Funds Exam 3
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
Specimen Collection Steps
Verify the order (right patient, right test, ect.)
Patient identification and education
Hand hygiene
collect the sample
label AT THE BEDSIDE (avoid errors)
transport the sample to the lab
Imaging Study Steps
Verify the order
Patient identification and education
Prep as needed for the ordered test
Monitor the patient as needed post test
Type and Screen Blood Test
Have two nurses during a “type and screen” blood test
Verify the patient
Verify where the blood is coming from
BOTH NURSES SIGN the tube of blood
WBC Count (WBC) value
5,000-10,000 mm³
Hemoglobin (Hgb) value
12-18 g/dL
Hematocrit (Hct) value
40-50 %
RBC Count (RBC) value
4.2-5.9 million mm³
Platelet Count value
100,000-400,000 mm³
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
WBC Count
Hemoglobin (Hgb)
Hematocrit (Hct)
RBC Count (RBC)
Platelet Count
Differential
Extension that includes the WBC
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Eosinophils
Basophils
Band Forms
WBC
low WBC means immunosuppression which is inability to fight infection
put patient on room precautions
Reverse Isolations = dawning PPE for the patient’s safety (not the nurses)
NEED an order to do
high WBC means infection and your body’s actively fighting something
Platelet
low platelet count means they can’t control their bleeding
not appropriate time to do difficult ADLs, soft toothbrush, no shaving, cutting toenails
Sodium value
135-145 mEq/L
Potassium value
3.5-5 mEq/L
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN) value
8-20 mg/dL
Creatinine value
0.7-1.4 mg/dL
Basic Metabolic Panel (BMP)
Sodium
Potassium
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Creatinine
8 components
Complete Metabolic panel (CMP)
14 components
Critical Values
require immediate action
first: assess patient
then: notify provider and give SBAR
Read back results on a call and REPEAT the numerical values
it is a nurse’s obligation to NOTIFY PROVIDER if you receive critical values
Coagulation Studies
Prothrombin Time (PT)
International Nurmalized Ration (INR)
Partial Thromboplastin Time/ Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT/aPTT)
Prothrombin Time (PT)
10-13.1 seconds
International Nurmalized Ration (INR)
0.88-1.16 seconds
2.0-3.0 for anticoagulation therapy
2.5-3.5 for mechanical heart valves
What do anticoags meds do to International Normalized Ratio (INR) and Prothrombin Time (PT)
Anticoagulants increase IRN and PT
Partial Thromboplastin Time/ Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (PTT/aPTT) (heparin drip)
27.5-37.4 seconds
Heparin therapy monitoring ref range: 58-99 seconds
Blood Cultures
Draw 1st
15 minutes apart
on one extremity, 15 minutes later do it on another extremity
Blood Cultures
First draw aerobic bottle
Then go to anaerobic to not add any air into the bottle
“AE before AN”
Germs can grow with or without air so know the type of infection you’re dealing with

Blood Tubes
Do blue first because it needs to be filled to the top
Coagulation tests NEED to be filled to the top
3.2 Sodium citrate additive
prevents blood from clotting by binding calcium
Lavender/Pink
Hematology and blood bank
Potassium EDTA additive
prevents clotting by binding calcium
Changes in potassium?
think about heart and use telemetry monitoring
24-Hour Urine Collection
Void in bedpan
Avoid toilet paper
DO NOT have bowel mvmt in the bedpan
note start time because the next nurse needs to know when to end 24/h
Radiography Types
X-rays
CT scans
MRIs
Ultrasound
X-rays
obstructions, strictures, fractures, ect.
