Lecture 1: Developmental defects of oral and maxillofacial regions
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
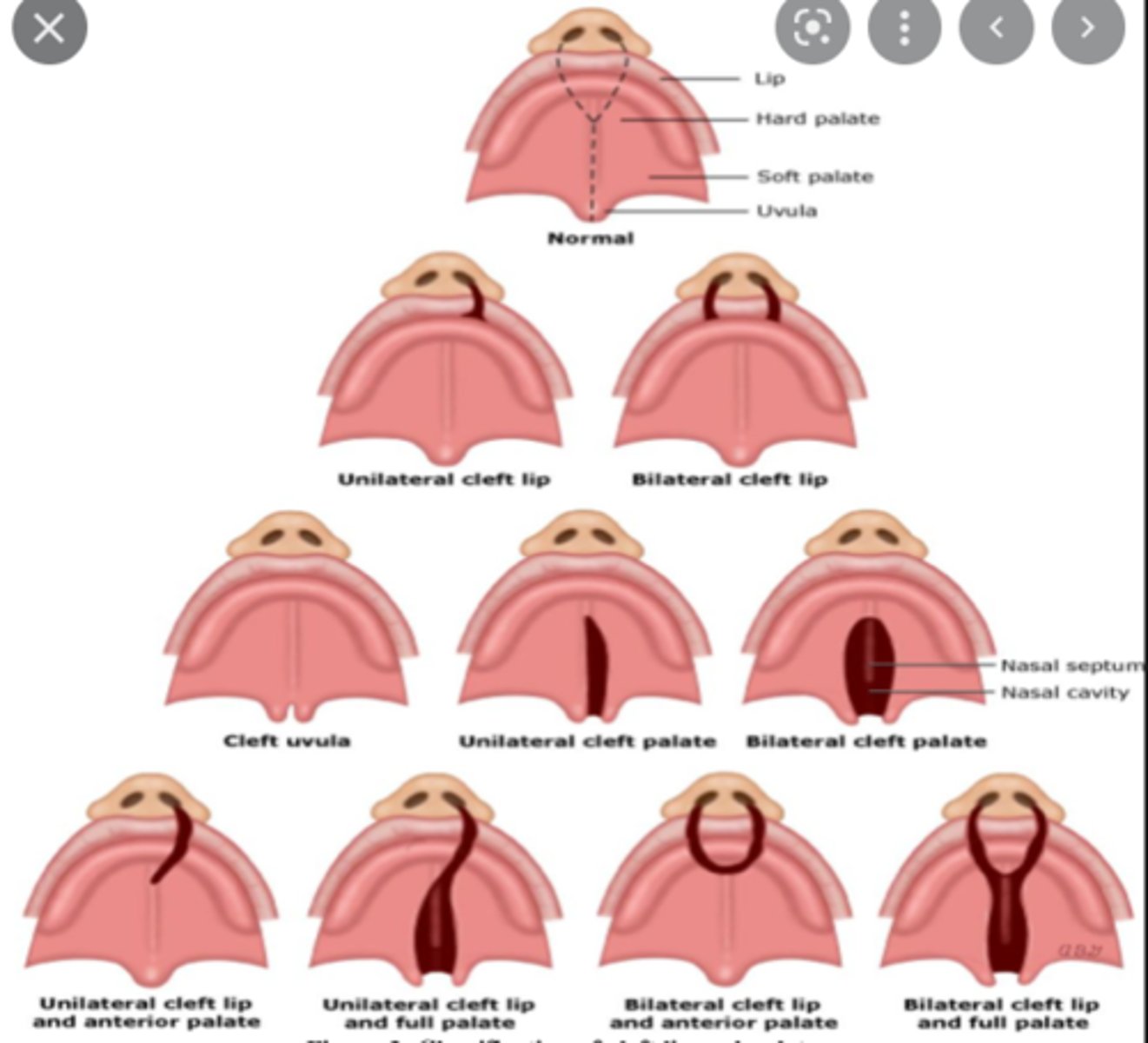
Oral clefts result from the disruption of what? (2)
orchestrated development and merger of tissue processes
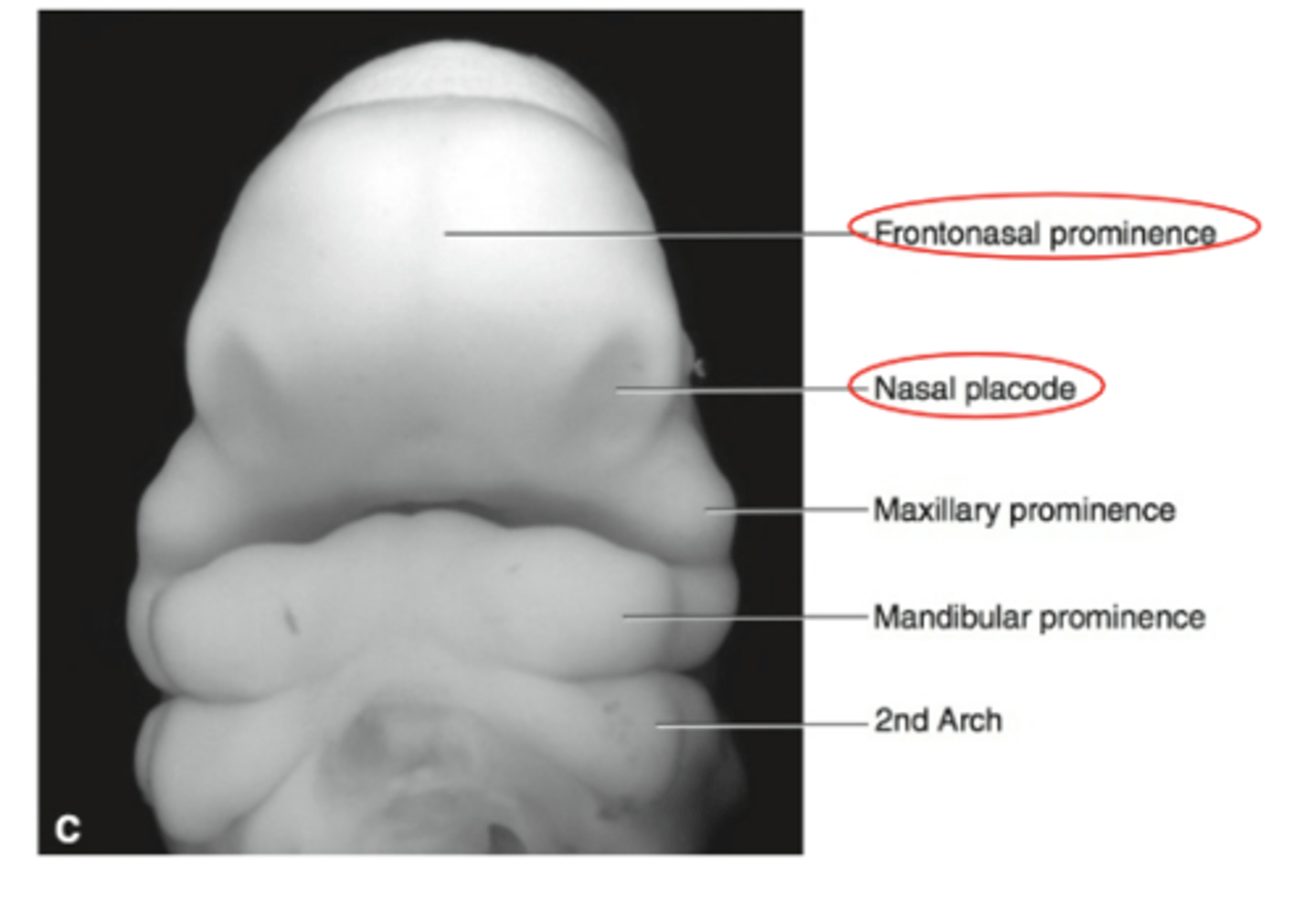
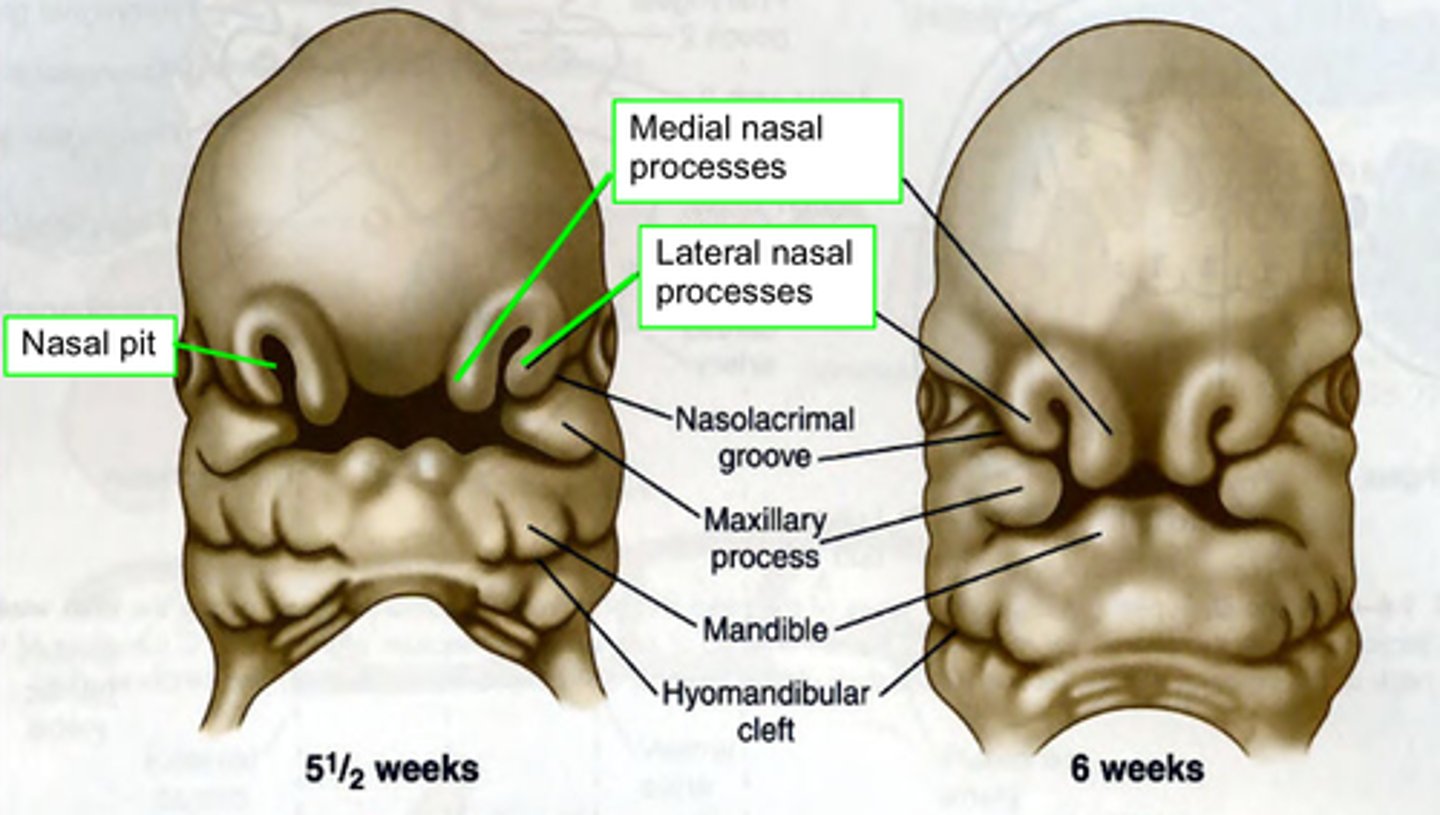
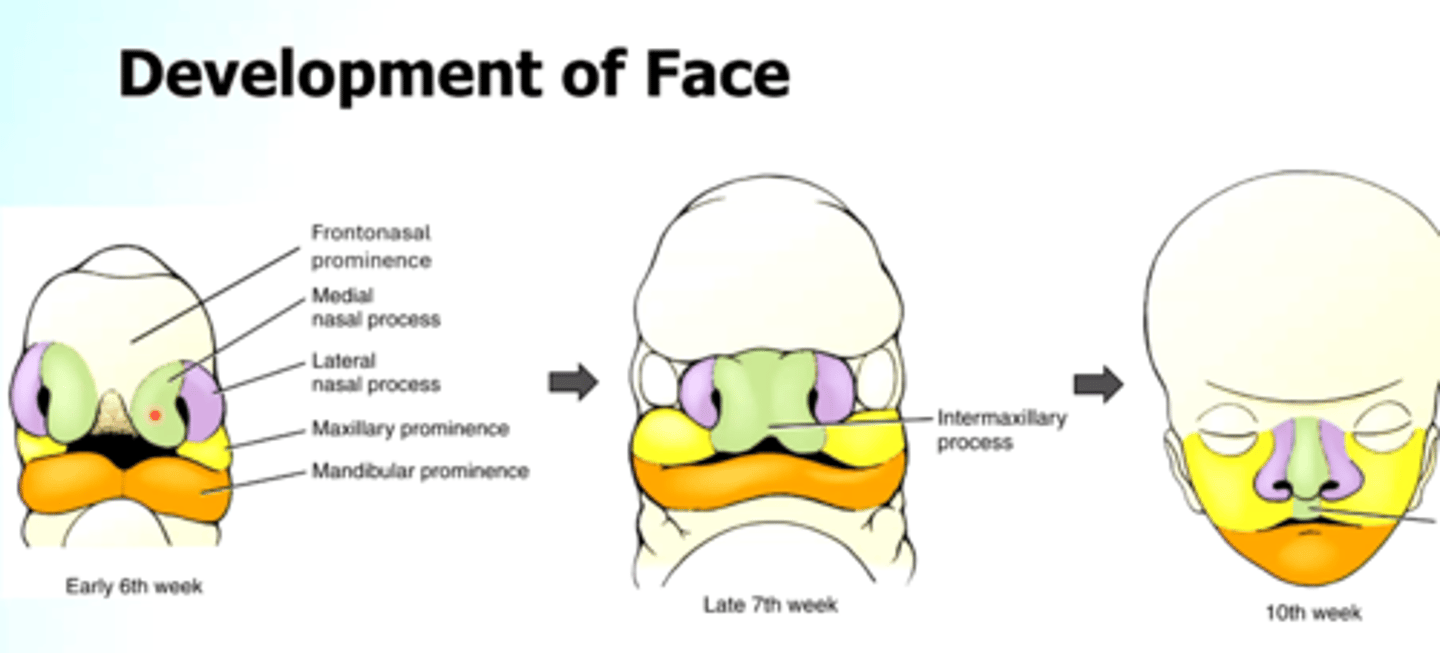
What do Nasal placodes appear lateral and inferior to of the central face?
frontonasal prominence
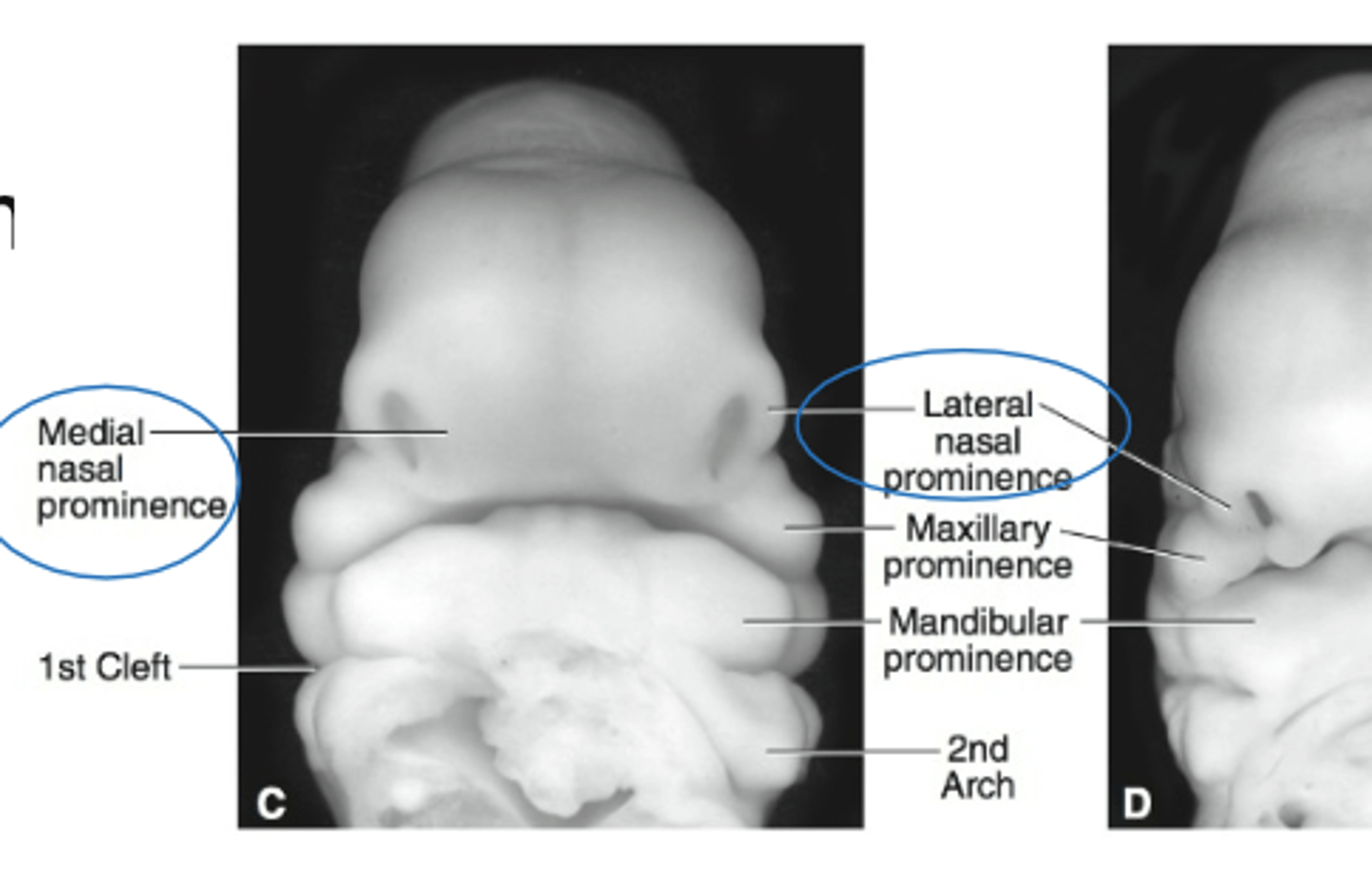
Proliferation of ectomesenchyme of the central face appear in the (2)
Medial and lateral prominences
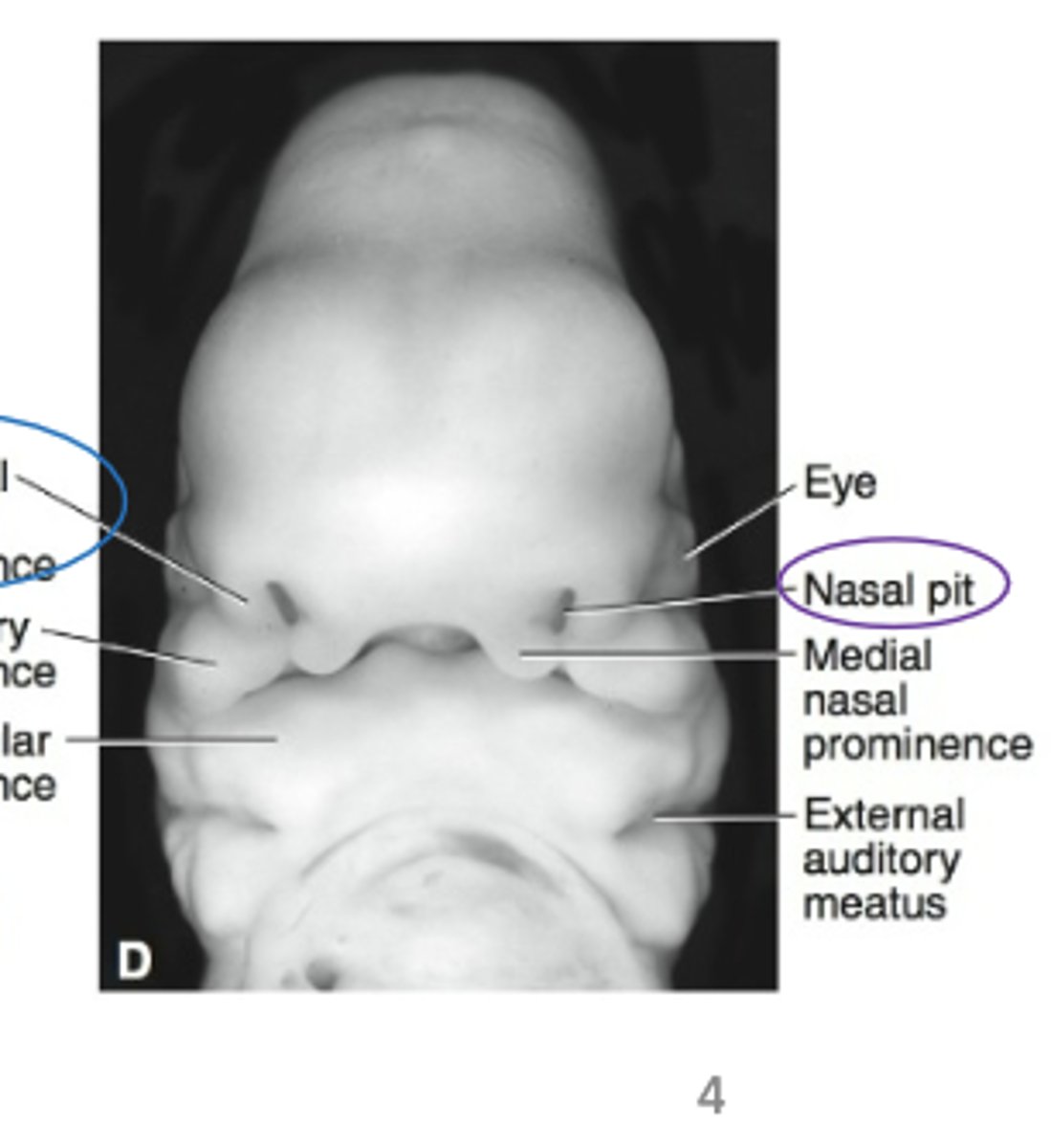
The nasal pit (depression) between each pair of nasal prominences represents
primitive nostril
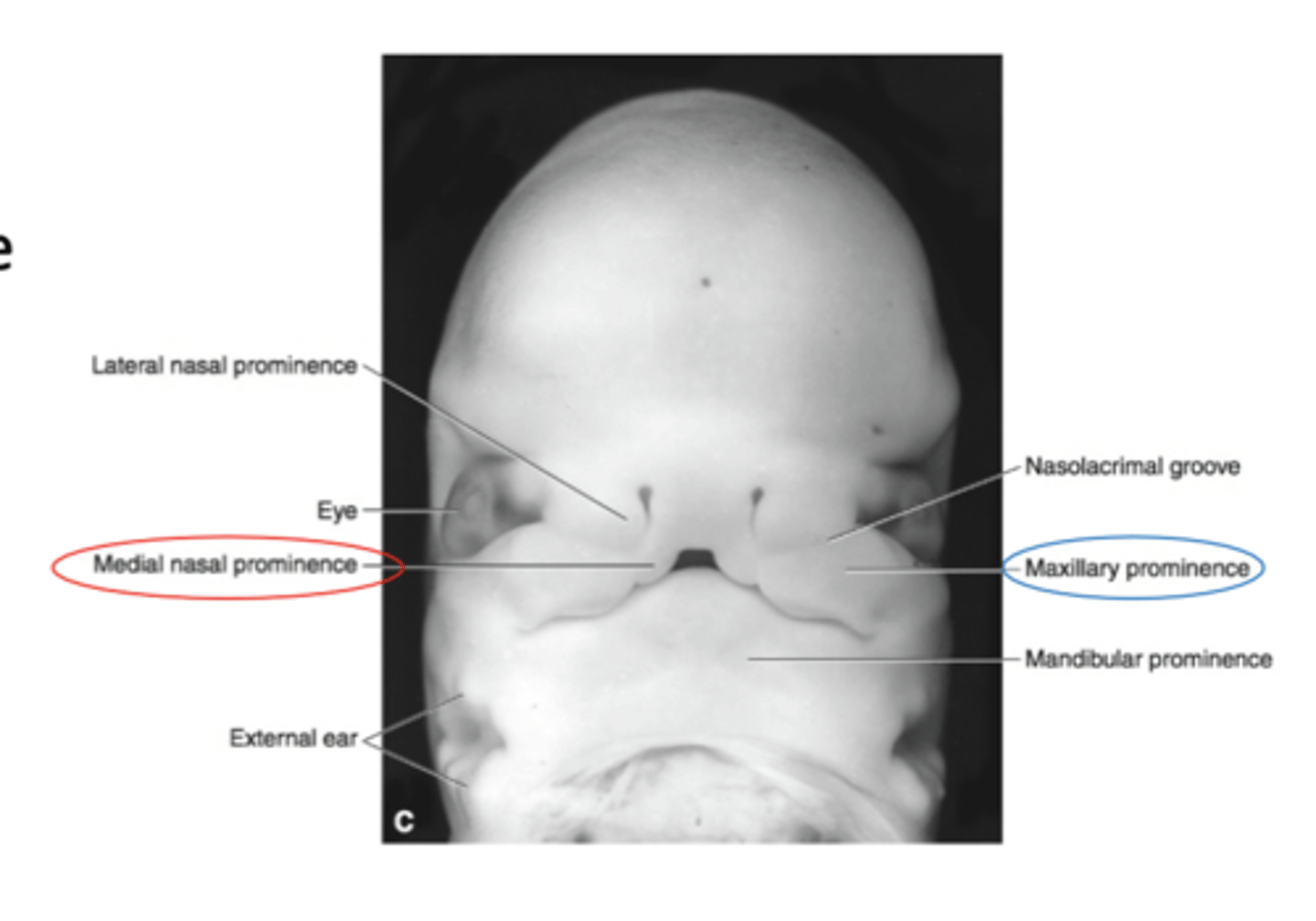
The Medial nasal processes merge with each other to form?
