Exam 2: OTC: Headache
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Prevalence of headaches
•Headache disorders affect 40% of the global population in 2021
•Females > males
•Tension headaches vs. migraine
•In 2021, 4.3% of adults >18 were bothered a lot by headache or migraine

Types of headaches
primary and secondary
Primary headaches
- 90% of headaches
- Do not have an underlying cause
ex: migraine, tension, cluster
Secondary headahces
- symptom of underlying cause
ex: head trauma, stroke, bacterial/viral causes, substance abuse or withdrawal, medication overuse (both underlying and withdrawal)
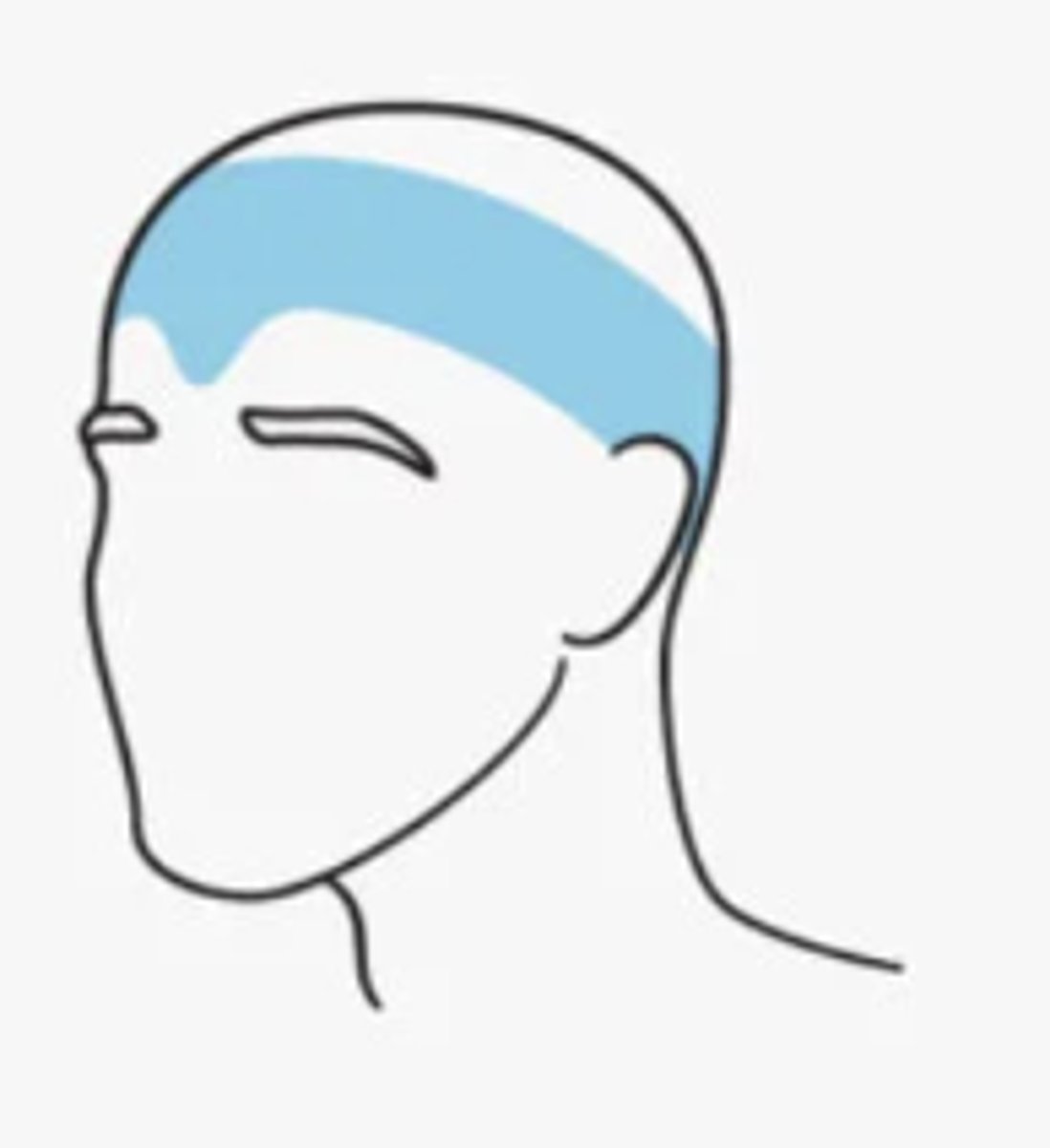
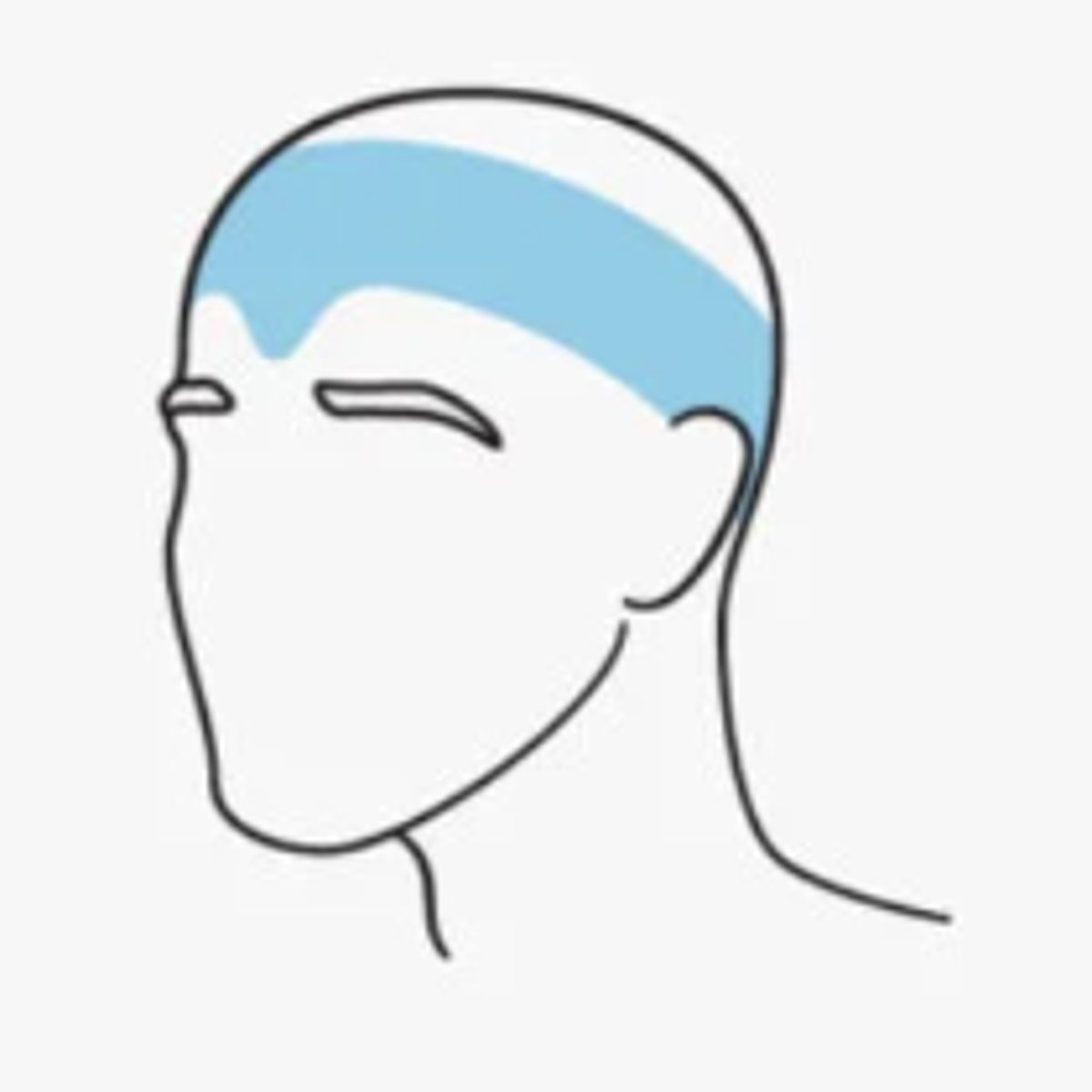
Tension headaches
- AKA stress headaches
- occur due to stress, anxiety, depression, emotional conflicts or other stimuli
- around the back of the head, the temples, and the forehead, almost as though a tight hat is squeezing the head
- onset: teenage years
- female > male
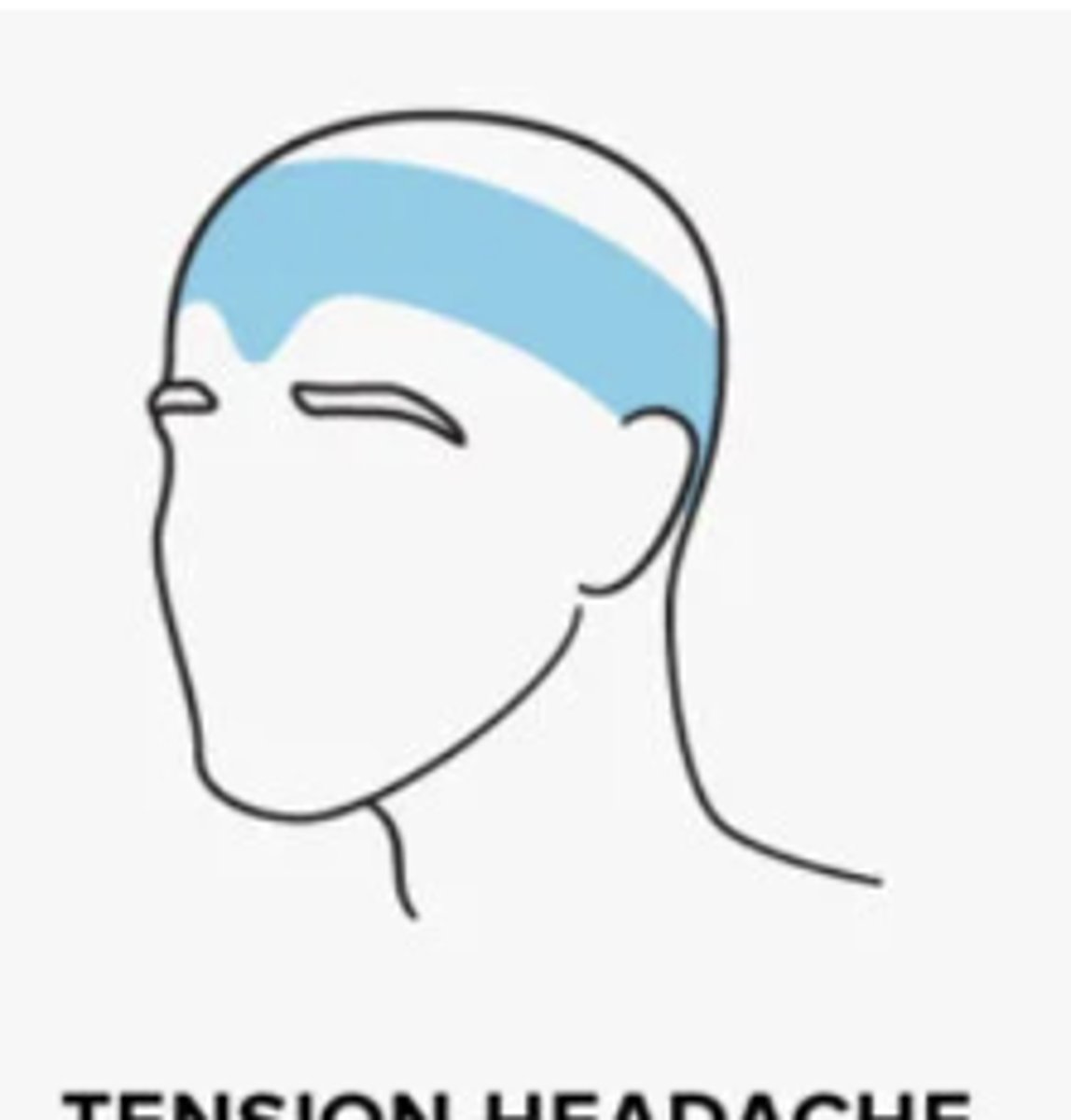

Chronic tension headaches occur...