No contrast used
ask patients if they’re allergic to shellfish
emits radiation
do not use during pregnancy
normal = negative
positive = problem
CT Scans
Cross-sectional images of bone and tissue
May use oral or IV contrast to illuminate images
may or may not use contrast
Emits radiation
Normal = negative
order BUN and Creatinine because you want the patient to be able to excrete the contrast in their urine output
MRIs
Detailed anatomic views
No radiation emitted
May use IV contrast to illuminate images
may use contrast
Normal = negative
NO METALS
implanted devices
pacemakers
piercings
no wheelchair
need oxygen? NO oxygen tank
Ultrasound
visualizes organs, soft tissue, blood flow through vessels, etc.
KIDNEYS, Carotid arteries, legs for DVT
No contrast used, no radiation
Normal = negative
If we have limitations regarding radiation or contrast, we wan’t to know out options so use an ultrasound
Activities of Daily Living (ADLs)
self-care activities such as bathing, dressing, toileting, transferring, continence, feeding
Contractures
permanently contracted state of a muscle
Footdrop
complication resulting from extended plantar flexion
Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADLs)
the activities of daily living needed for independent living such as managing finances and meal preparation
Isokinetic exercise
exercise involving muscle contractions with resistance varying at a constant rate (muscle contraction with resistance)
Isometric exercise
exercise in which muscle tension occurs without a significant change in muscle length (muscle contraction without shortening)
Isotonic exercise
movement in which muscles shorten (contract) and move (muscle shortening and active movement)
Range of Motion
complete extent of movement of which a joint is normally capable
AM Care
Before Breakfast
assist patient with toileting
wash face and hands
provide mouth care
cluster your activities = do skin assessment and wound care with AM CARE
After Breakfast
3Ps = pain, potty, positioning
toileting (every 2-4 hours after breakfast)
oral care
bathing (can delegate)
special skin measures
discourage the use of powders unless prescribed
hair care (shampoo and condition)
stay away from shaving patient’s face
dressing
positioning for comfort
refreshing or changing bed linens
tidying up bedside
lotions should be non-scented, ph-balanced, sensitive
can delegate to a PCT, but if patient has ointment that’s a med, CAN’T delegate
Encourage independence when possible?
Yes!
Don’t eat lying down
elevate head of the bed if they have an NG tube to avoid aspiration after AM Care
lock the bed
lower the bed when you leave
call bell within reach
personal items close by
As Needed Care (PRN) & Hour of Sleep (HS) Care
PRN
offer individual hygiene measures as needed
change clothing and bed linens of diaphoretic patients (over sweating)
provide oral care every 2 hours if indicated (ESPECIALLY if unconscious)
HS
offer assistance with toileting, washing, and oral care
offer a back massage
change any soiled bed linens or clothing
position patient comfortably
ensure that call light and other objects patient requires are within reach
Regular Pans vs Fracture Pans
Difference in hip height
RAISE BED TO WAIST LEVEL
patients with hip/spinal/neck fractures
Eye Care
clean from inner to outer canthus with wet, warm cloth, cotton ball, or compress
use artificial tear solution or normal saline q4H if blink reflex is absent (unconscious patients)
care for eyeglasses or contact lens, if indicated
for matted eyelashes, use warm compress
Ears & Nose Care
wash external ear with washcloth-covered fingers
NO Q TIPS, just outer ear!
perform hearing air teaching and care if indicated
do no lose, expensive
remove crusted secretions around nose by applying warm, moist compress
DO NOT trim nose hairs, ask them to blow their nose to clean
Hair Care
Note any history of hair/scalp problems
dandruff, hair loss, baldness, alopecia
Shampoo and groom hair
Can nurses remove contacts?
Yes!
raise upper and lower lids and squeeze down
Foot Care
avoid soaking the feet (get’s rid of moisture and a fall precaution)
dry feet thoroughly, including the area between the toes
moisturize the feet if they are dry
anti-fungal foot powder if necessary
avoid using scissors or nail clippers
consult a podiatrist
wear appropriate footwear
wear cotton socks
avoid using heating pads
Effects of exercise on body systems
Neurological
dec Anxiety/depression
dec Dementia
dec Risk of stroke
inc Cognitive function
Endocrine
dec Weight
dec Diabetes
dec LDL
inc HDL
Cardiovascular
dec mortality
dec coronary artery disease
dec blood pressure
cardiac rehab
Oncological
dec prostate cancer
dec breast cancer
dec bowel cancer
Musculoskeletal
dec osteoporosis
dec falls
dec disability
Encourage exercise, whatever form they can!