Central part of the upper lip
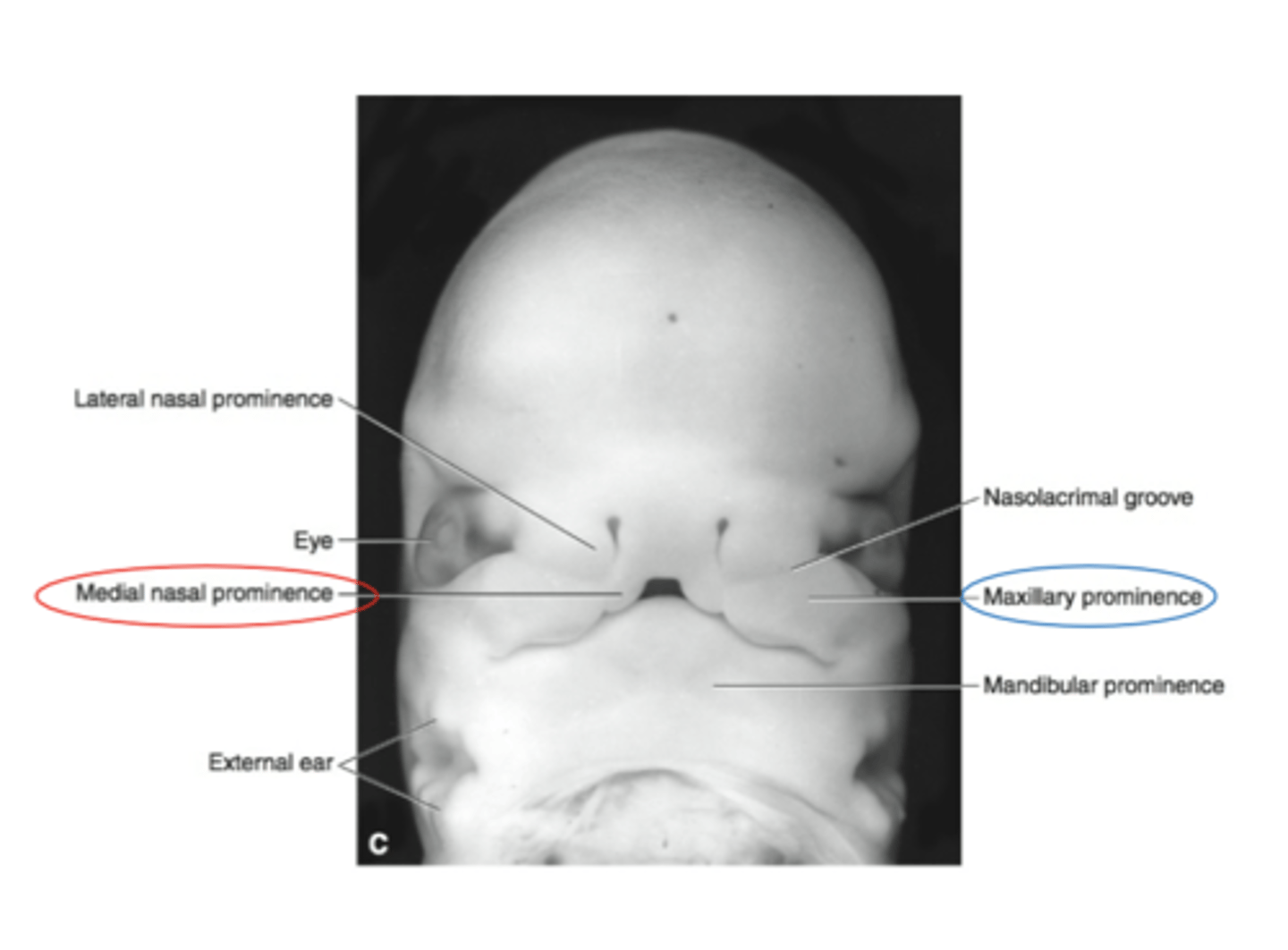
The maxillary process merge with the nasal prominences to form?
Lateral portions of the upper lip
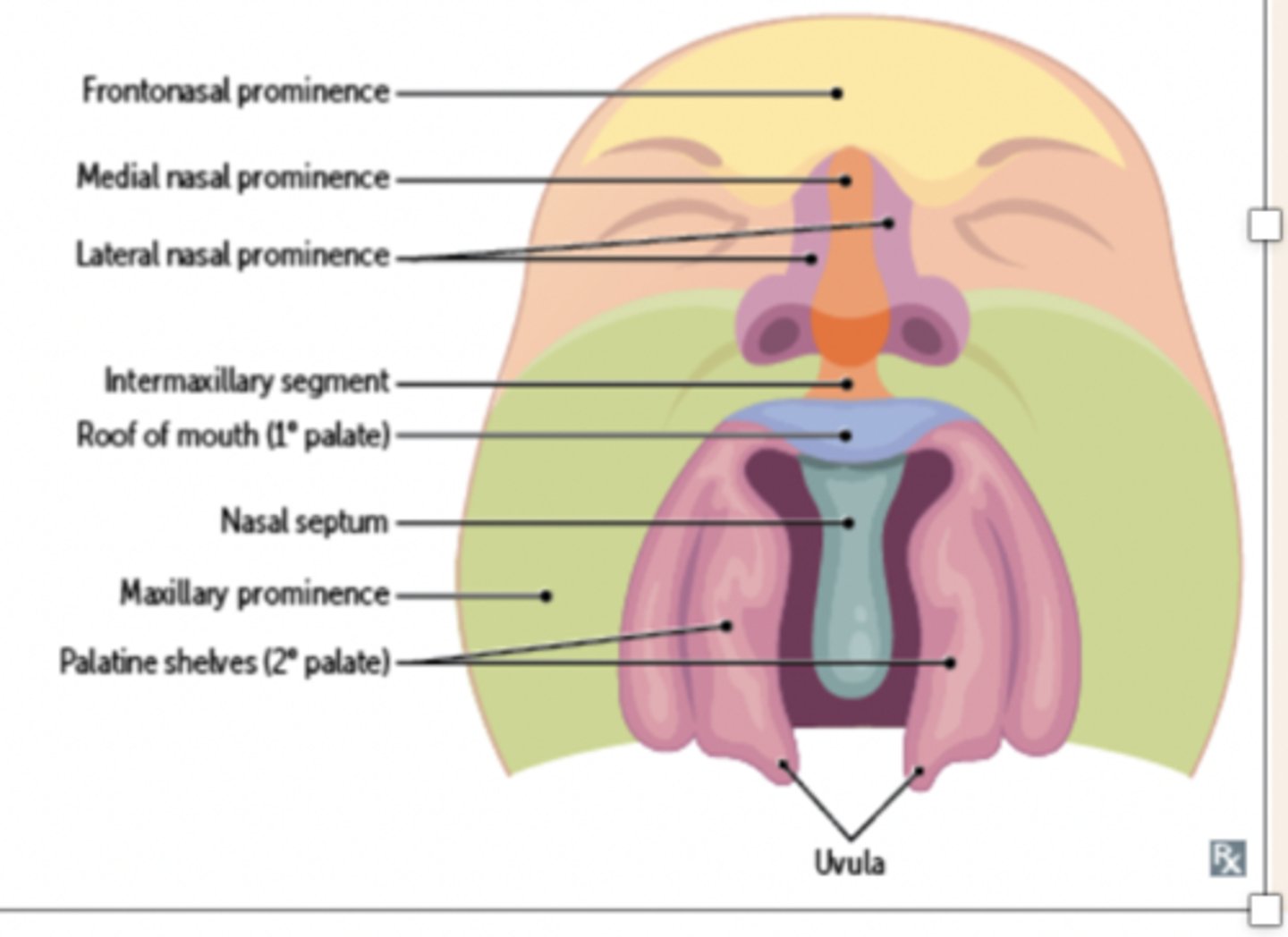
The Primary Palate (hard palate) is formed by what?
Merging of the medial nasal processes
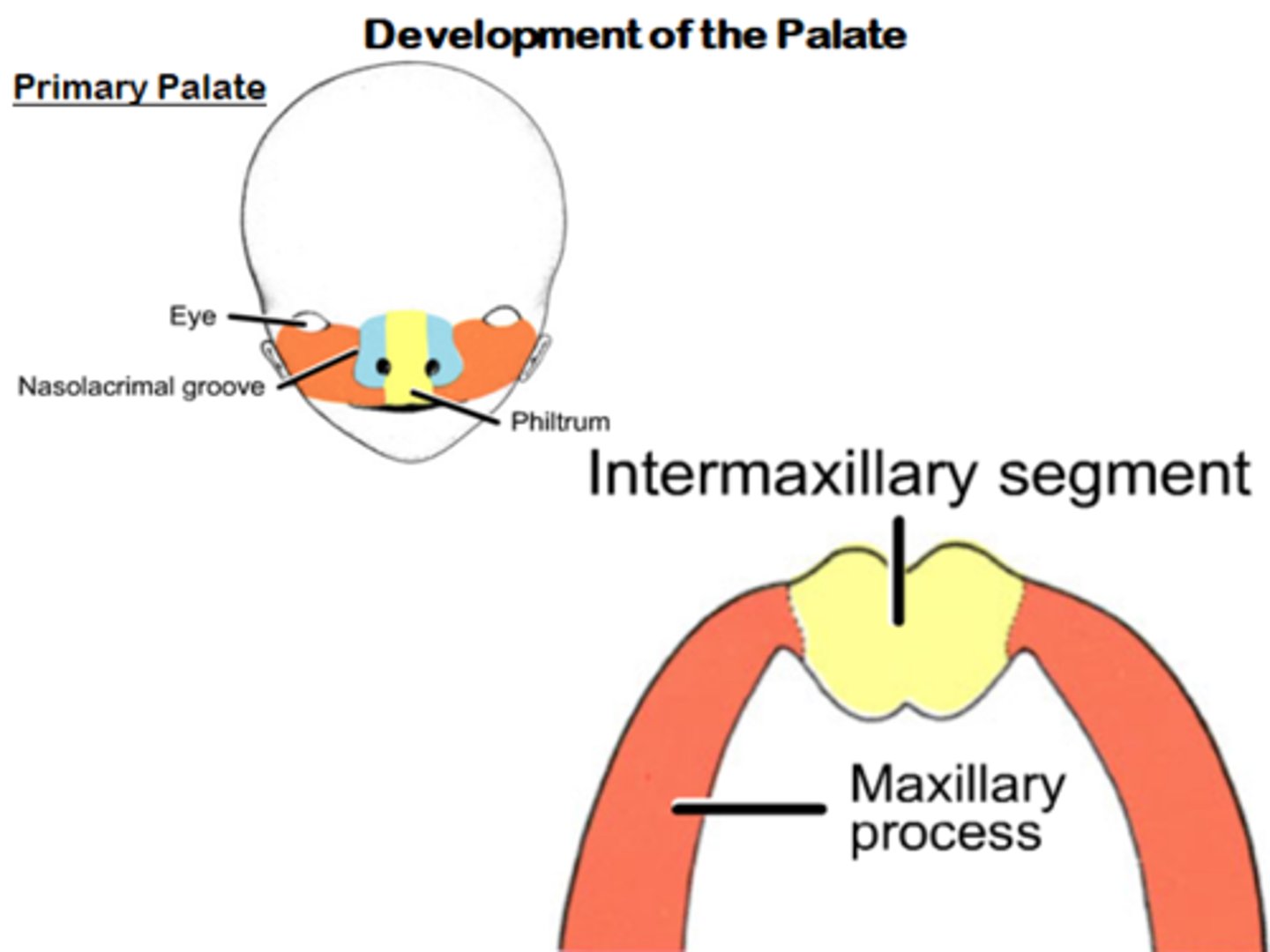
What does the primary palate from?
Forms the intermaxillary segment
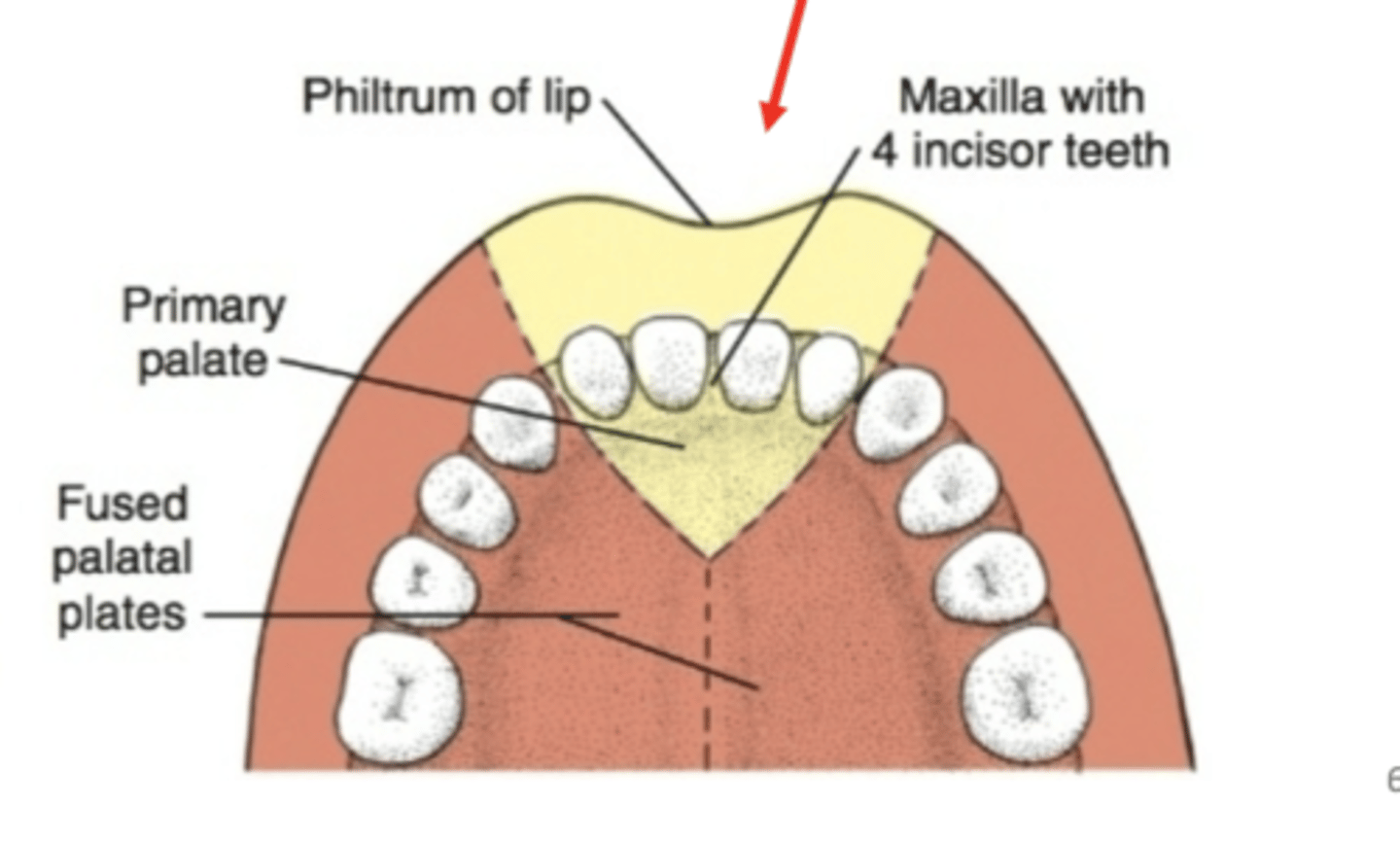
What are the three components of the intermaxillary segment
1. Labial: Philtrum
2. Upper jaw: carries four incisors
3. Palatal: forms primary triangular palate
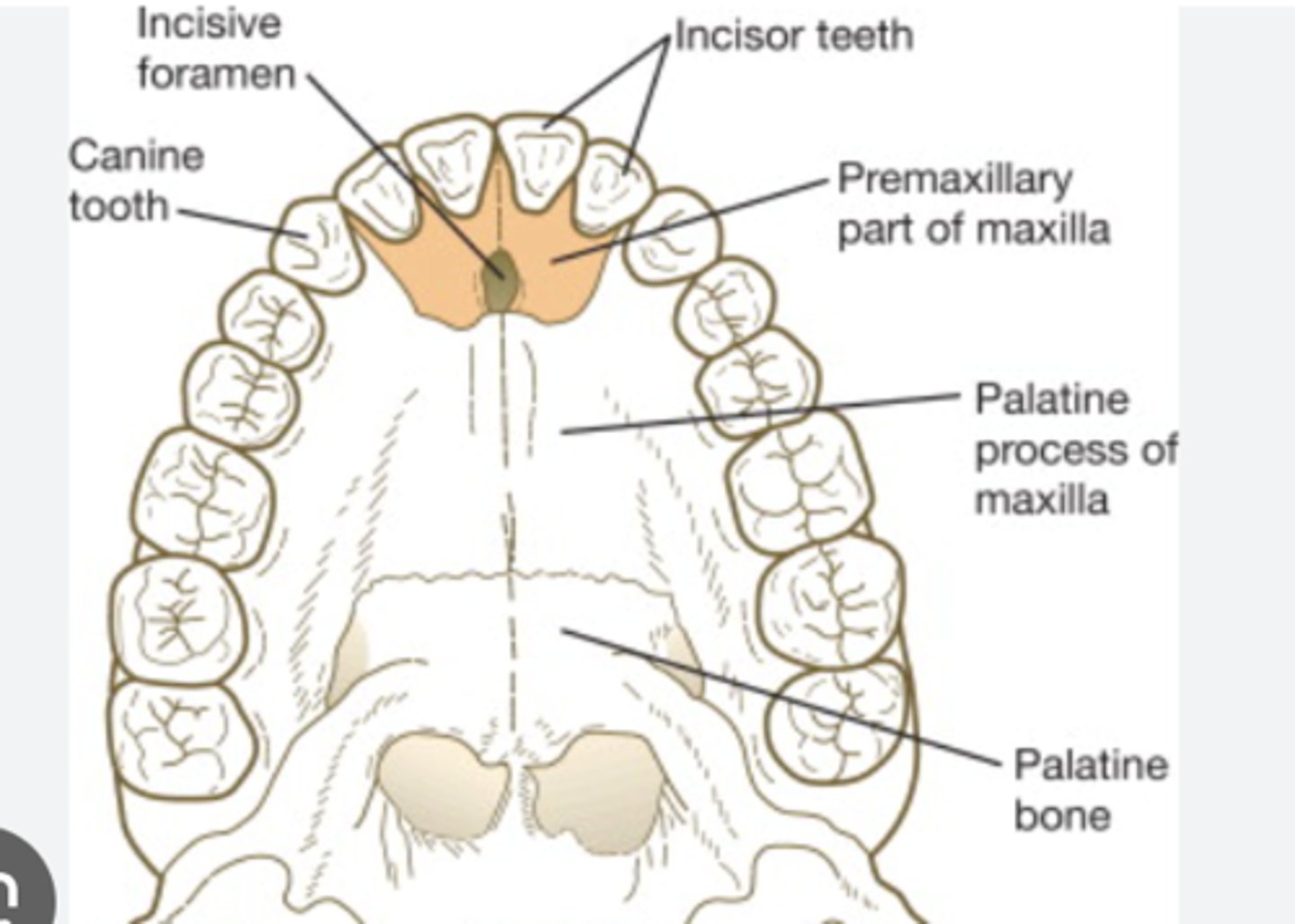
What does the intermaxillary segment give rise to?
Gives rise to premaxilla (triangularbone bearing the four incisors)
The secondary palate (hard and soft) is formed by?
merging of the maxillary processes from 1st pharyngeal arch
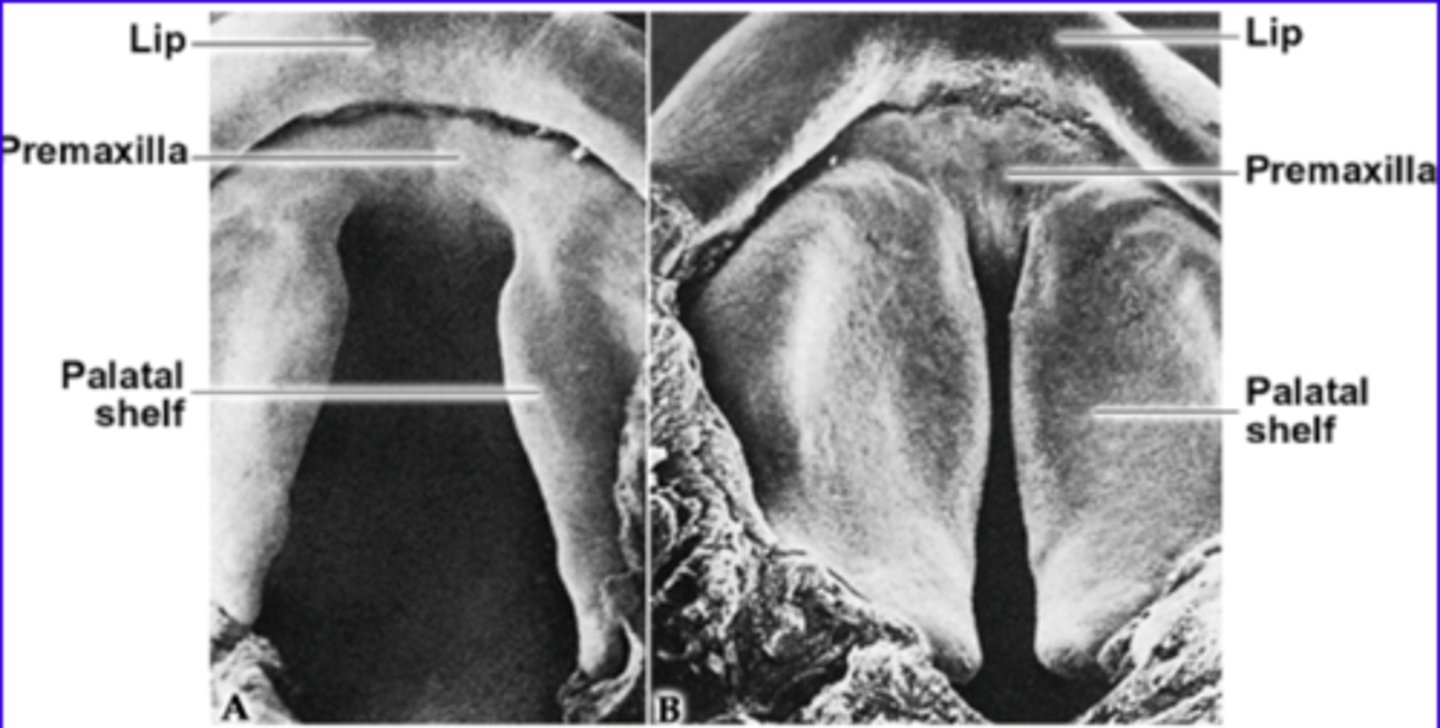
When is the fusion of the palatal shelves compete?
Week 12 of development
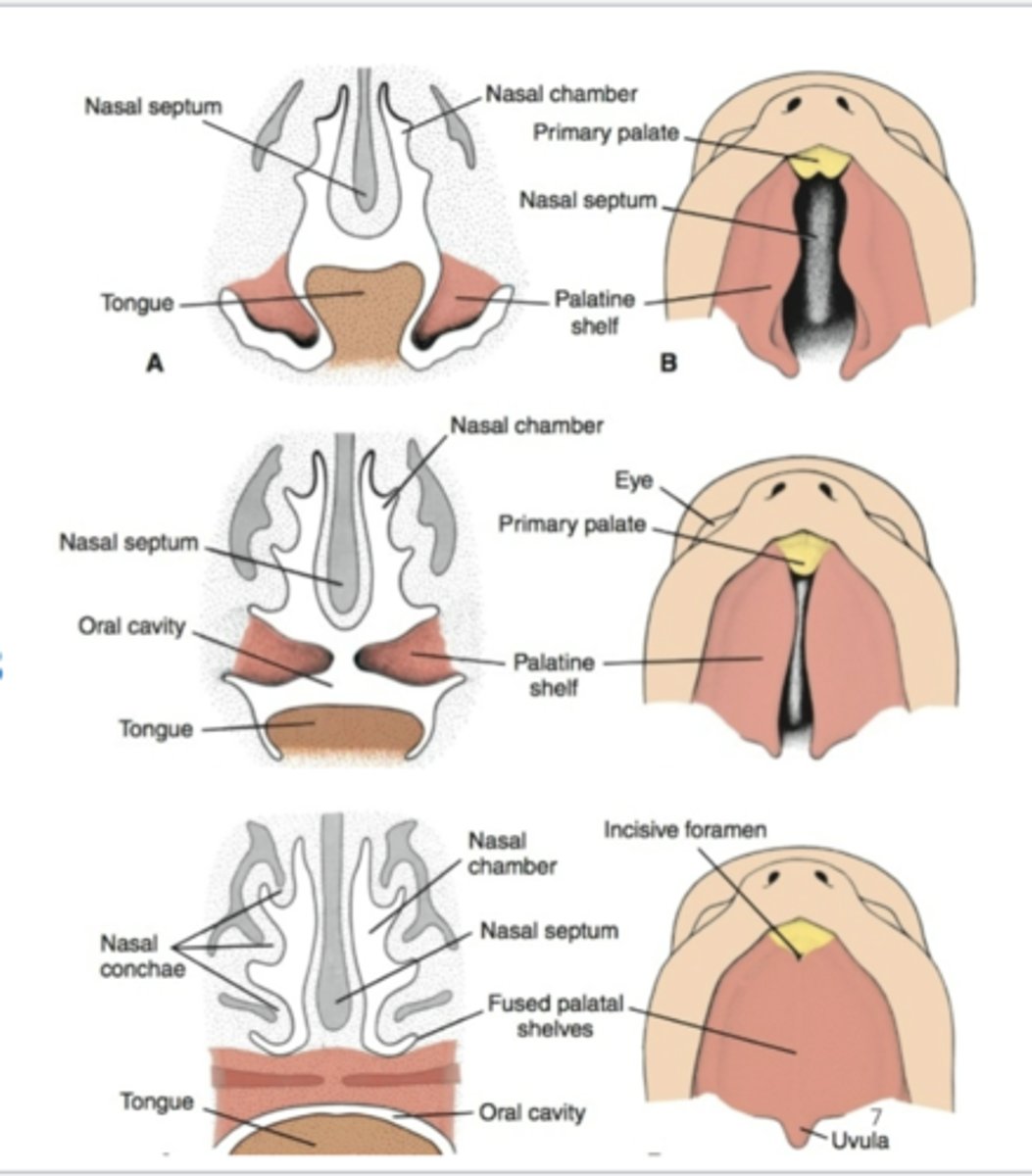
The fusion of the palatal shelves begin when? in what kind of direction? What does it simultaneously fuse with? (2)
Fusion of palatal shelves begins by week 8 in a cranio-caudal direction.
