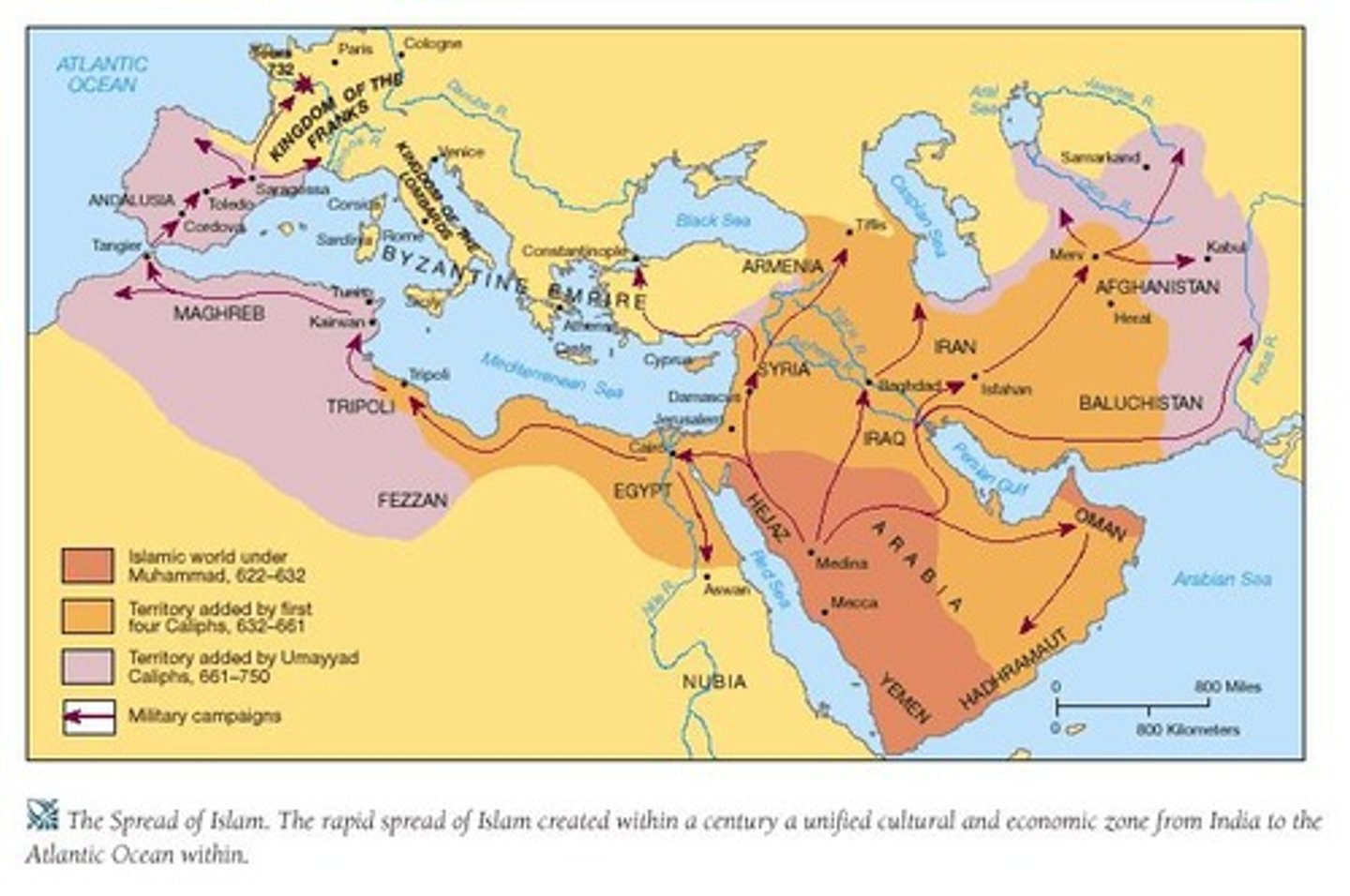
The Spread of Islam and Its Historical Impact
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Muhammad
Prophet and founder of Islam, died in 632.
