UE Orthoses
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Purpose of Static Splinting
immobilize or support
help prevent deformity
prevent soft-tissue contracture
allow attachment of assistive devices
block a segment
Basic Components
C-Bar
Connector bar
Crossbar
Cuff or strap
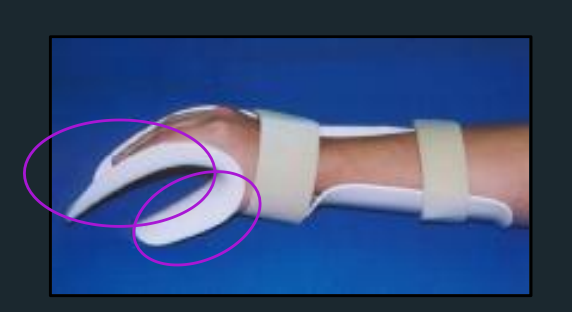
Deviation bar and pan
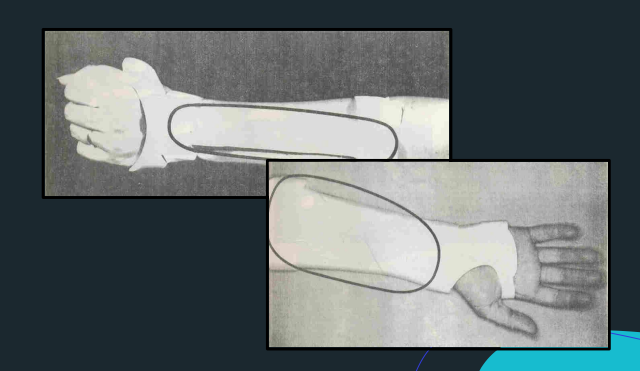
Forearm through
Anatomic bars
Thumb post
Thumb through
Bock
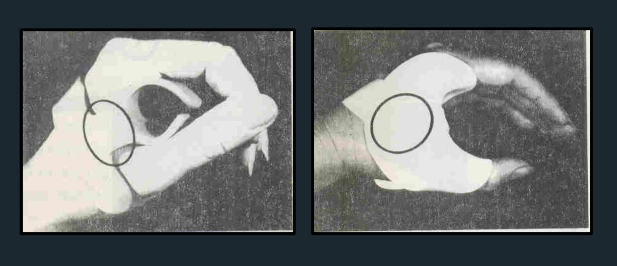
C-Bar
Connector Bar
Cross bar
Cuff or Strap
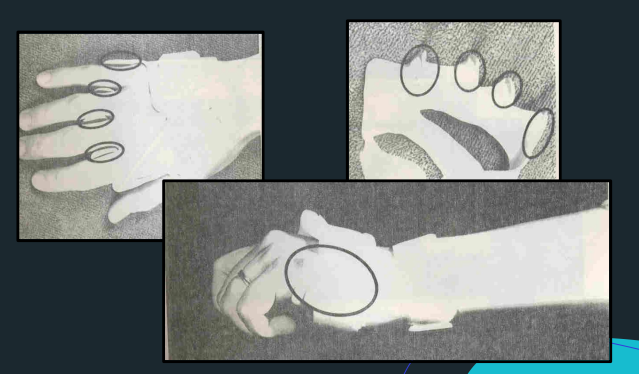
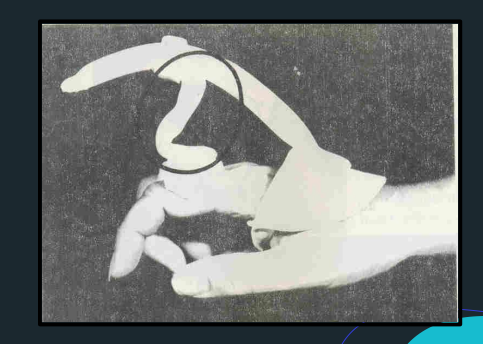
Deviation Bar
Pan and Thumb through
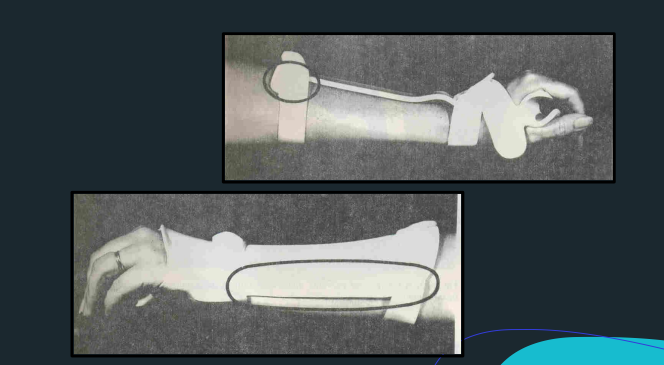
Forearm Through

Hypothenar Bar

Metacarpal bar
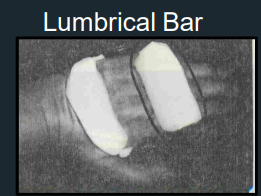
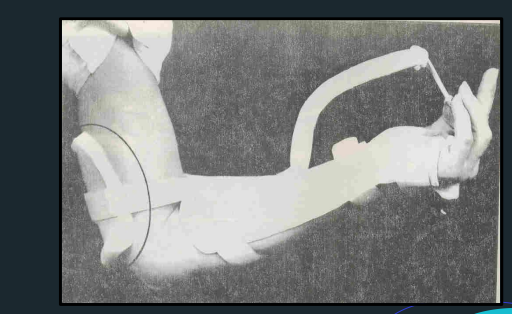
Lumbrical Bar
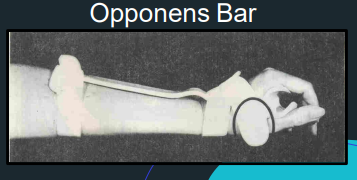
Opponens Bar

Thumb post

Blocks
Diagnostic Indications
fractures tendon injuries crush injuries amputation arthritis carpal tunnel release arthroplasty | tendon transfer tumor excision reconstruction of congenital defects overuse syndromes cumulative trauma disorders |
Treatment Goals
Prevent or Decrease edema
Assist in tissue healing
Relive pain
Allow relaxation