Simultaneous fusion with primary palate and nasal septum
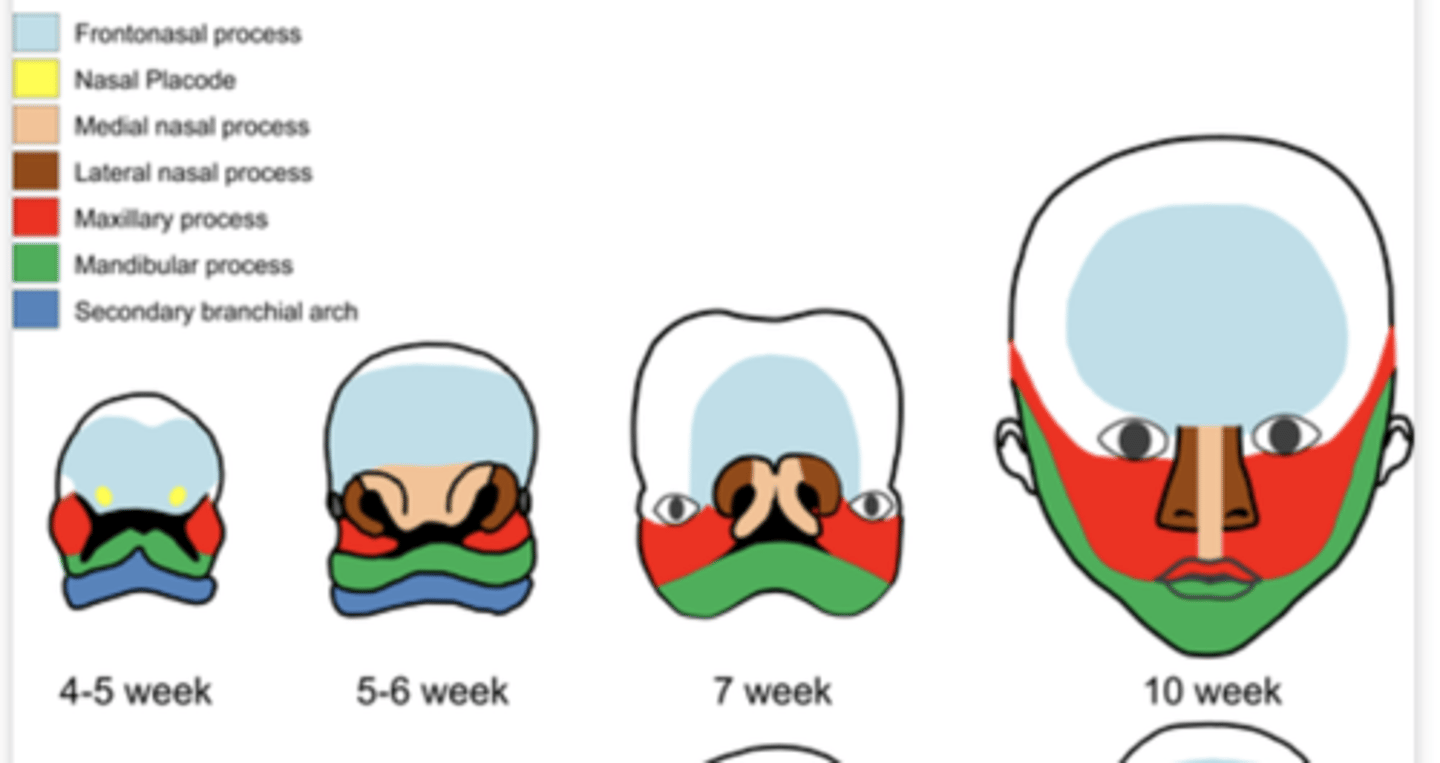
What is the cause of cleft lip?
Defective fusion of medial nasal processes with maxillary process
What is the consequence of a failure of the palatal shelves to fuse?
Cleft palate
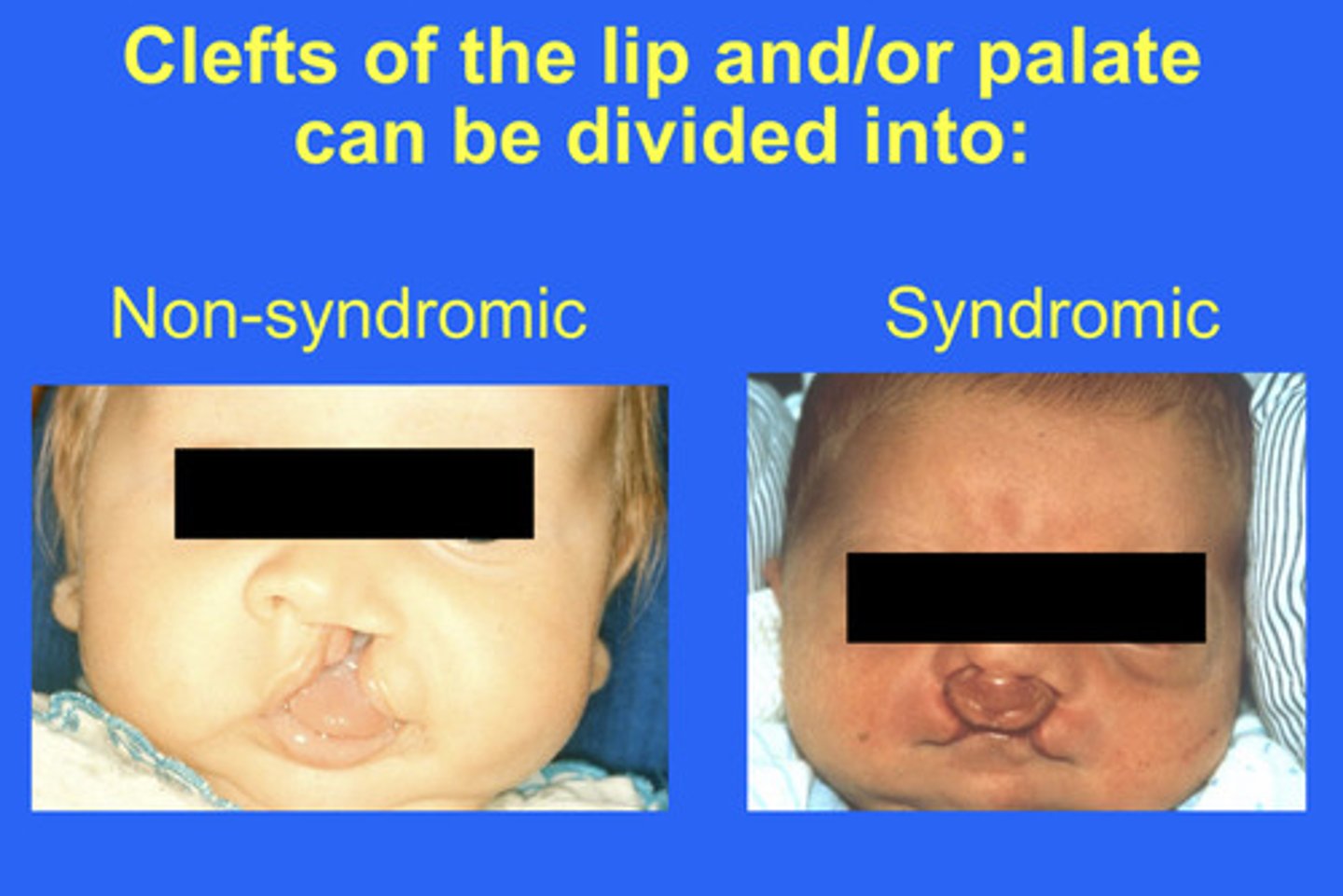
what are syndromic clefts caused by? (4)
1. Heterogeneous causes
- Major genes
- Minor genes
- Environmental factors
2. Maternal alcoholism (also increases risk of syndromic clefts)
3. Maternal tobacco use (twofold risk)
4. Use of anticonvulsant therapy (phenytoin up to tenfold risk)
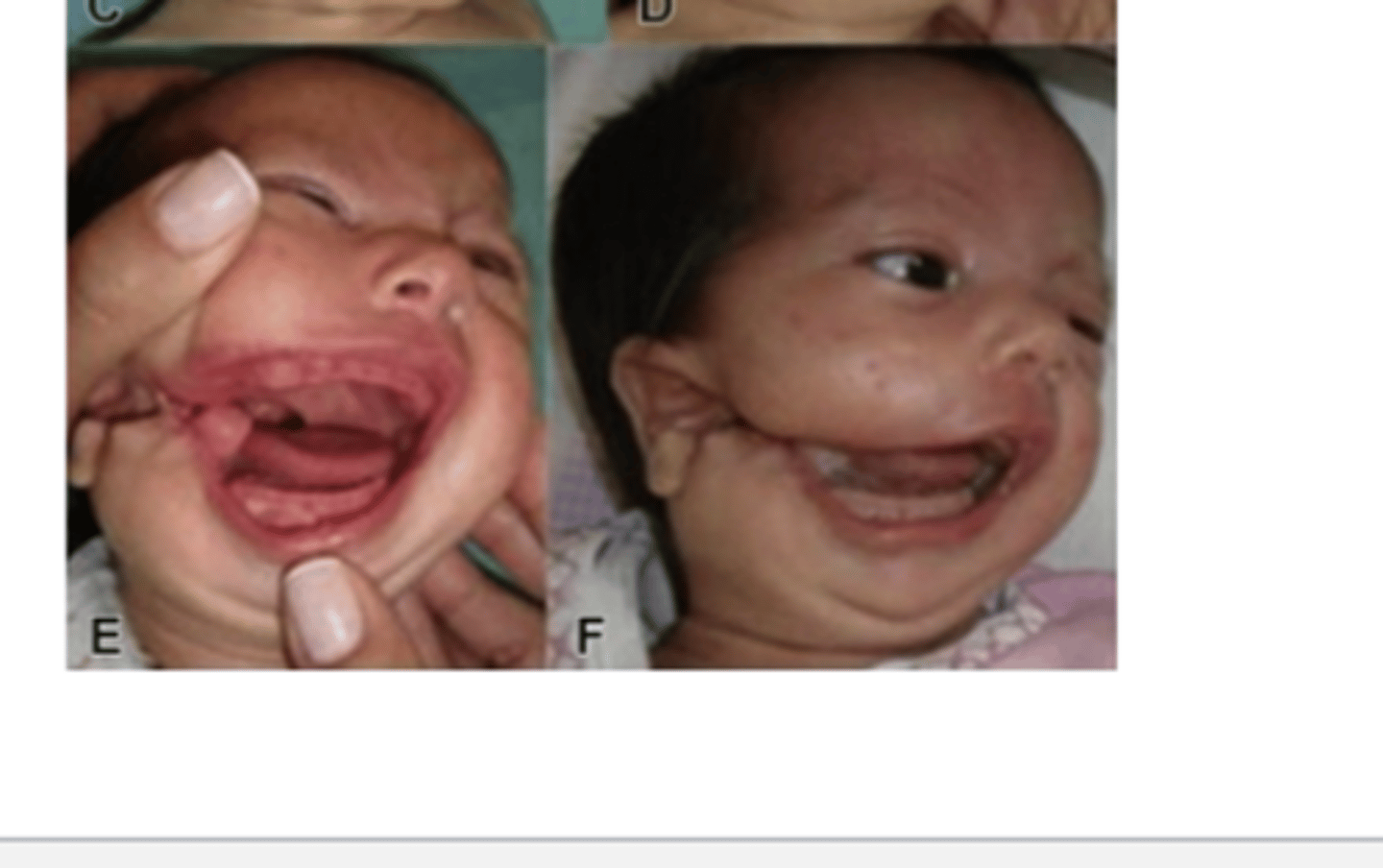
Lateral facial clefts (rare) are formed from the lack of fusion of what? (2)
Lack of fusion of the maxillary and mandibular processes
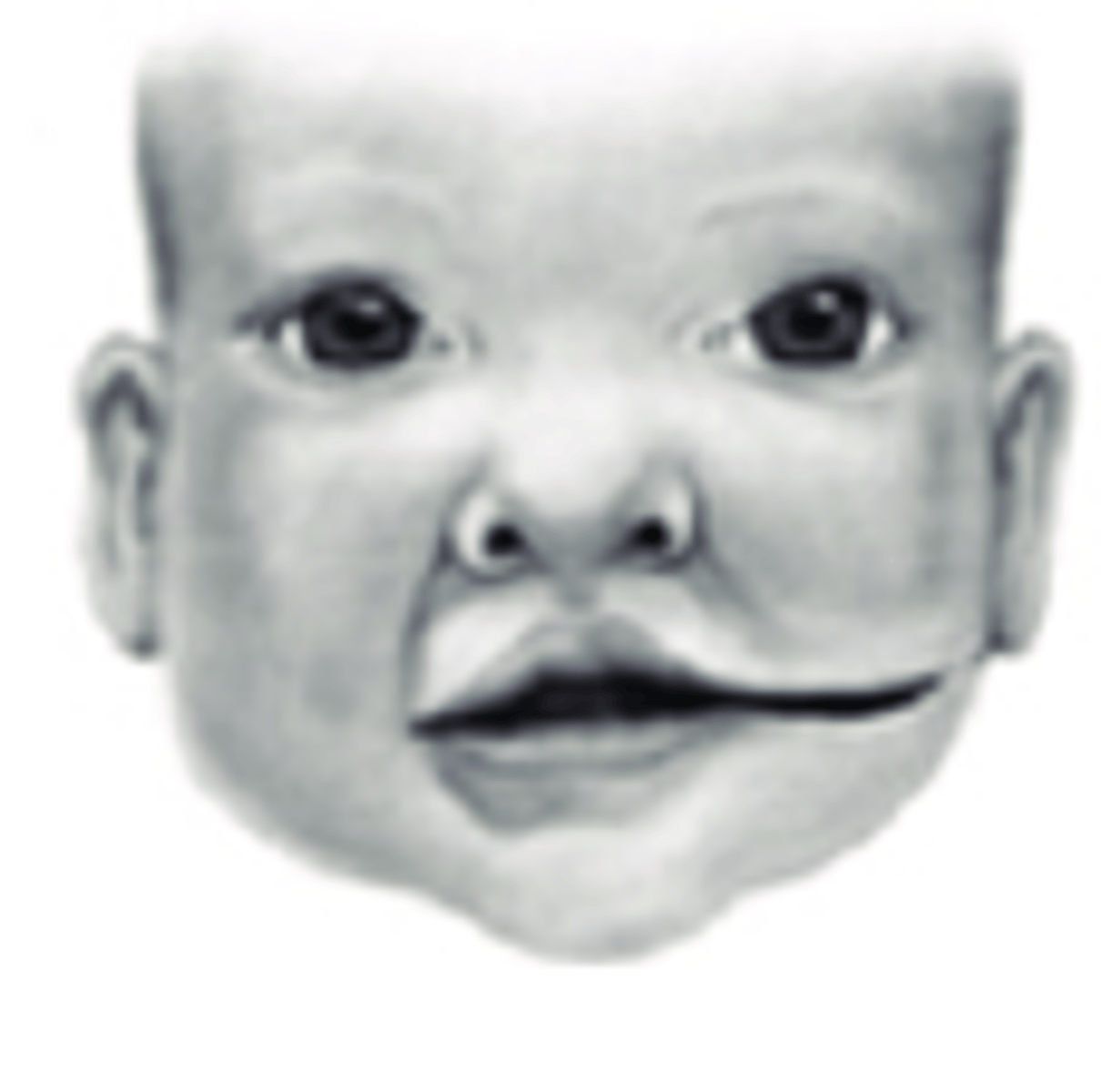
What are lateral facial clefts associated with? (3)
1. Accessory mandible
2. Absent parotid gland
3. Peripheral facial weakness
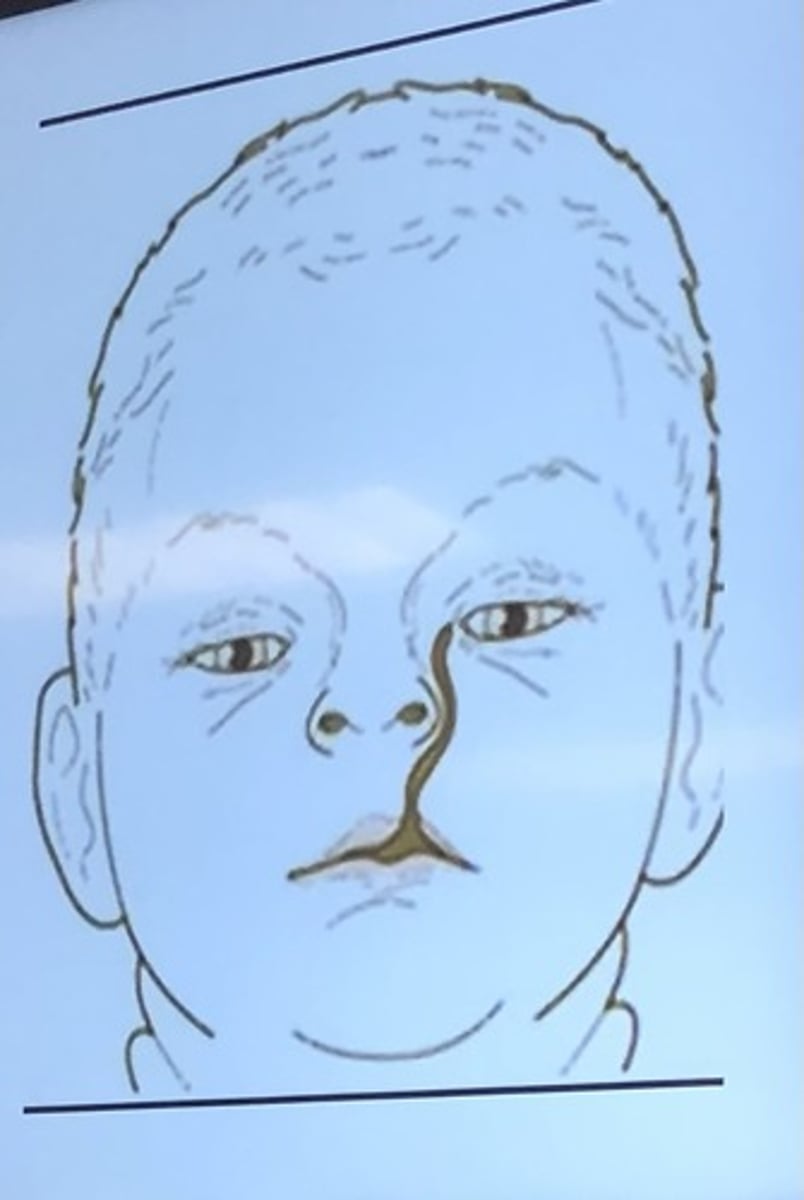

Oblique facial clefts are formed by the lack of fusion of what? (2)
lateral nasal process with the maxillary process
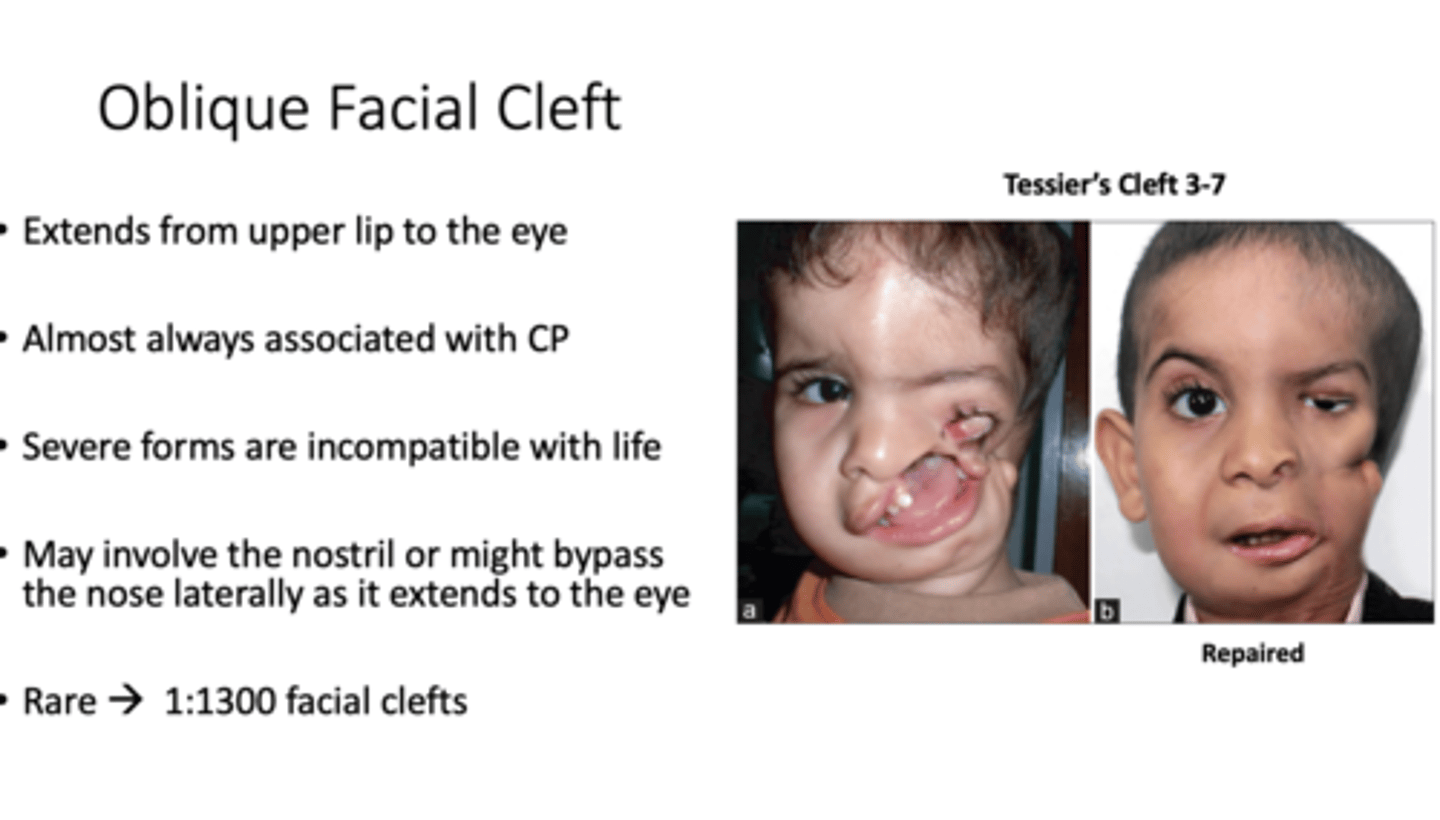
What is the oblique facial cleft (rare) extend from? what is it almost always associated with?
From upper lip to eye
almost always associated with cleft palate
Severe forms incompatible with life
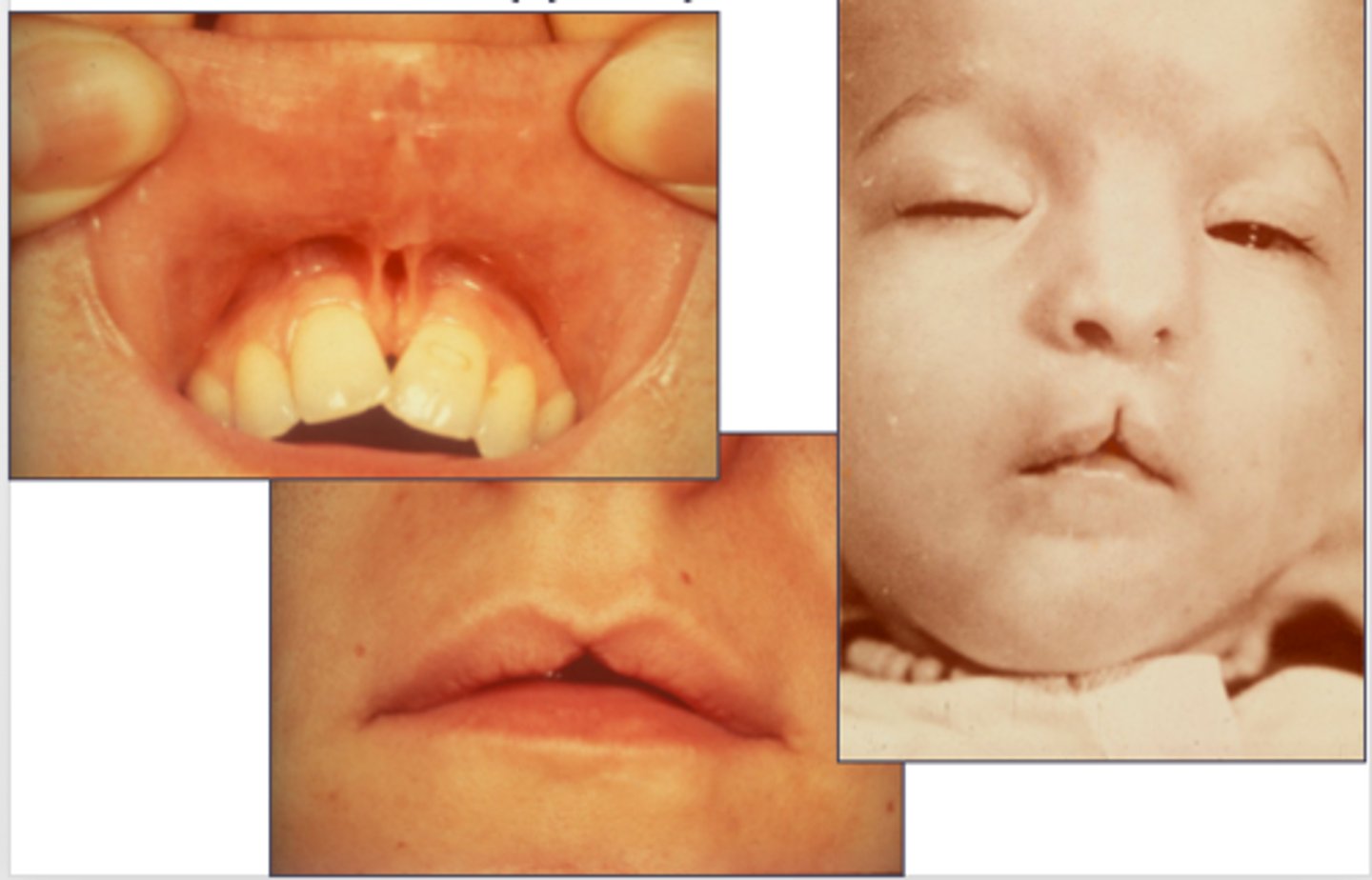
Median cleft of the upper lip (rare) is failure of fusion of what?