Abu Bakr
First caliph elected after Muhammad's death.
Caliphate
Islamic dynasty ruling over Muslim territories.
Sunni
Branch of Islam believing in elected caliphs.
Shi'a
Branch of Islam believing in Ali's descendants as leaders.
Imam
Religious leader in Shi'a Islam interpreting the Qur'an.
Sufi
Mystical Islamic group seeking personal connection with God.
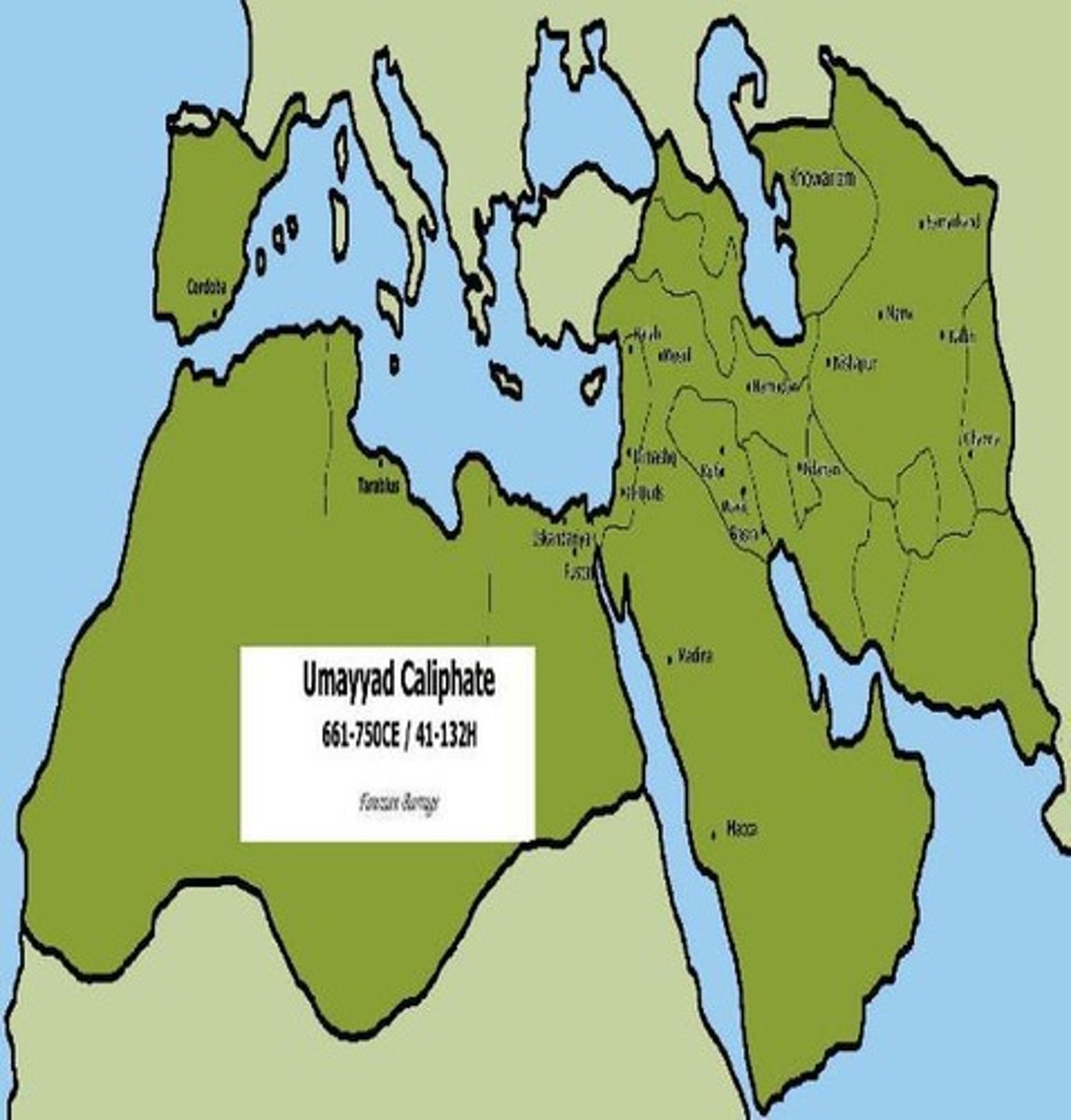
Umayyad Caliphate
Caliphate from 680 to 750, expanded Islamic territory.