Helps with constipation
Types of Exercise
Muscle Contraction
Body Movement
Muscle Contraction
Isotonic
muscle shortening and active movement
Isometric
facilitated exercise, muscle contraction without shortening = yoga
sitting position is isometric
extended plantar flexion = foot drops forward, prevent by exercise even while in bed, ask them to dorsiflex and then do a plantar flexion
Isokinetic
muscle contraction with resistance
rehab
Body Movement
Aerobics
Stretching
Strengthening and endurance
Movement and ADLs
housework, caring for a playful toddler, climbing stairs vs. elevator
General Ease of Movement
normal findings
body movements are voluntarily controlled (purposeful)
fluid
coordinated
Gait and Posture
normal findings
head erect, vertebrae are straight
knees and feet point forward
arms at side with elbows flexed
arms swing freely in alteration with leg swings
while one leg is in the stance phase, the other is in the wring phase
Alignment
normal findings
independent maintenance of correct alignment
in the standing and sitting position, a straight line can be drawn from the ear through the shoulder and hip
in bed, the head, shoulders, and hips are alligned
Joint structure and function
normal findings
absence of joint deformities
full range of motion
Muscle mass, tone and strength
normal findings
adequate muscle mass, tone and strength to accomplish movement and work
Endurance
normal findings
ability to turn in bed, maintain correct alignment when sitting and standing, ambulate, and perform self-care activities
NANDA Nursing Diagnoses: Activity
activity intolerance
impaired transfer ability
risk for activity intolerance
risk for constipation
because they are not moving around
risk for injury
footdrop can be an injury
Nursing Interventions: Activity
Ergonomics to prevent injury
Safe patient handling and movement
Safe transfer, equipment and assistive devices
gait belts, transfer devices, lifts
Positioning patient in bed
devices for correct alignment
foam wedges and pillows, trapeze, foot board or shoes (footdrop), hand roll, trochanter roll
can use special shoes for footdrop
offloading pressure, maintaining a specific position
protective positioning
repositioning q2H
trochanter roll
don’t have contracture of the hands, use a washcloth
Safe Handling of Patient with Dementia
Communication problems and weakness
Face the patient when speaking
Use clear, short sentences,
call patient by name
use calm, reassuring tone of voice
offer simple, step-by-step instructions
phrase instructions positively
don’t use the word “DON’T”
ask one question at a time, allow the patient to answer
identify the patient’s established patterns of behavior
Nursing Interventions: Activity
using graduated compression stockings (remove when bathing)
move a patient up in bed
moving a patient from bed to stretcher or chair
assisting with active/passive ROM exercises
assisting with ambulation
isometrics, dangling, 1-person assist, 2-person assist
walkers, canes, crutches, braces
MUST be prescribed by a provider
dangling to prevent orthostatic hypotension
Evaluation: Activity
general ease of movement and gait
body alignment
joint structure and function
muscle mass, tone and strength
endurance
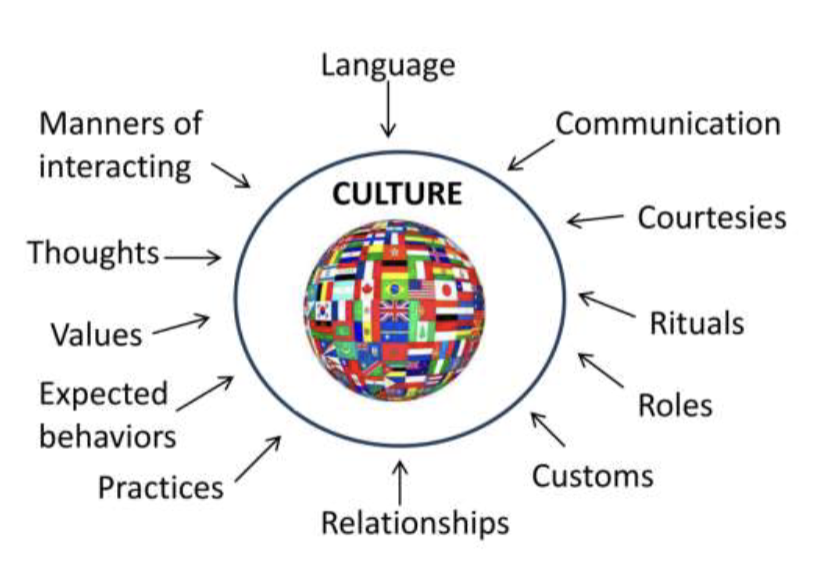
Culture
sum total of human behavior or social characteristics particular to a specific group and passed from generation to generation or from one to another within the group.