> 15 days/month for 3 months
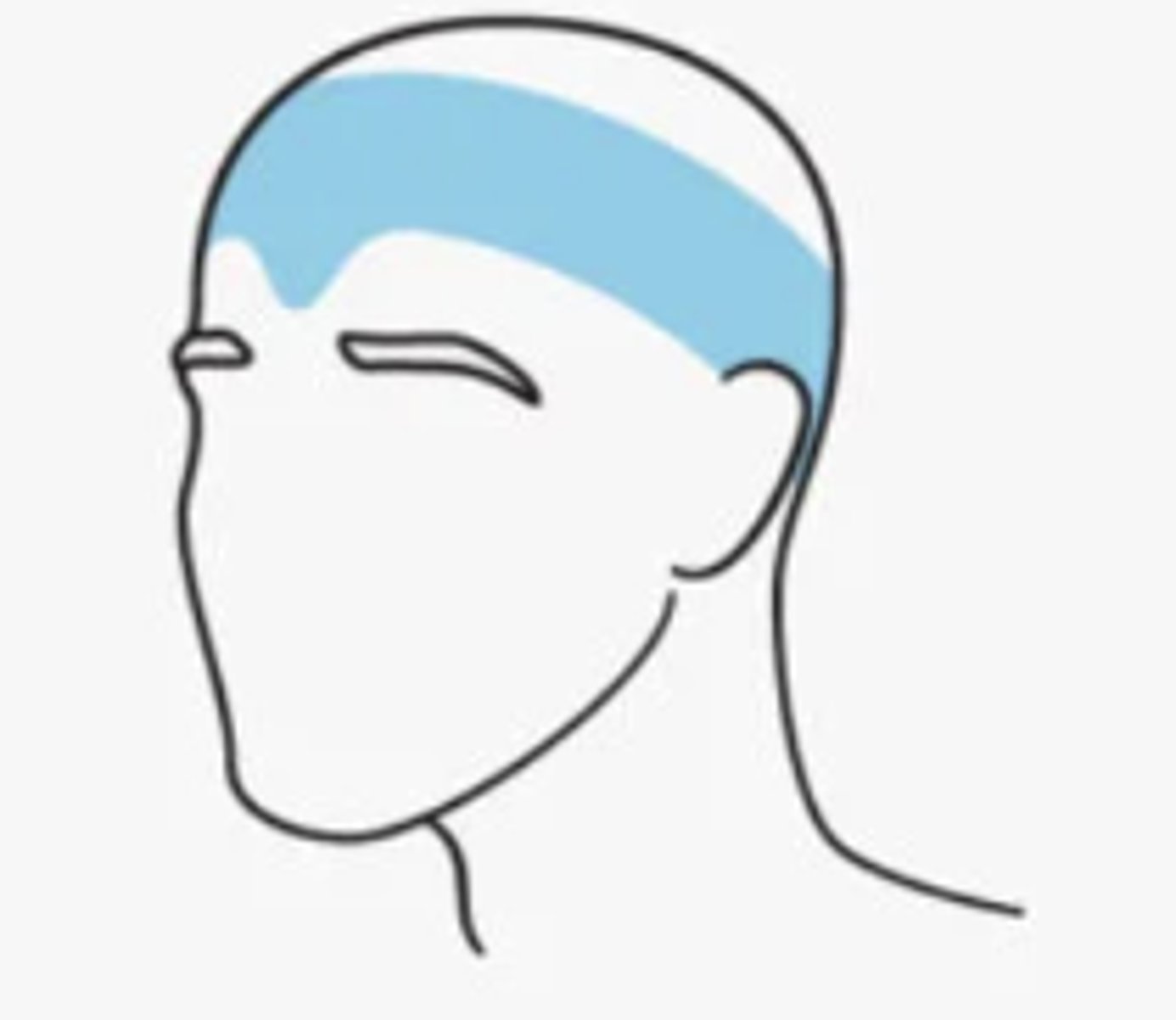
Episodic tension headaches occur...
< 15 days/month
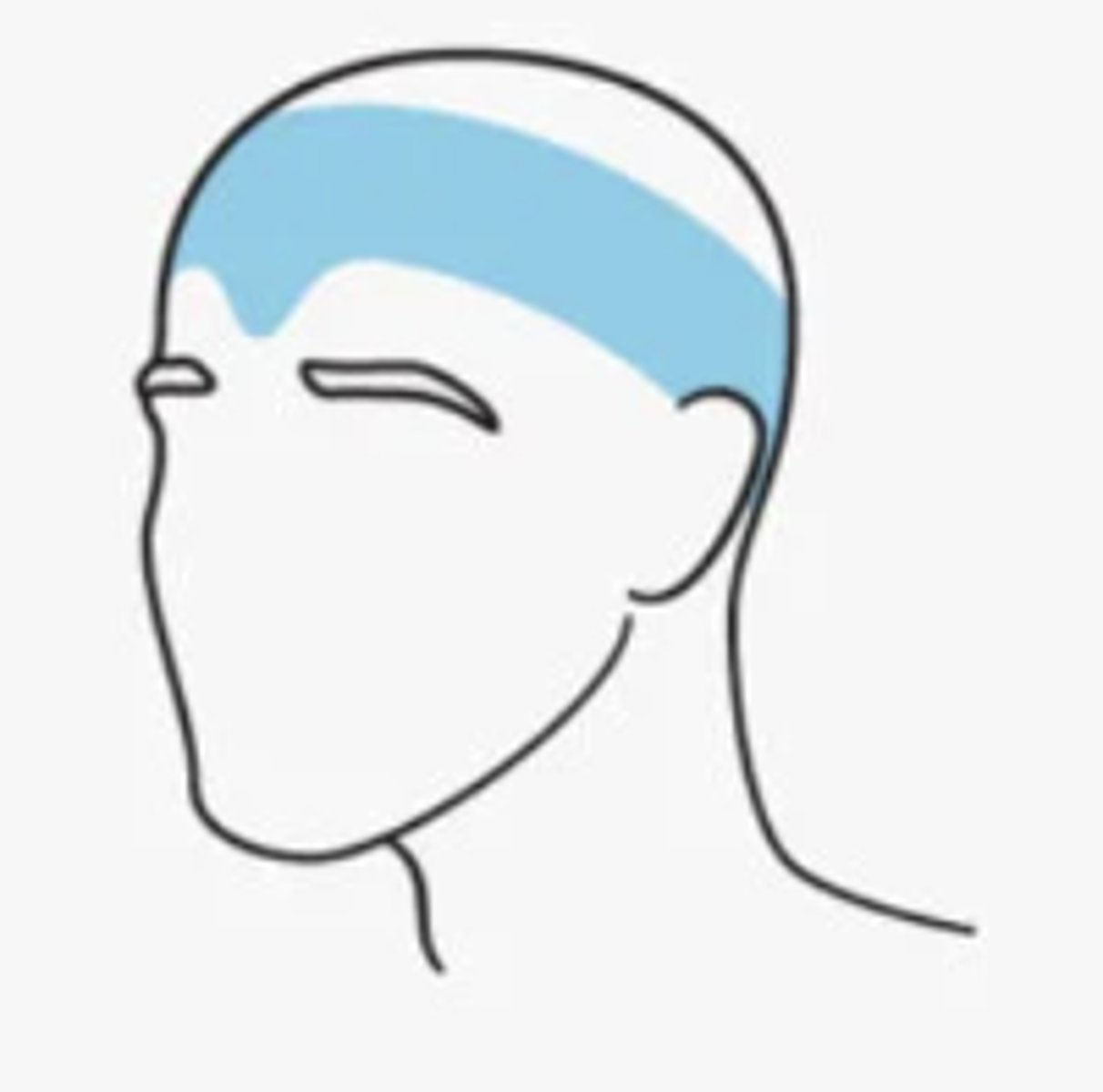
Frequent episodic tension headaches occur..
at least 10 that occur 1-14 days/month
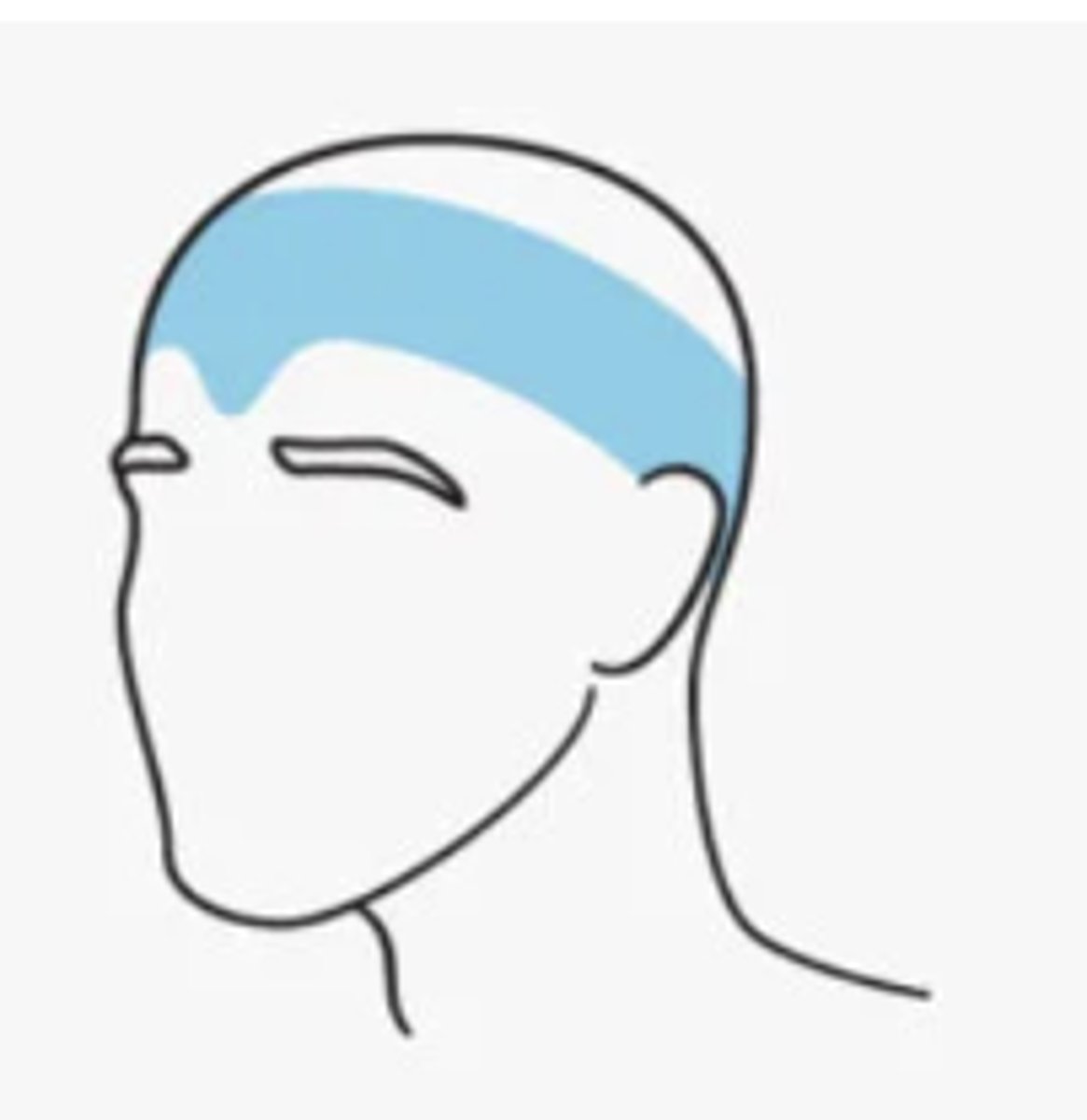
Chronic tension headaches characteristics
stimuli sensed by the CNS
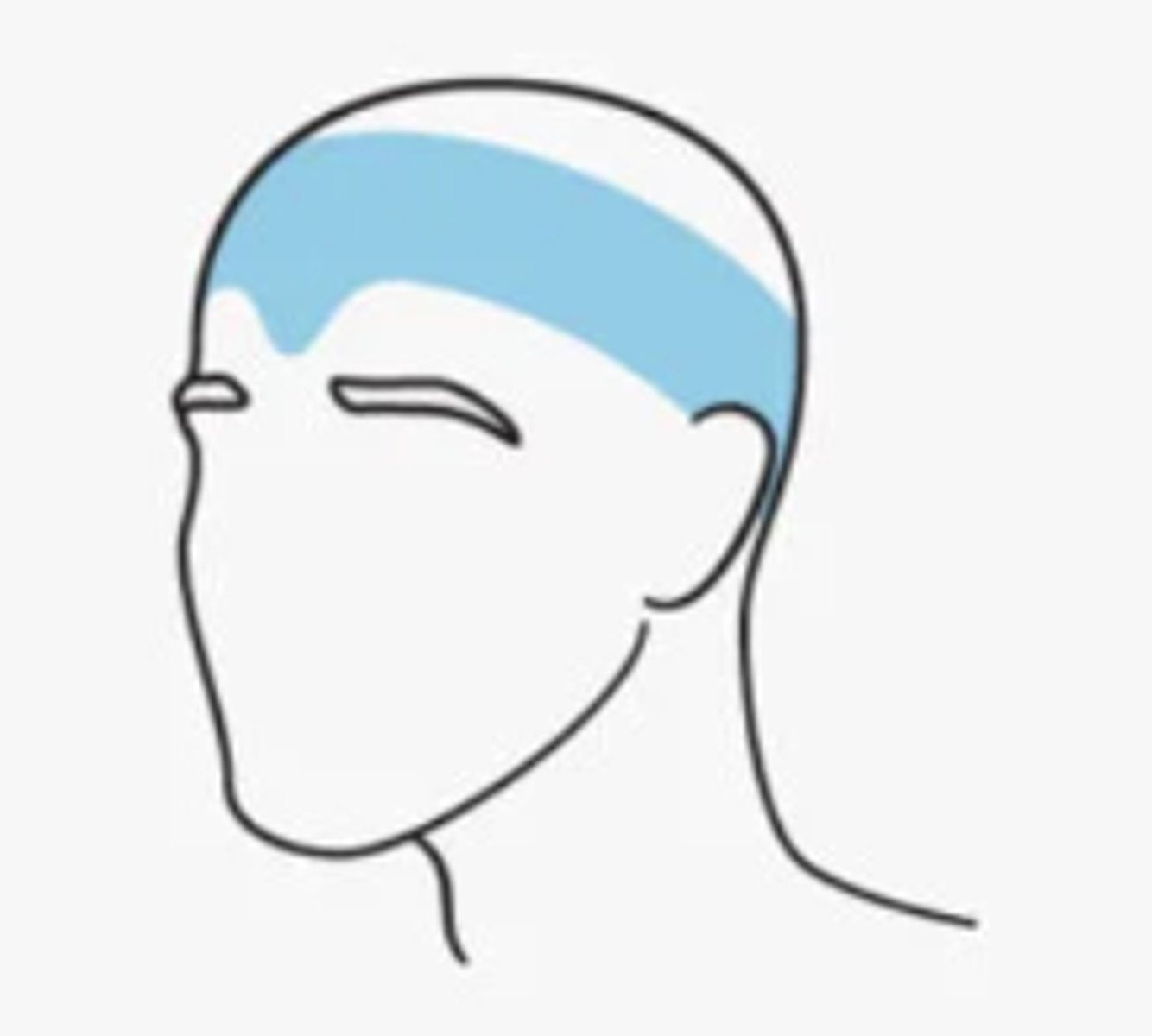
Episodic tension headache characteristics
pain sensed by the PNS
_________________ may play a role in predisposition of tension headaches
genetic component
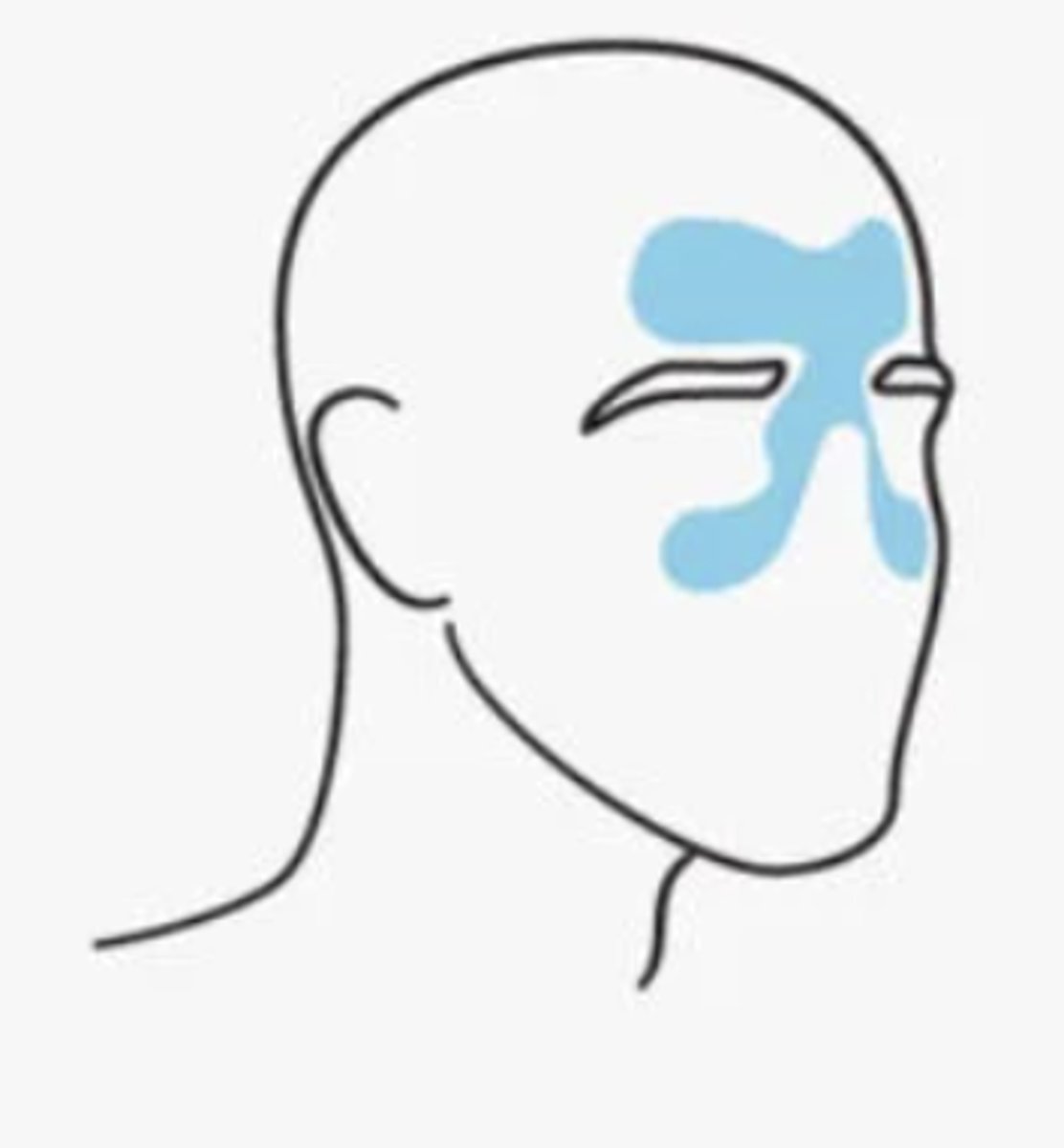
What are sinus headahces caused by?
