signaling molecules that can cross plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors in cytoplasm
Cytokinesis
Process by which the cell cytoplasm divides
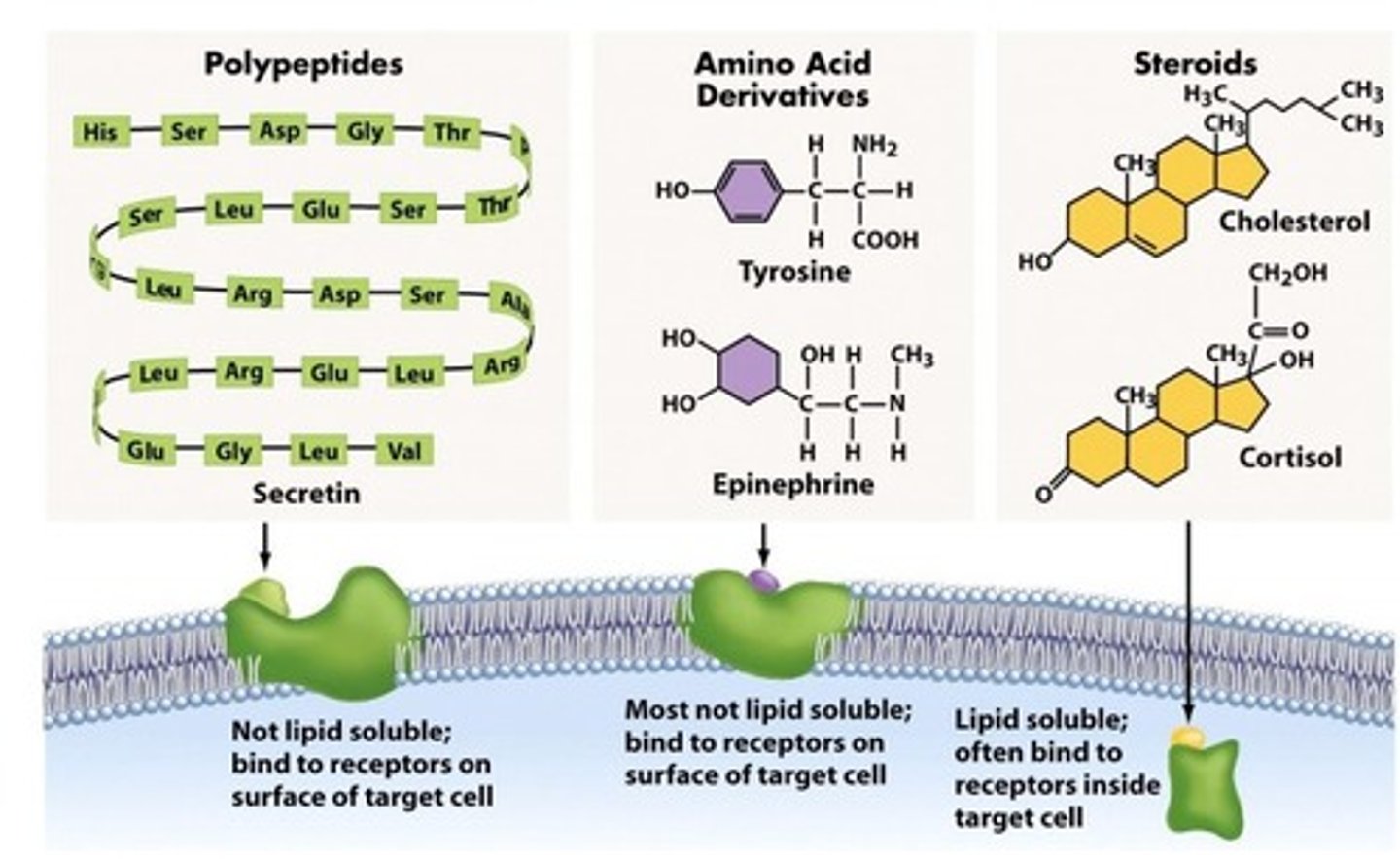
hydrophilic ligands
signaling molecules that cannot cross plasma membrane and bind to membrane receptors
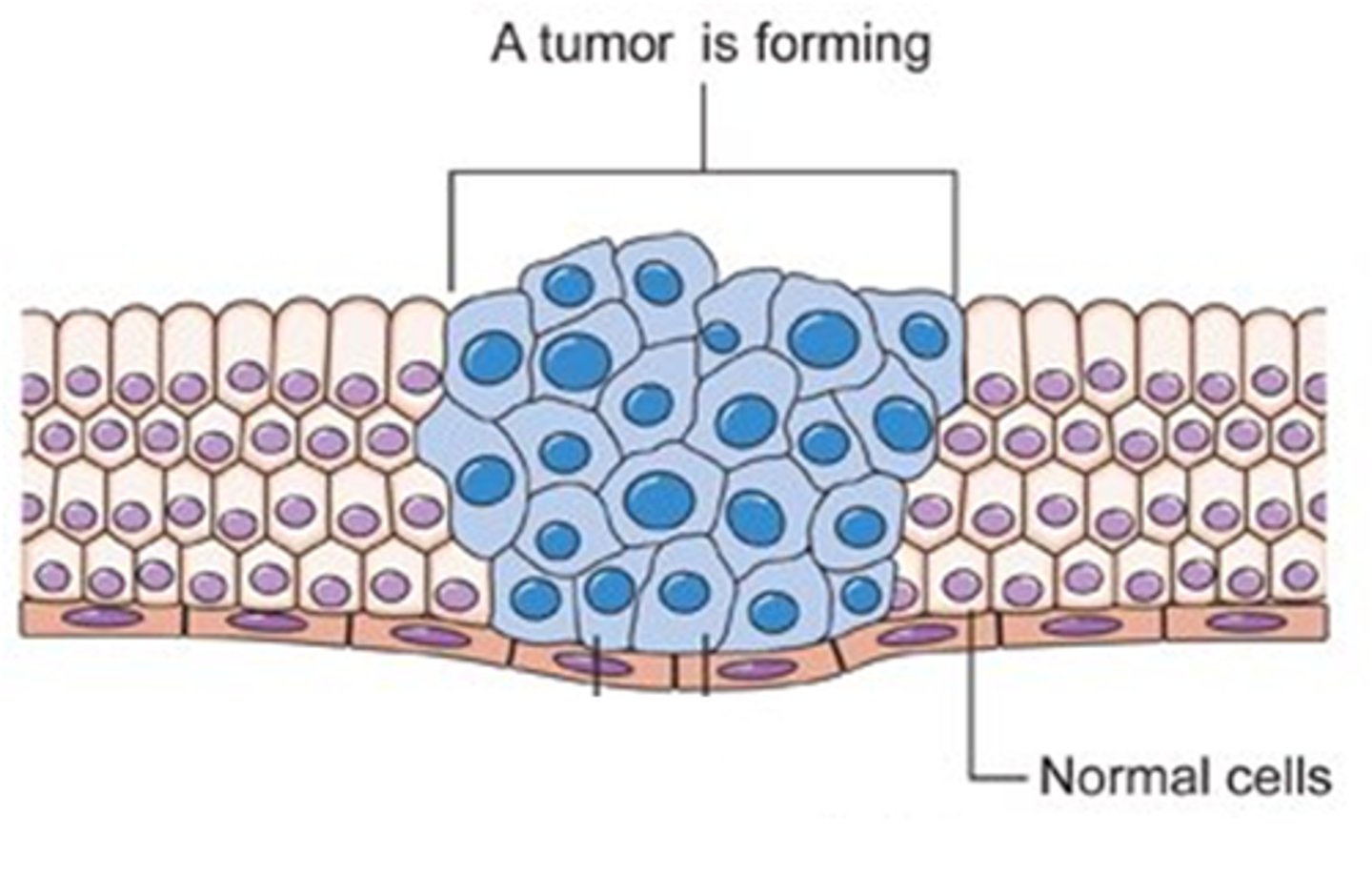
Cancer
A disease in which some body cells grow and divide uncontrollably, damaging the parts of the body around them.
receptor proteins
proteins in the plasma membrane that are sensitive to the presence of specific extracellular molecules called ligands
Tumor Suppressor Protein
have a damping or repressive effect on the regulation of the cell cycle
quorum sensing
The ability of bacteria to sense the presence of other bacteria via secreted chemical signals.
