5 - Regulation of the enzyme activity. Regulation by altering the absolute amount of the enzyme. Regulation by altering the activity of the enzyme – proenzymes, reversible covalent modification, allosteric regulation, etc.
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
sections
regulation of enzyme activity
allosteric enzymes
inhibitors
types of inhibitors
activators of enzyme reactions
regulation of enzyme activity
Metabolic processes are coordinated by:
Allosteric effectors – bind away from the active site to increase or decrease enzyme activity.
Covalent modification – chemical groups (e.g., phosphate) are added/removed to switch enzymes on or off.
allosteric enzymes
regulated by effectors that covalently binds to areas other than the active site
can alter affinity of enzyme to substrate
2 types:
- ve effectors inhibit
+ ve effectors increases enzyme activity
inhibitors
Enzyme Inhibition Summary:
Irreversible Inhibitors:
Cause covalent modification of the enzyme
Decrease active enzyme concentration → ↓ ES complex
Often toxic or poisonous
Effects not easily reversed
Reversible Inhibitors:
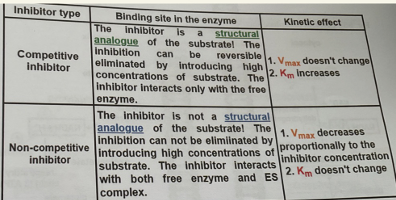
Competitive: Bind active site, compete with substrate, reversible by adding substrate
Non-competitive: Bind elsewhere, not reversed by substrate, ↓ Vmax, Km unchanged
Uncompetitive: Bind only to ES complex, ↓ both Vmax and Km
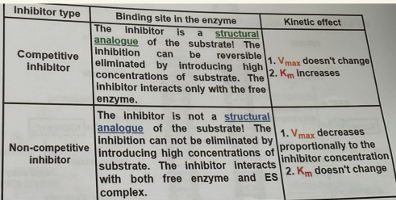
types of inhibitors
activators of enzyme reactions
Fe 2+
Mg 2+→ kinases
Anions → Cl- → salivary amylase activator