infection or blockage of the sinuses, resulting in inflammation & distention of the sinus walls--> pain & sensitivity
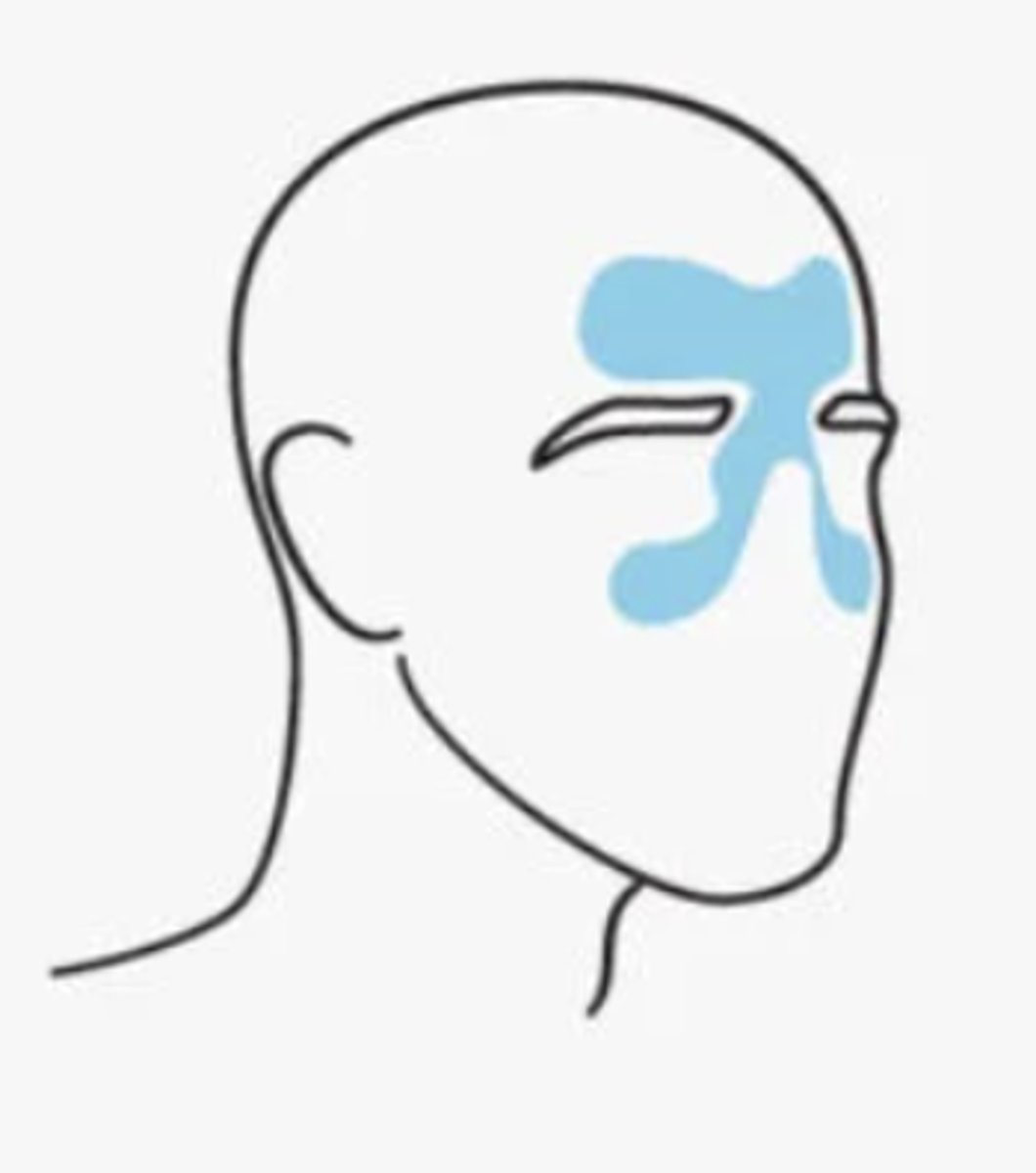
Sinus headaches can be....
•Bacterial
•Viral
•Allergic Rhinitis
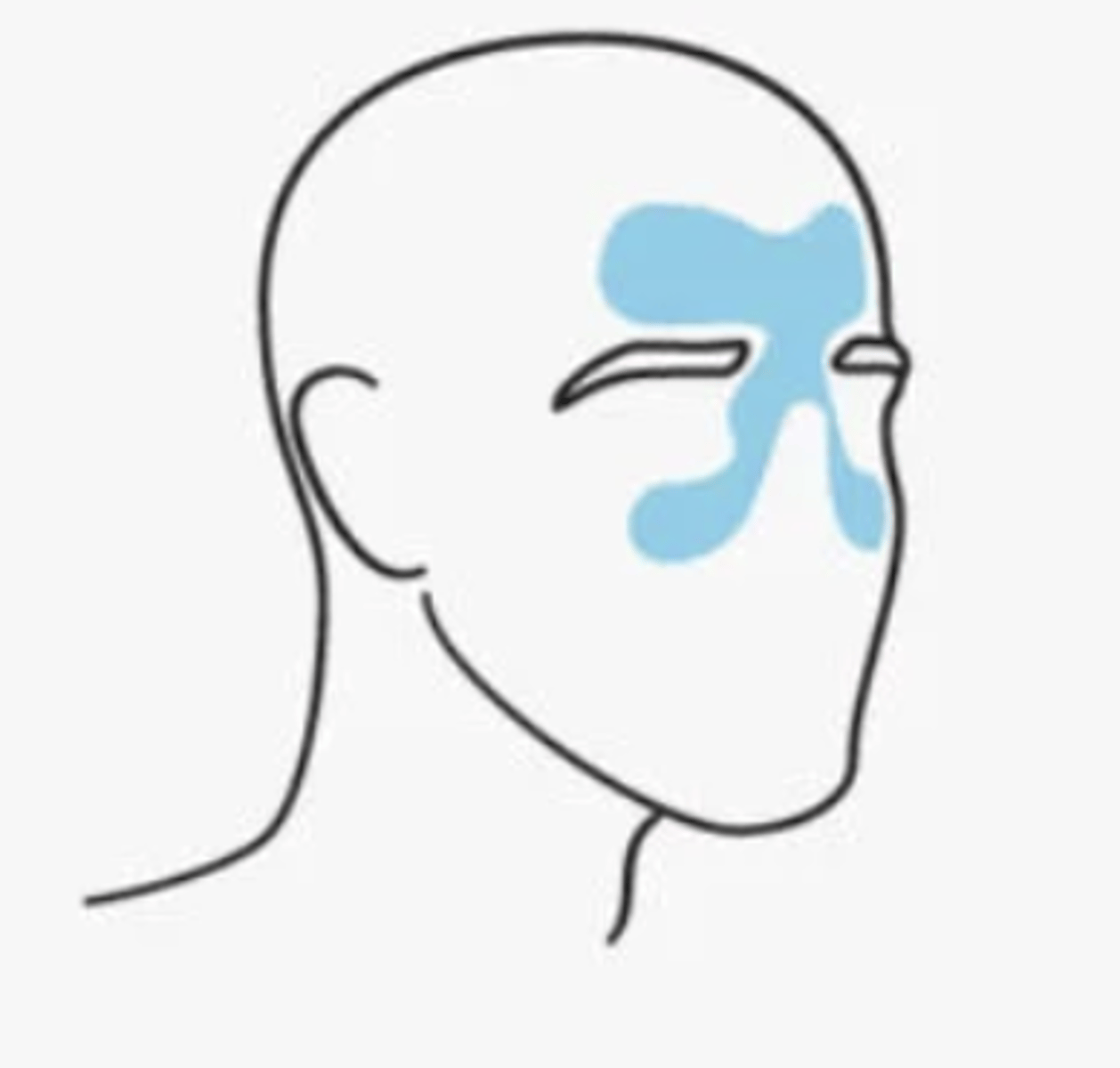
Sinus headache pain may feel...