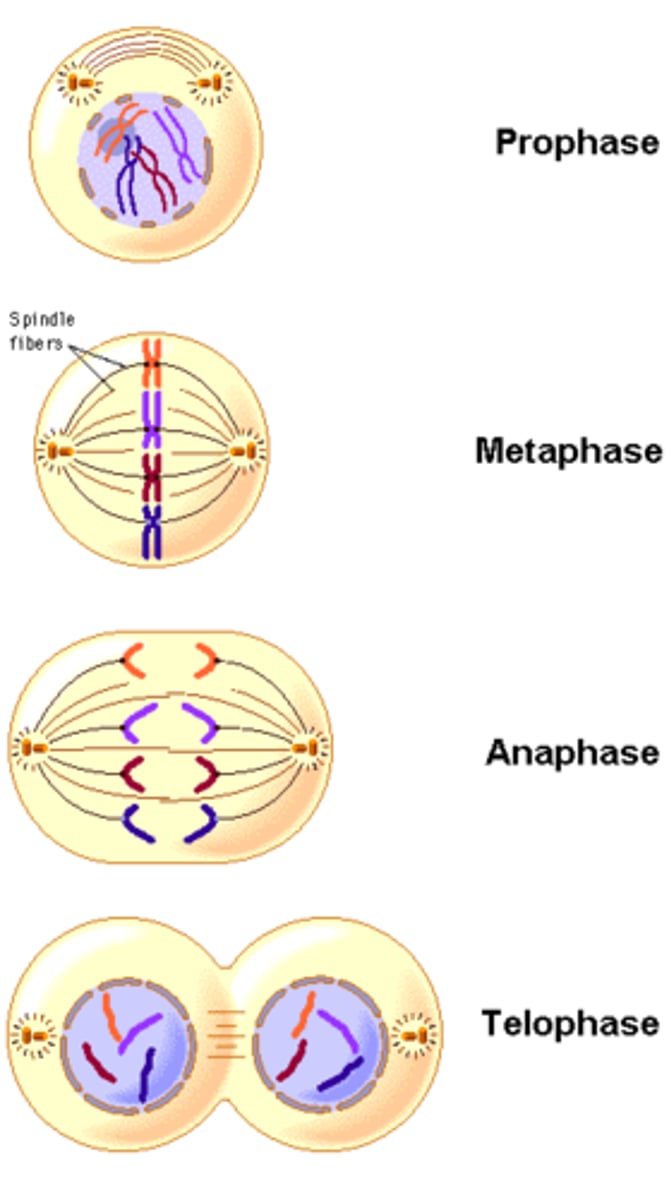
Prophase
Chromatin condenses,
chromosomes become visable, nuclear envelop dissolves, spindle forms

autocrine signaling
the target cell is also the secreting cell
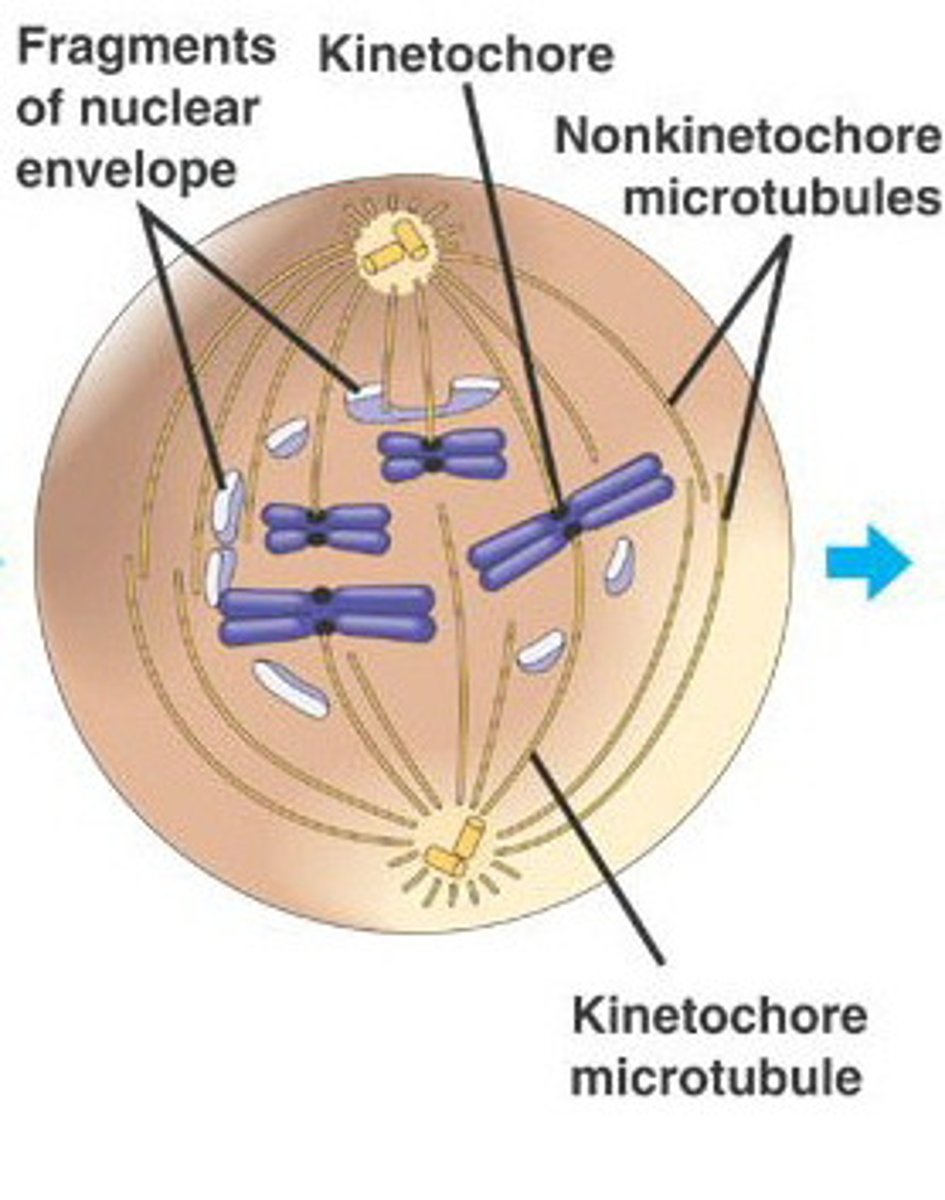
Prometaphase
The second stage of mitosis, in which discrete chromosomes consisting of identical sister chromatids appear, the