Prevent, misuse, disuse, and overuse of muscles
Avoid joint jamming or injury
Redevelop motor & sensory function
Finger Orthosis
Type
Static or Dynamic
Region
Volar or dorsal
joint crossed
Function
Static Volar DIP Extension Splint
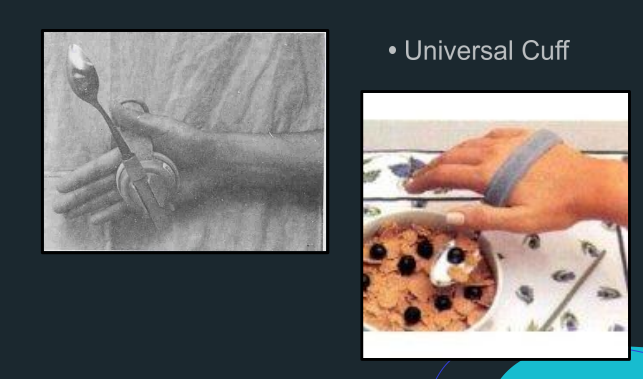
Universal Cuff
Wrist Cock-up splint maintains the wrist in _________ position
wrist in the neutral or mildly extended position
Wrist Cock-Up Splint immobilizes the wrist while allowing ____________
full MCP flexion and thumb mobility
Wrist Cock-Up Splint - Contraindications
Active MCP synovitis
Joint inflammation resulting to volar subluxation and ulnar deviation
Wrist Cock-Up Splint - Disadvantages
Interferes with tactile sensibility on the palmar surface of the hand
Dorsal strap can impede lymphatic flow
Dorsal Wrist Cock-Up Splint - Better tolerated by ___________
edematous hand
Advantages of Dorsal Wrist Cock-Up splint
stronger mechanical support of wrist and freeing up some of the palmar surface for sensory input
Distributes pressure over the larger dorsal wrist surface area
Conditions that benefit from Dorsal Wrist Cock-Up Splint
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Radial nerve palsy
Wrist extensor tendinitis
Colle’s fracture (closed reduction)