Failure of fusion of the medial nasal processes
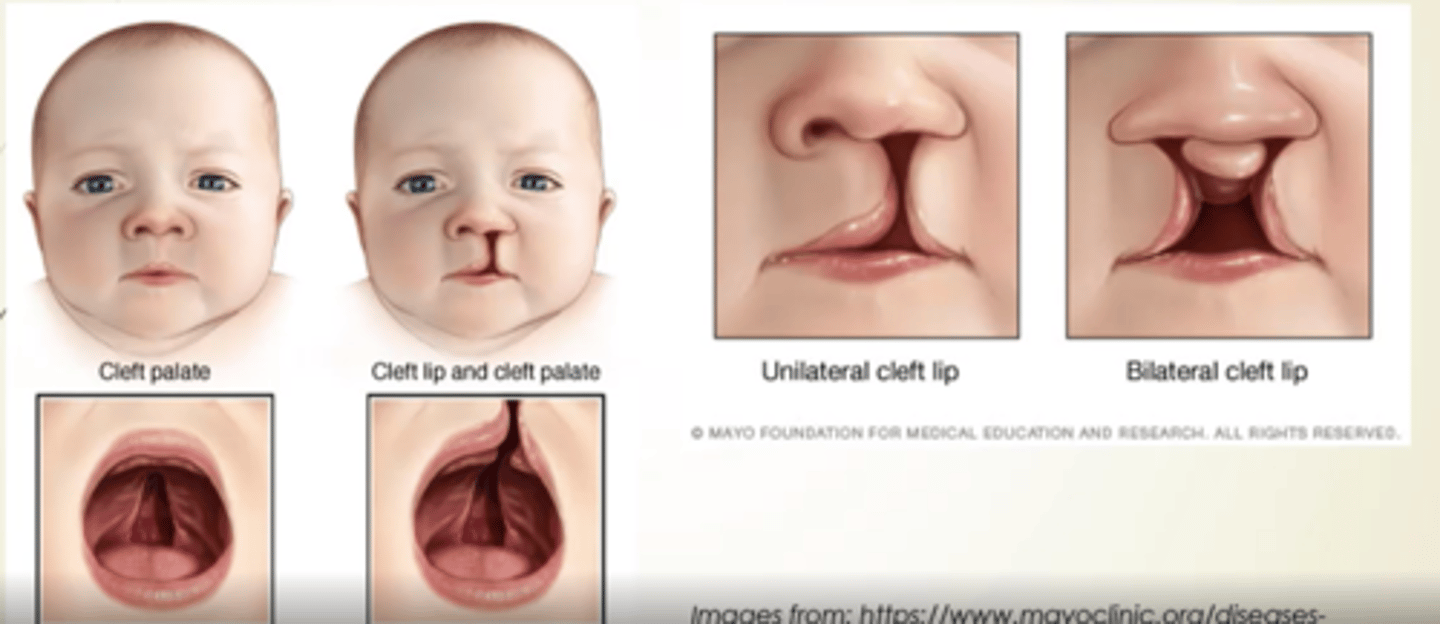
What is one of the most common major congenital defects?
Clefting
What race has the highest prevalence of cleft lip and cleft palate (CL + CP)? What race has the lowest?
Native Americans: the highest prevalence - 3.6 of 1000 births
African Americans: the lowest prevalence - 0.4 of 1000 births
________ is less common than CL + CP
Cleft palate only (CPO)
What sex is CL ± CP more prevalent in?
Severe CL ± CP higher in males
What sex is CPO more prevalent in?
more prevalent in females
- Severe CPO higher in females
Prevalence of clefts of both hard and soft palates are twice as common in what sex?
Females
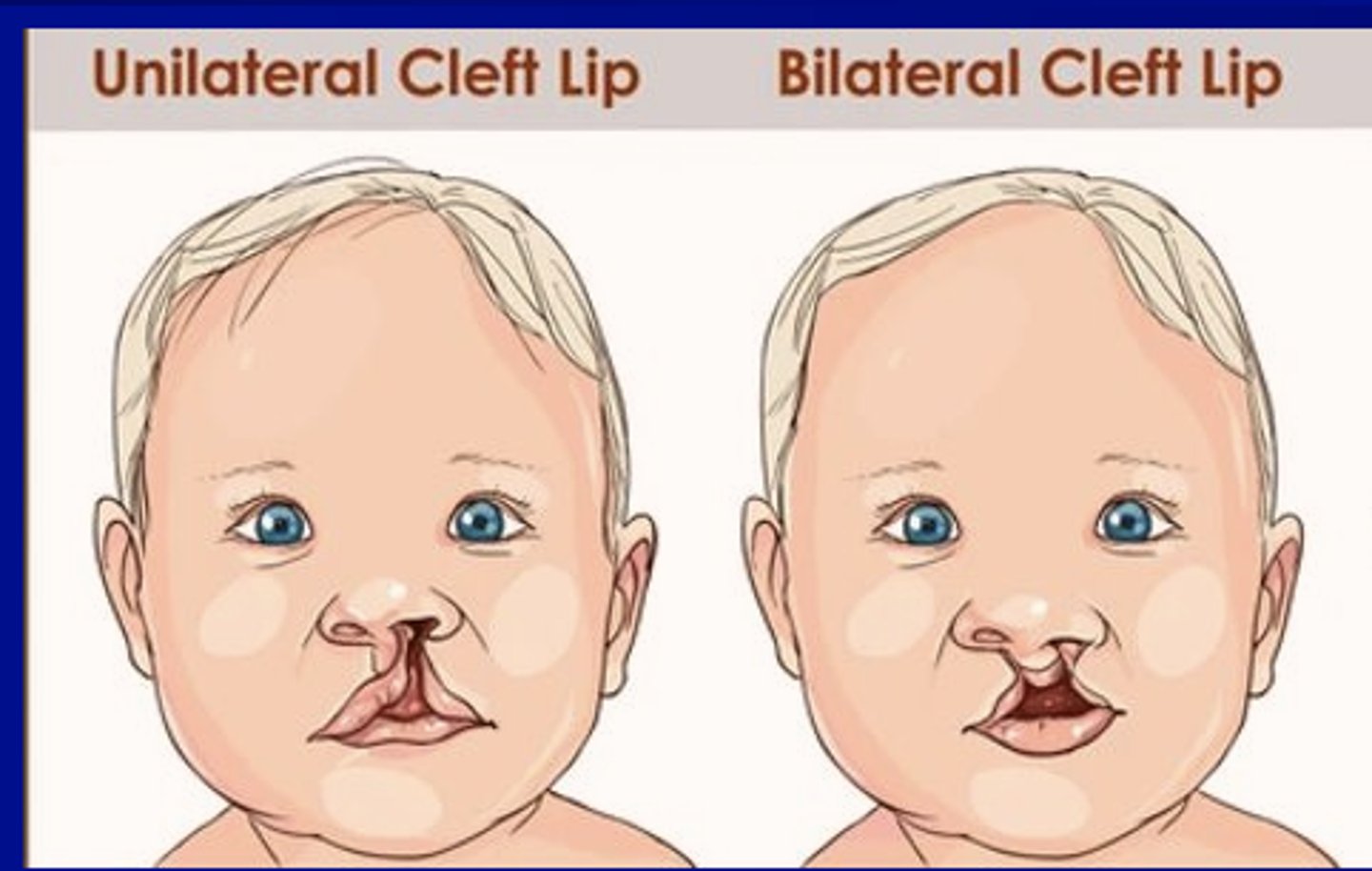
Is unilateral or bilateral cleft lips (CP) more prevalent?
Unilateral CL more prevalent (80%)
Bilateral CL less prevalent (20%)
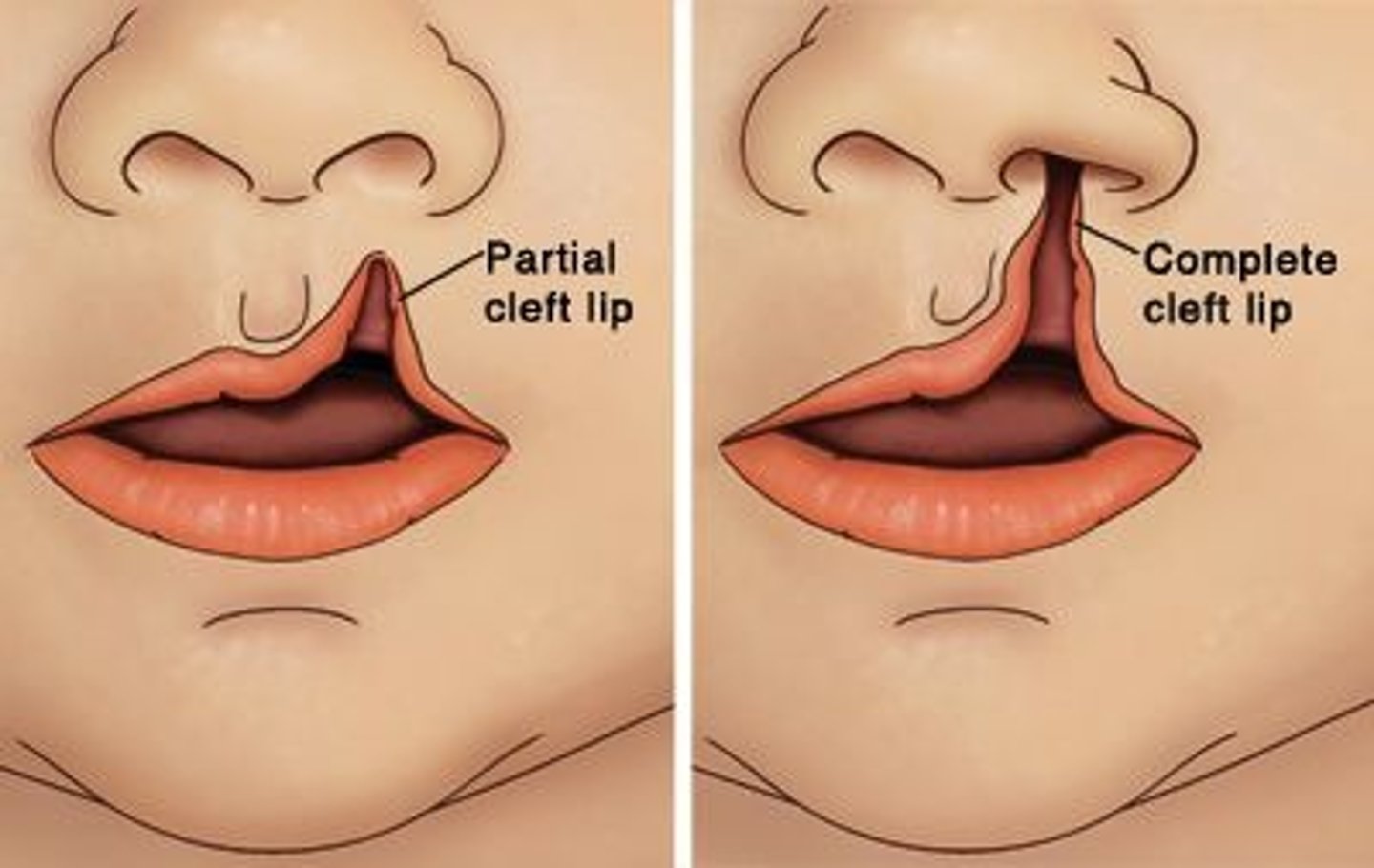
What does complete cleft lip (CCL) extend from?
From the lip to the nostril
incomplete CL: Nose not involved
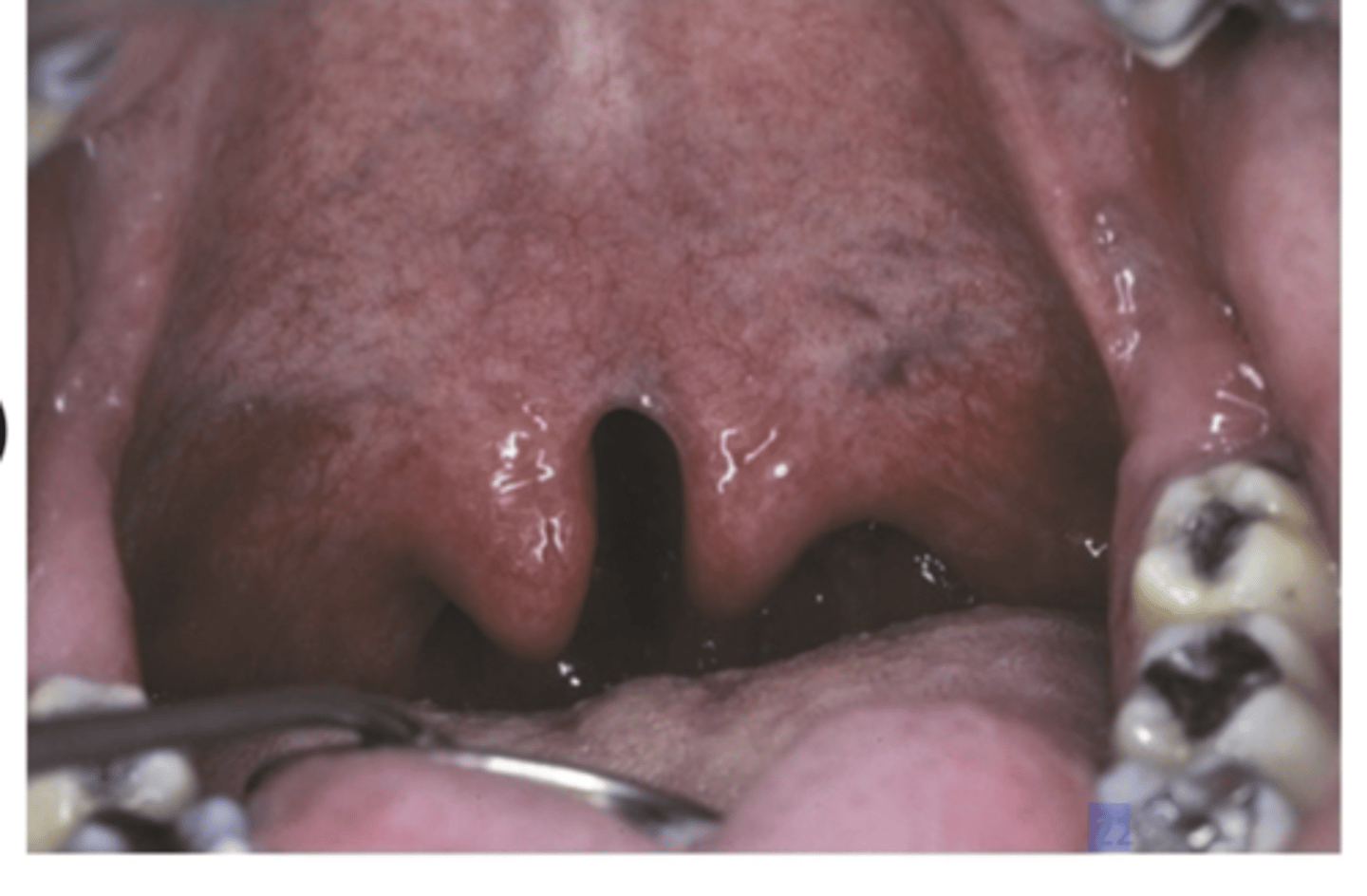
Cleft uvula has a higher prevalence than what? what race is it seen higher and lower in?
Higher prevalence than CP
Asian and Native Americans: 1 in 10 (highest)
African Americans: 1 in 250 (lowest)
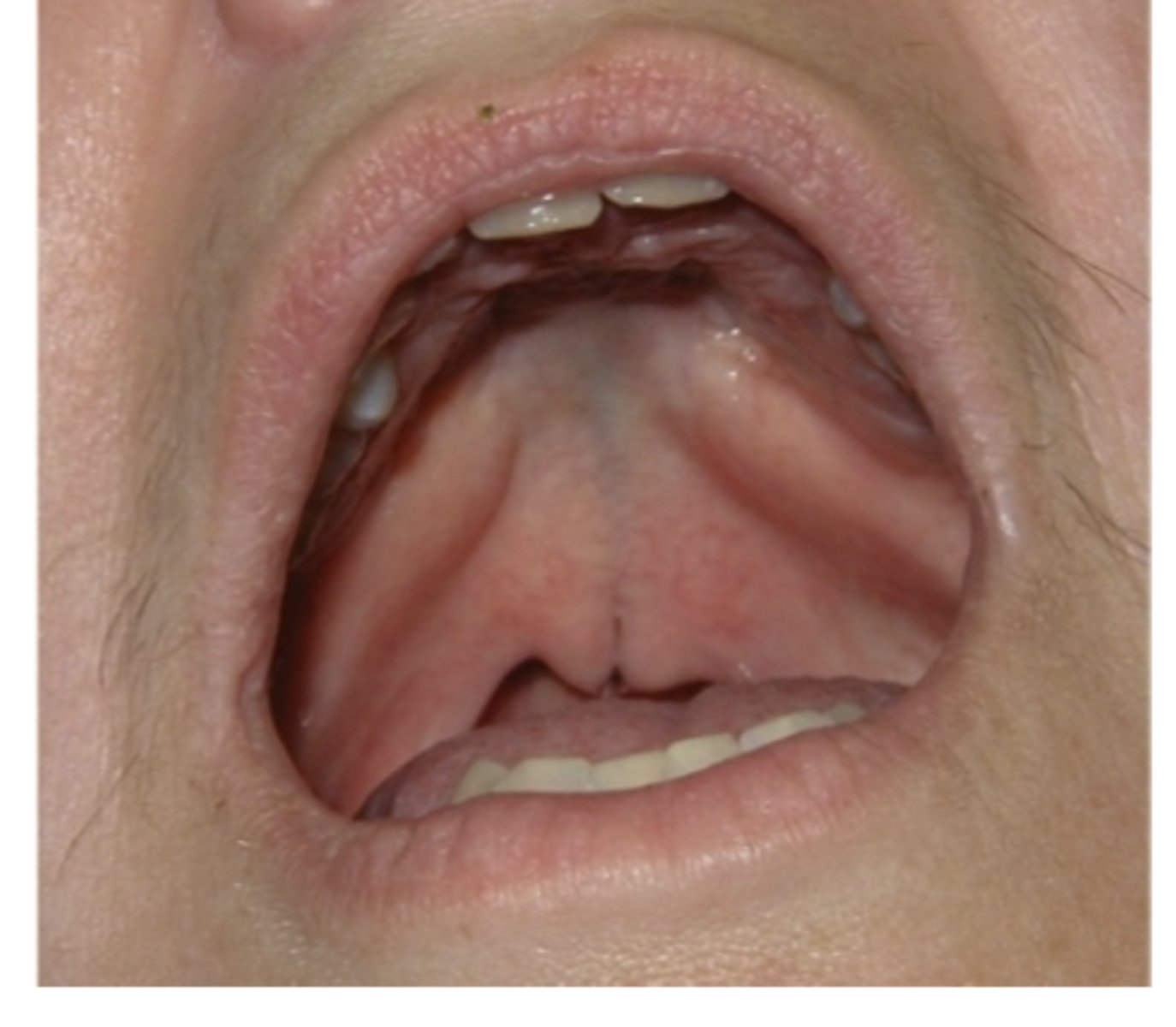
What is submuscous palatal cleft defect in?
Defect of muscles of soft palate
Frequent notch in bone along posterior margin of hard palate.
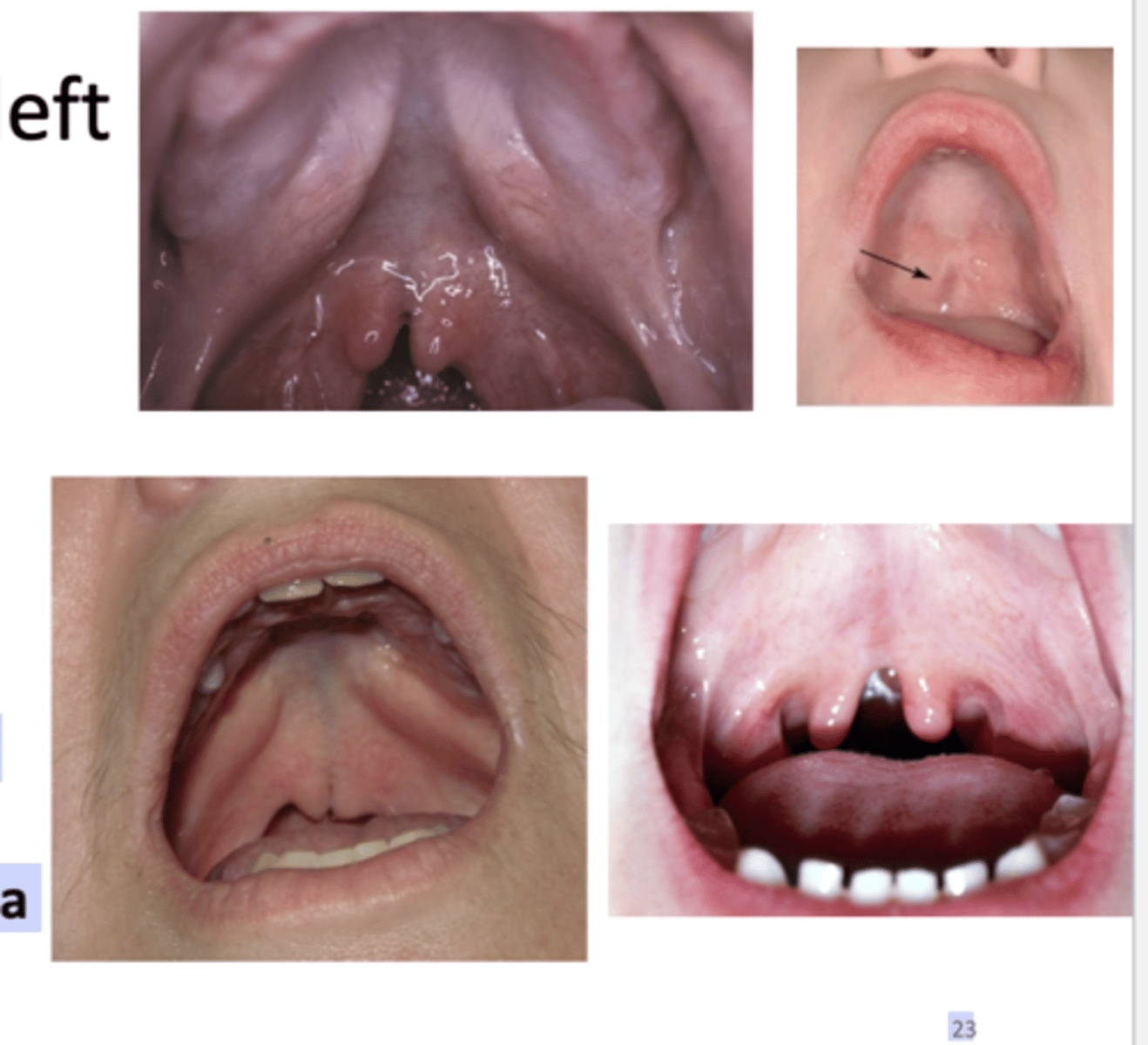
How is submucous palatal cleft appear as? how is it best identified? what is it asscoiated with?
- Occasionally appears as a bluish midline discoloration
- Best identified by palpation with blunt instrument
- Can be associated with cleft uvula
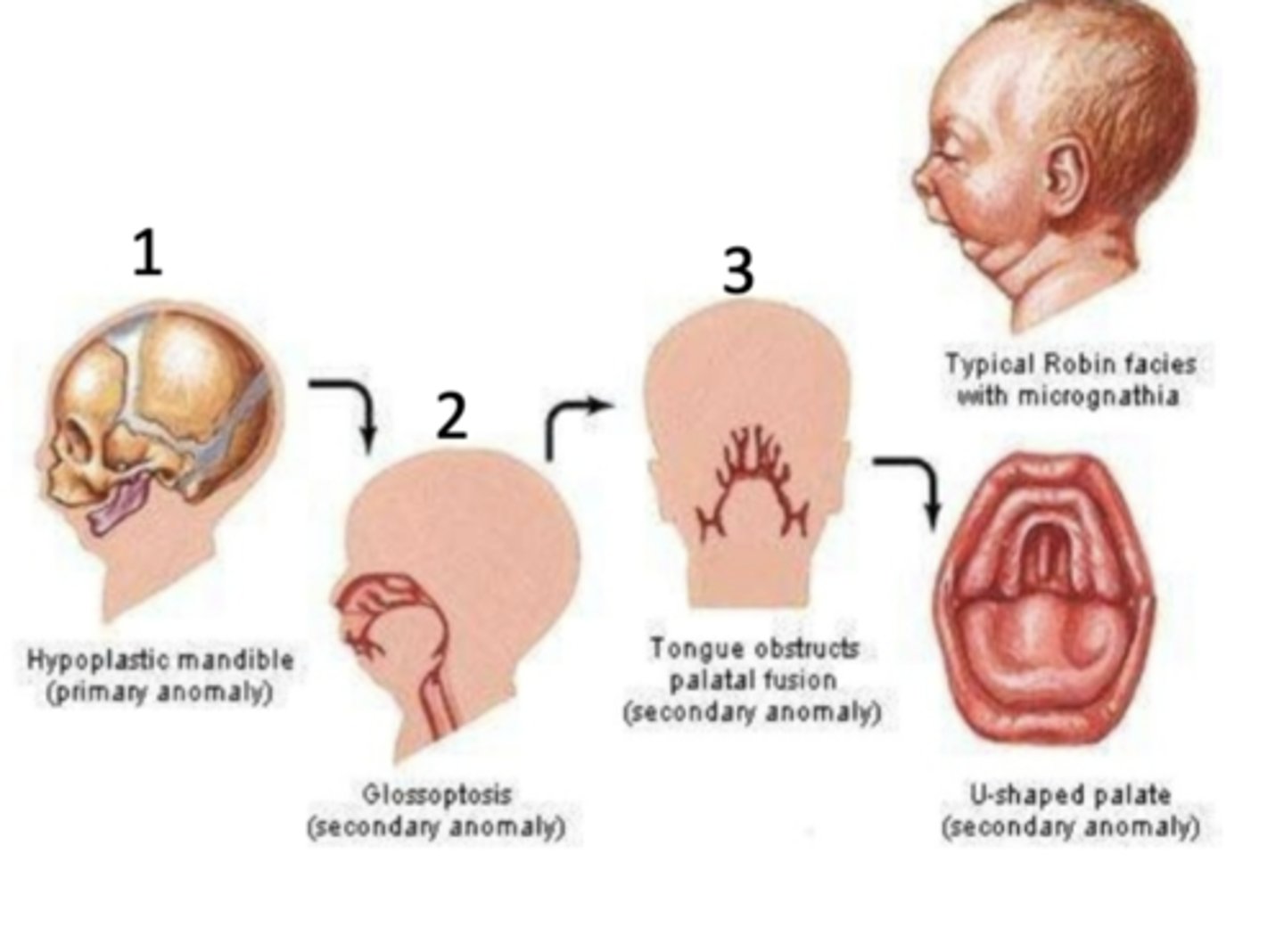
What are the three key features of Pierre Robin Sequence?