spindle microtubules attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes
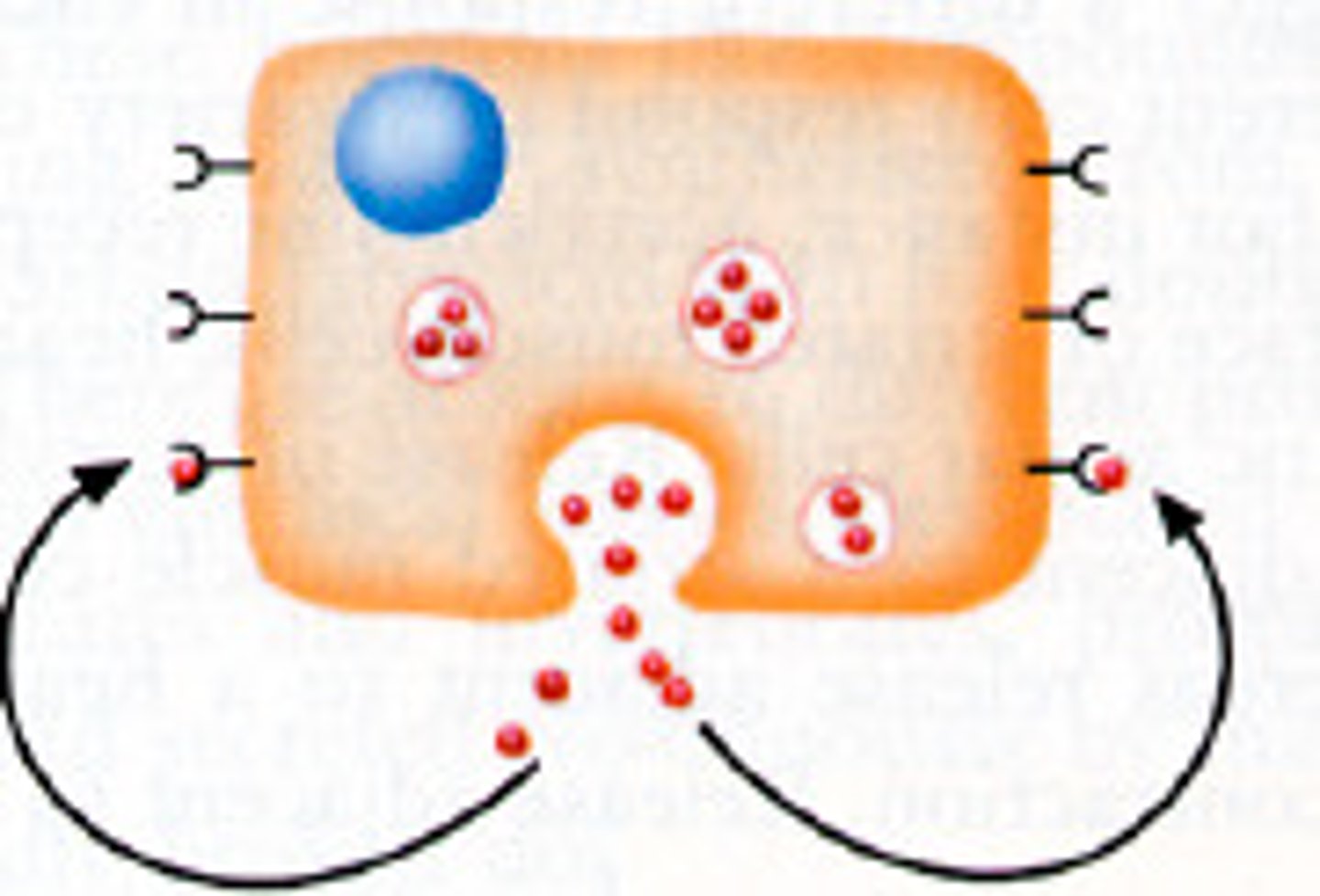
paracrine signaling
the target cells lie near the secreting cells
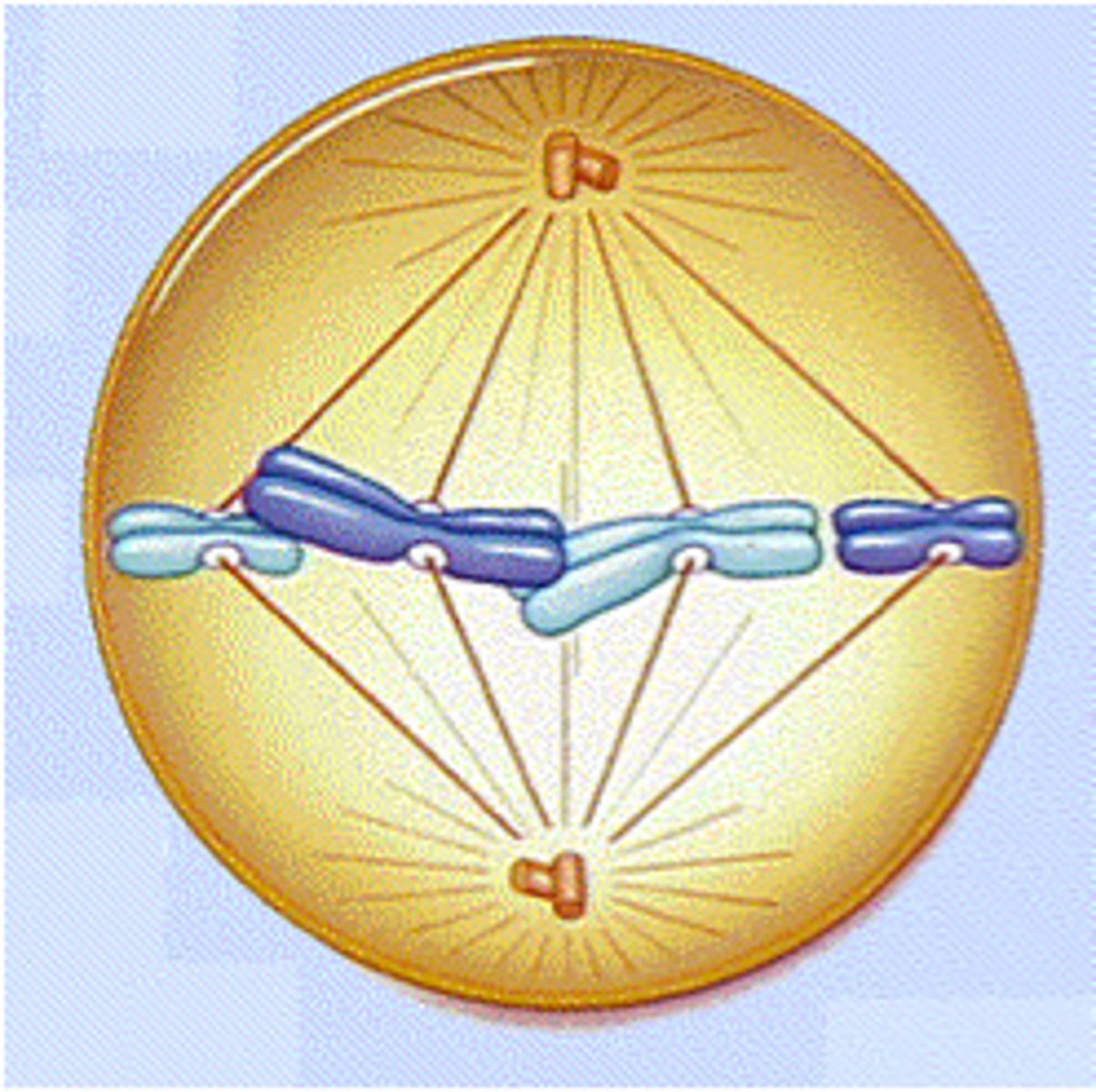
Metaphase
Centromeres of duplicated chromosomes are aligned at plate. Fully formed spindle attach to the sister chromatids from opposite poles