may be dull and feel like pressure
- inside the forehead, cheekbones, and nasal cavity
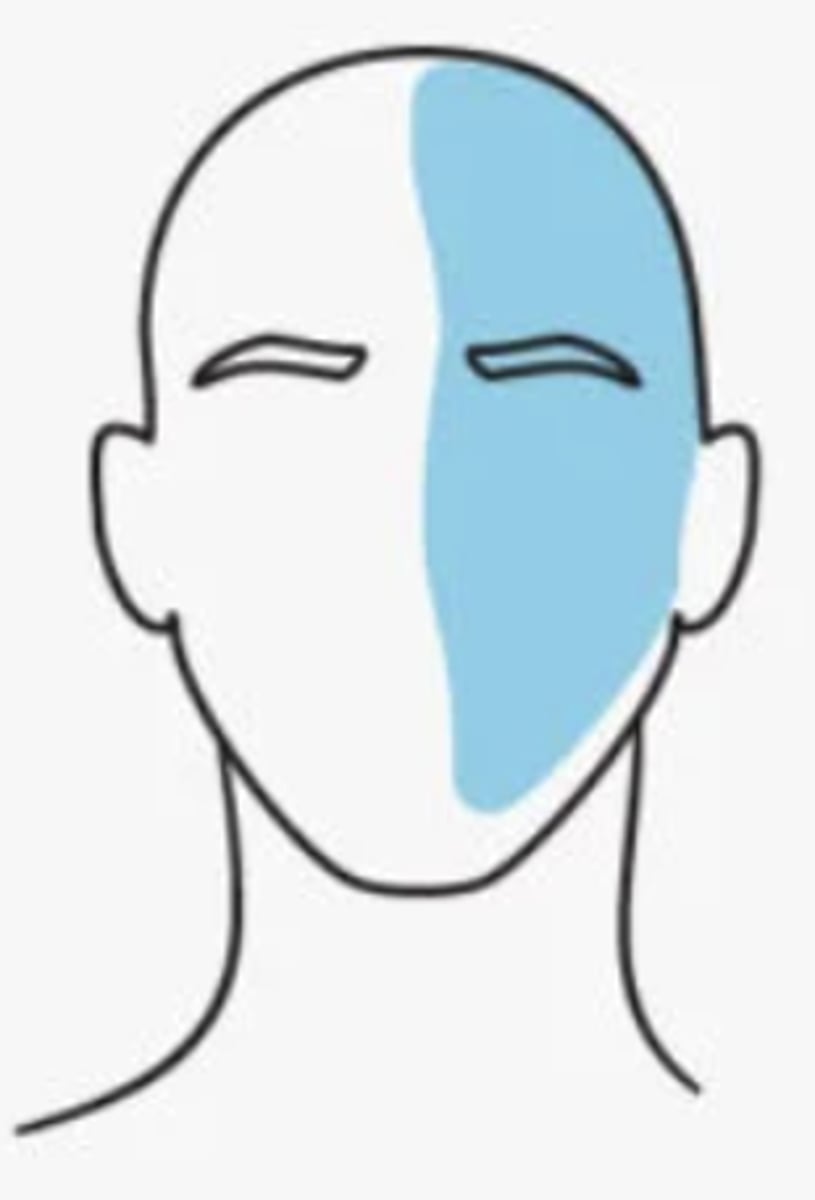
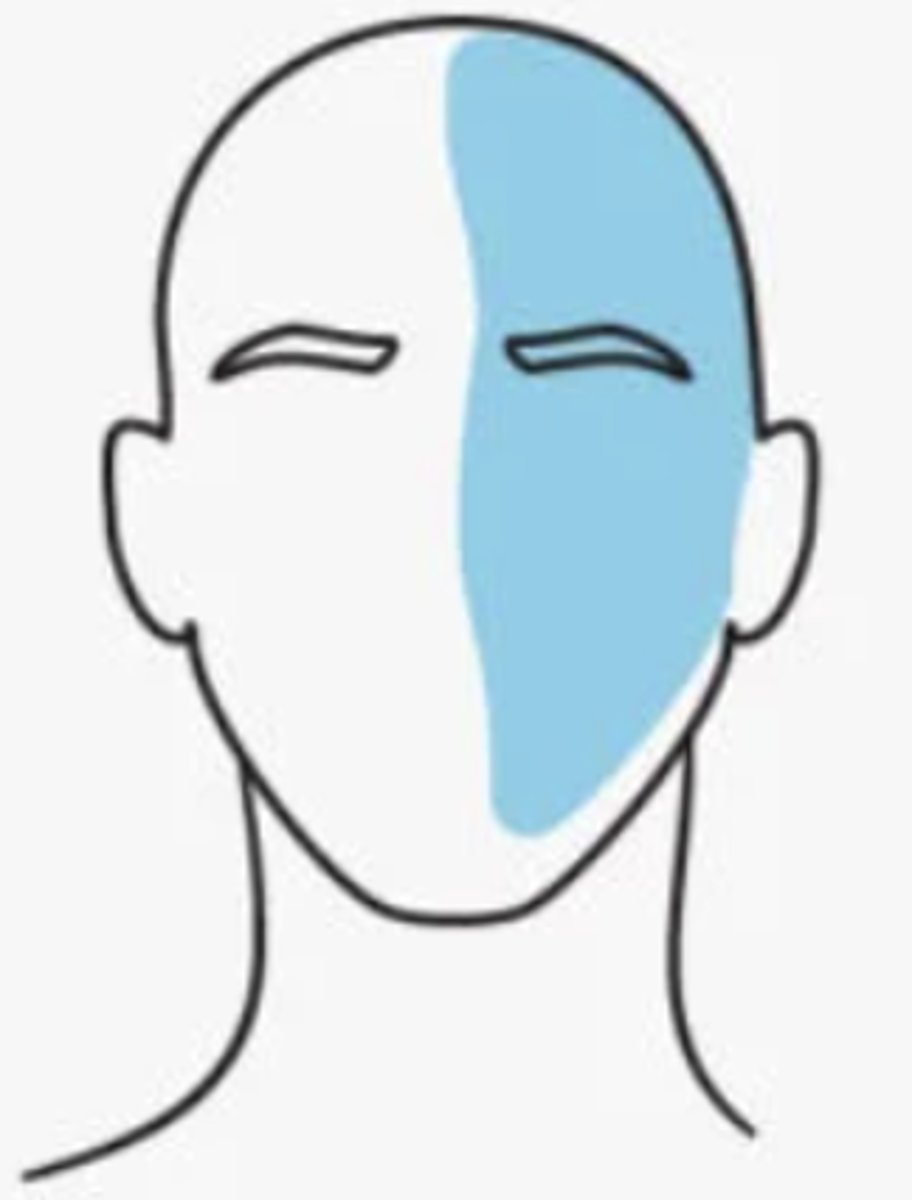
Migraines involve the activation of which nerve?
the trigeminal nerve
- typically occurs on one side of the head
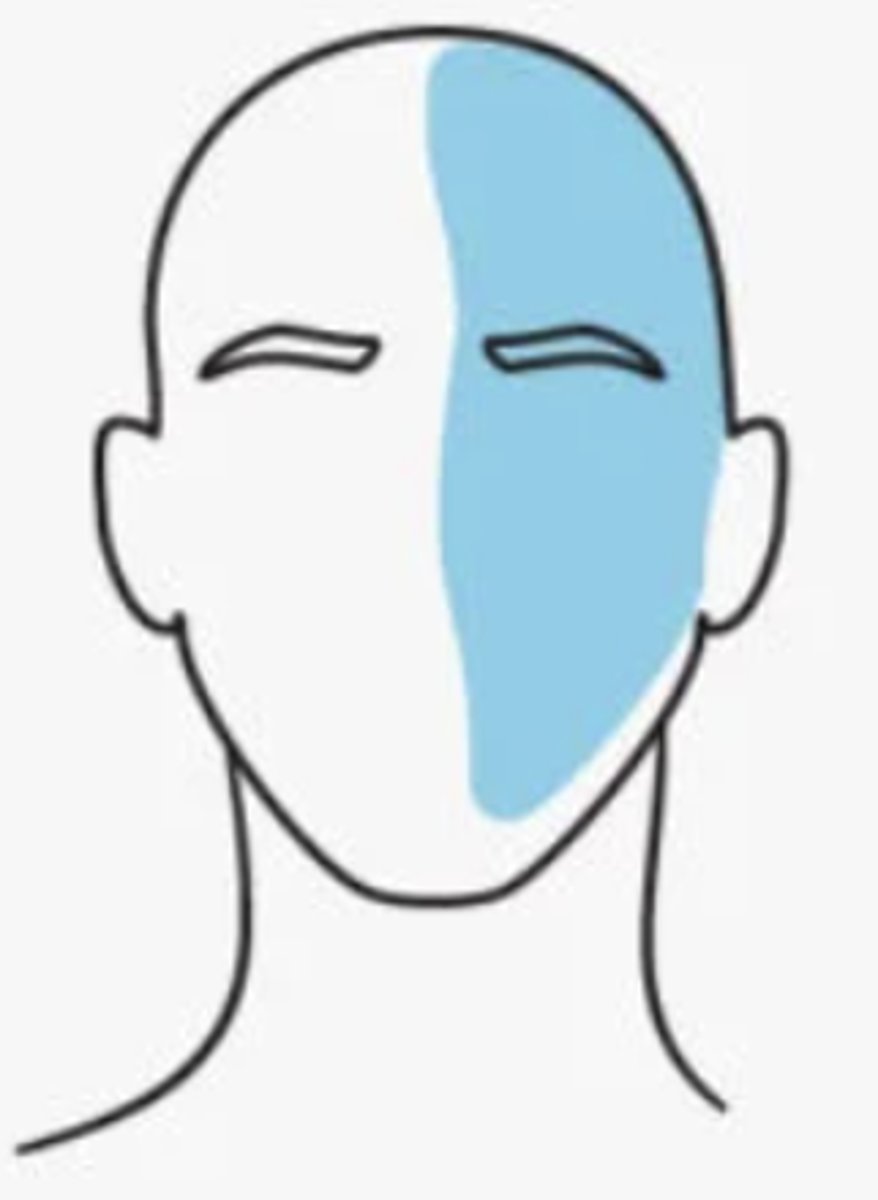
What are migraine episodes associated with?
either nausea/vomiting or photophobia/phonophobia, sinus symptoms, tinnitus, vertigo
- can be with or without aura
How long is the duration of a migraine?
4-72 hours
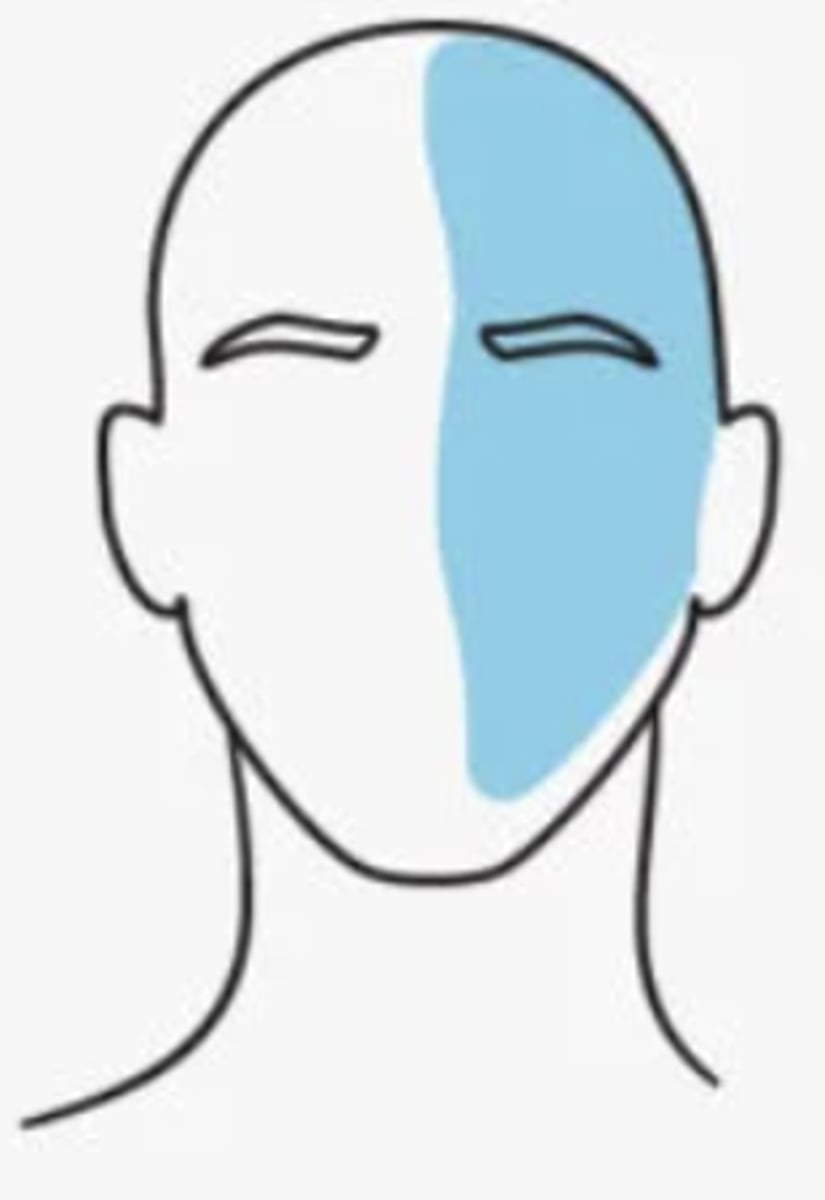
Must have at least 2 of the following to be considered a migraine: (3)
•Moderate to severe head pain
•Unilateral pain pulsating quality of pain
•Aggravation of pain by routine physical activity
Aura
present before or at onset. neurological manifestations include:
- visual
- sensory
- speech
- motor
- should be considered w or w/o HA if at least one of these develops over 5 minutes, lasts 5-60 min and resolves fully
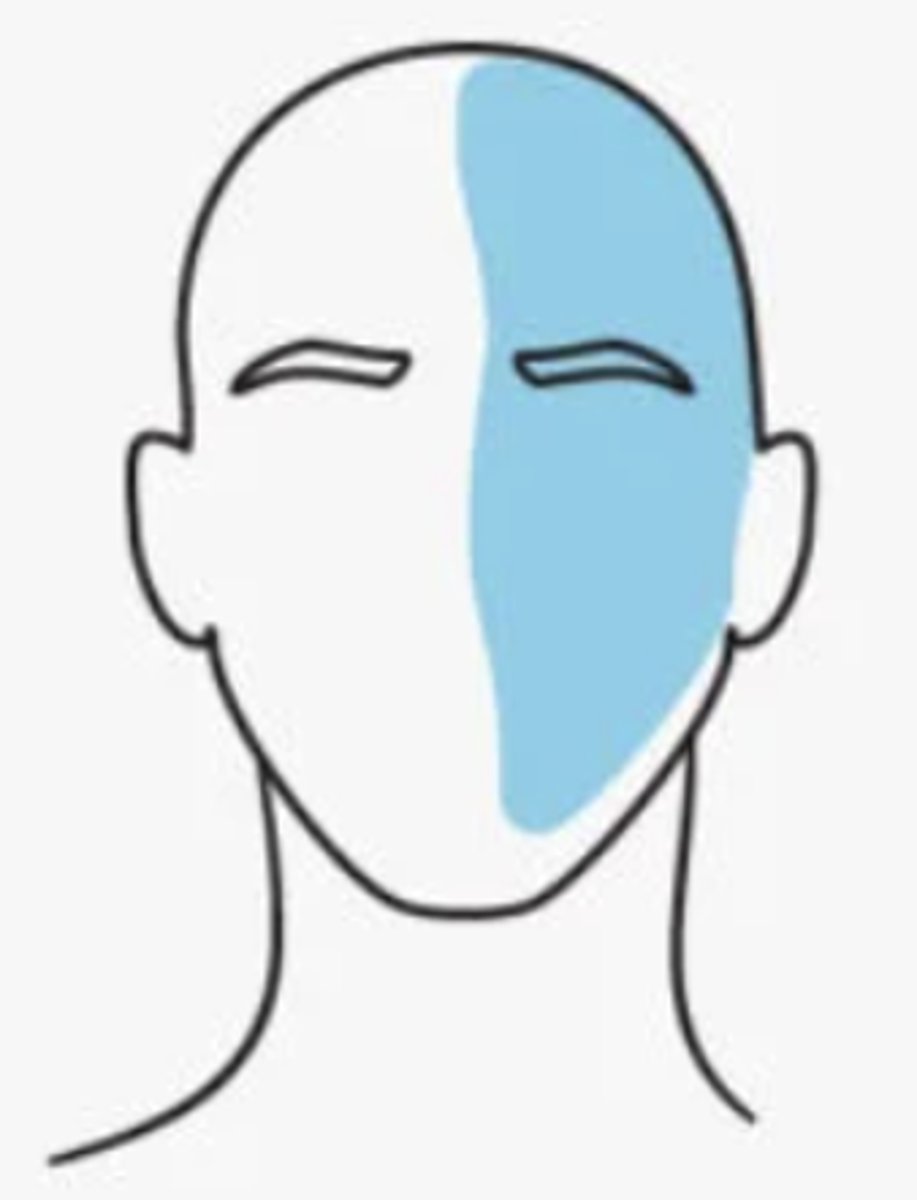
Possible migraine triggers
•Stress
•Changes in sleep patterns
•Fatigue
•Fasting
•Smoking
•Changing in pressure
•Lights
•Sounds
•Smoking
•Caffeine
•Alcohol
•Changes in female hormones (not associated with aura)
•Medications: oral contraceptives, postmenopausal hormones, nitrates
Medication Overuse headache
- associated with frequent use of analgesic medication
- ≥ twice weekly use for 3 months or longer
- worst on awakening
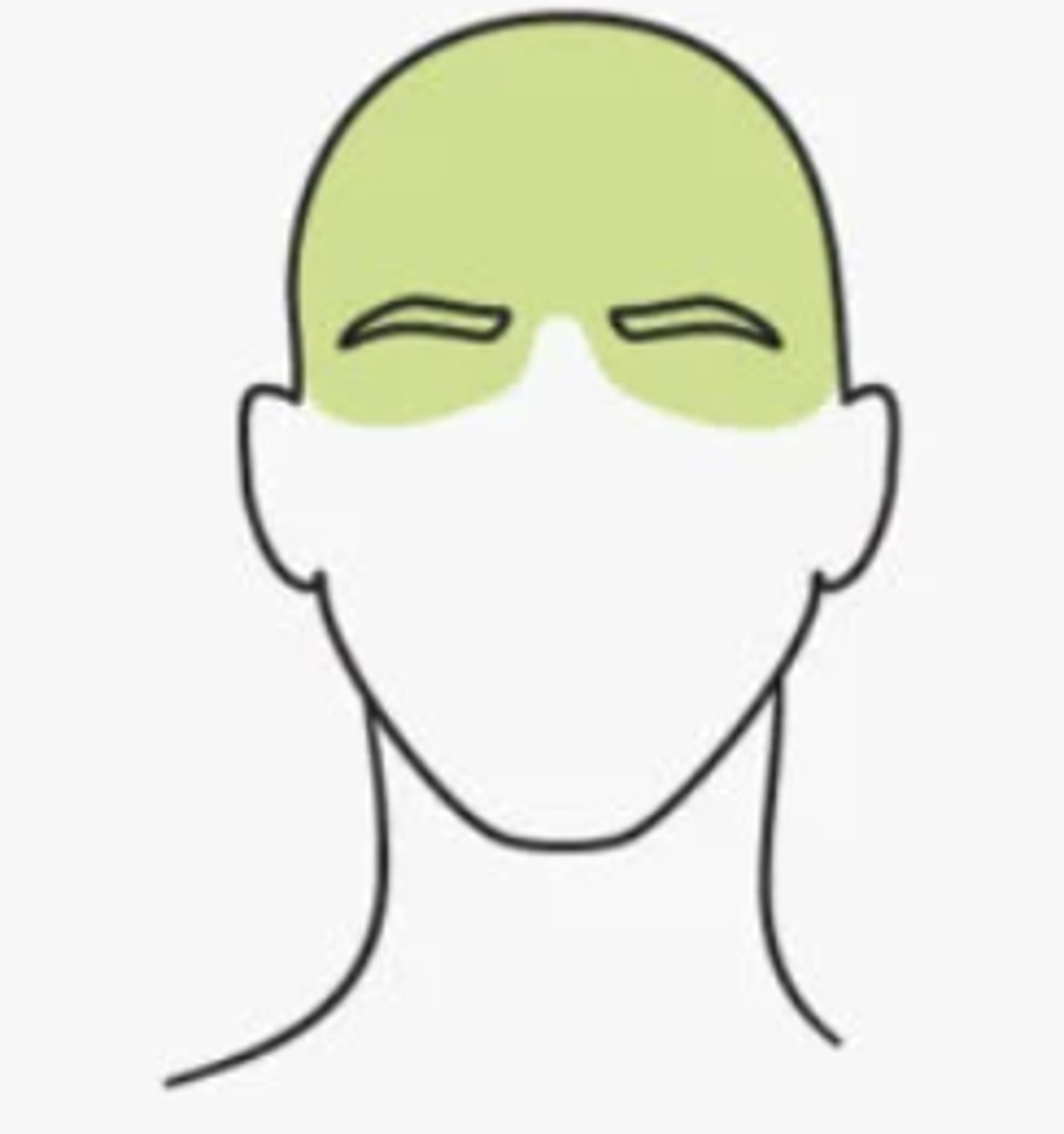
medication overuse headaches should be considered when patient experiences what?
HA > 15 days/month when using acetaminophen, ibuprofen or other NSAIDs

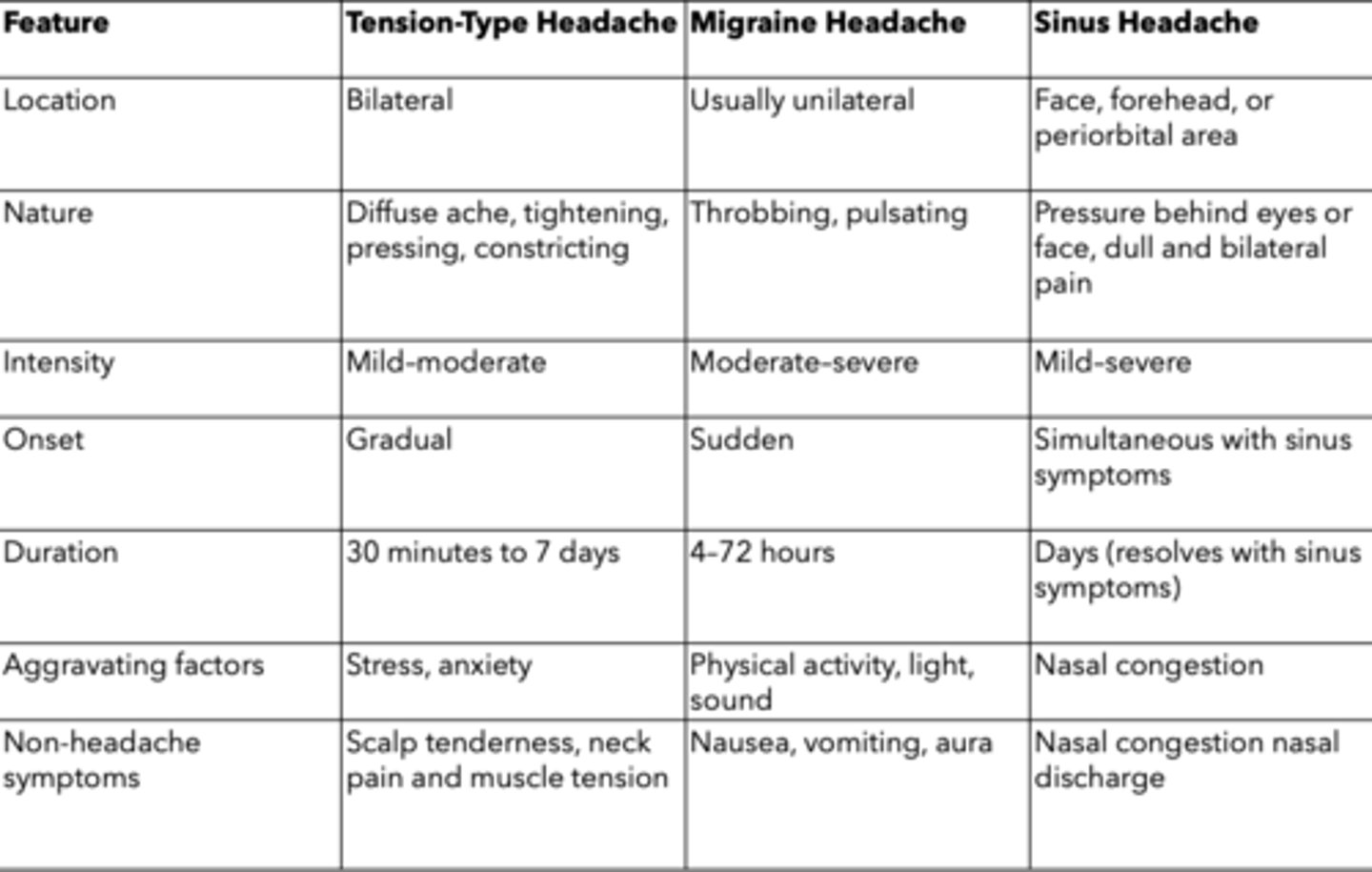
Different headaches chart
Headache treatment goals (5)
1. Alleviate the pain and severity
2. Return to normal activities
3. Prevent reoccurrence
4. Minimize adverse events
5. Chronic Has: reduce frequency
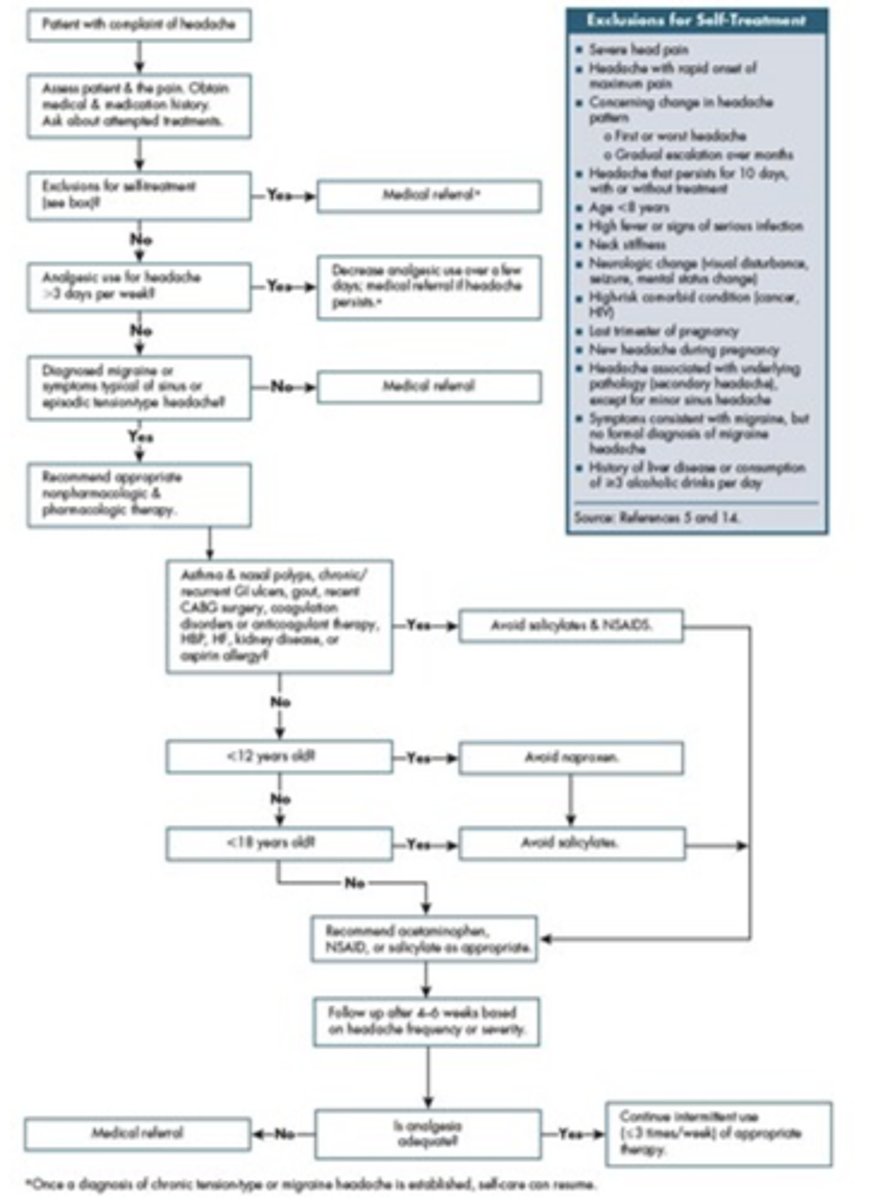
Headache Exclusions for Self Treatment
- severe head pain
- headache with rapid onset of maximum pain
- concerning change in headache pattern- first or worst headache, gradual escalation over months
- headache that persists for 10 days with or without treatment
- age <8 years
- high fever or signs of serious infection
- neck stiffness
- neurologic change
- high-risk comorbid condition
- last trimester of pregnancy
- new headache during pregnancy
- headache associated with underlying pathology
- symptoms consistent with migraine, but no formal diagnosis of migraine headache
- history of liver disease or consumption of ≥3 alcoholic drinks per day

Headache treatment algorithm
Nonpharmacologic headache treatments
- Headache diary (keep for 8 weeks to record frequency, duration, symptoms, triggers, med use and menstruation schedule)
- Acupuncture (reduce intensity & frequency)
- Stress management and PT
Nonpharm treatments for migraines
- Maintain a regular schedule:
- Setting:
- Avoid potential food triggers:
Maintain a regular schedule
•Sleep, eating and exercise
•Stress management
Setting
•Dark, quiet room
•Ice pack with pressure to forehead or temple areas
Avoid potential food triggers
