Parasitology 13 Ectoparasites
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
T/F: Mosquitoes are ectoparasites
False
What species carries malaria?
Anopheles mosquito
Arachnid bugs
Arachnids, ticks, mites
Insect bugs
lice, flea
Cimex spp.
common name?
UNUSUAL vector of?
cause what symptoms?
other traits?
bed bugs
T. cruzi
allergic inflammation from bites
stink glands that cause distinctive odor
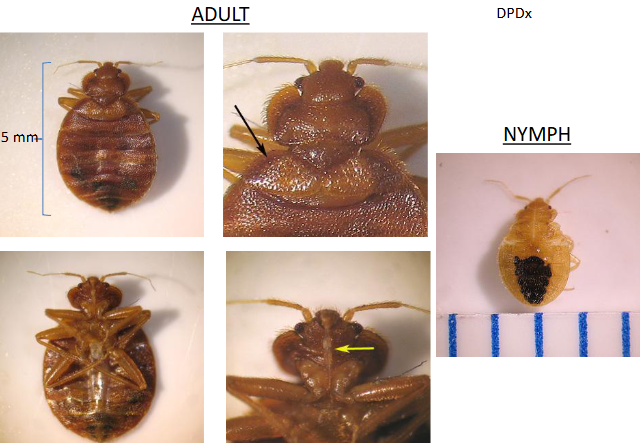
What is this?
Cimex (bed bugs)
Myiasis — what is it?
infection with the larval stage of various flies
What flies cause myiasis?
Dermatobia hominis (botfly)
Cochliomyia hominovorax or Chrysoma bezziana (screwworm)
Cordylobia anthropophaga (tumbu fly)
Cuterebra, Oestrus, Wohlfahrtia
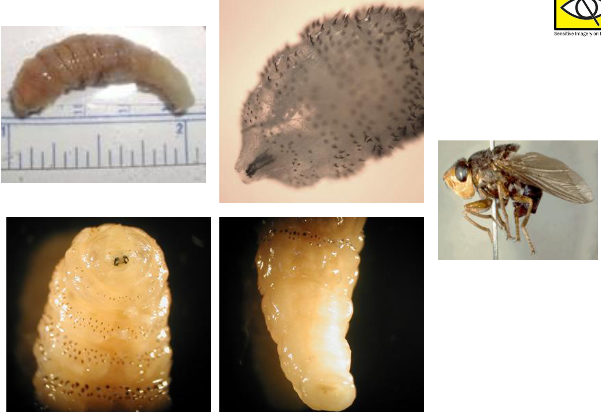
What is this?
botfly
Cerebral myiasis
is it rare?
what species causes it?
how does it attack?
yes
Cochliomyia hominovorax
invades viable tissue
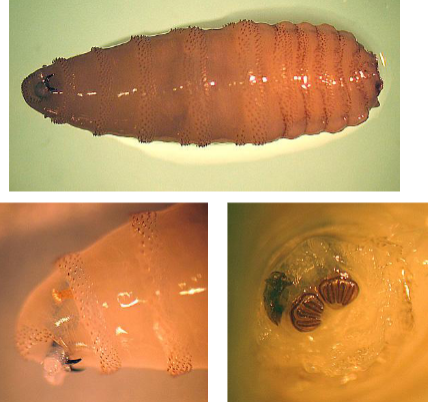
What is this?
Cochliomyia hominovorax (screwworm)
Cordylobia anthropophaga (tumbu fly)
distribution?
causes what?
eggs laid where?
how infect host?
life stages and times?
tropical Africa
myiasis
laid on feces or urine stained soil or clothes
larvae hatch in 4 days; penetrate skin
leave host in 8-10 days
Lucilia sericata
“good maggot” because determines time of death and used for maggot therapy
causes disease in sheet or other liverstock
Definitive identification of ectoparasites through what?
spines and spiracular plates
Head/body lice
which species is which?
who is infected?
distribution?
who more at risk?
P. capitis is head lice
P. corporis is body lice
humans only
feeds on blood several times
worldwide distribution
children and females
P. humanus humanus
resides where?
eggs where?
resides on clothing; eggs glued to clothes
P. humanus capitis
resides where?
eggs where?
resides in scalp; no known vectors; eggs found in hair
Treatment for lice
lice-killing lotion/shampoo with 1% permethrin
second defense is lindane
Sarcoptes scabiei (itch mite)
distribution
where on the body?
how it infects
most at risk?
worldwide
warm/moist areas
burrows into subcorneal layers of skin
HIV/AIDS patients
Scabies diagnosis? Treatment?
skin scraping
permethrin cream (5%) or ivermectin if immunosuppressed
wash clothes in hot water
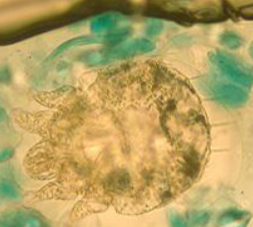
What is this
Scabies mite/itch mite
Ixodidae (hard ticks)
list the genus’ and how many hosts they have
Amblyomma
Dermacentor - 3
Hyalomma - 2
Ixodes - 3
Soft ticks (argasidae)
list the genus’ and hosts they have
Rhipcephalus - 1 or 3 hosts (mainly birds)
Ornithodoros - multihost
Which hard tick species causes babesiosis?
Ixodes
Tick paralysis
caused by
symptom
what is required
caused by Dermacentor and Ixodes
acute ascending paralysis — fatal
tick must be attached 4 days before symptoms
What happens when you consume mammal-derived products (milk, meat, cheese, etc) after a tick bite?
you get a serious allergic condition
Tick life cycle amongst hosts
larva attaches to and feeds on first host in summer
nymphs attach to second host in spring
nymphs molt and attach to third host as adults in fall for feeding/mating
lay eggs in spring
brown recluse spider (loxoscele reclusa)
hobo spider
lives in gardens and burrows — no spider web
cause skin necrosis, kidney failure, hemolysis, shock

What is this
brown recluse
Black widow spider (L. mactans)
warm, southern USA
sexual cannibalism
potent venom
lack powerful chelicerae
Lactrodectism phases, lengths, symptoms
exacerbation phase is 24 hours (pain at bite, muscle cramps, dizziness, insomnia, etc)
Dissipation phase is 1-3 days post bite (symptoms decline)
residual phase is weeks to months (muscle spasm, tingling, weakness, paralysis)