1. Cleft Palate (CP)
2. Mandibular micrognatia (abnormally small lower jaw (mandible))
3. Glossoptosis (posterior displacement of the tongue)
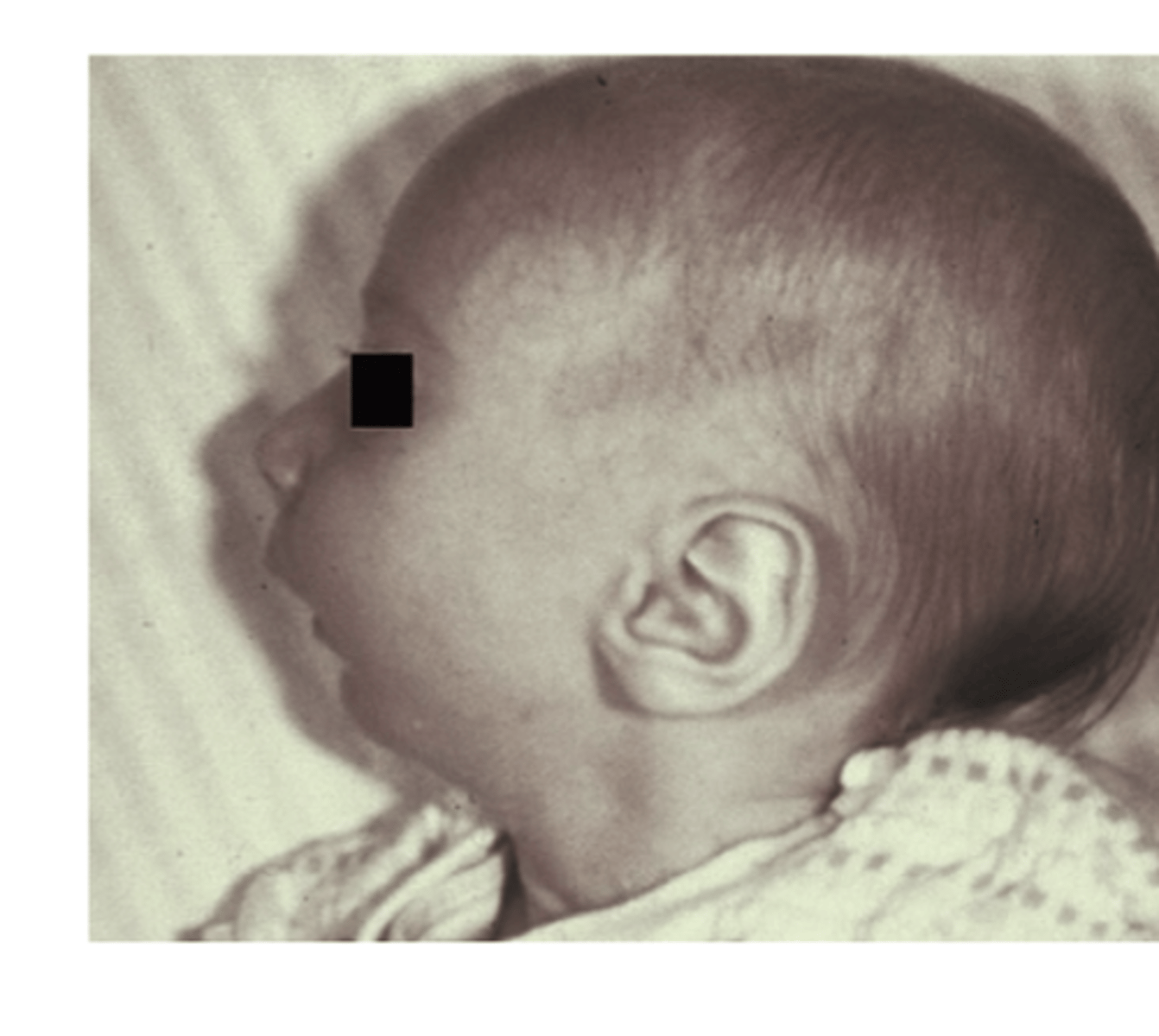
What issue does Pierre Robin Sequence cause?
Airway obstruction due to Lower posterior displacement of tongue
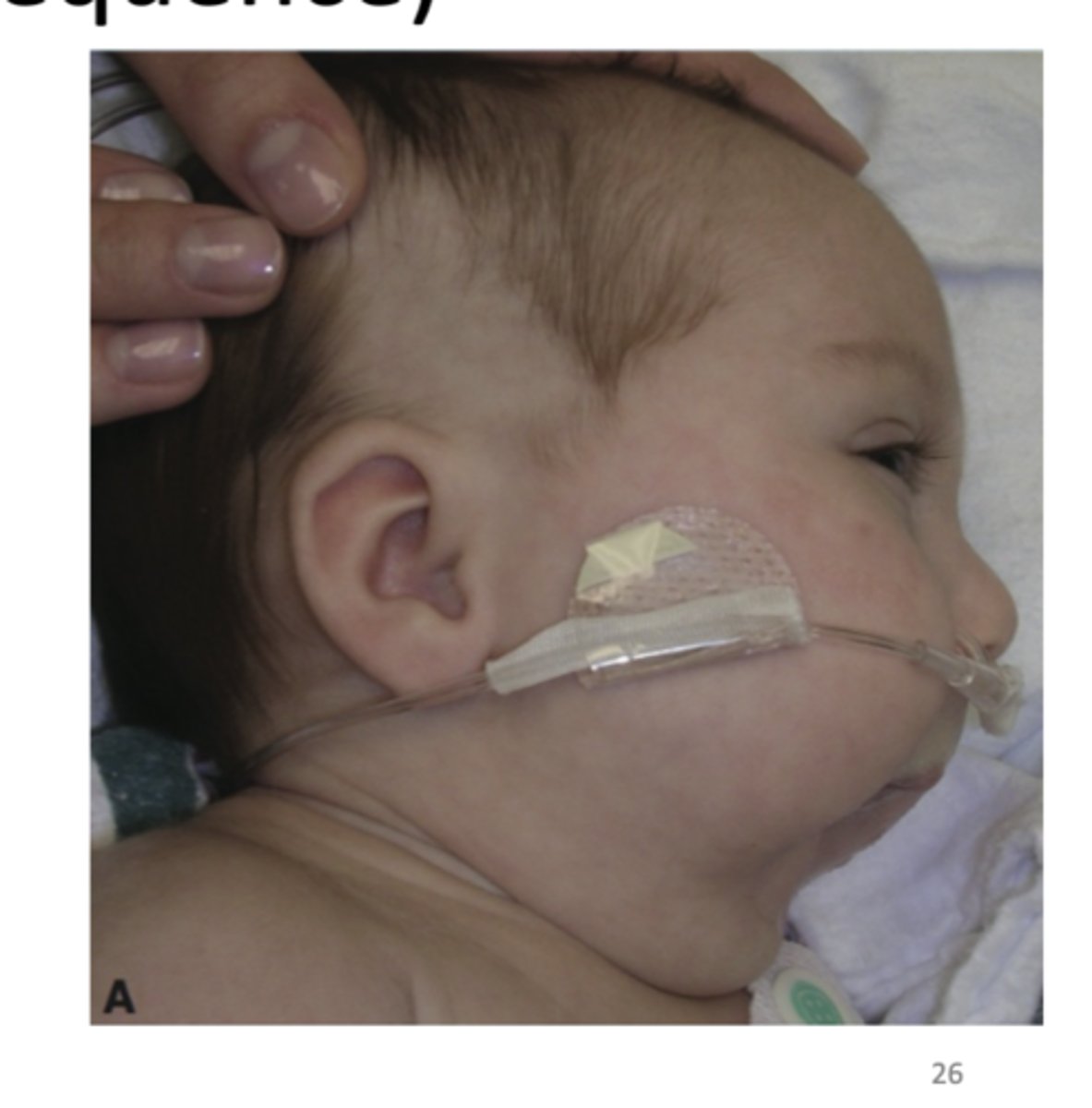
What are some clinical manifestations of the Pierre Robin sequence?
1. Respiratory difficulty mostly in supineposition
2. Can cause asphyxia
3. U-shaped palatal cleft
4. Psychosocial difficulties
5. Feeding and speech difficulties
6. Malocclusion: Collapse of maxillary arch
- Missing teeth
- Supernumerary teeth
The treatment of orofacial clefts is a Multidisciplinary approach which can include what physicians?
1. Pediatrician
2. Oral and maxillofacial surgeon
3. Otolaryngologist
4. Plastic surgeon
5. Pediatric dentist
6. Orthodontist
7. Prosthodontist
8. Speech pathologist
9. Geneticist
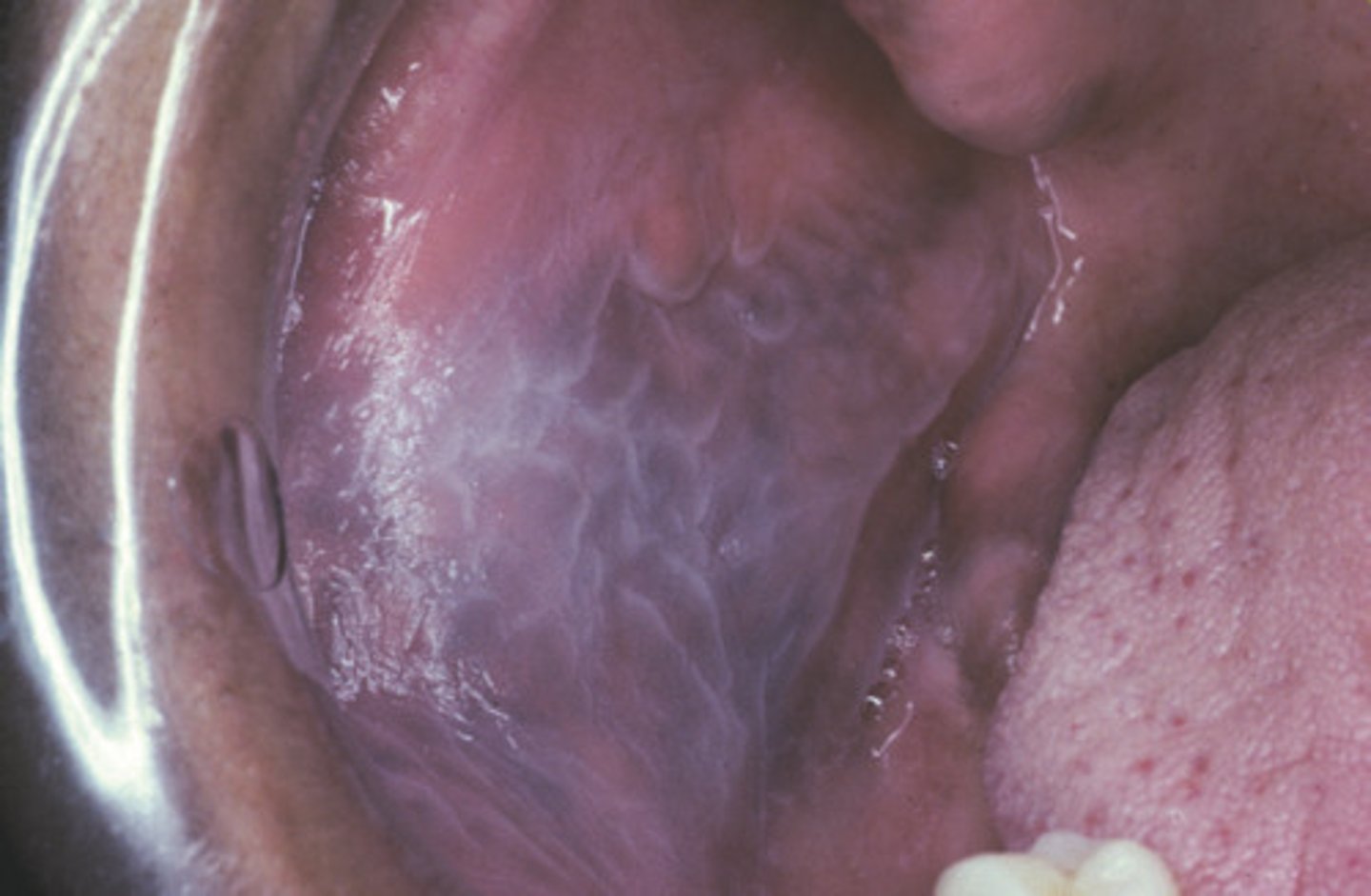
Leukoedema is what? what is the known cause and what race is it more prevalent in?
Common oral mucosa condition
- Unknown cause
- More prevalent in African Americans
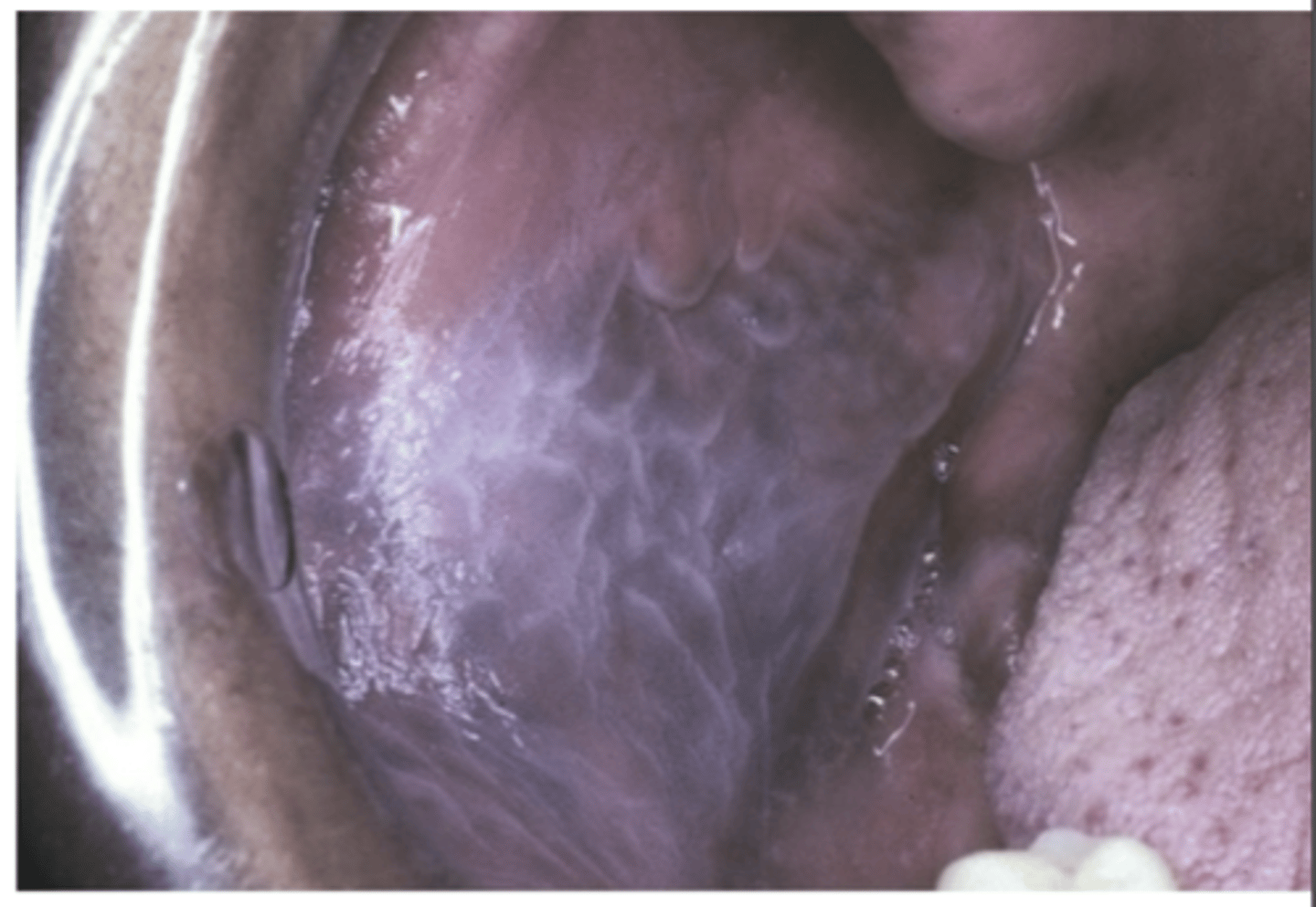
What is Leukodema considered? Who is it more common and severe in? What type of condition is it?
Considered an anatomical variation
- More common and severe in smokers
- Less pronounced with smoking cessation
- Benign condition
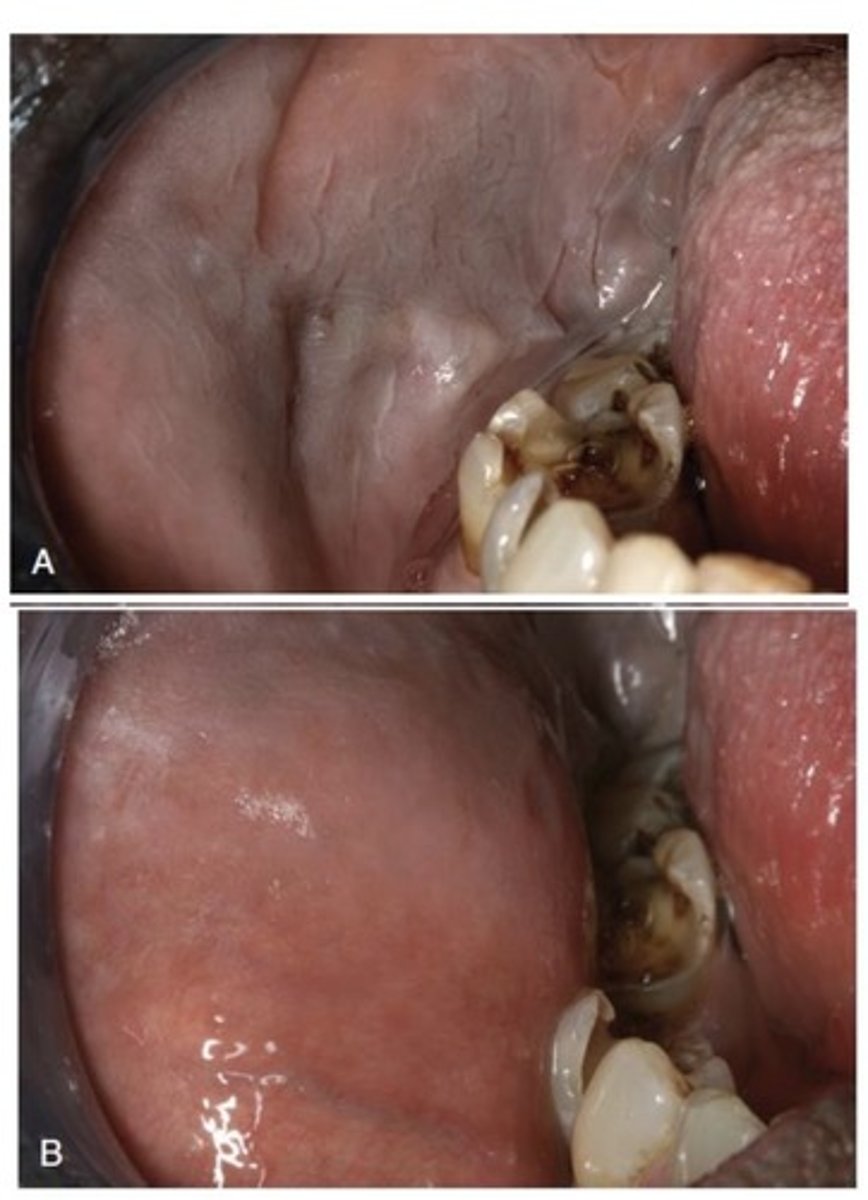
How does Leukodema appear? What is it typically?
- Diffuse, gray-white, milky, opalescent appearance
- Folded surface
- Wrinkles or whitish streaks
- Lesions do not rub off
- Typically bilateral in oral mucosa
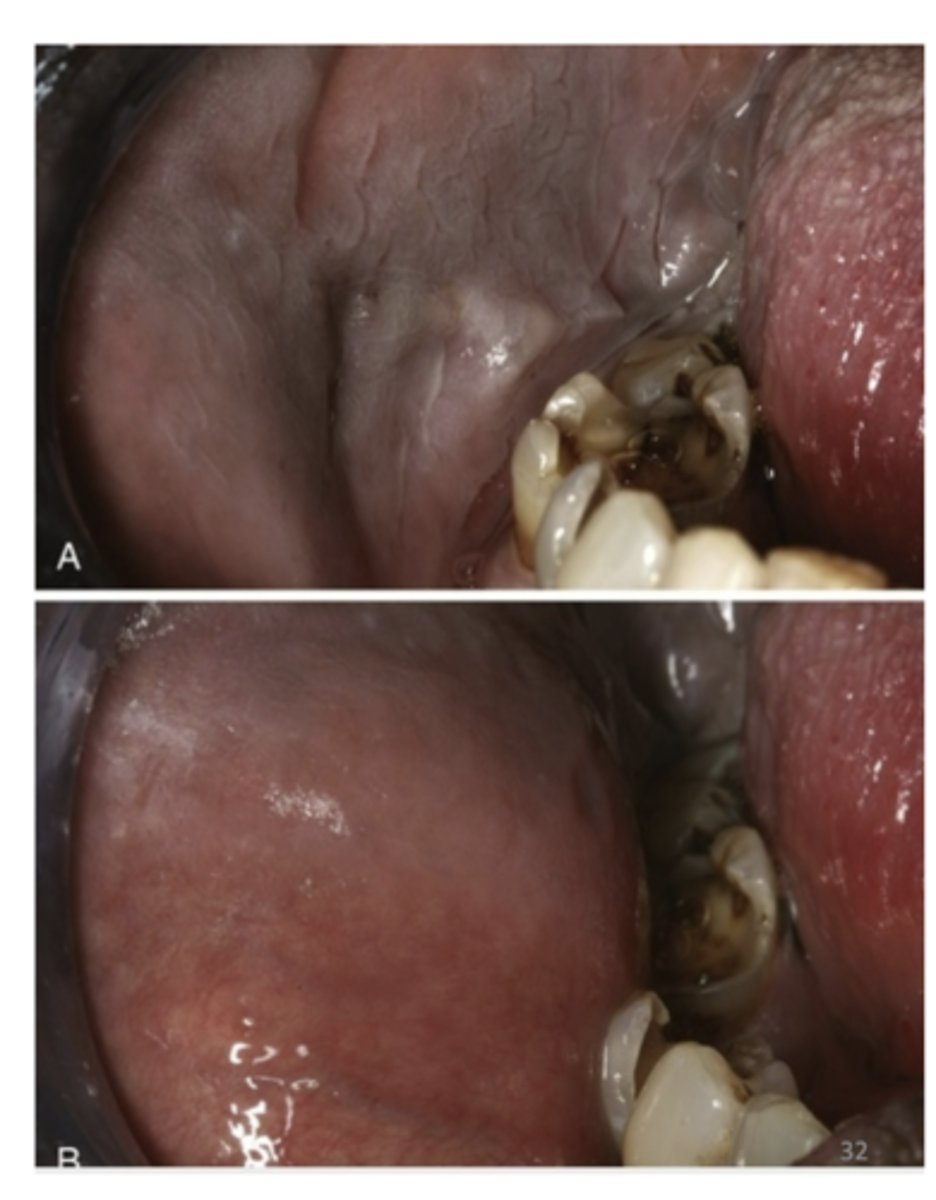
What is the Diagnosis of Leukodema?
White appearance diminishes or disappears with eversion of the cheek (pulling of the cheek)
What is the differential diagnosis of Leukodema? (3)
1. Leukoplakia
2. Candidiasis
3. Lichen planus
If it stayed white when pulling the cheek it's more than likely Leukoplakia.
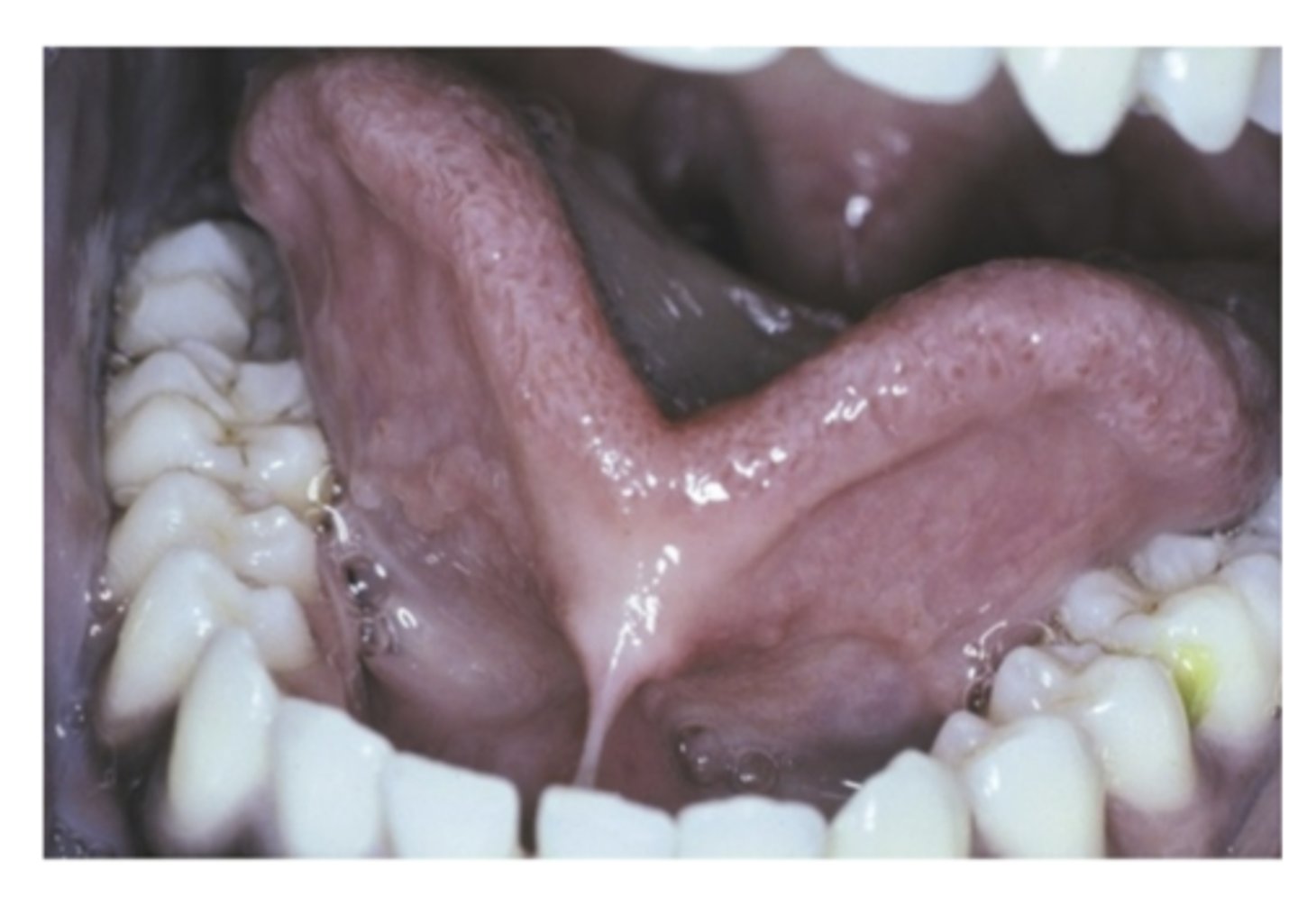
What is Ankyloglossia? what is it caused by? What sex is more affected?