• Nitrites (cured meats), tyramine (red wine and aged cheese)
• Phenylalanine (artificial sweeteners), caffeine, theobromine (chocolate)
• Monosodium glutamate (found in Asian food)
Treatment for episodic tension headaches
acetaminophen, NSAIDs
Treatment for chronic tension headaches
acetaminophen, NSAIDs, same but limit use to <3 days/week or 14 days/month
Non pharm treatment for tension headaches
PT and relaxation techniques
T/F: You do not need a diagnosis for a migraine before recommending OTC products
FALSE
must have a diagnosis first before recommending OTC
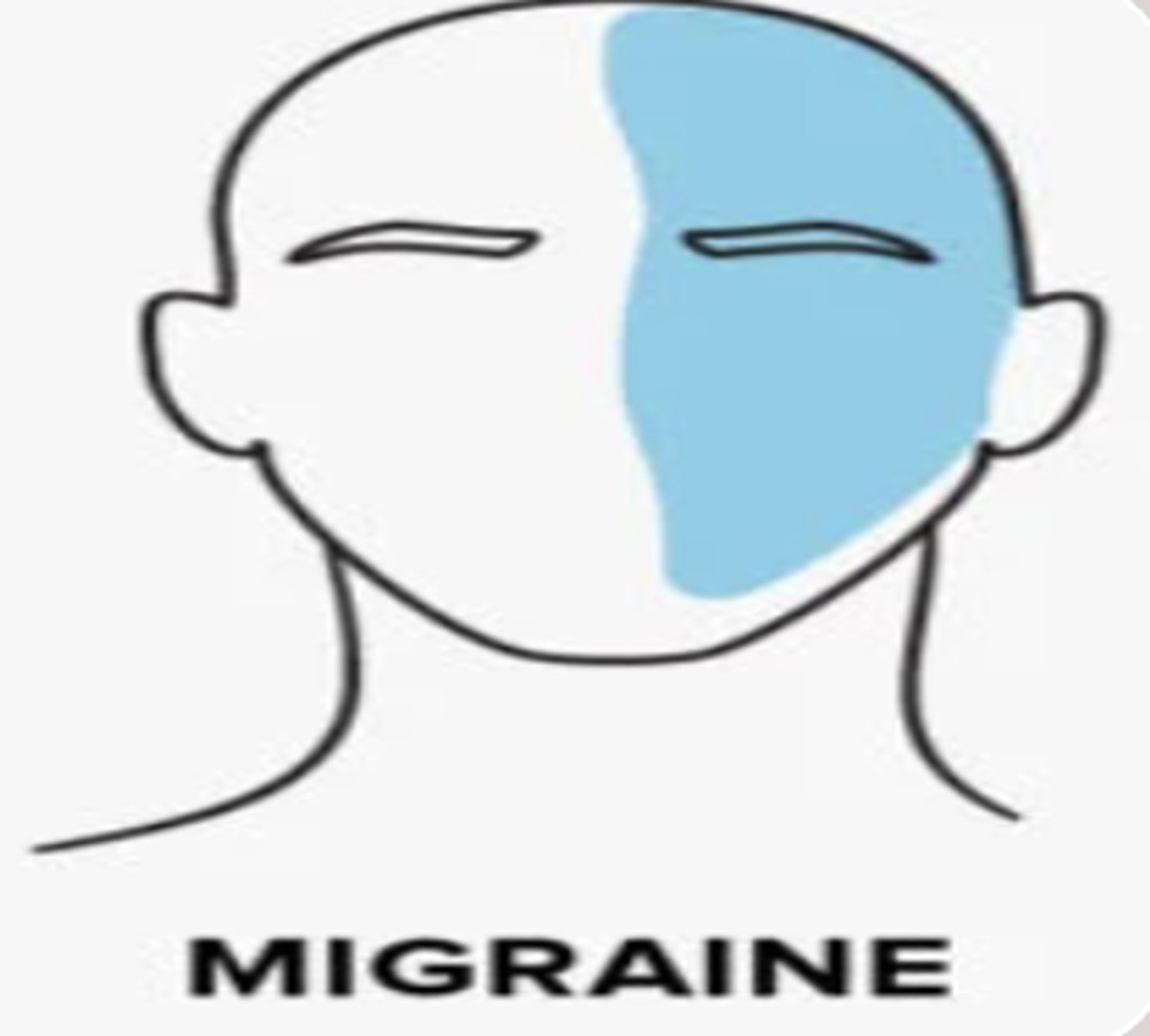
First line treatment for migraines
triptans, NSAIDs or combo of triptan with APAP or NSAID
- best taken at early stages of HA or before exposure to trigger if known
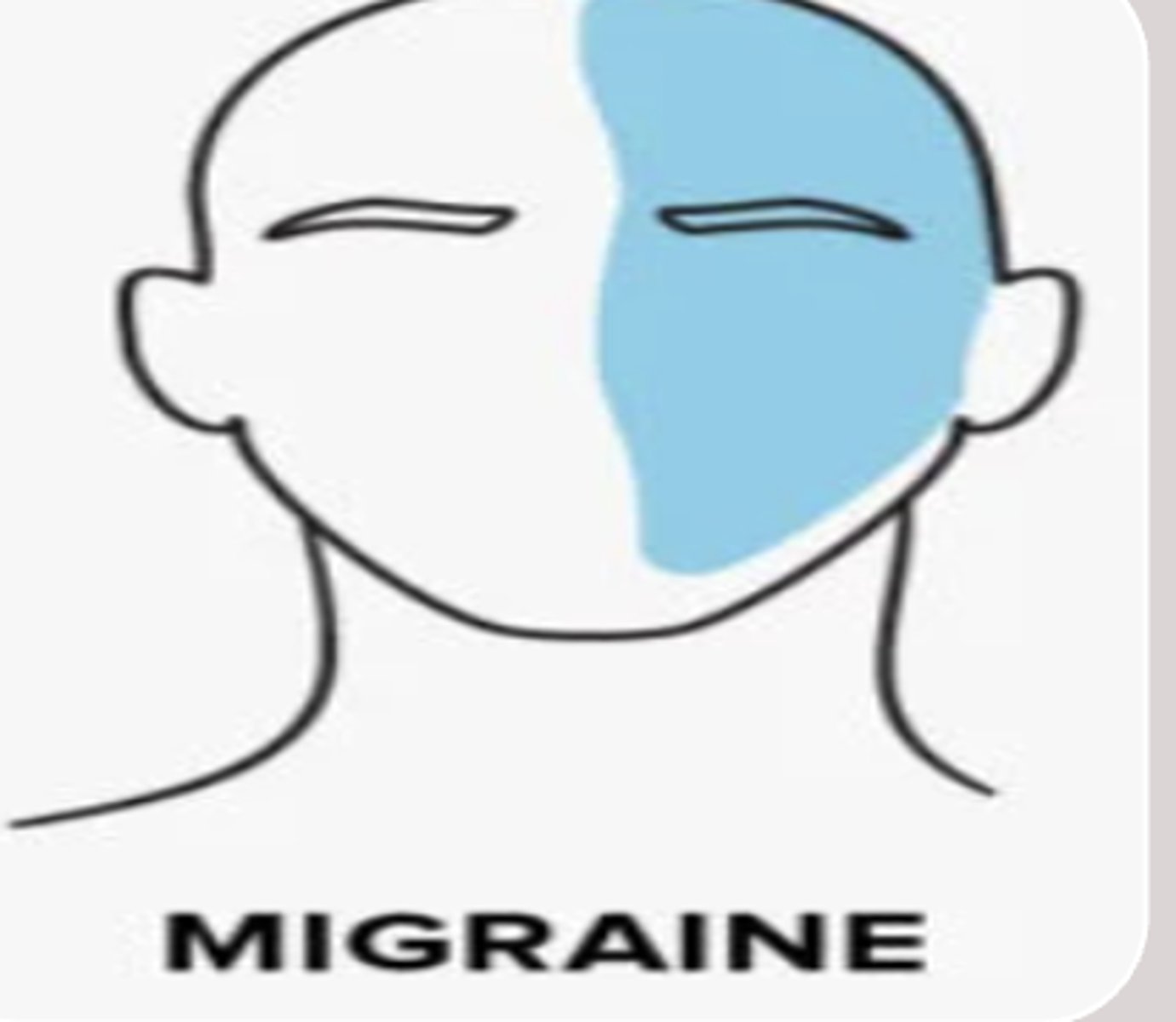
Treatment for medication overuse headaches
discontinue use of the medications
- should be done for about 1 month
- should have medical supervision if prescription meds needed during this period
Treatment for sinus headache
- oral or nasal decongestants to open the sinus passages
- use of OTC pain medications will also help
Acetaminophen
MOA:
Absorption:
Onset of action:
Metabolism:
Duration: (IR, ER)
MOA: Not fully understood, thought to produce pain relief through central inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis
Absorption: absorbed rapidly through the GI tract
Onset of action: 30 minutes
Metabolism: metabolized in the liver to inactive glucuronic & sulfuric acid conjugates. Also, by CYP450 system to an intermediate metabolite detoxified by glutathione
Duration: IR: 4 hours, ER: 6-8 hours

T/F: Acetaminophen can be used alone for migraines
FALSE
must be used in combo, should not be alone, but CAN BE USED for other types of HA as single regimen
Acetaminophen indication
mild to moderate pain, fever reducer
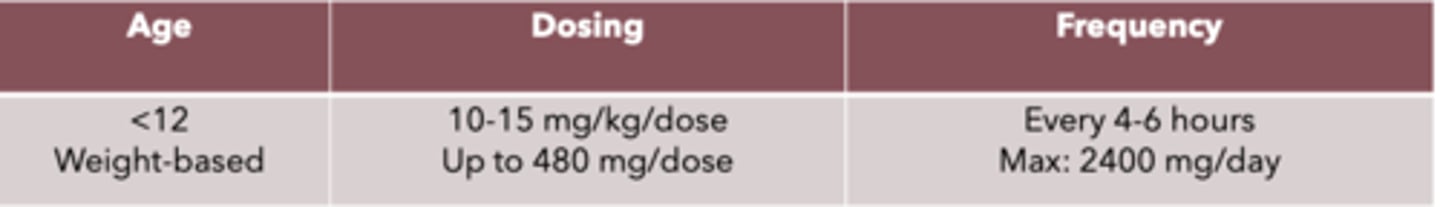
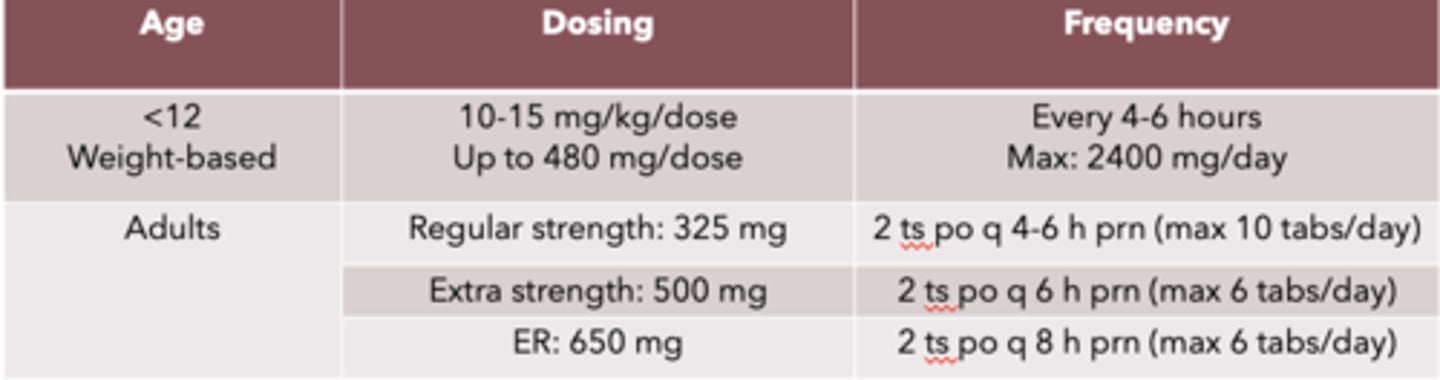
Acetaminophen dosing and frequency for <12 year olds
weight-based
Dosing: 10-15 mg/kg/dose, up to 480 mg/dose
Frequency: every 4-6 hours, max: 2400 mg/day
Acetaminophen dosing and frequency for adults
Dosing:
- regular strength: 325 mg
- Extra strength: 500 mg
- ER: 650 mg
Frequency:
- regular strength: 2 ts po q 4-5 h prn (max 10 tabs/day)
- Extra strength: 2 ts po q 6 h prn (max 6 tabs/day)
- ER: 2 ts po q 8 h prn (max 6 tabs/day)
Adverse reactions of acetaminophen
no common, risk of allergic skin reactions
Do not exceed ___________ daily of acetaminophen due to hepatotoxicity
4 g
Acetaminophen DDIs (2)
- alcohol
- Warfarin
Acetaminophen DDI with alcohol:
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- Increased risk of hepatotoxicity
Management:
- avoid use if possible, limit alcohol intake when taking acetaminophen
Acetaminophen DDI with warfarin:
Interaction:
Management
Interaction:
- Increased risk of bleeding
Management:
- limit acetaminophen use to occasional; monitor INR levels
Available acetaminophen products
• 325 mg, 500 mg (extra strength), 650 mg (ER, arthritis), 500mg/5ml liquid
• for children: liquid 160 mg/5ml, 160 mg chewable tablets, 80 mg and 120 mg suppositories