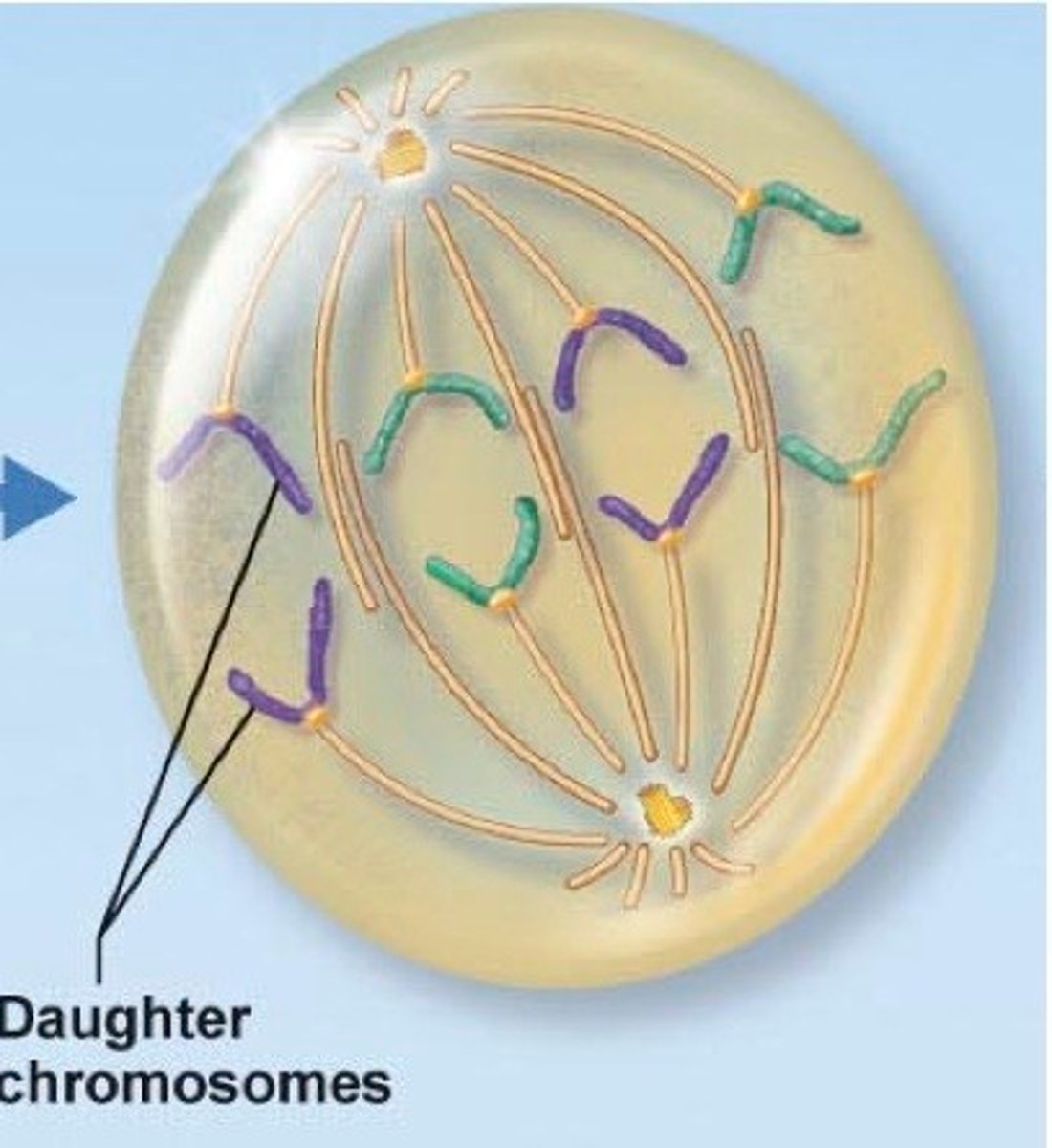
Anaphase
Phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell
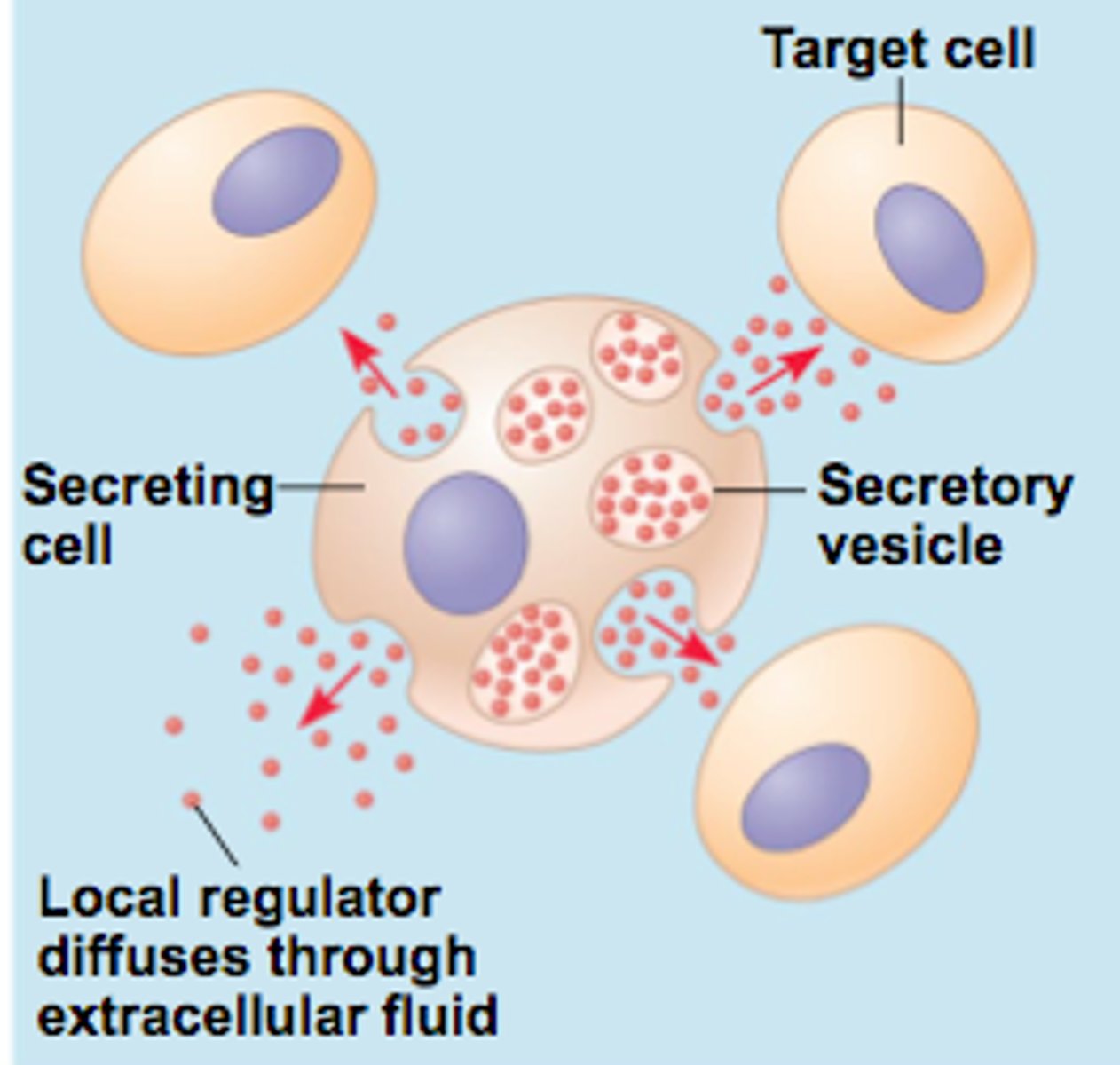
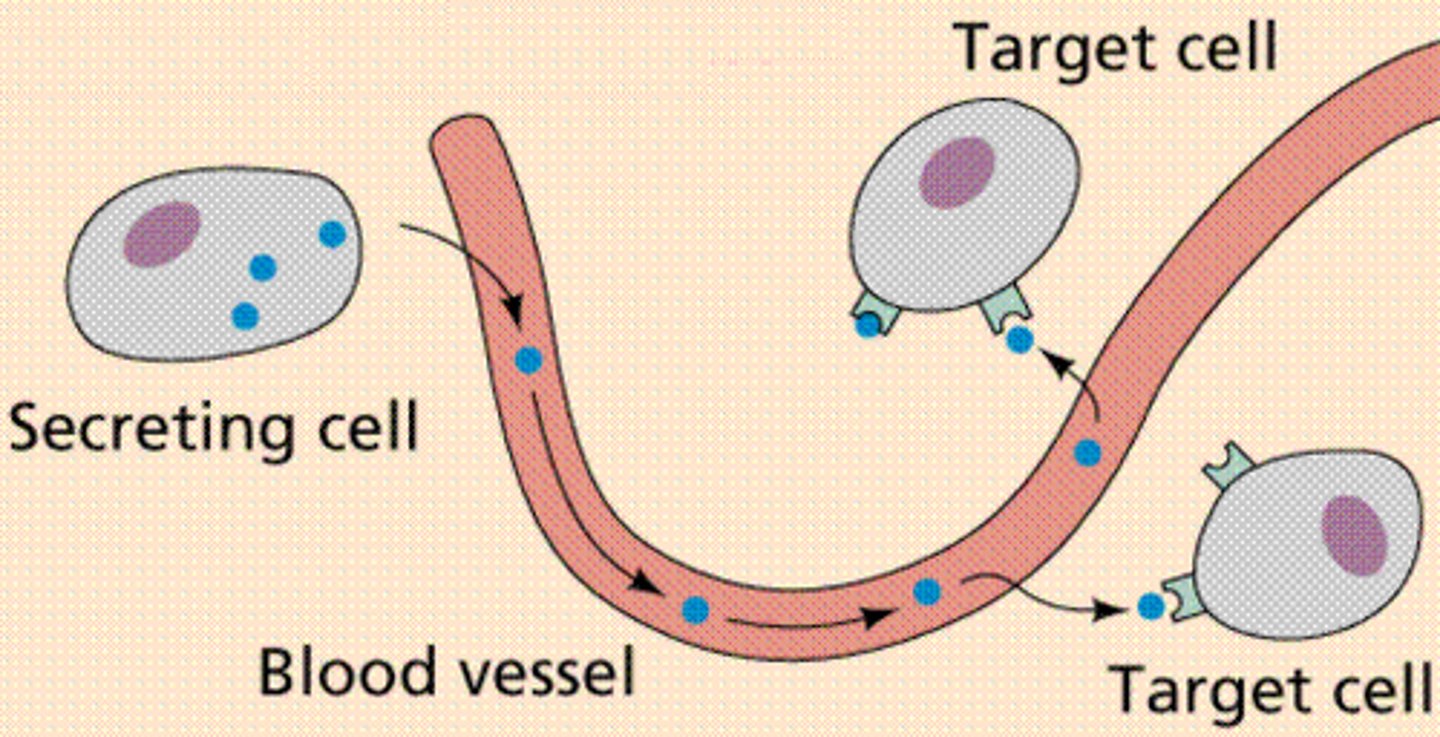
endocrine signaling
secreted molecules diffuse into the bloodstream and trigger responses in target cells anywhere in the body
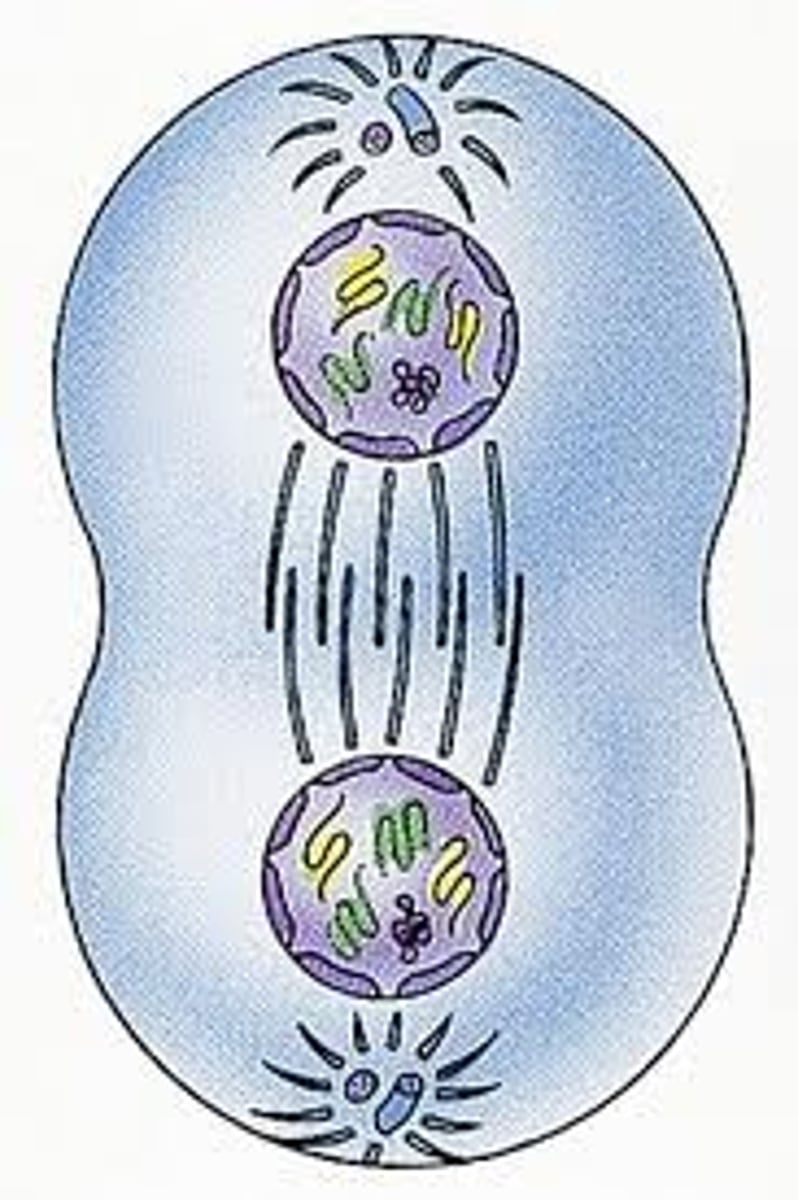
Telophase