Tongue-Tie
Developmental condition
- Short and thick lingual frenum
- Limitation of tongue movement
Males are more affected.
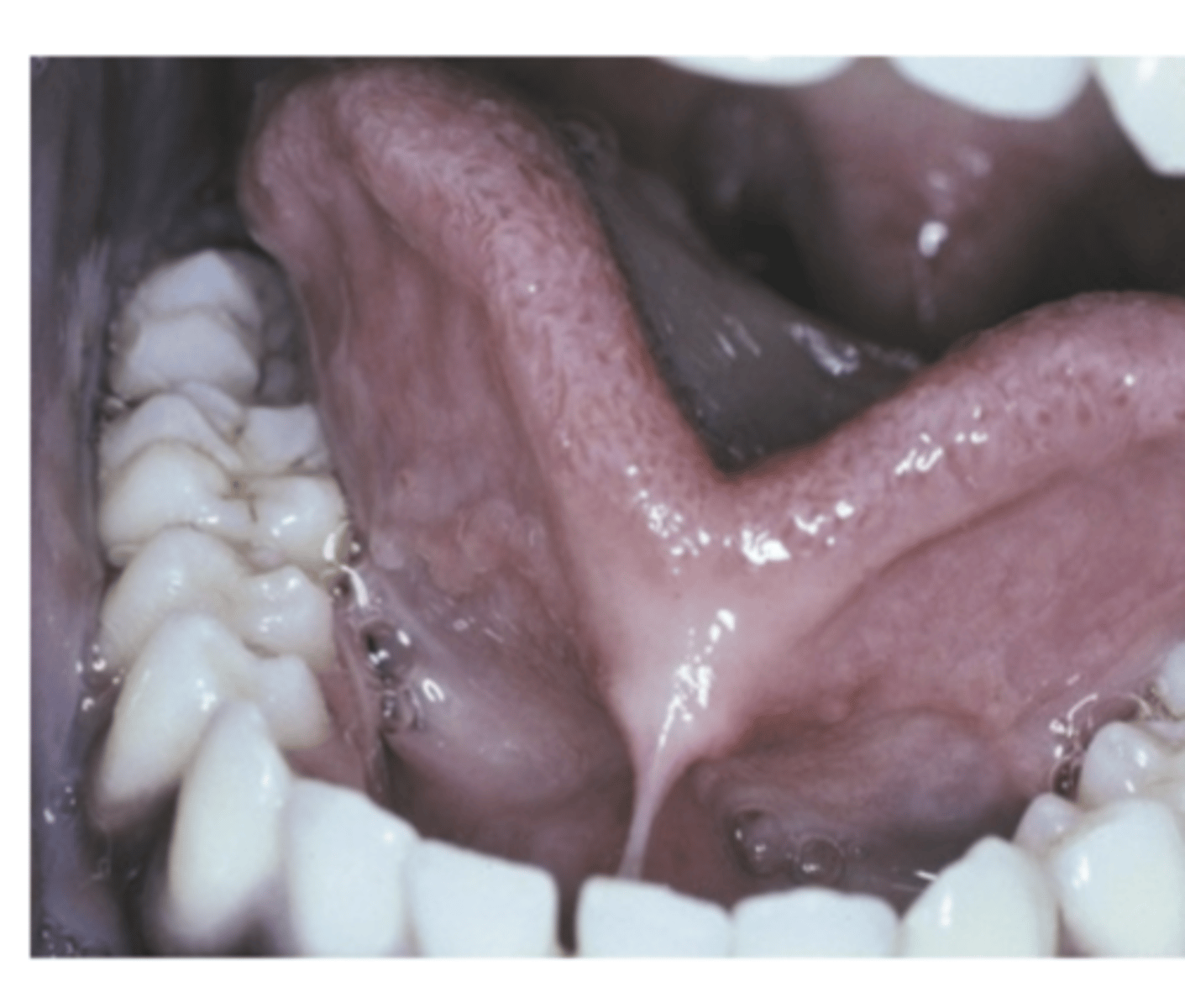
What are the severe cases of Ankyloglossia (3)?
- Fusion of the tongue to the floor of the mouth
- Occasional fusion of frenum to the tip of the tongue
- Slight clefting of the tip
Speech difficulties (mostly minor)
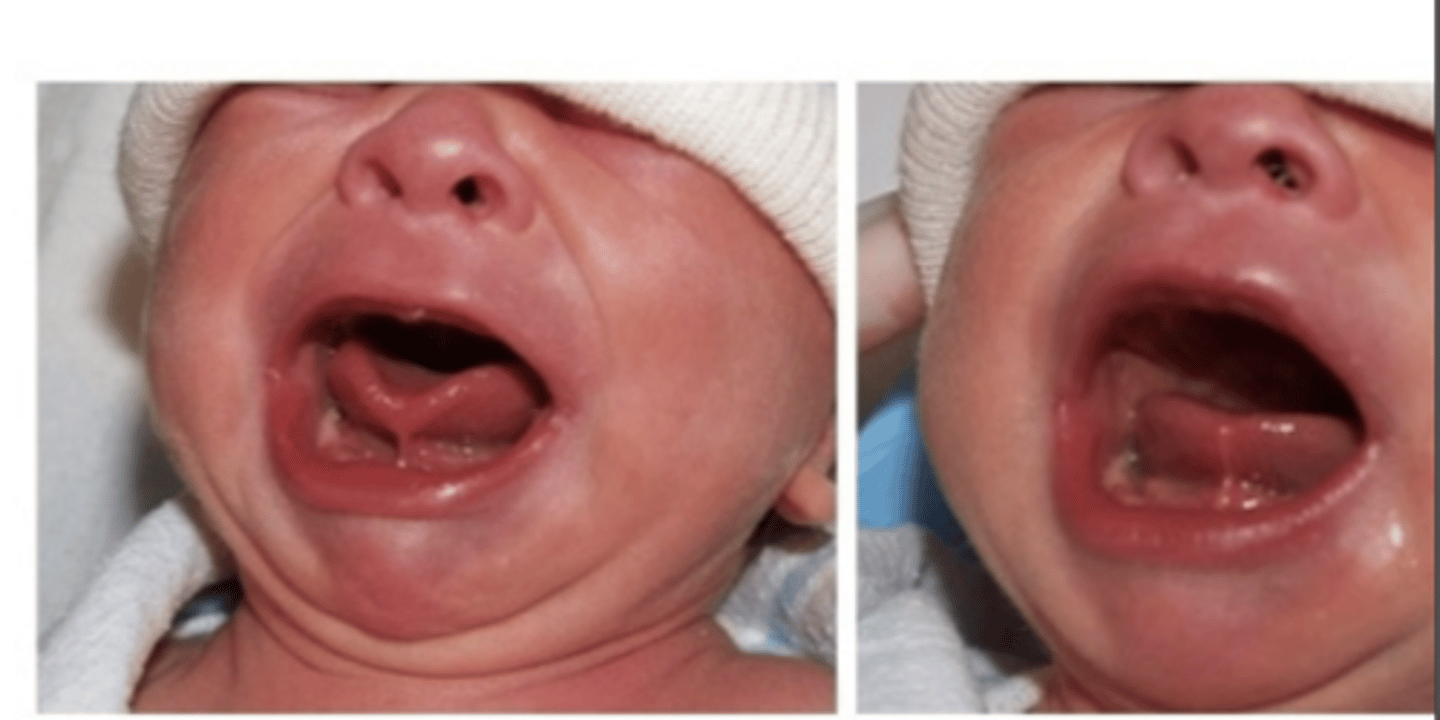
What is the treatment for Ankyloglossia in severe cases for infants?
Frenotomy
Infants with specific breast-feeding problems
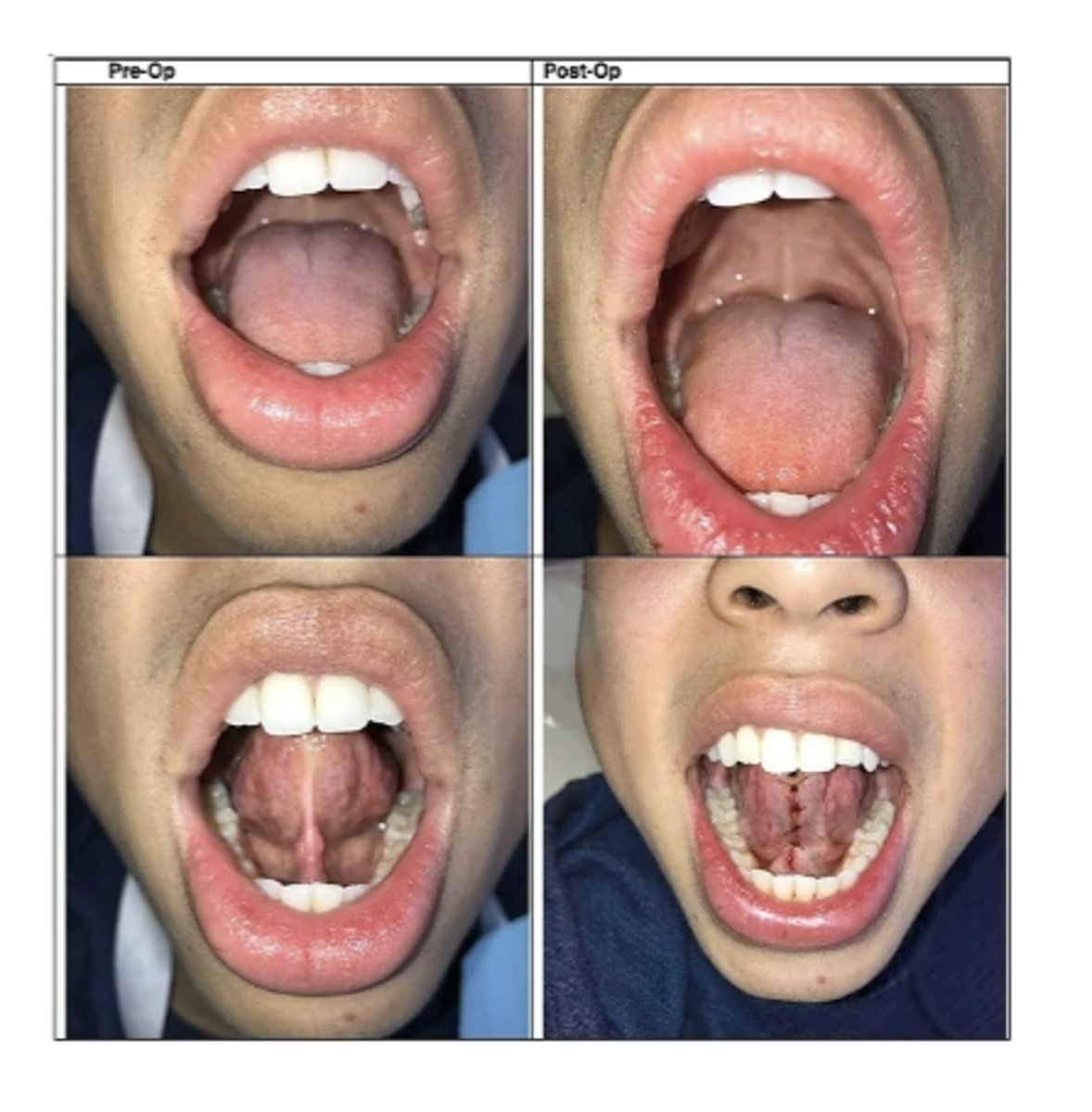
What is the treatment for Ankyloglossia in severe cases for 4-5 year old children or Adults?
Frenuloplasty
Children and adults with functional or periodontal difficulties
- Increases tongue mobility
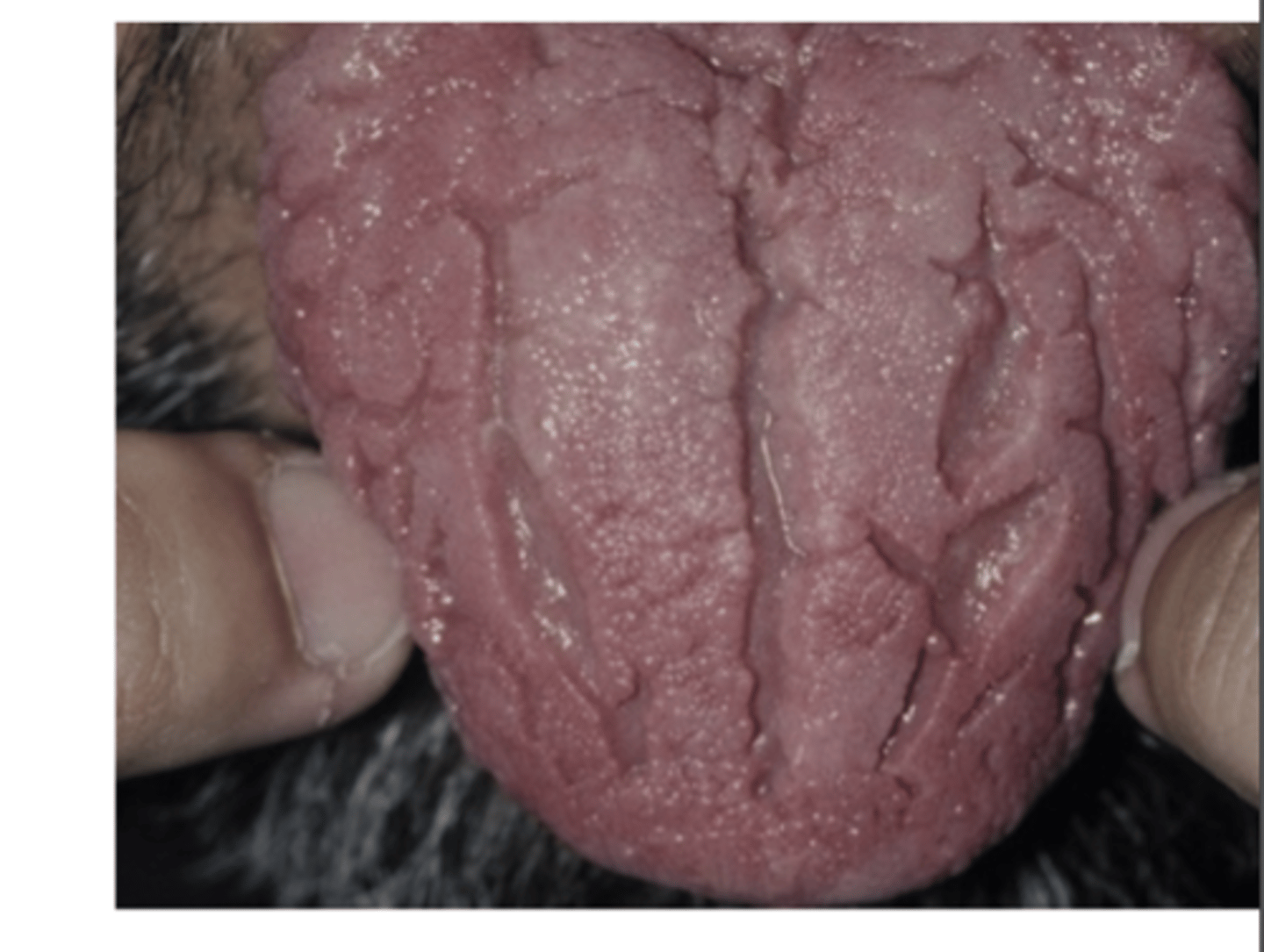
What is Fissured Tongue? What is the cause?
Relatively common
Multiple grooves or fissures on dorsal lingual surface
- Unknown cause
Possible role of heredity, either
1. Polygenic trait
2. Autosomal dominant trait with incomplete penetrance
- Contributing factors
1. Age
2. Environment
What is the treatment for Fissured Tounge?
No treatment needed
- Benign condition
Prophylaxis against accumulation of debris
- Encourage patients to brush the tongue
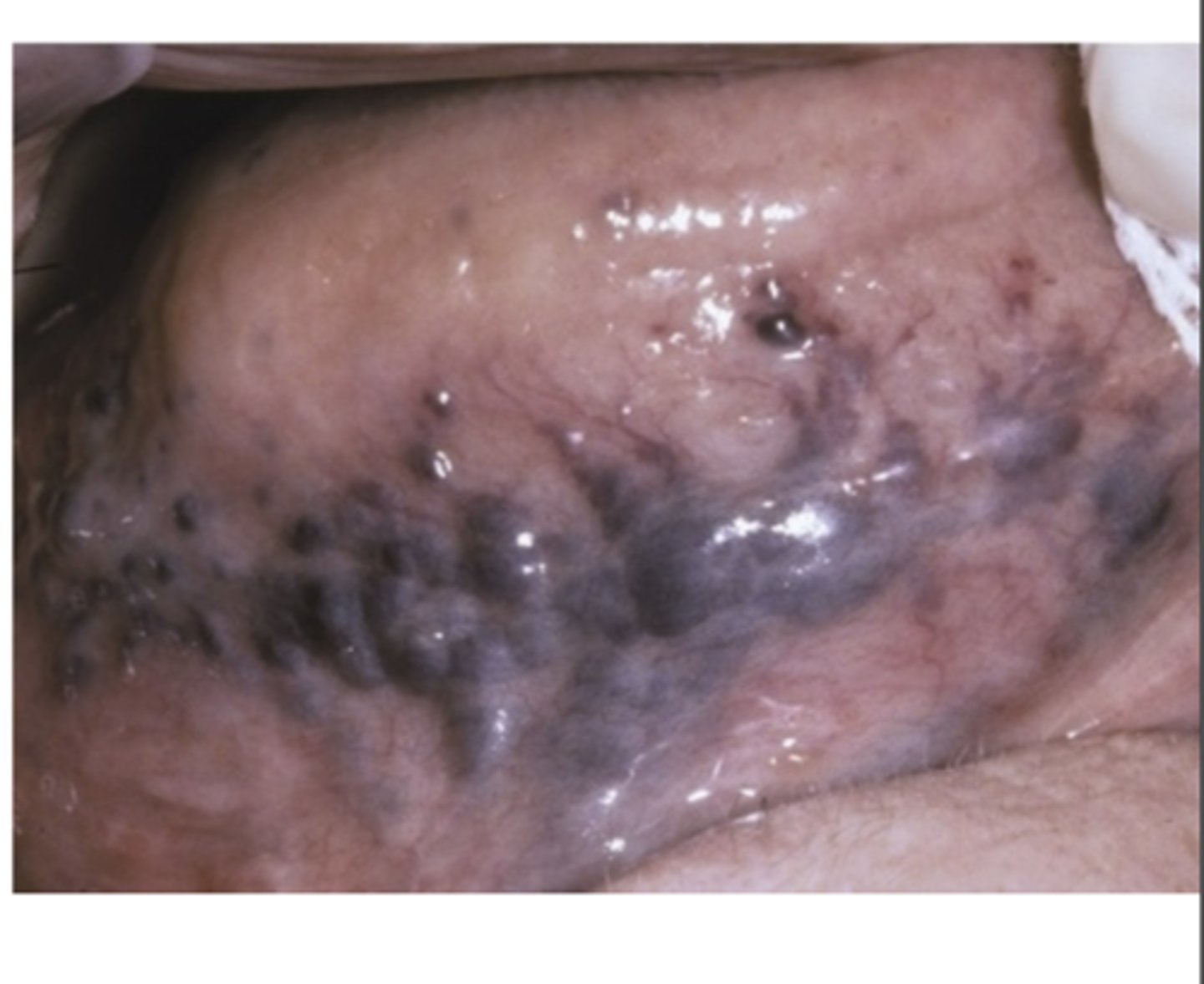
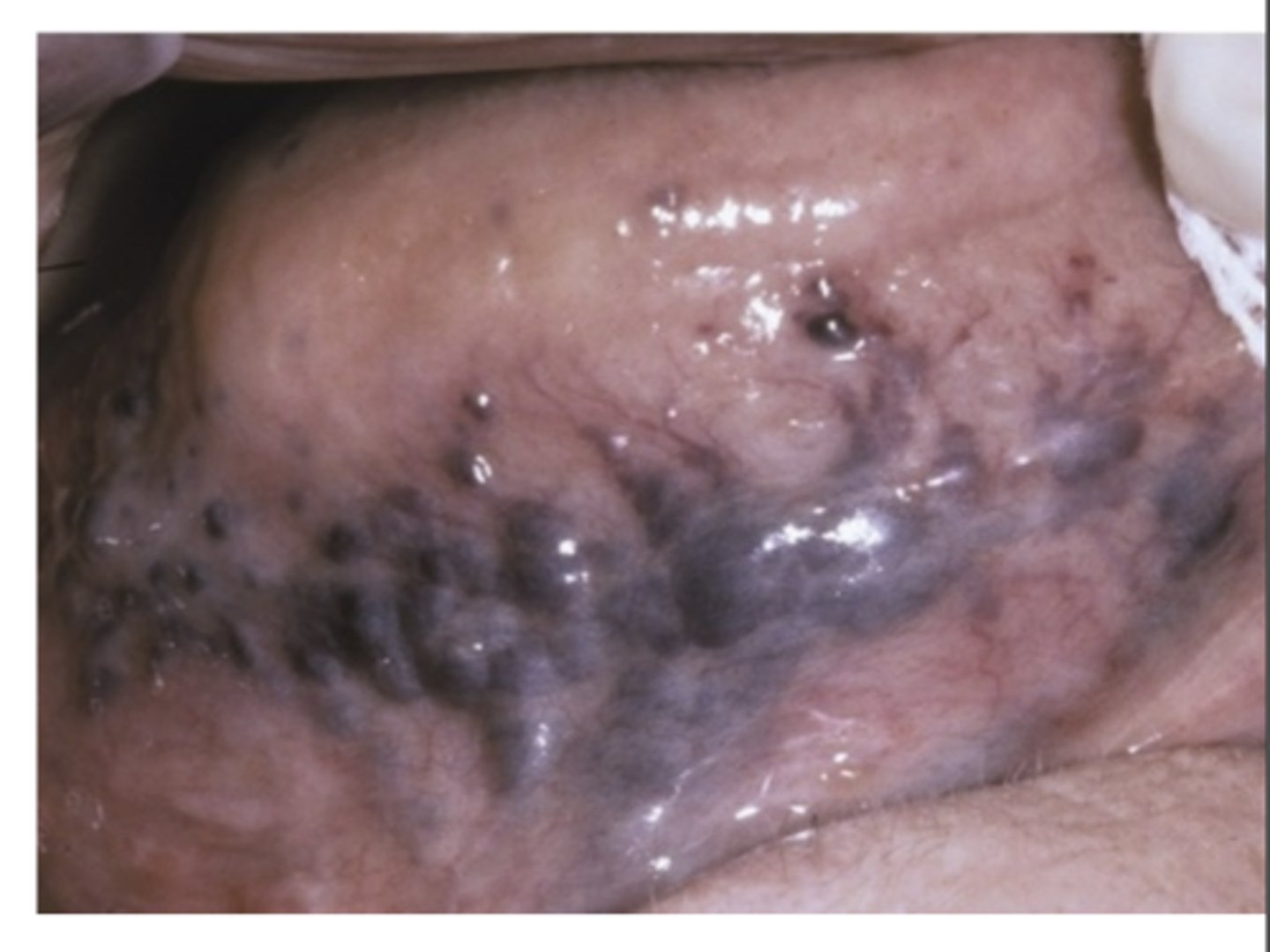
What are Varicosities? What age are they most common in?
Abnormally dilated, tortuous veins
- Rare in children
- Common on elderly
What are Varicosities association between? (2)
1. Association between leg varicosities and tongue varicosities
2. Association with smoking and cardiovascular disease
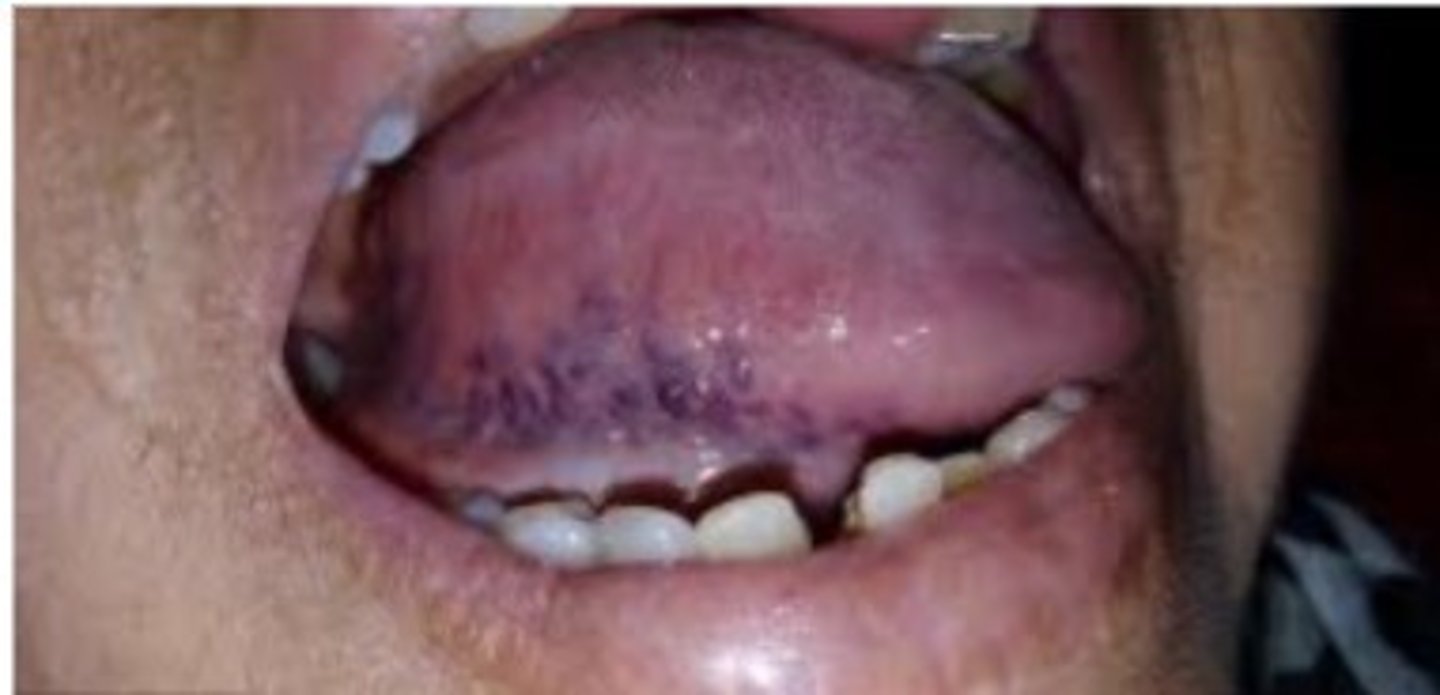
What is the most common type of Varicosities?