Periods of swelling and joint inflammation
Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
Wrist joint synovitis or tenosynovitis
Functions of Resting Hand Splint
Immobilize to reduce symptom
Position in functional alignment
Retard further deformity
Resting Hand splint - Special Considerations
For burns: make adjustments as bandage bulk changes
Preventing infection: when open wound has exudates, clean splints with warm soapy water, hydrogen peroxide, or rubbing alcohol
Patients in the ICU: use sterile materials; follow protocol of the facility
RA patients benefit from thin thermoplast (less than 1/8 inch)
Conditions that benefit from Resting Hand Splint
RA
Trauma / Crush injuries of the hand
Burns
Thumb SPICA splint help stabilize __________
CMC, MCP, IP joints
Conditions that benefit from Thumb SPICA Splint
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
RA
Gatekeeper’s thumb
Other Static Splints
PURPOSE OF SPLINTING: DYNAMIC
To substitute for loss of motor function
To correct an existing deformity
Provide controlled directional movement
Aid in fracture alignment and wound healing
Physiologic Consideration - List
Too great stretch
Too little stretch
Enough Stretch
Physiologic Consideration - Too great stretch
Fatigued
Injury
Failure
Physiologic Consideration - Too little stretch
Atrophy and weaken
Skin, tendons, ligaments, and joint capsules will shorten in the absence of habitual tensile forces
Physiologic Consideration - Enough stretch
Three degrees of gain in ROM per week, with a range of 1-10 deg, is acceptable (Cummings et al 1992)
High intensity short term stretching actually promotes _________
stiffness
Physiologic Considerations - The client should sense _____ in the tissues but feel no ___
sense tension but feel no pain
GUIDELINES FOR DYNAMIC SPLINTING
The stretch should not be perceived as a “stretching” force until at least 1 hour has passed
Client should remain comfortable with the orthosis for up to 12 hours
After removal, the client should feel no more than a stiffness or mild ache
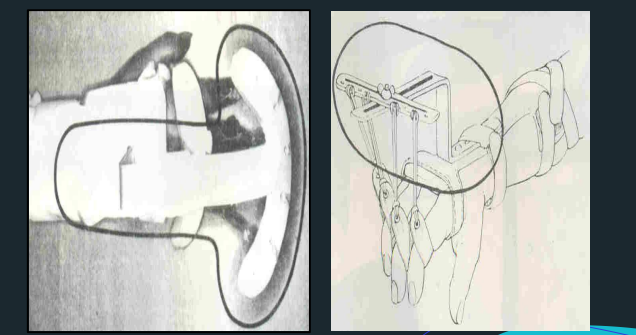
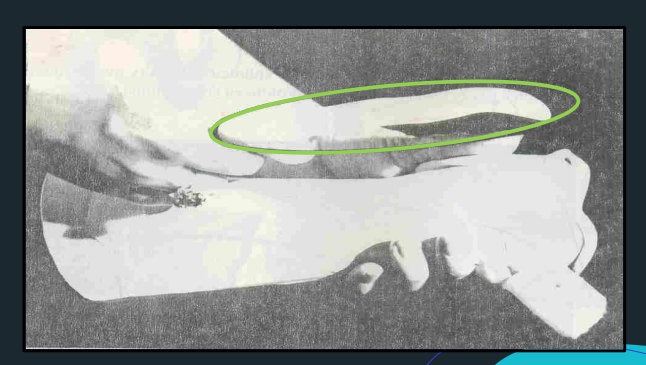
Outrigger
Dynamic Assist

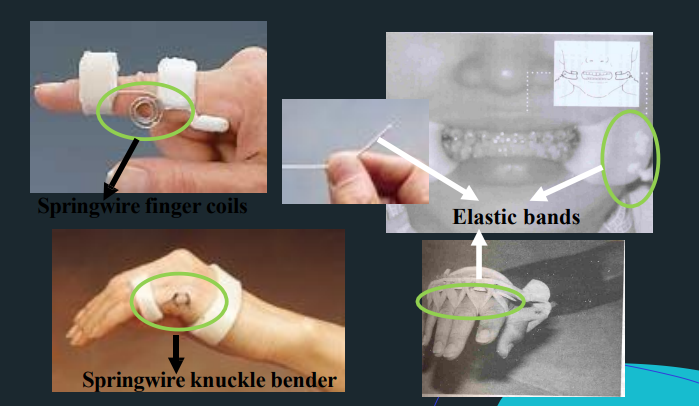
Finger cuff
Reinforcement bar
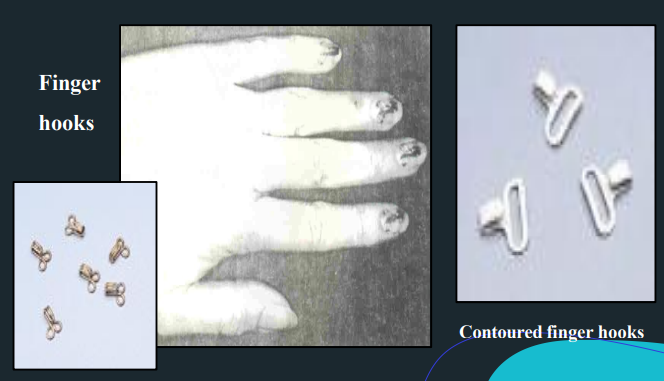
Fingernail attachments
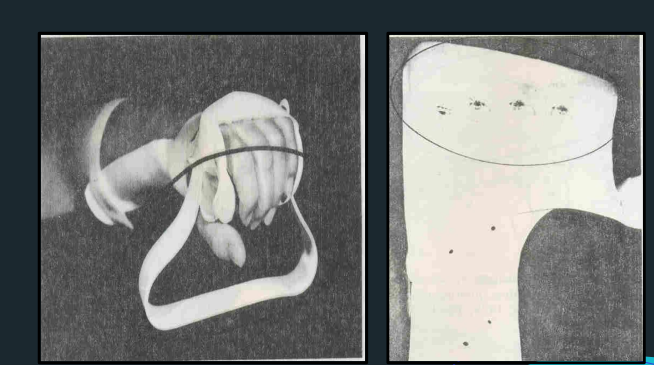
Phalangeal Bar / Finger Pan
Dynamic Finger Extension Splint - Objectives
Immobilize the wrist in functional position
Passively extend the MCP to 0*
Permit full active MCP flexion and unrestricted IP motion