Final phase of mitosis during which chromosomes uncoil, a nuclear envelope returns around the chromatin, and a nucleolus becomes visible in each daughter cell
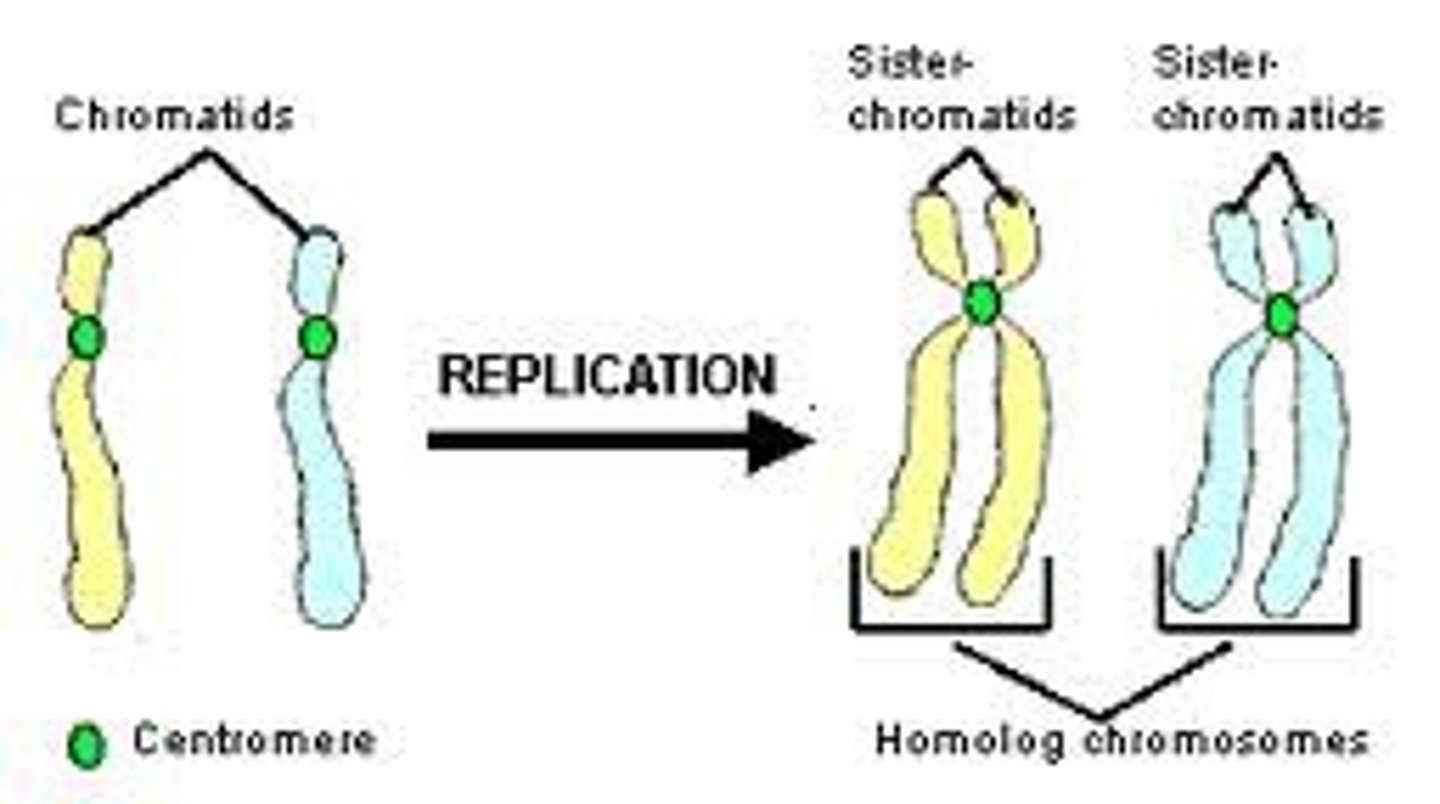
Sister Chromatids
Replicated forms of a chromosome joined together by the centromere and eventually separated during mitosis or meiosis II.
Spindle Fibers