Sublingual varix
- In 2/3 of people older than 60 y/o
- Normally asymptomatic
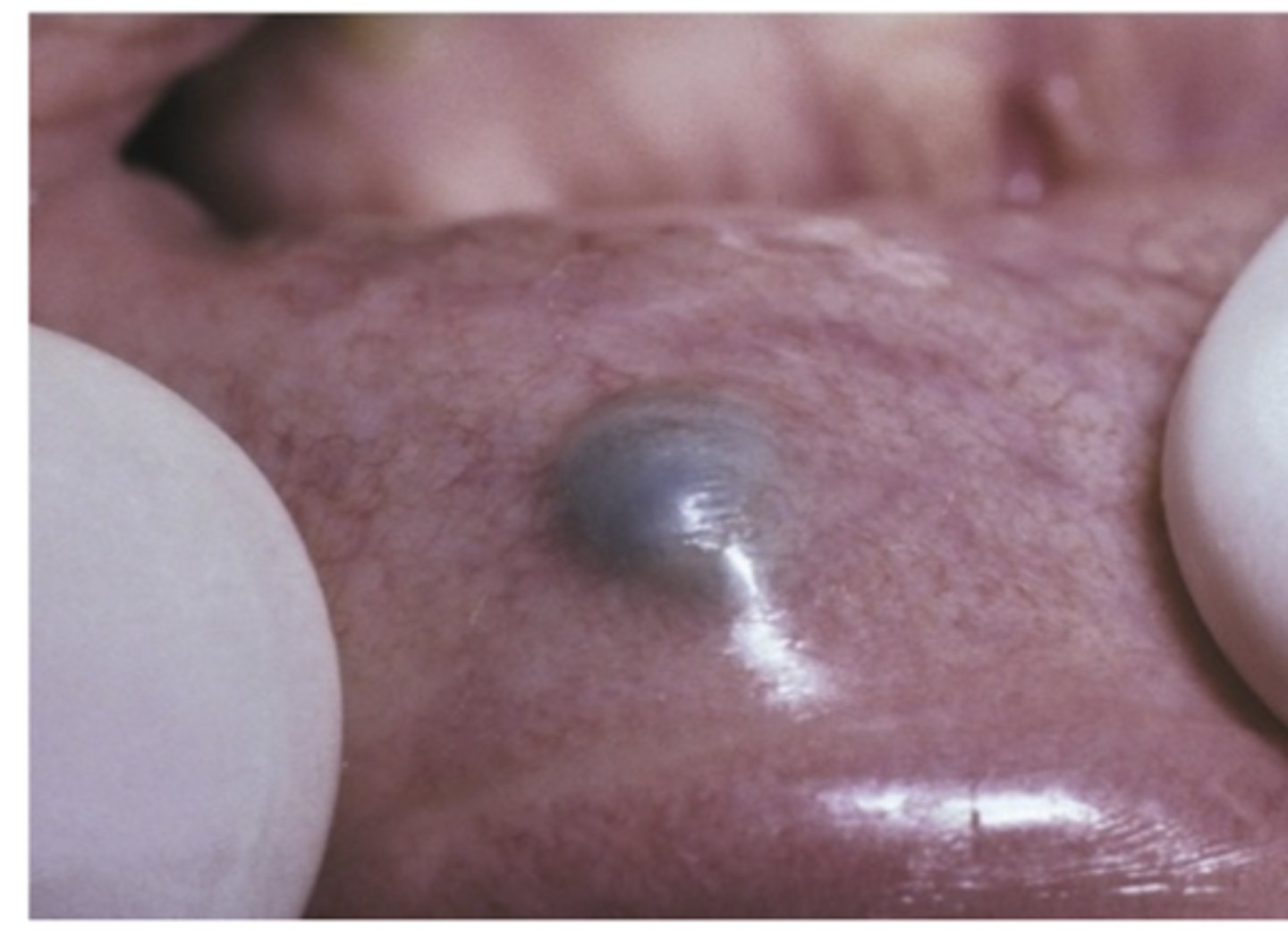
What is the least common Varicosities?
Solitary varices
-Present in other areas of mouth
- Lips and buccal mucosa
- Usually noted after thrombosis
What is the treatment of Varicosities?
No treatment when asymptomatic
- Surgical removal for Solitary varices
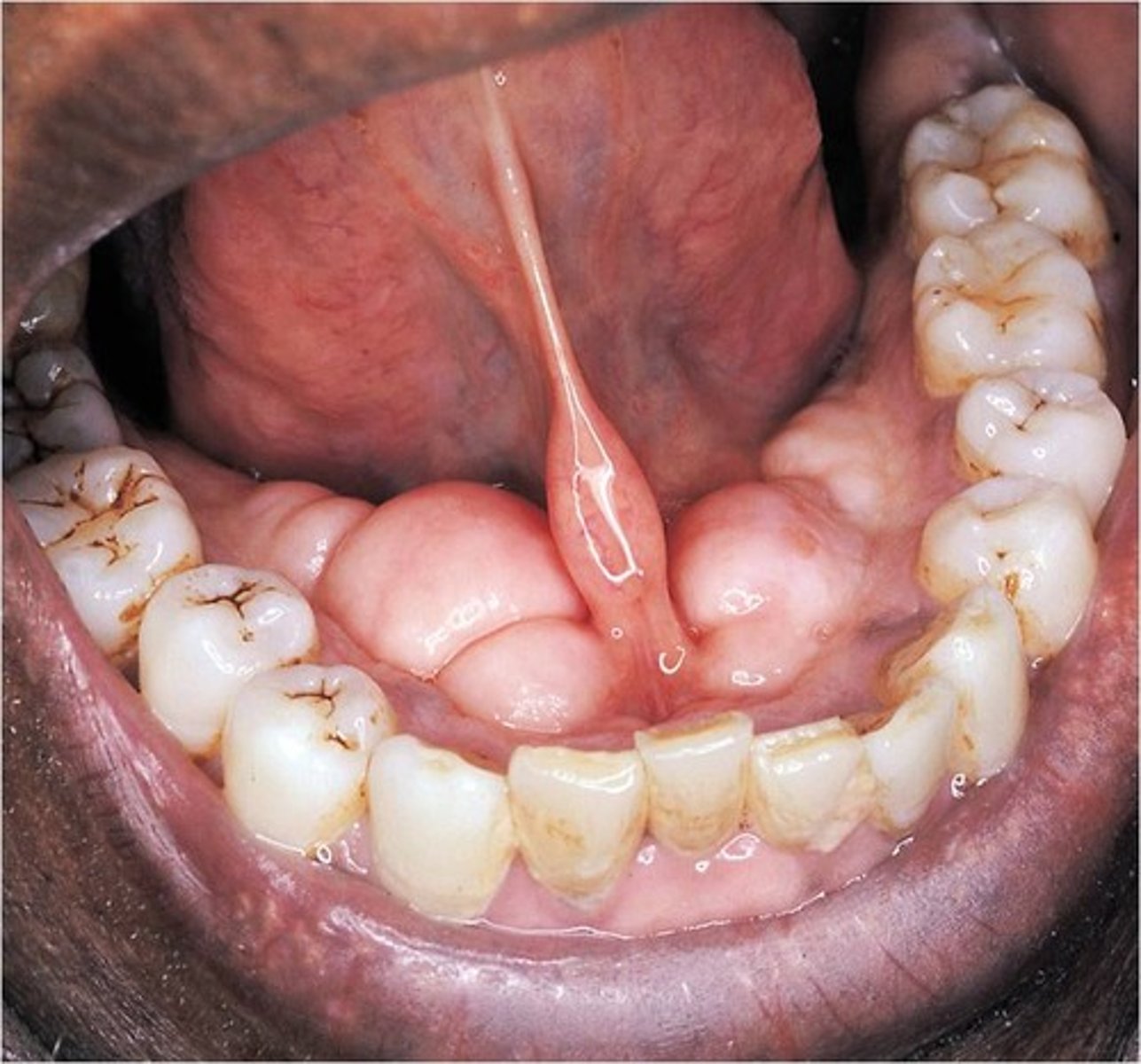
What are Exostoses? What do they arise from?
Benign bony protuberances (Tori)
- Arise from cortical plate
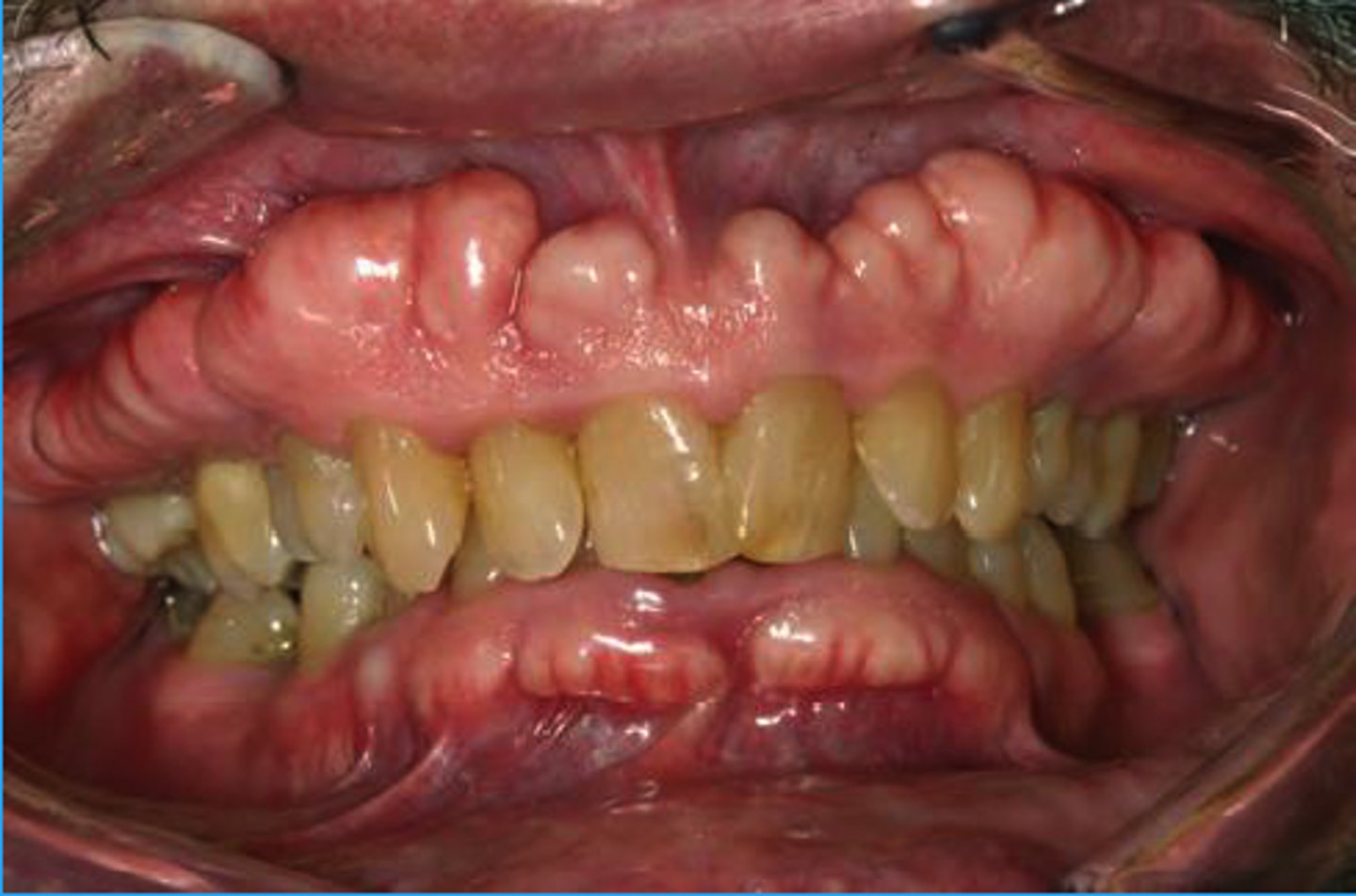
What are buccal exostoses?
Bilateral row of bony nodules in facial aspect of maxillary and/or mandibular alveolar ridge
- Usually asymptomatic
- Surface mucosa can result ulcerated
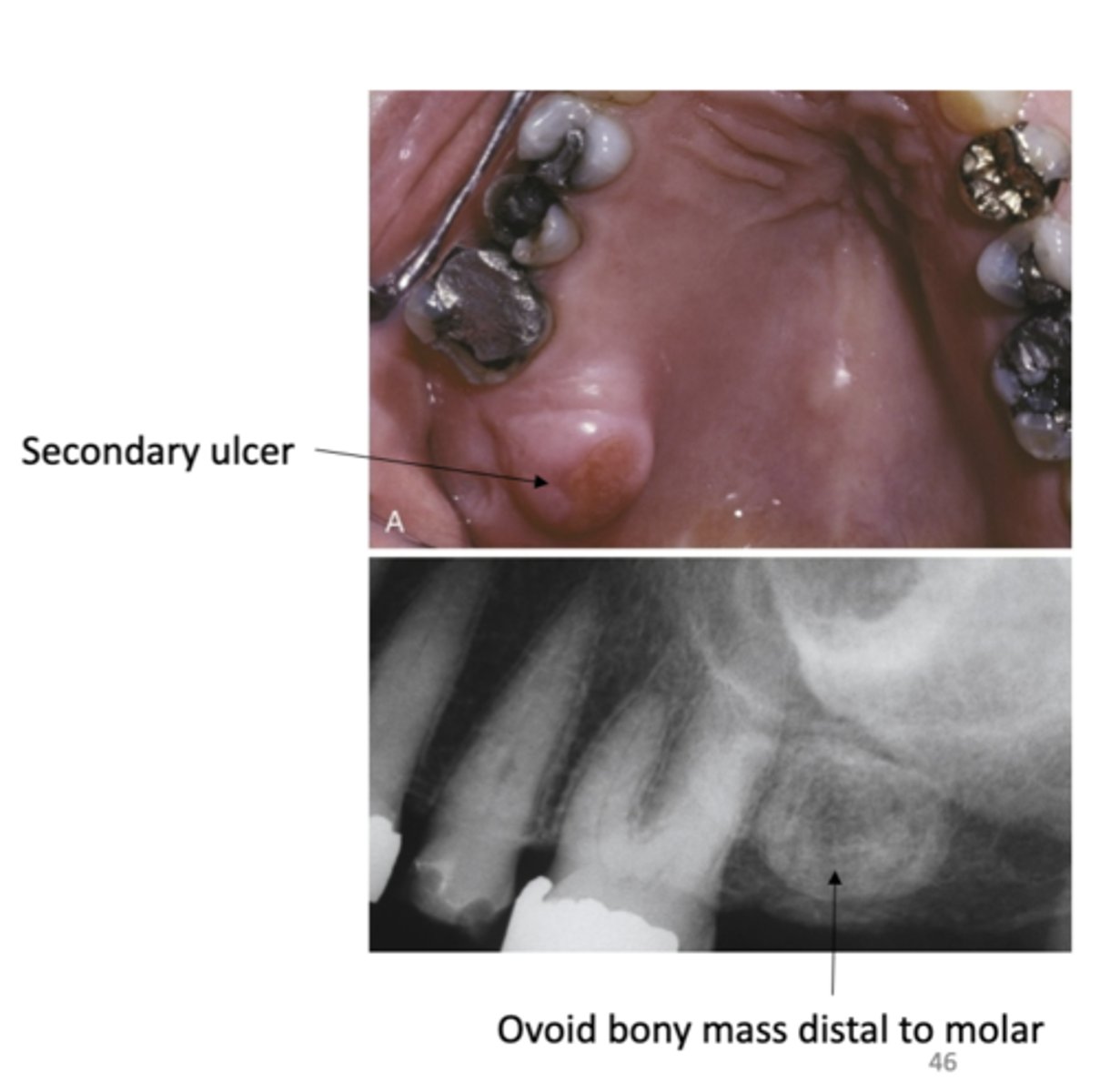
What do palatal exostoses develop from?
Develop from lingual aspect of maxillary tuberosities
- Bilateral or unilateral
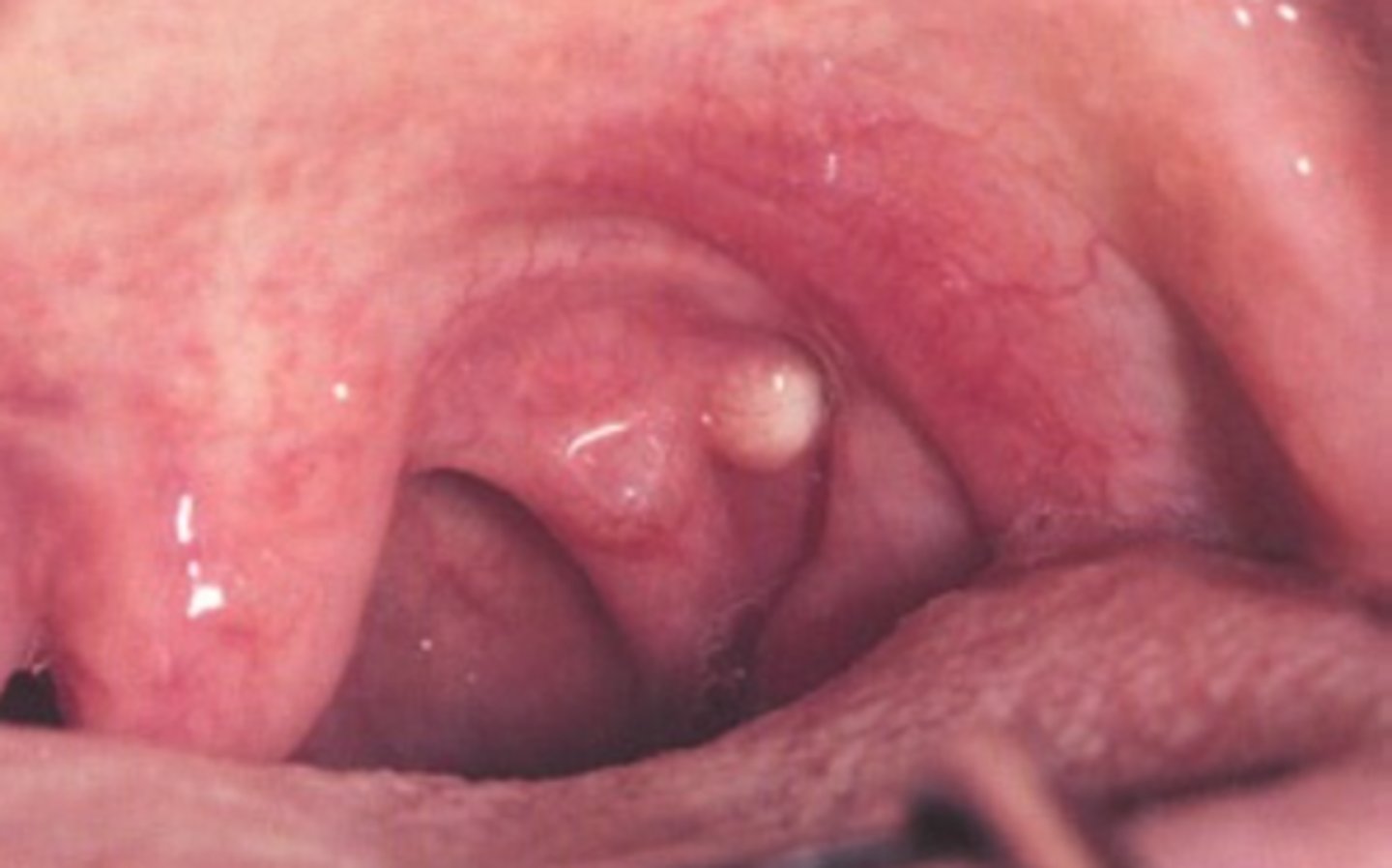
What are Cyst?
A pathologic cavity usually filled with fluid and lined by epithelium.
- Must have a slow increase in size
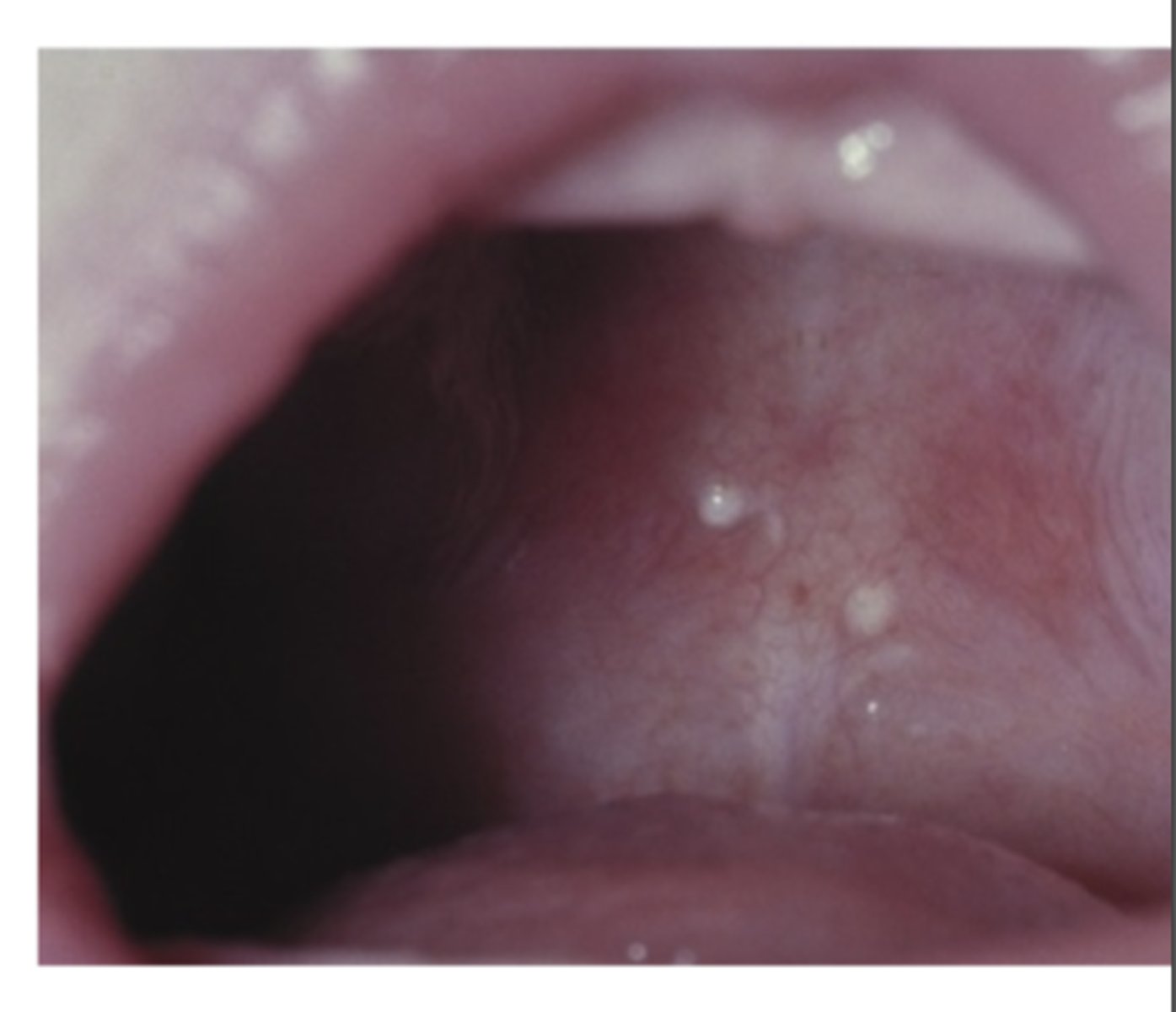
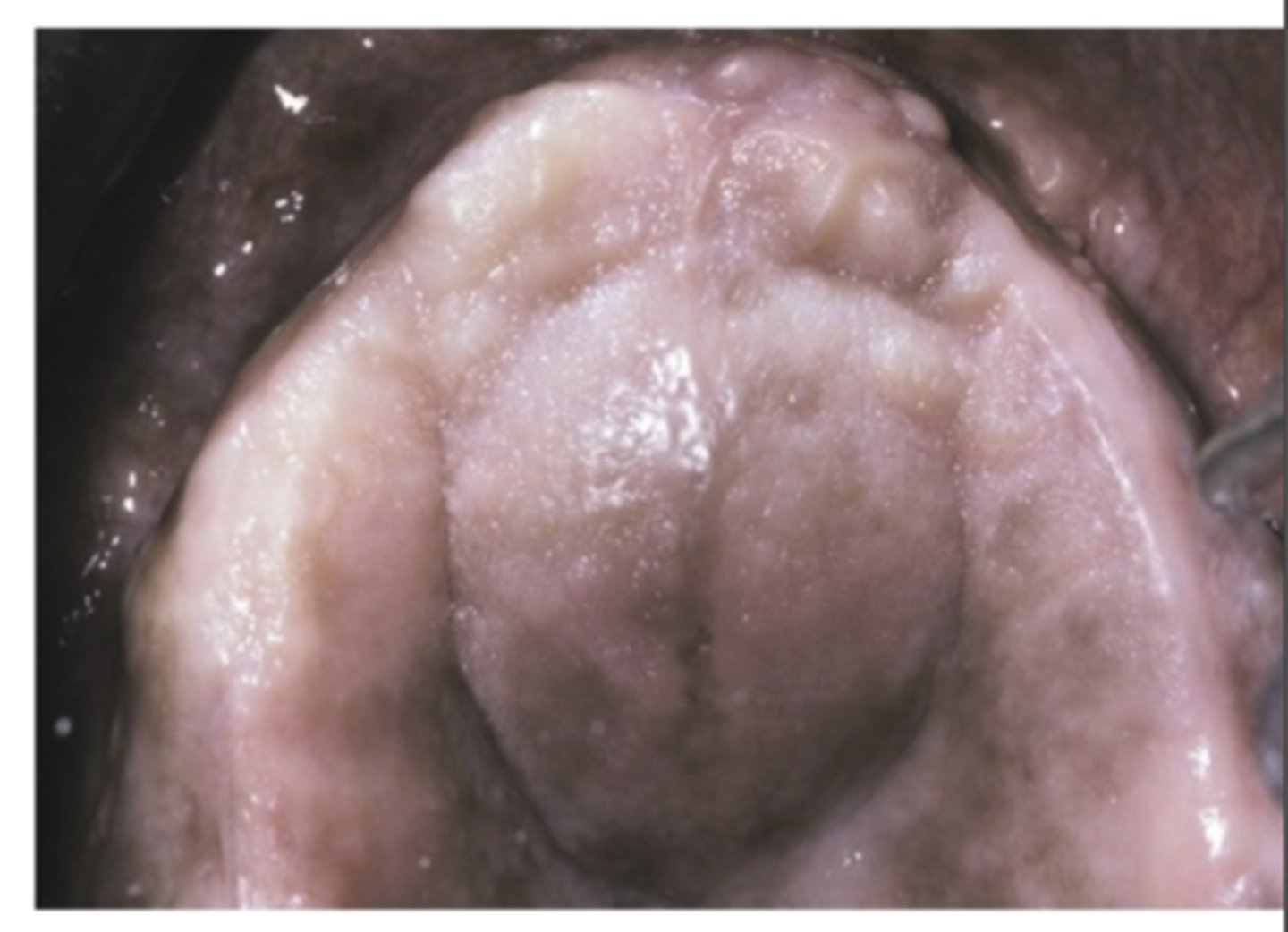
Where are palatal cysts of the newborn found? how do they appear? what is the treatment?