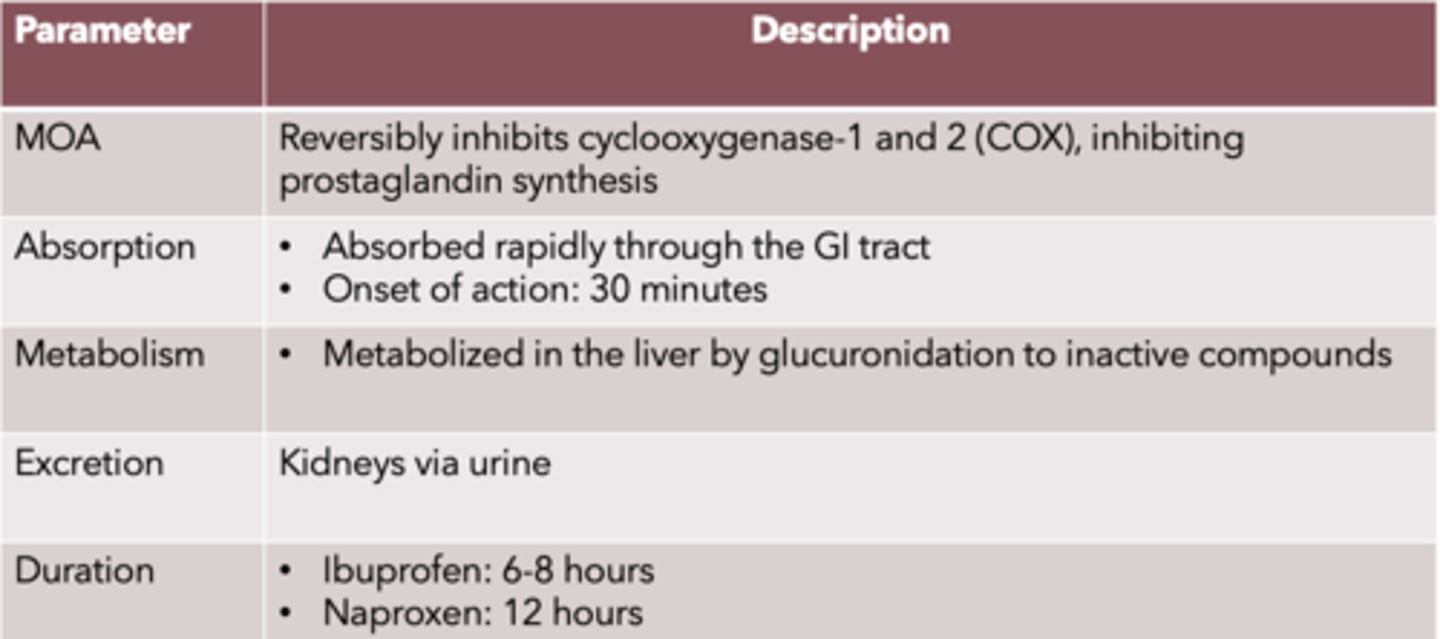
NSAID drugs:
MOA:
Absorption:
Onset of action:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Duration: (ibuprofen, naproxen)
MOA: reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 and 2 (COX), inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis
Absorption: absorbed rapidly through the GI tract
Onset of action: 30 mins
Metabolism: metabolized in the liver by glucuronidation to inactive compounds
Excretion: kidneys via urine
Duration: ibuprofen: 6-8 hrs., naproxen: 12 hrs
Indications of NSAIDs
fever reducer and mild to moderate pain from headaches, menstrual cramps, toothache, muscle ache, backache, arthritis
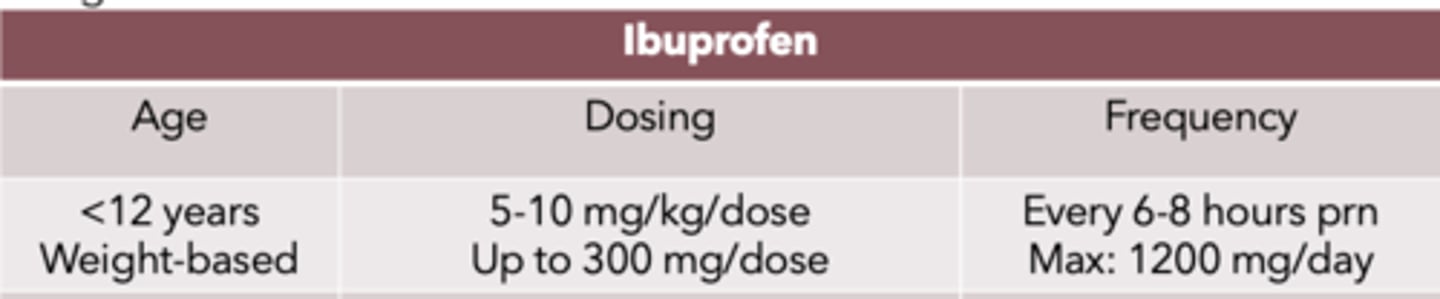
NSAID dosing and frequency for <12 year olds: Ibuprofen
weight-based
Dosing:
- 5-10 mg/kg/dose
- up to 300 mg/dose
Frequency:
- q 6-8 hrs prn
- max: 1200 mg/day
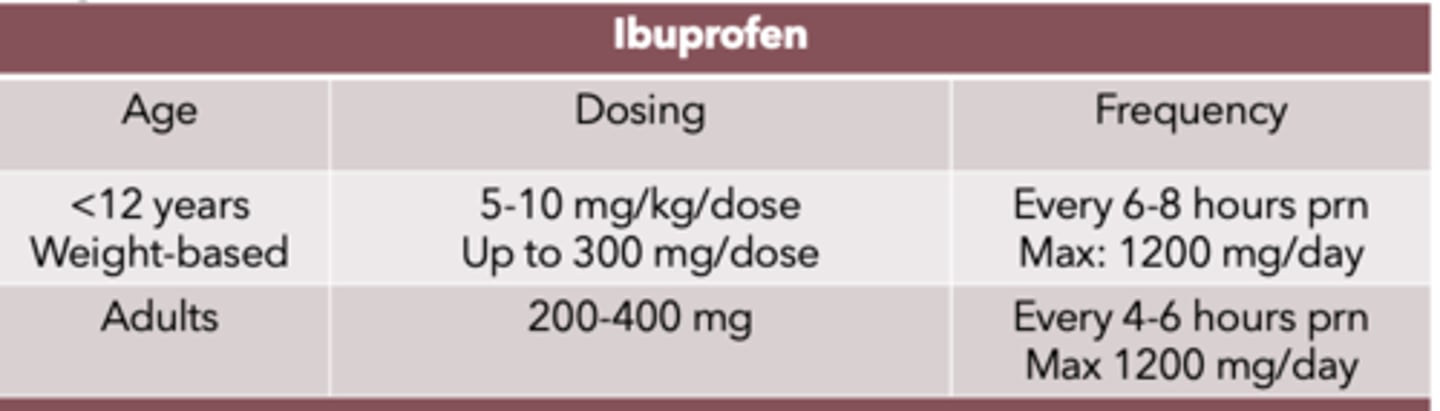
NSAID dosing and frequency for adults: Ibuprofen
Dosing:
- 200-400 mg
Frequency:
- q 4-6 hrs prn
- max 1200 mg/day
*max is less than prescription
NSAID dosing and frequency for adults: Naproxen (cant be given to those under 12)
Dosing:
- 220 mg
Frequency:
- q 8-12 hrs (2 tabs initial dose)
- Max: 660 mg/day
Administration of NSAIDs
Take with food to help with AE, do not crush or chew if sustained release or enteric coated
Adverse effects of NSAIDs
- dyspepsia
- heartburn
- nausea
- epigastric pain
Serious adverse events of NSAIDs
- GI ulceration, perforation and bleeding
- risk factors: >60 years, previous ulcer disease, anticoagulant use, high and long duration of tx, > 3 alcoholic drinks/day
- avoid use in those at high risk for CV disease: hypertension, stroke, MI, diabetes
- avoid use in those with renal disease, congestive heart failure
NSAID drug interactions (6)
- digoxin
- antiplatelets
- antihypertensives
- anticoagulants
- alcohol
- methotrexate
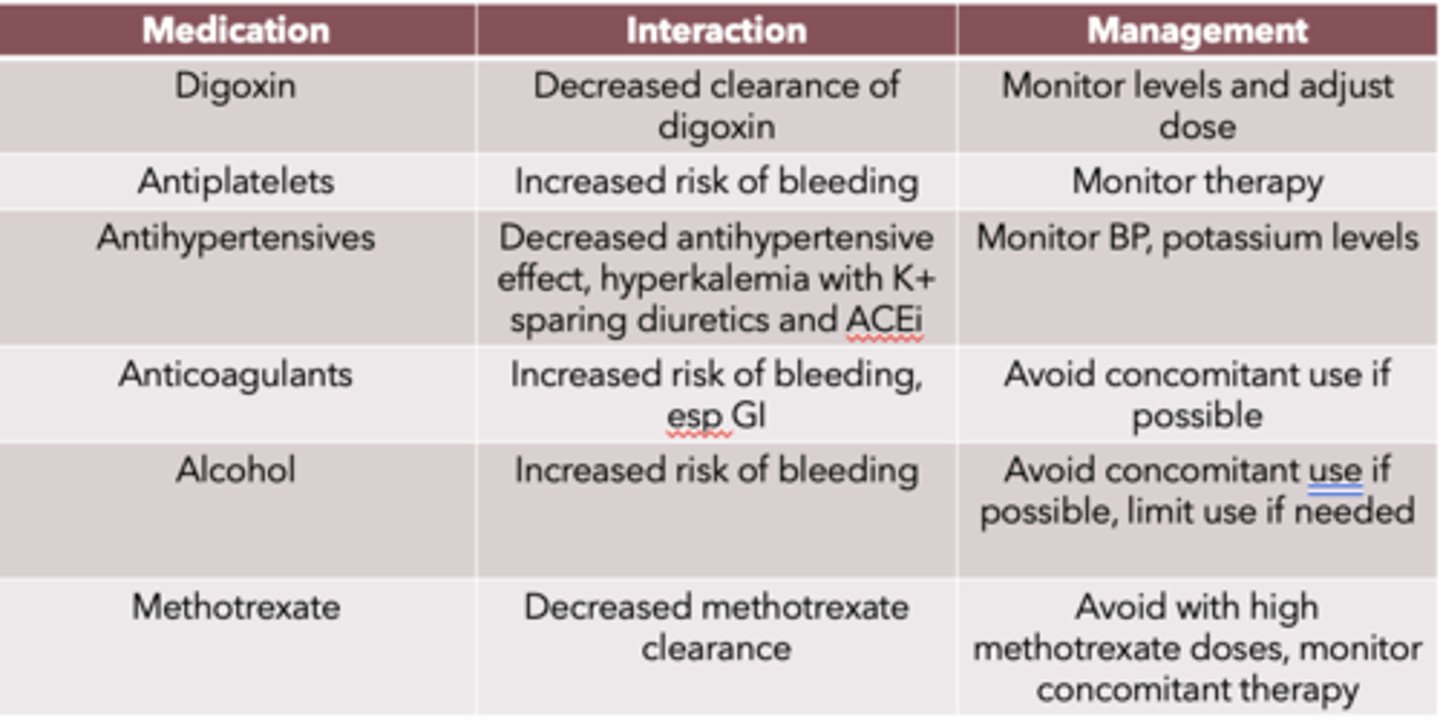
NSAID drug interaction: Digoxin
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- decreased clearance of digoxin
Management:
- monitor levels and adjust dose
NSAID drug interaction: antiplatelets
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- increased risk of bleeding
Management:
- monitor therapy
NSAID drug interaction: antihypertensives
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- decreased antihypertensive effect
- hyperkalemia with K+ sparing diuretics and ACEi
Management:
- monitor BP, potassium levels
NSAID drug interaction: anticoagulants
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- increased risk of bleeding, especially GI
Management:
- avoid concomitant use if possible
NSAID drug interaction: alcohol
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- increased risk of bleeding
Management:
- avoid concomitant use if possible, limit use if needed
NSAID drug interaction: methotrexate
Interaction:
Management:
Interaction:
- decreased methotrexate clearance
Management:
- avoid with high methotrexate doses
- monitor concomitant therapy
Available NSAID products
Ibuprofen
- Children: liquid 100 mg/5 ml, chewable 100 mg
- adults: 200 mg tablets, capsules
Naproxen