Made of microtubules that connect centrioles to kinetochores of chromosomes and that separate sister (mitosis) or homologous (meiosis) chromosomes during cell division
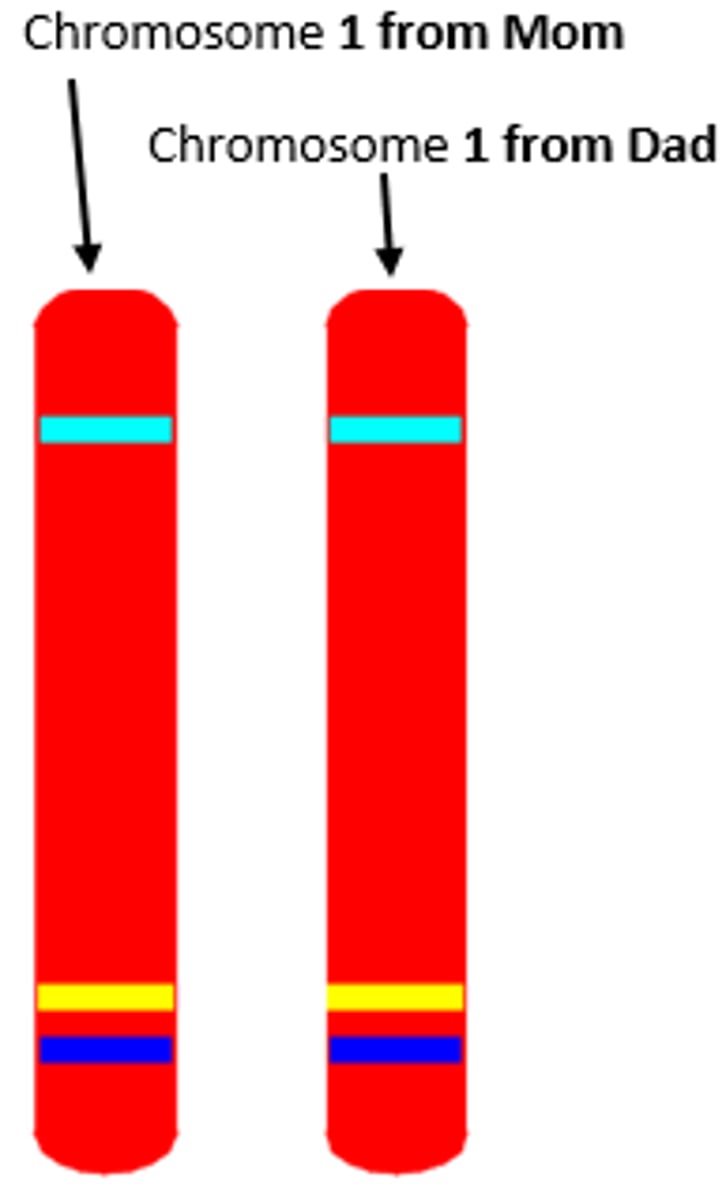
Homologous Chromosome
Chromosomes that are similar in size, shape, and genetic content
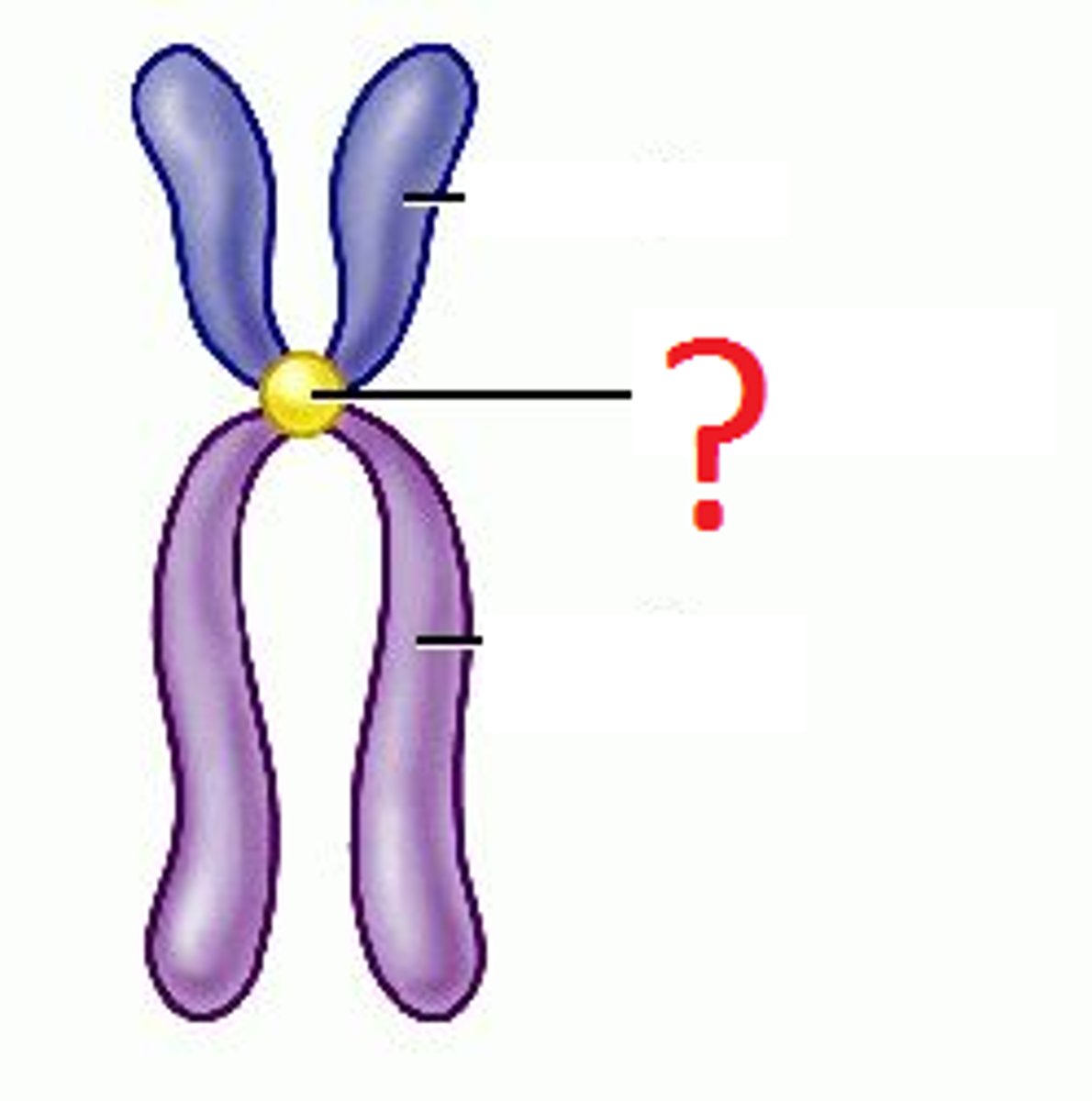
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