- White or yellow-white papules
- Often along midline
- Near junction of soft and hard palates
- Single or clusters of two to six lesions
- Asymptomatic
- No treatment necessary
- Self-healing
- Rarely persist after few weeks
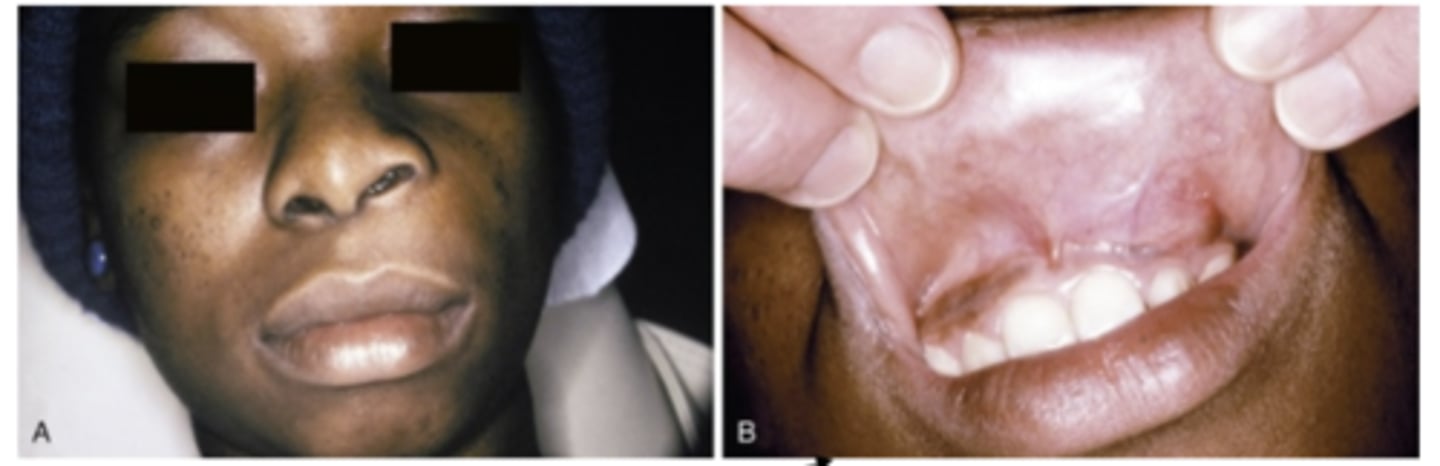
What do Nasolabial cyst cause? where are they located?
Obliteration of the maxillary mucolabial fold
- Nasal obstruction
- Interfere with the wearing of denture Pain uncommon, usually if secondary infection occurs
Rupture may happen
- Drain into oral or nasal cavities
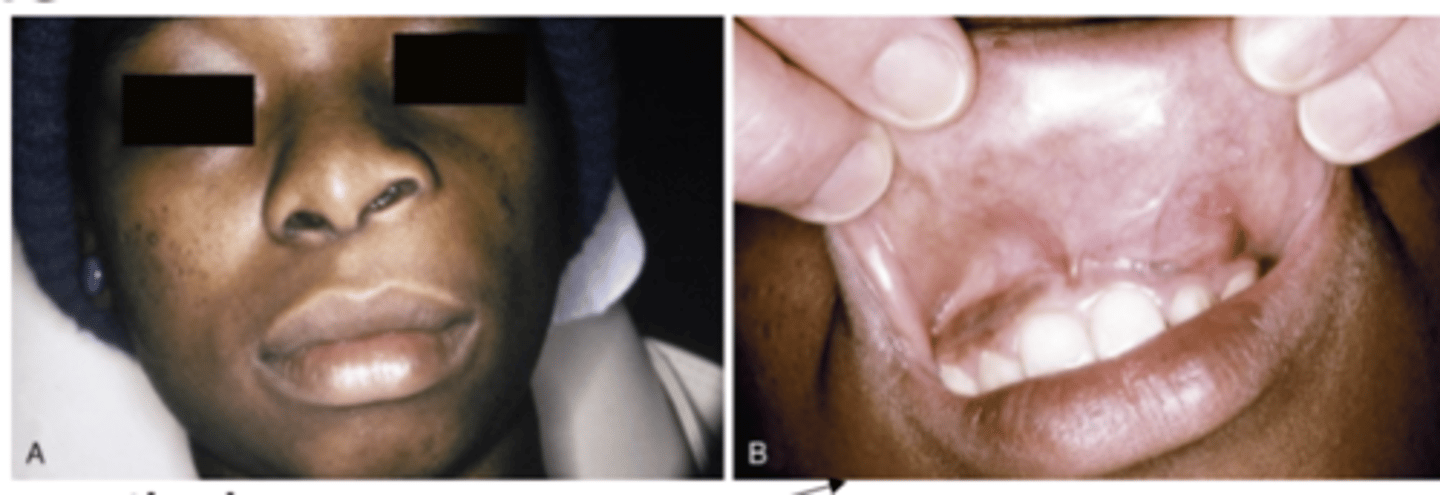
What is the treatment of Nasolabial cyst?
Complete surgical excision
- Recurrence is rare
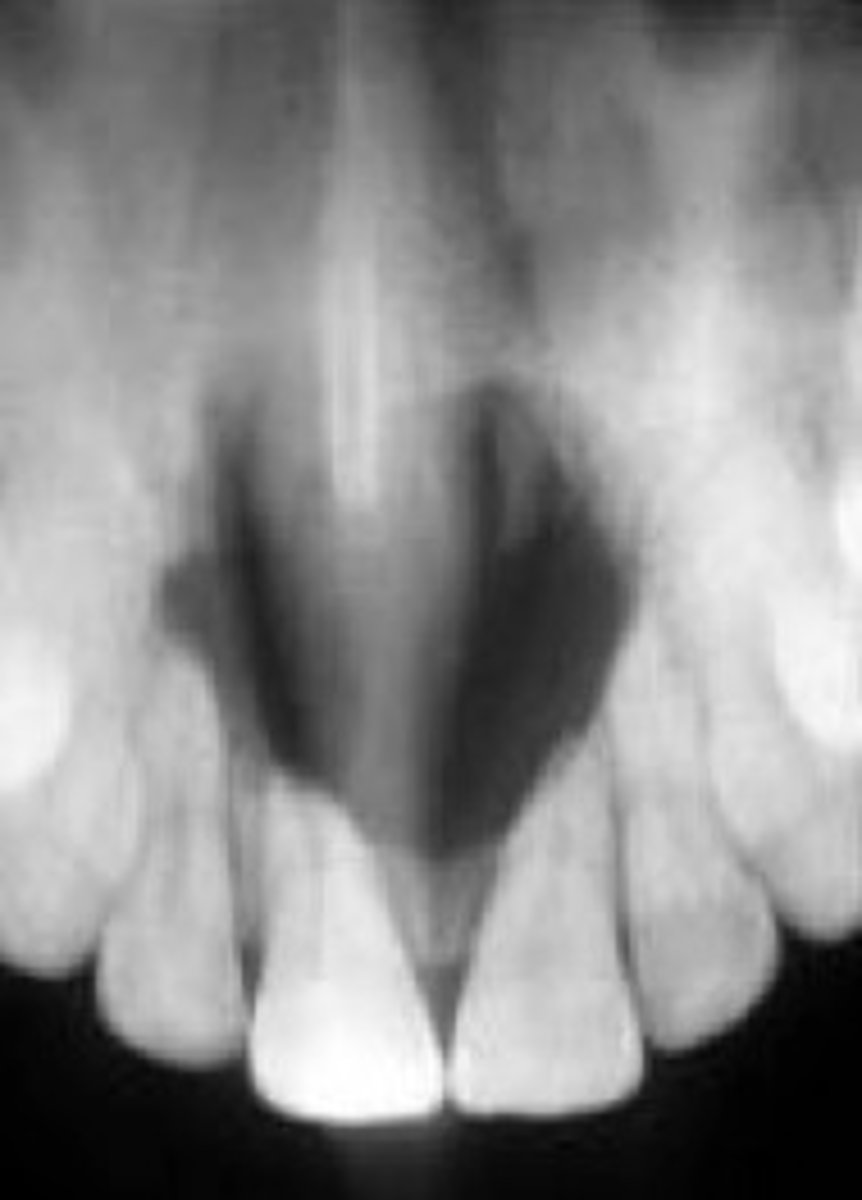
What is the most common of nonodontogenic cysts (not tooth related) of the oral cavity?
Nasopalatine duct cyst
What are the three presenting symptoms of Nasopalatine duct cyst?
1. Swelling of anterior palate
2. Drainage
3. Pain
What is the treatment of Nasopalatine duct cyst?
Surgical enucleation (a surgical procedure that involves removing an oral cyst or tumor, along with the surrounding tissue)
- Biopsy recommended
- Recurrence is rare
- Malignant transformation is very rare
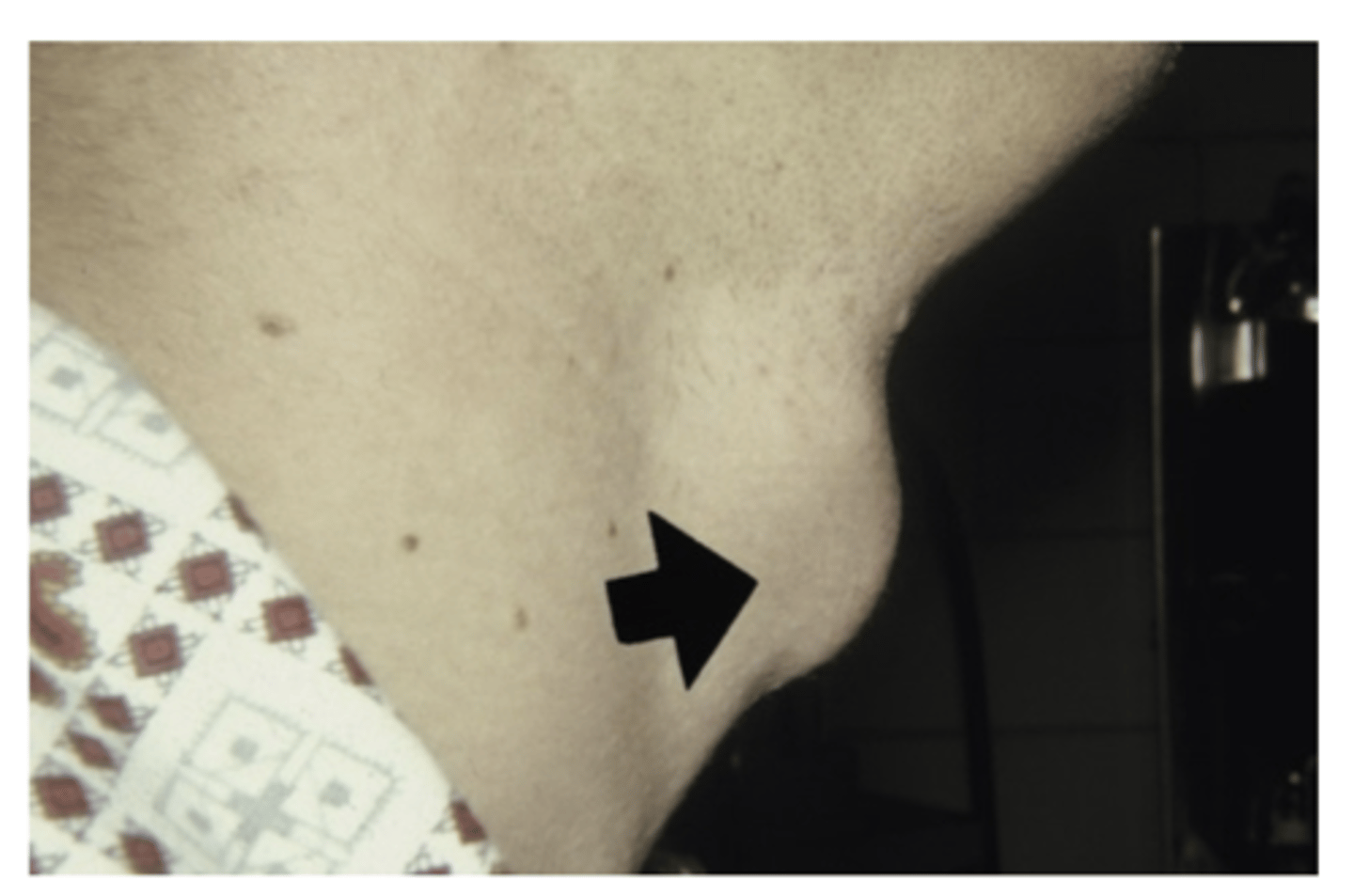
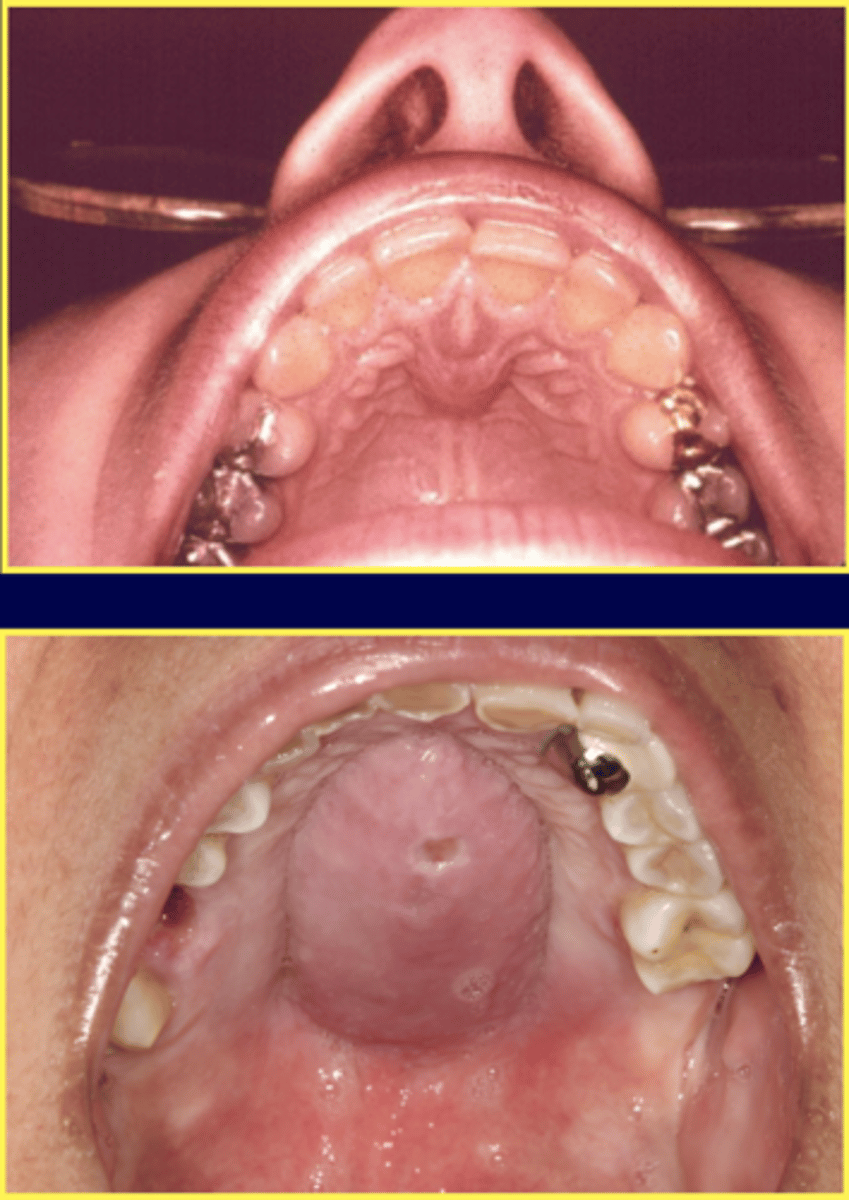
What is a Thyroglossal duct cyst? Where do they develop? What are they typically adjacent to?
Remnant of the epithelium of the thyroglossal tract
- Develop classically in the midline
-adjacent to hyoid bone
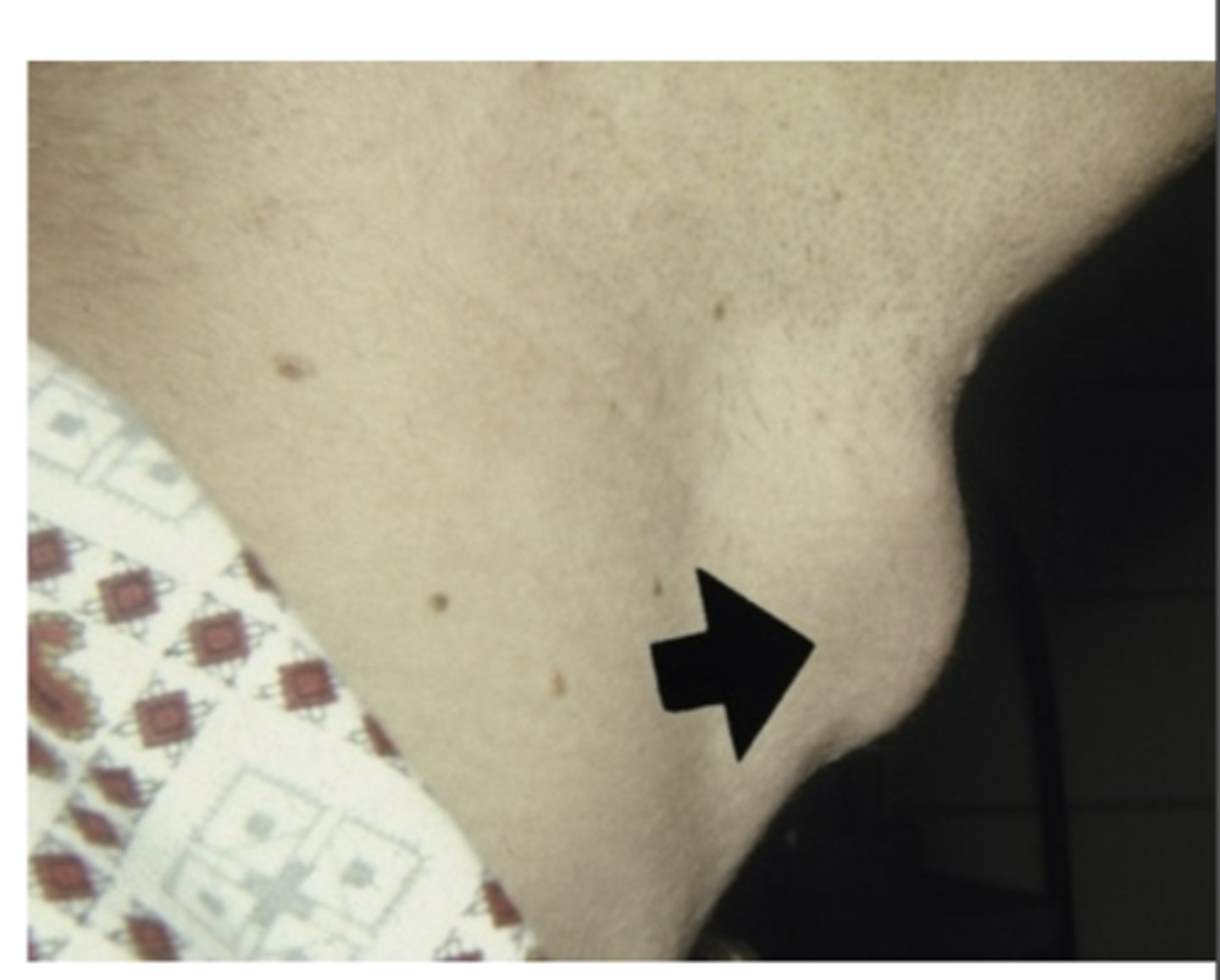
What are the clinical manifestations of a Thyroglossal duct cyst?
Presents as a swelling
1. Painless
2. Movable
3. Fluctuant
- Secondary infections may occur
- Cyst in the base of the tongue cause laryngeal obstruction
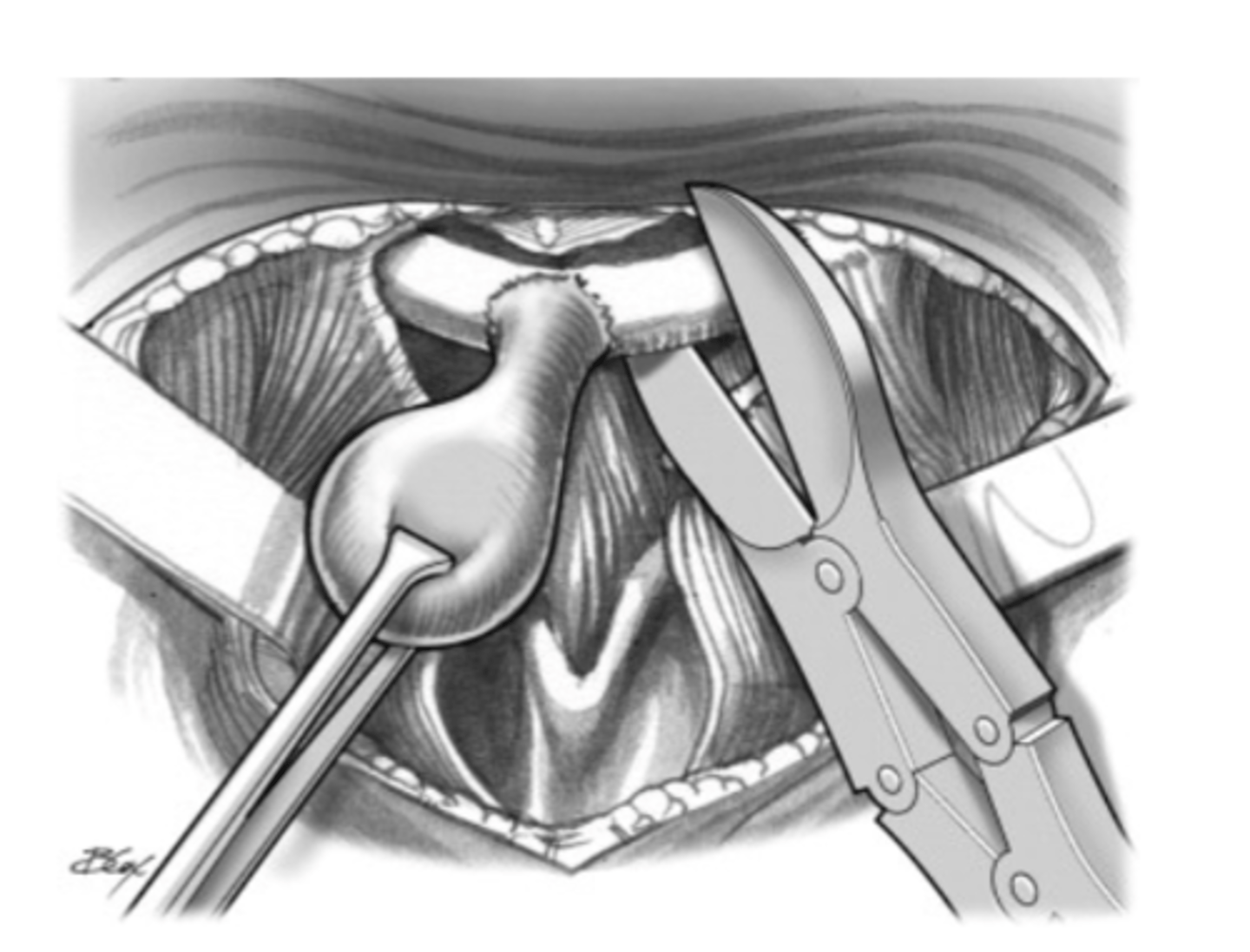
What is the treatment for Thyroglossal duct cyst?
Sistrunk procedure
Removal of
1. Cyst
2. Midline segment of hyoid bone
3. Portion of muscular tissue along entire thyroglossal tract
- Recurrence is less than 10%
- Higher recurrence with less aggressive surgery
- Carcinoma can occur in 1% to 2% of cases