- 220 mg tablets, capsules

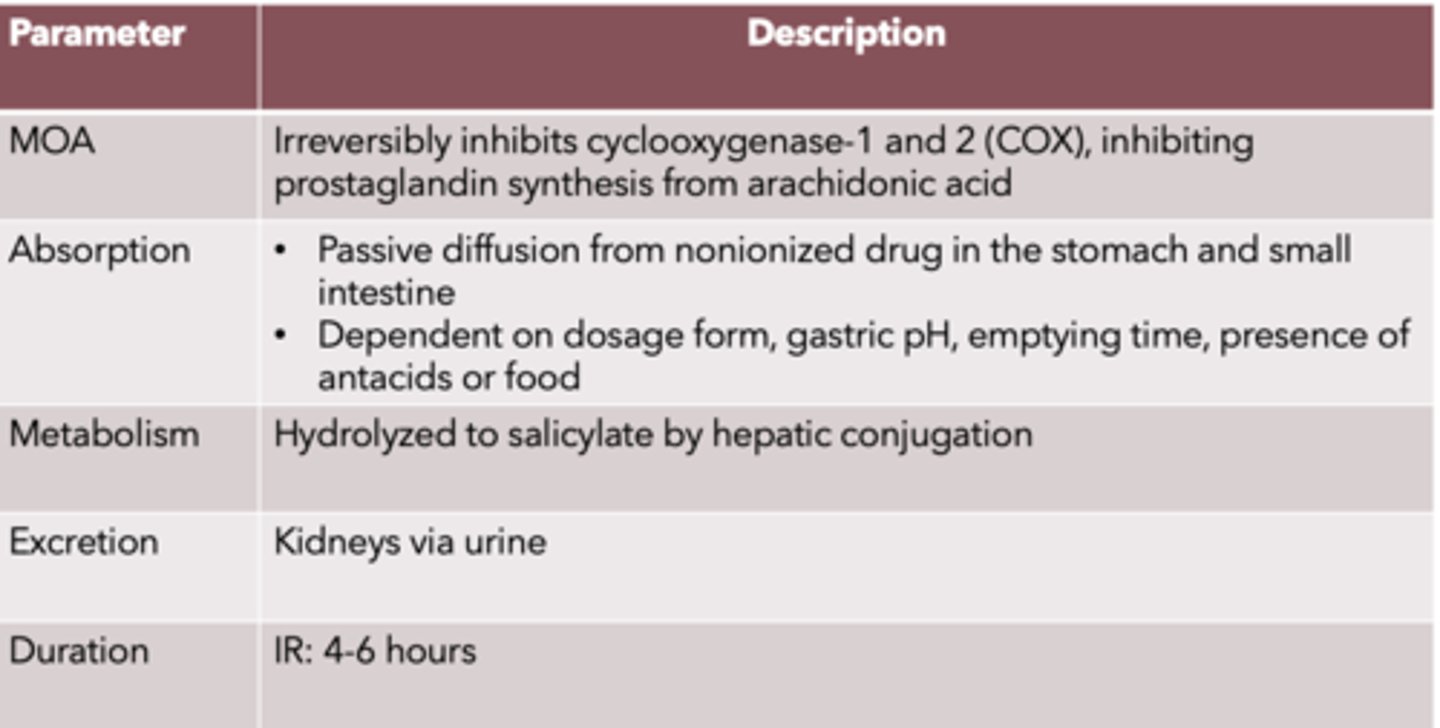
Salicylates
MOA:
Absorption:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Duration:
MOA: Irreversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase-1 and 2 (COX), inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid
Absorption:
• Passive diffusion from nonionized drug in the stomach and small intestine
• Dependent on dosage form, gastric pH, emptying time, presence of antacids or food
Metabolism: hydrolyzed to salicylate by hepatic conjugation
Excretion: kidneys via urine
Duration: IR: 4-6 hours
Indications of salicylates
fever reducer and mild to moderate pain for musculoskeletal conditions, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis
Salicylates dosing and frequency for adults: Aspirin
Dosing:
- 325-1000 mg
Frequency:
- q 4-6 h prn
- Max: 4000 mg/day
Salicylates dosing and frequency for adults: Magnesium salicylate
Dosing:
- 1160 mg
Frequency:
- q 4-6 hrs prn
- Max: 4640 mg/day
Administration of salicylates
take with food to help with adverse events, do not crush or chew if sustained release or enteric coated
Salicylates adverse effects
dyspepsia
Serious adverse events of salicylates
• GI ulceration, perforation and bleeding
• Risk factors: >60 years, previous ulcer disease, anticoagulant or NSAID use, long duration of tx, >3 alcoholic drinks/day, infection with H.pylori
• Avoid use in those at high risk for CV disease: hypertension, stroke, MI, diabetes
• Avoid use in those with renal disease, congestive heart failure
Salicylate drug interactions (7)
- NSAIDs including COX-2 inhibitors
- antiplatelets
- antihypertensives
- alcohol
- methotrexate
- sulfonylureas
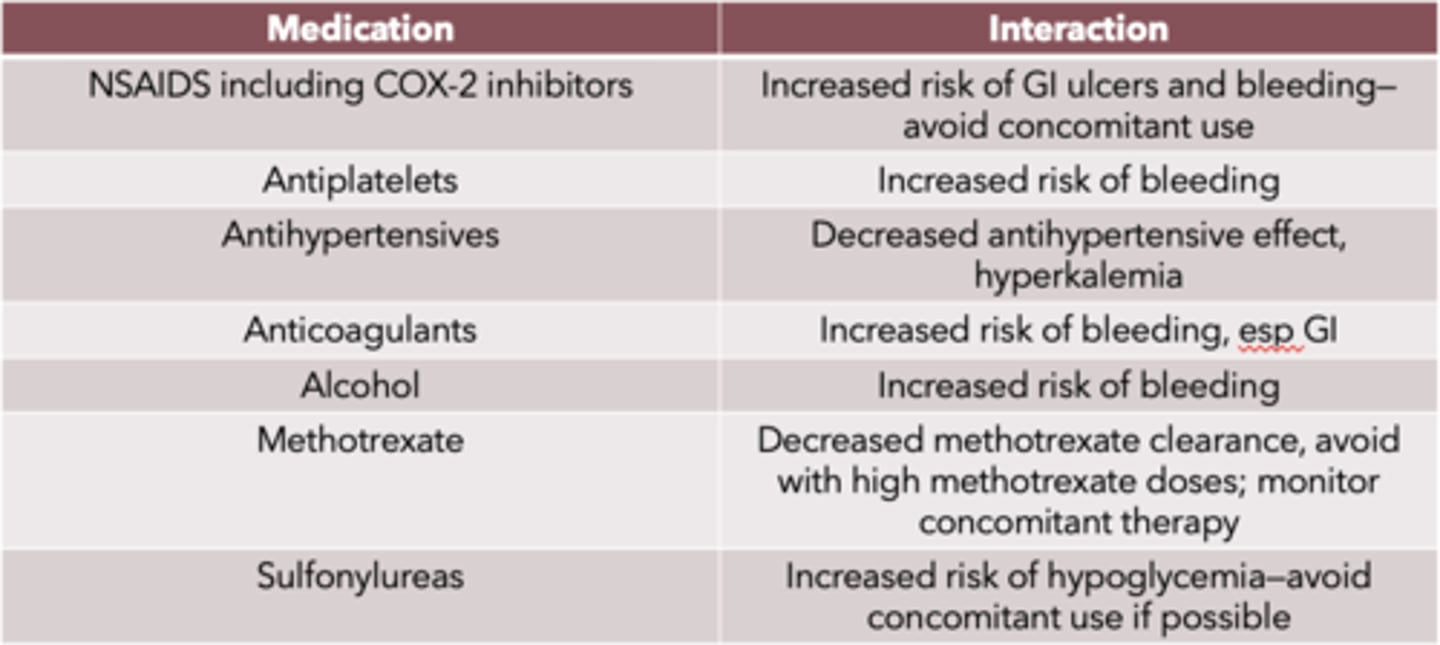
salicylate drug interaction: NSAIDs including COX-2 inhibitors
Increased risk of GI ulcers and bleeding
—avoid concomitant use
salicylate drug interaction: antiplatelets
Increased risk of bleeding
salicylate drug interaction: antihypertensives
Decreased antihypertensive effect, hyperkalemia
salicylate drug interaction: anticoagulants
Increased risk of bleeding, esp GI
salicylate drug interaction: alcohol
Increased risk of bleeding
salicylate drug interaction: methotrexate
Decreased methotrexate clearance
- avoid with high methotrexate doses
- monitor concomitant therapy
salicylate drug interaction: sulfonylureas
Increased risk of hypoglycemia
—avoid concomitant use if possible
Available salicylate products
Aspirin:
- 81 mg tablet and chewables
- 325 mg EC and DR tablet
- 500 mg extra strength tablet
Magnesium salicylate:
- 325 mg tablet
- 580 mg tetrahydrate tablet
Oral decongestants
MOA:
Absorption:
Onset of action:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Duration:
MOA: reduce congestion by causing vasoconstriction in the nasal passages
Absorption: rapid
Onset of action: 30 minutes
Metabolism: metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO) and catechol-O-methyltransferase in the GI
Excretion: renal
Duration: IR: 3-8 hours
Indications of decongestants
nasal congestion
decongestant dosing and frequency for adults: Pseudoephedrine
Dosing:
- IR: 60 mg
- ER: 120 mg or 240 mg