Culture conflict
situation that occurs when people become aware of cultural differences, feel threatened, and respond by ridiculing the beliefs and traditions of others to make themselves feel more secure about their own values.
Culture shock
those feelings, usually negative, a person experiences when placed in a different culture.
Ethnocentrism
belief that one’s own ideas, beliefs, and practices are best, superior, or most preferred to those of others; using one’s cultural norms as the standard to evaluate others’ beliefs.
Cultural assimilation
process that occurs when a minority group, living as part of a dominant group within a culture, loses the cultural characteristics that made it different.
Cultural blindness
the process of ignoring differences in people and proceeding as though the differences do not exist.
Cultural competence
care delivered with an awareness of the aspects of the patient’s culture.
Cultural imposition
tendency of some to impose their beliefs, practices, and values on another culture because they believe that their ideas are superior to those of another person or group.
Linguistic competence
ability of caregivers and organizations to understand and effectively respond to the linguistic needs of patients and their families in a health care encounter.
getting a translator!
Stereotyping
assigning characteristics to a group of people without considering specific individuality.
Transcultural nursing
providing nursing care that is planned and implemented in a way that is sensitive to the needs of individuals, families, and groups representing the diverse cultural populations within our society.
Factors Inhibiting Sensitivity to Diversity Practice Problems

Cultural Influences on Health Care
reactions to pain
pain is whatever the patient says it is
biological sex roles
language/communication
by law can receive interpreter services
food and nutrition
can bring food on restricted diet because they can learn the new diet
family support
socioeconomic status
transfers are incredibly difficult to get to the hospital
Culturally Respectful Nursing Care
Develop an awareness of one’s own existence, sensations, thoughts, and environment in relation to others
Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the patient’s culture, health-related needs, and culturally specific meanings of health and illness
Accept responsibility for one’s own education in cultural competence
Not assuming that the health care provider’s beliefs and values are the same as the patient’s
Accept and respect cultural differences
Be open to and comfortable with cultural encounters
Resisting judgmental attitudes
Ask patient about their religious affiliation
Add cultural/spiritual healers
Culturally Competent Nursing Care - Patient in Pain
recognize that each person holds various beliefs about pain and that pain is what the patient says it is
respect the patient’s right to respond to pain in one’s own fashion
never stereotype a patient’s responses to pain based on the patient’s culture
be sensitive to nonverbal signals of discomfort, such as holding or applying pressure to the painful area or avoiding activities that intensify the pain
how to see nonverbal pain: wincing, guarding, clenching teeth, vital signs
Cultural Assessment:

Cultural Assessment/Areas Nurses need to understand
beliefs, values, traditions and practices of a culture
culturally defined, health-related needs of individuals, families and communities
culturally based belief systems of the etiology of illness and disease and those related to health and healing
attitudes toward seeking help from health care providers
Elements of Cultural Competence
developing self-awareness
demonstrating knowledge and understanding of a patient’s culture
accepting and respecting cultural differences
not assuming that the health care provider’s beliefs and values are the same as the client’s
resisting judgmental attitudes such as “difference is not as good”
being open to and comfortable with cultural encounters
accepting responsibility for one’s own cultural competency
Guildelines for Providing Culturally Competent Nursing Care
develop cultural self-awareness
develop cultural knowledge
accommodate cultural practices in health care
respect culturally based family roles