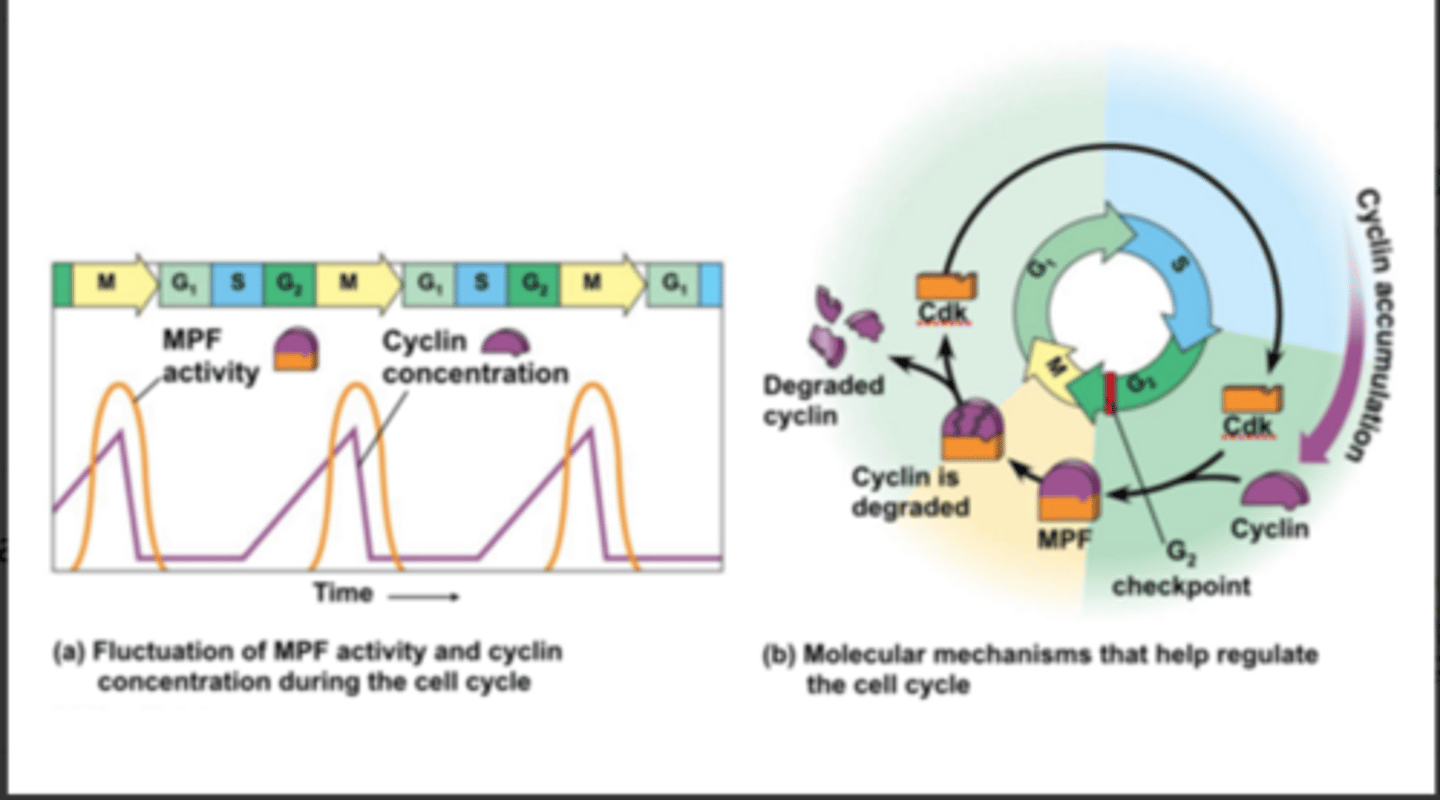
Cdk
A key protein in the control of the cell cycle; combines with cyclin.

Cyclin
A cellular protein that occurs in a cyclically fluctuating concentration and that plays an important role in regulating the cell cycle. Will bind to Cdk forming MPF

MPF
A cyclin-Cdk complex that triggers the cell's passage past the G2 checkpoint into mitosis?
