09 - Tree to seed
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
what are flowers
modified leaves
Sepals
Protect inner flower organs before bud opens
Frequently green
Can be free or fused to form tube
Petals
Typically colorful to attract pollinators
Can be free or fused to form tube
Stamen
Filament + anther
pollen producing
how many pollen sacs do anthers have
4
stigma
Sticky landing platform for pollen
sometimes its key and lock
style
Connects stigma with ovary
helps pollen go down to oavry
Ovary
An ovary can have one to many ovules
An ovule only has one egg cell
Carpels versus pistils
4 free carpels = 4 pistils
3 partially fused carpels* = 1 pistil
3 fully fused carpels* = 1 pistil
One carpel, one pistil, one ovary, one ovule
example
Cherry, peach, apricot, almond, olive
feritlization of single egg cell → cherry pit
Many carpels, many pistils, 1 ovary each, 1 ovule
Blackberry, raspberry
3 carpels, 1 pistil, 3 ovaries, many ovules per ovary
Cucumber, zucchini
Generalized flower structure
1. Sepals (0-3-4-5-many)
2. Petals (0-3-4-5-many)
3. Stamen (0-many)
4. Pistils (0-many)
why is there so many ways flowers reproduce
all the variations = big diversity of reproductive sflowers
sexual organ types plants
Hermaphroditism
Monoecy
dioecy
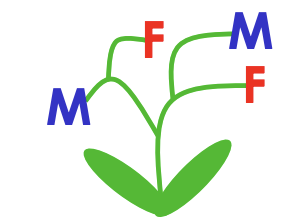
Hermaphroditism
Complete flower
have female and male organgs on all flowers in the plamt
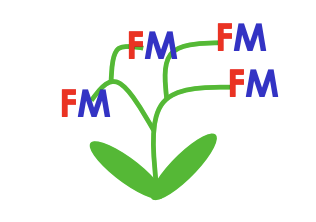
Monoecy
have only male or only female in each flower, but both in the plant
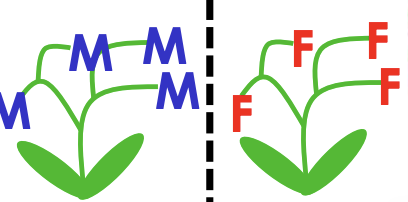
dioecy
plant only have male/ femlae flowers
percent of Hermaphroditism
and exmaple
75
raspberry, trillium
percent of Monoecy and exmaple
17
corn
hazel nut
percent of dioecy and exmaple
6
hemp, asparagus
Hermaphroditism - ways they reproduce
selfing within flower
selfing between flower
outcrossing
Monoecy - ways they reproduce
selfing between flower
outcrossing
dioecy - ways they reproduce
outcrossing
selfing
within same plant
outcrossing
between diff plants
who can self polinate
Adaptive under certain circumstances
hermaphrodite
which is better selfing or outcrossing
outcrossing
inbreeding can lead to inbredding depresion
how do Monoecious & hermaphroditic species avoid selfing
a. Temporal separation
b. Spatial separation
c. Self incompatibility
a. Temporal separation
Sexual phases separated in time
females open at one time and the males
example of male opening first
fireweed
example of female opneing first
blood root
b. Spatial separation
sexual organs within flowers are spaced out
Special type of spatial separation
(1) Individuals with high anthers and short styles
(2) Individuals with low anthers and long styles
c. Self incompatibility
make it so its gentcially imposible to mate
No fertilization with own pollen! Biochemical self recognition
out of all inbreeding avoidance which is the best
self incompatibility
Self incompatibility
situation in many other tree species in the Rose family
apple, pear, cherry, plum
• Temporal & spatial separations is best for
Gender specialization (mechanics) (getting pollen on insect )
what is self incompability the best for
Selfing avoidance
exam with Spatial, temporal separation AND self incompatibility!
sage
why does sage need all 3 mechanisim
T and S separations: ease of pollen pickup and delivery
→ better mechanics (less pollen waste)
Self-incompatibility: ultimate selfing avoidance!
what did invention of flowers: trigger
largest diversity of plants ever
Forces behind the evolution of flowers
Assurance of seed set
Sheer mechanics, bring female and male gametes together
Inbreeding avoidance
Create high-quality offspring, avoid selfing → avoid inbreeding depression
Pollination syndromes specilization
• Floral architecture to optimize pollen uptake and deposition
• Adaptation to pollinators’ senses for precise attraction (sight, smell, taste, touch)
• Adaptation to food requirements of pollinators (fitting reward) → Flower shape, color, odor; nature of reward
type of Pollination
abiotic and biotic
what is abiotic pollination
non directed and can not be trained
wind, water
what is biotic pollination
directed and cann be tarined
→ pollinator needs reward (pollen, nectar)
→ specialized organ construction
animals
how many plants are wing pollinated
10%
where is wind pollination most common
• Higher latitudes and altitudes
• Dry environments
• Open vegetation '
• Island floras
Habitats with fewer insects or generally more wind
examples of wind pollinated
grass
characteristics of wind pollinated
Small, inconspicuous flowers
No special colors
No nectar
Long filaments
Long (feathery branched) styles/stigmas
not as pretty
Very small fraction of pollen reaches stigma
→ cheap but not very efficient ‘
→ large quantity of pollen necessary
types of Biotic pollination
Specialists and Generalist
Specialists
rely on a more narrow group of pollinators Sometimes: exclusive relationship → one pollinator serves one plant = tight co-evolution
Generalist
flowering plants attract wide range of pollinators
example of generalist species
golden rod
charcetristics of generalist
Multiple flowers making up landing platforms for insects of different sizes to roam
Non-specialized food; pollen and nectar
have to deal with getting pollen from othre species cuz visits many other types of flowers
types of biotic specilized pollinators
bees, flies, butterflies, moths, hummingbirds
is bee polination that importnat and why
Bees: most important pollinator group
Pollinate more plant species than any other animal group
Bees originated appr. 80 MYA → diversified along with the evolutionary radiation of flowering plants
Adult bees live on nectar → nectaries, 30-35% sugar
Larvae (juveniles) live on pollen (rich in protein)
Bee pollination characteristics
Bright colors yellow, blue, UV '
→ bees do not see red
Nectar guides '
Nectar hidden → only bees can reach it (architecture) or open it (power)
Cheating flowers (bees) results
→ limits cost of reproduction
→ relies on the fact that there are more honest than cheating flowers
Cheating flowers (bees) example
→ smell, touch, form mimics female bees
→ attraction of males
→ males try to copulate
→ pollen uptake and deposition
→ coevolution!