Frequency:
- IR: q 4-6 h prn
- ER: q 12 h or q 24 h, Max: 240 mg/day
decongestant dosing and frequency for adults: Phenylephrine
Dosing:
- 10 mg
Frequency:
- q 4 h prn for <7 days
- Max: 60 mg/day
Administration of decongestants
may take with or without food
Adverse effects of decongestants
- CV stimulation (high BP, palpitations, tachycardia)
- CNS stimulation (anxiety, insomnia, restlessness, etc.)
Warnings/precautions of decongestants
those with diabetes, heart disease, enlarged prostate or narrowing of bowel
Decongestant DDIs (7)
- Ergot derivatives
- Antiplatelets
- Antihypertensives
- Anticoagulants
- Alcohol
- Methotrexate
- Sulfonylureas
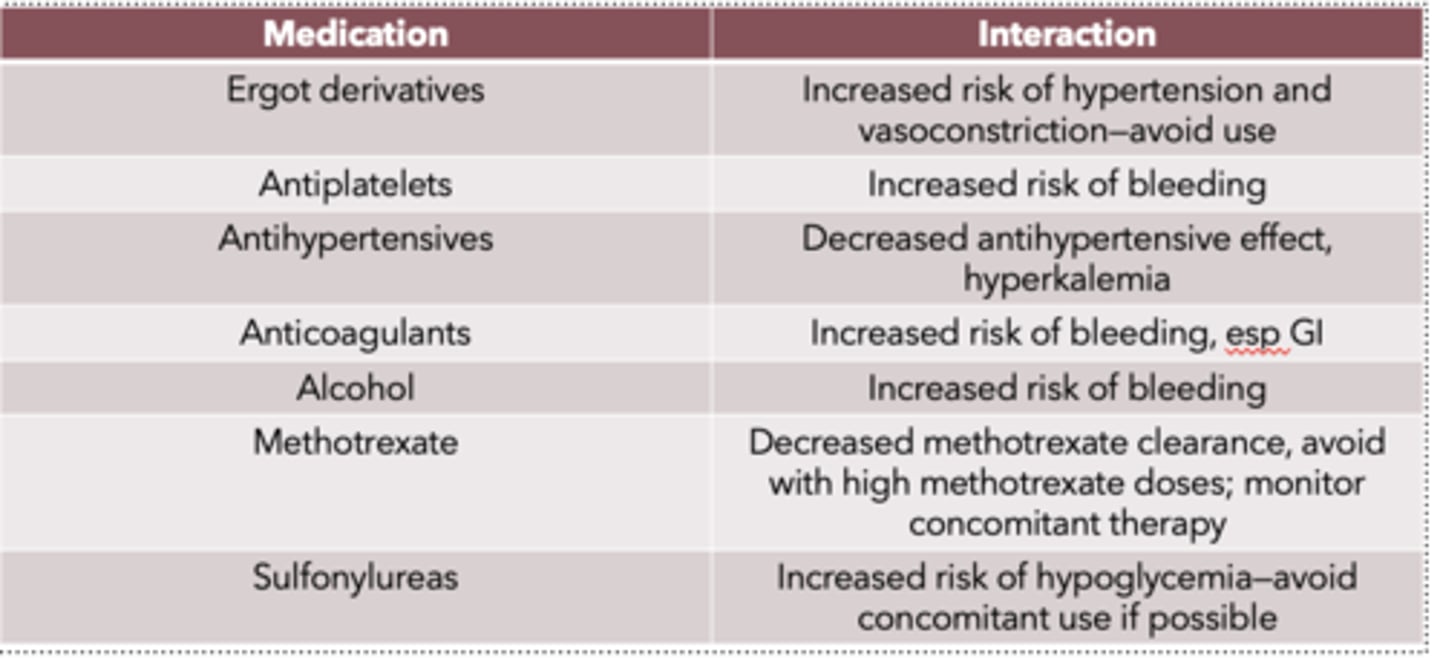
Decongestant DDI: ergot derivatives
- Increased risk of hypertension and vasoconstriction
—avoid use
Decongestant DDI: antiplatelets
- increased risk of bleeding
Decongestant DDI: antihypertensives
- decreased antihypertensive effect
- hyperkalemia
Decongestant DDI: anticoagulants
increased risk of bleeding, esp GI
Decongestant DDI: alcohol
Increased risk of bleeding
Decongestant DDI: methotrexate
Decreased methotrexate clearance
- avoid with high methotrexate doses
- monitor concomitant therapy
Decongestant DDI: sulfonylureas
Increased risk of hypoglycemia
—avoid concomitant use if possible
Combination products: Excedrin
Tension HA:
Migraine:
PM HA:
• Tension HA : APAP 500 mg and caffeine 65 mg
• Migraine: Acetaminophen 250 mg, Aspirin 250 mg, caffeine 65 mg
• PM HA: Acetaminophen 250 mg, Aspirin 250 mg, diphenhydramine 38 mg
Combination products: NSAIDs (4)
• Advil Cold and Sinus: Ibuprofen 200 mg, pseudoephedrine 30 mg
• Advil Sinus Congestion and Pain: Ibuprofen 200 mg, phenylephrine 10 mg
• Motrin PM: ibuprofen 200 mg, phenylephrine 10 mg
• Aleve D: naproxen 220 mg, pseudoephedrine 120 mg
Pediatric populations
• Children ________ years can use ibuprofen and acetaminophen
• Children _____ years can use naproxen
• Can you use aspirin in children?
• Children > 2 years can use ibuprofen and acetaminophen
• Children >12 years can use naproxen
• Do not use aspirin or aspirin containing products in children and teens due to risk of Reye syndrome
Older adults
• Increased risk of side effects due to...
• More sensitive to ____ and _______________ of NSAIDs and salicylates
• Which is the drug of choice?
• Increased risk of side effects due to comorbid conditions
• More sensitive to GI and renal side effect of NSAIDs and salicylates
• Drug of choice: acetaminophen
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
• Is acetaminophen considered safe?
• NSAIDs are contraindicated in third trimester due to....
• Is ibuprofen safe for breastfeeding?
• Acetaminophen is considered safe in both
• NSAIDs are contraindicated in third trimester due to increased risk of prolonged labor, bleeding and CV effects
• Ibuprofen is safe in breastfeeding
Alternative therapies of headaches
• Butterbur, feverfew, riboflavin, coenzyme Q-10
• Commonly used for the prevention of migraine
• Limited efficacy for other types of headaches
• Essential oils: peppermint to forehead (tension), inhalation of aromatized lavender (migraine)