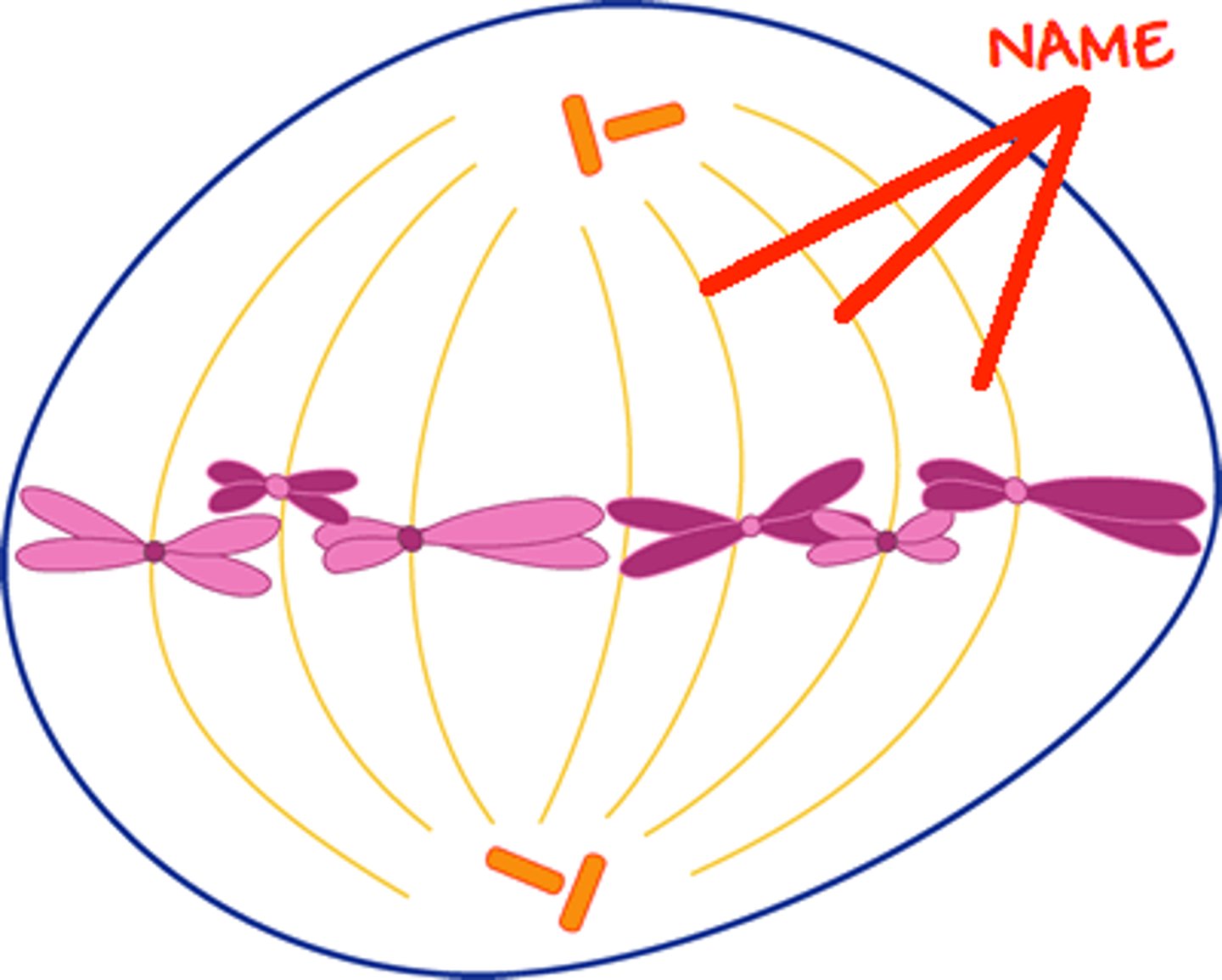
Diploid
A cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes, (homologous chromosomes) one from each parent.
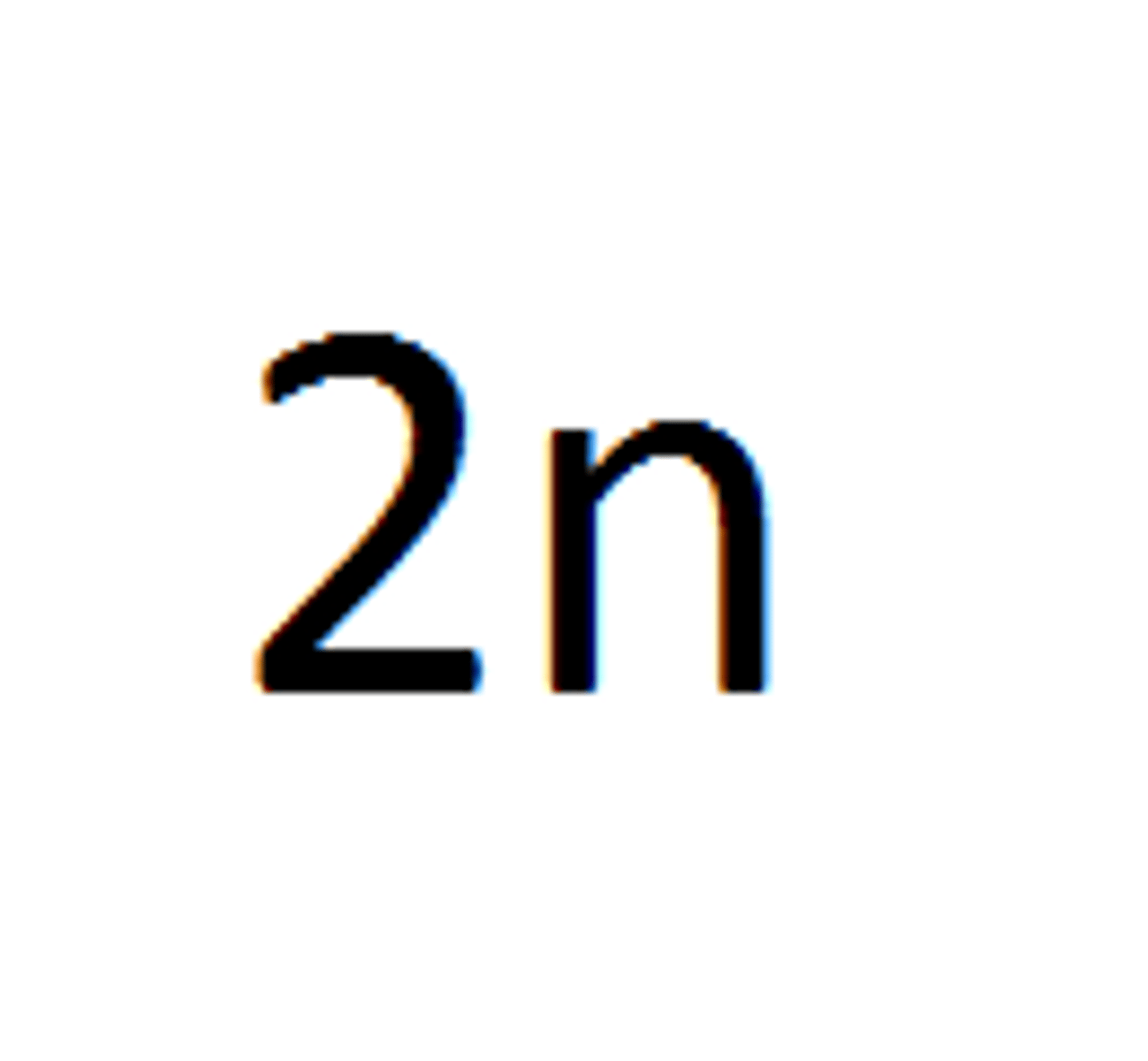
Centrioles
a minute cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
Chromatin
DNA and protein that makes up chromosomes