Dynamic Finger Extension Splint - Indications
paralysis of wrist, MCP, finger extensors
Dynamic Finger Extension Splint - Advantages
Relatively has a less obtrusive shape as compared to the outrigger design
The hand can be slipped through a loose sleeve with the orthosis on
Dynamic Finger Extension Splint Parts
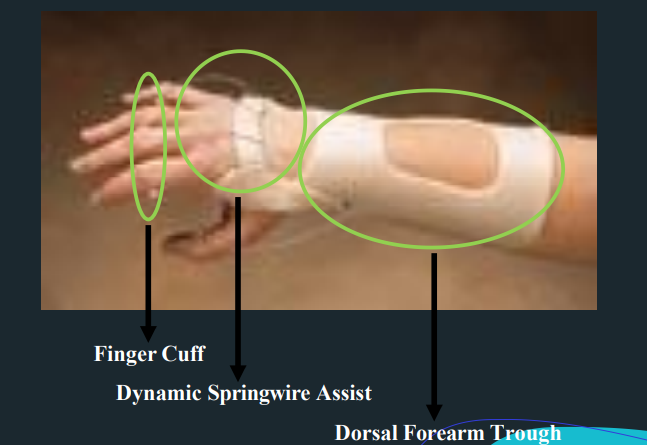
Dynamic Wrist Extension Splint - Objectives
passively extends the wrist while allowing wrist flexion
to prevent contracture of unopposed, innervated wrist flexors
Dynamic Wrist Extension Splint - Indications
weak or paralyzed wrist extensors
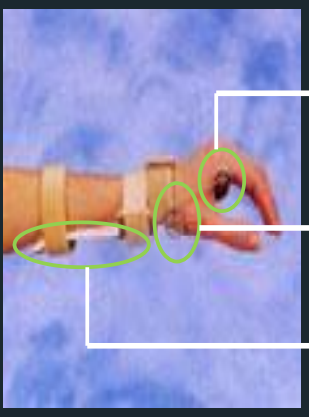
Dynamic Wrist Extension Splint - Parts
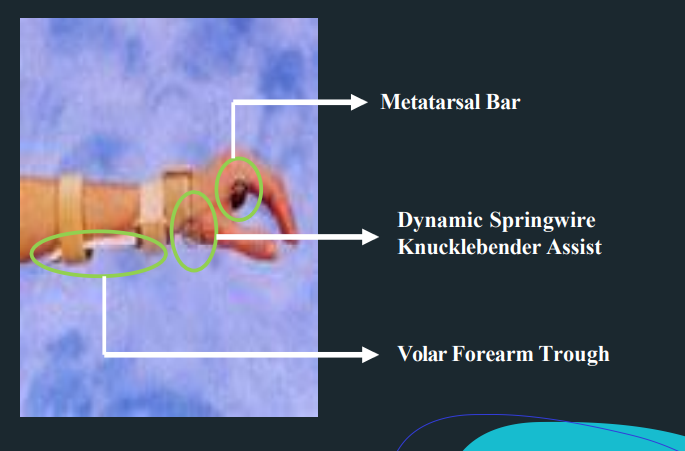
Tenodesis Training Splint - Objectives
train tenodesis grasp
promote a strong tripod pinch with wrist extension
allows finger opening with wrist flexion
Tenodesis Training Splint - Indication
C6 quadriplegia with grade 3 strength of wrist extensors
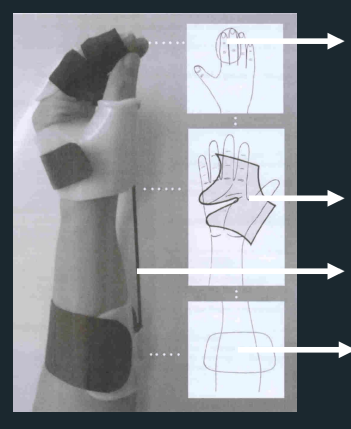
Tenodesis Training Splint - Parts
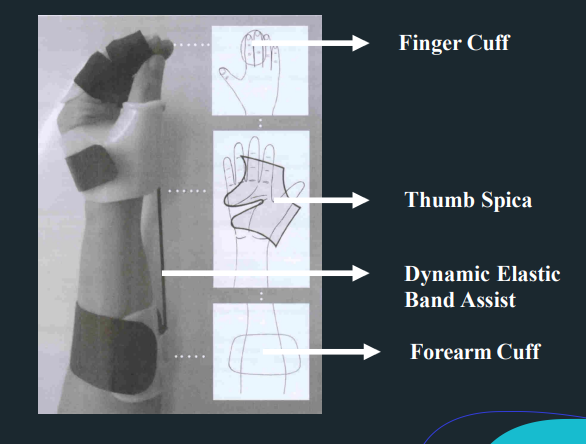
Dynamic Ulnar Nerve Splint is AKA
Dynamic anti-claw deformity splint
Wynn Perry Splint
Dynamic Ulnar Nerve Splint - Objectives
passively flex the 4th and 5th MCPs