avoid mandating change
seek cultural assistance
Factors Influencing Communication
developmental level
sociocultural differences
roles and responsibilities
space and territoriality
physical, mental, and emotional state
values
environmental
be eye level with child
Forms of Communication
verbal (language)
nonverbal (body language)
facial expressions, tough, eye contact
posture, gait, gestures
general physical appearence
mode of dress and grooming
sounds, silence (silence can mean respect)
electronic communication (make sure messages are encrypted)
hand gestures
bouncy happy walk doesn’t always mean happy (masking depression)
Levels of Communication
Intrapersonal
self-talk, communication within a person
Interpersonal
occurs between two or more people with a goal to exchange messages
Group
small-group
organizational communication
group dynamics
mutual respect is important with group dynamics
Electronic Communication
Social media
Both the American Nurses Association (ANA) and the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN) have issued guidelines for RNs regarding use of social media.
Email and test messages
The risk for violating patient privacy and confidentiality exists any time a message is sent electronically.
Health care agencies usually have security measures in place to safeguard e-mail and text communications
do not text on your personal phone EVER
Phases of the Helping Relationship
Orientation phase
where you collect data from a patient… why are you hospitalized? How are you feeling?
Working phase
providing direct patient care
Termination phase
when patient is discharged, upgraded to a higher level of care, when nurse leaves and goes to another place of employment
Goals of the Orientation Phase
the patient will call the nurse by name
the patient will accurately describe the roles of the participants in the relationship
the patient and nurse will establish an agreement about:
goals of the relationship (working towards what)
location, frequency, and length of the contacts
duration of the relationship
the patient will actively participate in the relationship
patient WORKS ALONGSIDE nurse to meet goal
the patient will cooperate in activities that work toward achieving mutually acceptable goals
the patient will express feelings and concerns to the nurse
Goals of the Termination Phase
The patient will participate in identifying the goals accomplished or the progress made toward goals
The patient will verbalize feelings about the termination of the relationship
Factors that Promote Effective Communication
Dispositional Traits
warmth and friendliness
openness and respect
empathy
honestly, authenticity, trust
caring
competence
taking responsibility for your strengths and weaknesses
No cliches!!
Rapport builders
Specific objectives
Comfortable environment
Privacy (provide privacy!!! do not speak about potential loudly)
Confidentiality
Patient vs. task focus
Utilization of nursing observations
Optimal pacing
Assertive
stand up for yourself and other with open, honest, and direct communication; clear, concise I statements
Aggressive
asserting one’s own rights in negative manner that violates the rights of others; aggressive communication tries to assert superiority through destructive comments targeted at others (*note: cocky borders on this)
Non-assertive
failing to stand-up for oneself or to communicate in clear, confident manner; often non-assertive person will feet hurt or angry after the communication
Characteristics of the Assertive Nurse’s Self-Presentation
Confident; open body posture
Use of clear, concise “I” statements
Ability to share effectively one’s thoughts, feelings, and emotions
Working to capacity with or without supervision
Remaining calm under supervision
Asking for help when necessary
Giving and accepting compliments
Admitting mistakes and taking responsibility for them
The Helping Relationship
Does not occur spontaneously
Purposeful and time limited
Characterized by an unequal sharing of information & unequal focus: patient-centered
build on the patient’s needs
the nurse is the helper, and the patient is the person being helped
nurse is professionally accountable for actions & outcomes
Communication is the means used to establish rapport and helping-trust relationships
Dynamic