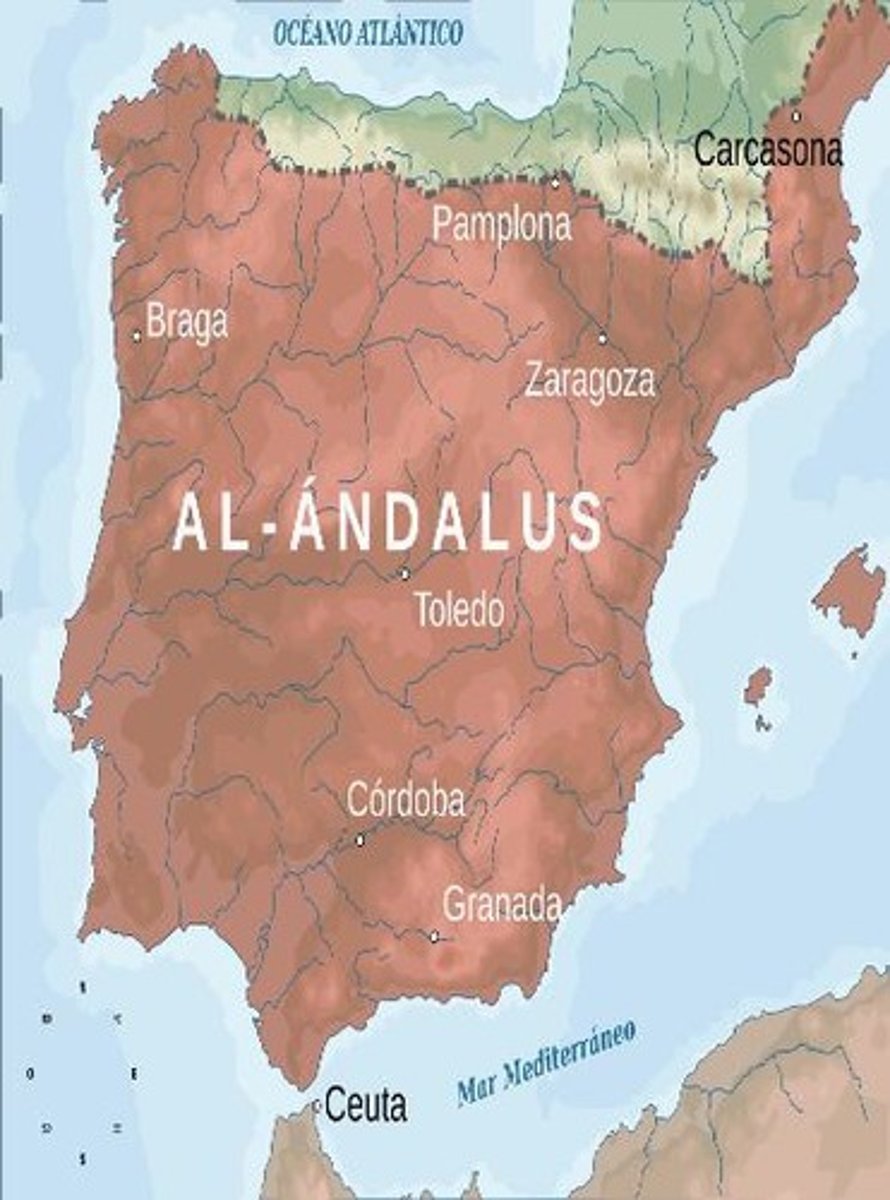
Al-Andalus
Muslim state in Spain, capital Córdoba.