To prevent shortening of the MCP collateral ligaments
Promote active IP flexion
Dynamic Ulnar Nerve Splint - Indication
ulnar nerve lesion
Dynamic Ulnar Nerve Splint - Parts
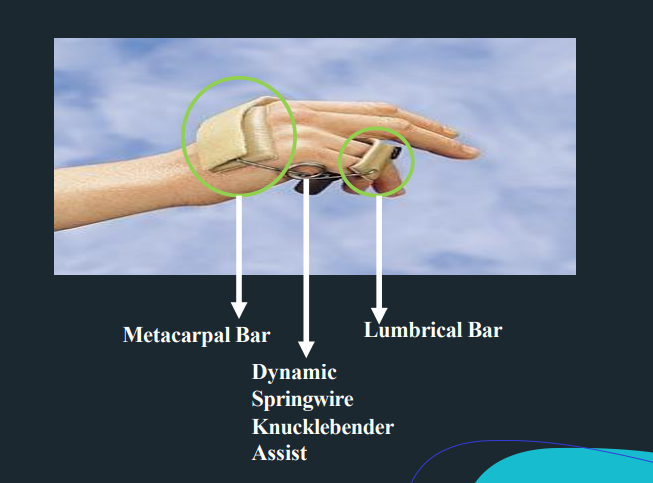
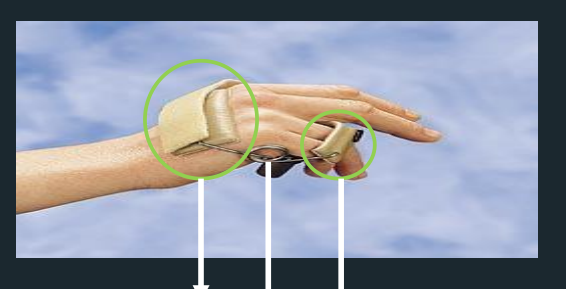
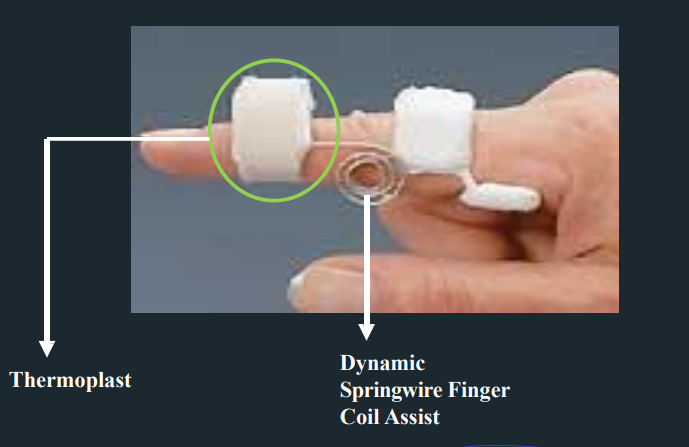
Capener Splint
dynamic spring wire splint for PIP extension
Capener Splint - Objectives
passively extend the PIP
allow active IP flexion
Provide stability to PIP
Promote restabilization of lateral bands and prevent rupture of the central slip
Capener Splint - Advantage
“no profile” minimizing its visual presence
Capener Splint - Indications
PIP flexion contracture
PIP dorsal dislocation
Volar plate injury
Flexor tendon repair with resulting PIP flexion contracture
Partial or complete tear of the collateral ligament
Boutonniere deformity
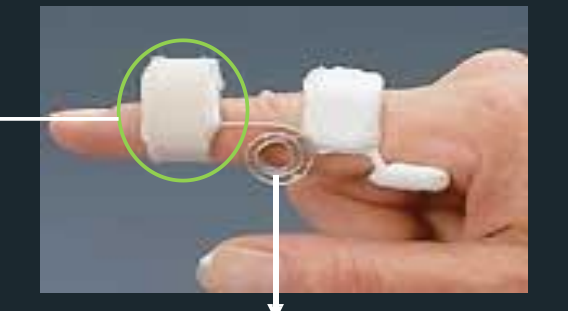
Capener Splint - Parts
General Precautions
be aware of and make adjustments for pressure areas
check for presence of edema
Timing
Compliance
Skin reactions
Initial Fitting
Worn for about 5 – 30 minutes and inspect for persistent red marks
Red marks should disappear within 20 minutes.
Materials used of UE Orthoses
plastic
Metal
Leather
Rubber
Carbon Graphite