Fly pollination
Dull, white or reddish flowers
Putrid or otherwise deceptive smell
melt away snow and pokes out atrract flies
Butterfly pollination
Sight and smell is nice and sweet
Red and orange as the most distinct colours
Long narrow flower tube → long proboscis of butterflies → no nectar robbing by non-pollinating insects
plat form for lands cuz they cant hover
Moth pollination
Moths: night-active
White or dull flowers with a very strong smell (mostly emitted after sunset)
Long and narrow floral tube
Hummingbirds pollination
Good sense of colour, attracted to red or yellow
Bad sense of smell → little flower odour
Birds lap up nectar with their tongue → more fluid nectar than for insects, and more of it
Long, tubular corolla suited to long beak, wider than for moths/butterflies
no platforms cuz can hover
What plant sexual system is described in the following statement?
Each individual flower contains both male and female organs
Hermaphroditic
Where are pollen produced
In the anthers
What plant sexual system is described in the following statement?
Each individual flower is unisexual and hence contains either male or female organs, but both sexes are present on one plant individual, ie one plant individual has more than one flower and sex
Monoecious
What plant sexual system is described in the following statement?
Each individual flower and individual plant is unisexual, thus this sex expression is identical to the most common form among animal
Dioecious
In which sexual system is selfing impossible?
Dioecy
Which sexual systems needs mechanisms to avoid selfing? Choose all appropriate answers
Hermaphroditism, Monoecy
What is the (legitimate) pollinator most likely after when visiting a flower which is dark red, relatively large and giving off a smell of decaying flesh?
Rotting animal protein for its offspring
What syndrome/mechanism is described in the following sentence?
Tissue of a particular part of the carpel recognizes the genetic makeup of a pollen grain or a germinating pollen tube and rejects genetically similar or identical pollen tubes from fertilization
Complete self-incompatibility
If the farmer Rajit wants to grow and harvest fruits like apples, cherries or pears, how many individuals of trees per species does he need to plant at least on his farm? Note that all these tree species are hermaphroditic.
2
What type of pollen dispersal syndrome is described as the cheapest
wind
Your granddad comes home from a walk in the Rouge Urban National Park and tells you about a beautiful flower he discovered. It was blue and he had never before seen a flower of that color. He sat down next to it because he wanted to see who would pollinate the flower, but it was rather windy and cold, so no pollinators came while he waited. What is the most likely pollinator?
bee
Depending on the sexual system and number of flowers per plant individual of a particular plant species, in which of the three adaptations (temporal separation of genders, spatial separation of genders, complete self-incompatibility) can selfing accidents happen? Choose all appropriate solutions
Temporal separation of sexes
Spatial separation of sexes
What fits the following description?
Typically, multiple small flowers make up a two- or three-dimensional structure for pollinators of various sizes and identities to land and collect pollen and nectar
Generalist pollination
What fits the following description?
Typically, a flower is constructed to suit the body size and shape of one particular pollinator (group). Also, the floral reward and advertisement are tailored toward one particular pollinator (grou
Specialist pollination
In sexually deceptive orchids, what is the most likely pollinator?
Male bee
In sexually deceptive orchids, through what means is a visitor made to believe that the flower is a sexual partner? Choose all appropriate answers
Through deceptive odors,
Through deceptive surface structures,
Through deceptive visual cues
What is the most likely pollinator of the inflorescence in the photo? On the left is a shot of the whole inflorescence, while on the right is a close-up of individual flowers.
Generalist pollinators
What costs can a flower targeting insects as pollinators mimicking rotting flesh avoid?
nectar
The flower is small and inconspicuous. There is no nectar or odor
- Wind
The flower is orange, it produces nectar and a pleasant odor
- Butterfly
The filaments are very long and weak which leads to anthers dangling loosely
- Wind
The flower is red, does not produce any odor but a lot of runny nectar presented at the bottom of a long corolla (floral tube) which is approximately 7 mm wide
- Hummingbird
The flower is dark red, relatively large and if gives off a smell of decaying flesh
- fly
The flower is green and the stigma is strongly dissected or branched and extending as much as possible away from the flower
- Wind
The flower is red, it has a small landing platform for the pollinator to rest on while visiting, and the flower tube is long and narrow
- Butterfly
The flower is white, it has a very small landing platform for the pollinator to rest on while visiting, and it produces nectar hidden at the bottom of a long and narrow corolla
- Hawkmoth
The flower has a small landing platform for the pollinator to rest on while visiting, and it produces a strong and pleasant odor just in the night.
- Hawkmoth
The flower is blue and has dark stripes pointing towards the center of the flower
-Bee