Great Mosque of Damascus
Significant architectural achievement of the Umayyad Caliphate.
Dome of the Rock
Islamic shrine in Jerusalem, built by Umayyads.
Golden Age of Islam
Period of cultural, scientific, and economic flourishing.
Baghdad
Capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, central trade hub.
Checks
Banking innovation during the Abbasid Caliphate.
Córdoba
Cultural center of Al-Andalus, known for architecture.
Alhambra
Famous hilltop fortress in Granada, Spain.
Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
Rivers crucial for Baghdad's trade and defense.
Cultural Tolerance
Coexistence of multiple faiths in medieval Spain.
Haggadah
Jewish text for Passover rituals.
Public Works
Infrastructure projects enhancing urban living in Baghdad.
2 million residents
Estimated population of Baghdad at its medieval height.
University of Al Karaouine
Oldest existing degree-granting university, founded 859 CE.
Fatima Muhammad Al-Fihri
Founder of University of Al Karaouine in Morocco.
One Thousand And One Nights
Collection of Middle Eastern folk tales and stories.
Abbasid Decline
Weakening of Abbasid Empire due to internal revolts.
Fatimids
Shia dynasty that established independence in Egypt, 832.
Buyids
Persian dynasty that emerged in the 800s.
Byzantine Empire
Eastern Roman Empire that regained territories in Anatolia.
Turks
Central Asian peoples with diverse religious practices.
Ghazis
Islamic border warriors, often Turks, defending against non-Muslims.
Seljuks
Turkic group that established an empire in Central Asia.
Sultan
Title for Muslim sovereign, recognized by Abbasid caliphs.
Rum Seljuks
Branch of Seljuks that occupied former Byzantine lands.
First Crusade
1096-1099 military campaign to reclaim Jerusalem.
Al Mu'tasim
Abbasid caliph who began Turkish slave recruitment.
Mamluks
Turkish slave soldiers who established their own state.
Crusades
Religious wars that weakened the Abbasid Empire.
Baghdad Fall
Mongol conquest leading to Baghdad's destruction in 1258.
Anatolia
Region in Turkey, significant in Byzantine and Seljuk history.
Mongol Conquests
Military campaigns that devastated Middle Eastern territories.
Persian Mercenaries
Soldiers hired by Abbasids, viewed as less trustworthy.
Turkish Writing System
Developed script used by Turks for communication.
Nomadic Turks
Turks who migrated and lived a mobile lifestyle.
Crusader States
Territories established by Crusaders after the First Crusade.
Zengi
Mosul's governor who initiated the Second Crusade.
Second Crusade
Crusade launched in response to Zengi's actions in 1144.
Salah al-Din
Leader of the Fatimids expanding into Syria.
Ayyubids
Dynasty founded by Salah al-Din after his death.
Mamluks
Turkic slave soldiers used by Ayyubids.
Mongol Empire
Empire expanding into Central Asia and the Middle East.
Khawarazm-Shah Empire
Empire conquered by the Mongols during their expansion.
Merv
City flooded by Mongols, resulting in 700,000 deaths.
Abbasid Caliphate
Islamic caliphate ended by Mongol conquest in 1258.
Hulegu
Mongol leader who invaded the Middle East.
Battle of Ayn Jalut
Turning point where Mamluks halted Mongol advance.
Shajar al-Durr
Female ruler who became Sultan of Ayyubids in 1249.
Louis IX
French king captured by Mamluks during the Seventh Crusade.
Seventh Crusade
Crusade led by Louis IX, resulting in Mamluk victory.
Mongol Tactics
Brutal strategies including slaughtering civilians and leaders.
Mamluk Rule
Characterized by military prowess and eventual governance of Egypt.
Mongol Conquest
Invasion leading to the destruction of cities and cultures.
Turkic Origin
Background of Mamluks taken as boys for military training.
Georgian and Armenian Christians
Allies of Hulegu in the Mongol invasions.
Damascus Surrender
City that capitulated without resistance to Mongol forces.
Factors for Mamluk Decline
Multiple reasons leading to the weakening of Mamluk power.